lipid solubility and melting point
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Saturated fatty acid solubility and melting point
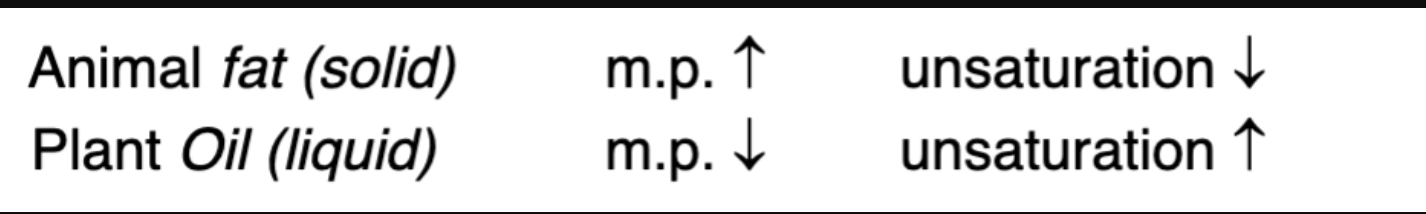
Saturated fatty acid chains have no double bonds, so their hydrocarbon tails are fully "saturated" with hydrogen atoms and remain straight and flexible. Because of this straight, extended conformation, the chains can align closely side-by-side without kinks or bends. This tight, orderly packing allows strong van der Waals (London dispersion) forces between adjacent chains, making the structure more stable and solid at room temperature. This close packing increases the melting point and decreases solubility in water.
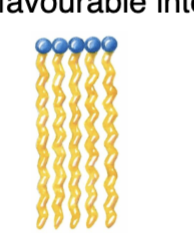
What happens to the melting point of saturated fatty acids as chain length increases?
The melting point increases.
What happens to the solubility of saturated fatty acids as chain length increases?
The solubility decreases.
Stearic Acid (18:0)
A saturated fatty acid with 18 carbons and no double bonds; has a melting point around 70°C.
Why do unsaturated fatty acids pack less regularly than saturated fatty acids?
Because the cis double bonds create kinks in the hydrocarbon chain, preventing tight, orderly packing.
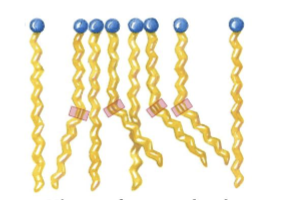
How does the kink caused by a cis double bond affect fatty acid interactions?
It lowers the number of favorable van der Waals interactions between chains.
lowering the melting point - bc less thermal energy is needed to disrupt the disorded packing.
How do trans fatty acids compare to cis fatty acids in packing and melting point?
Trans fatty acids pack more regularly due to their extended conformation and have higher melting points than cis fatty acids.
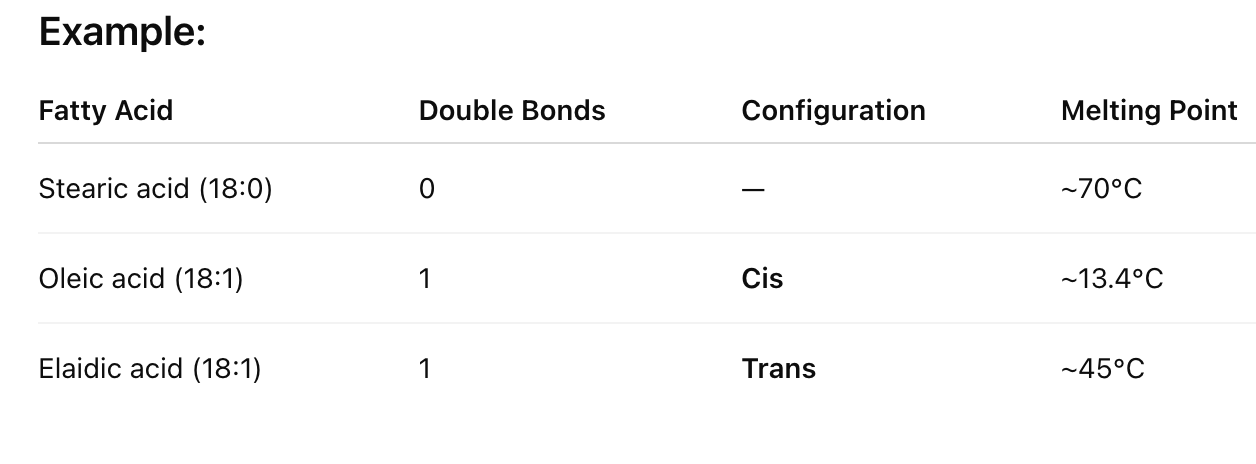
saturated > trans > cis
Q: Which of the following fatty acids is likely to have the highest melting temperature?
A. CH₃(CH₂)₁₆COOH
B. CH₃(CH₂)₁₄COOH
C. CH₃(CH₂)₇CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH
D. CH₃(CH₂)₄CH=CHCH₂CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH
(Note: all double bonds are cis)
A
because it is a fully saturated fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms, allowing tight packing and strong van der Waals interactions, resulting in the highest melting point among the options.
longer than B so has higher melting point (more bonds to disrupt)
What do carboxylic acids and alcohols form when they react?
Esters
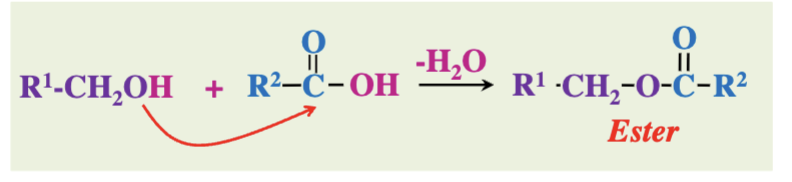
(loss of water)
CONDENSATION REACTION
What do two carboxylic acids form when they react?
Acid anhydrides
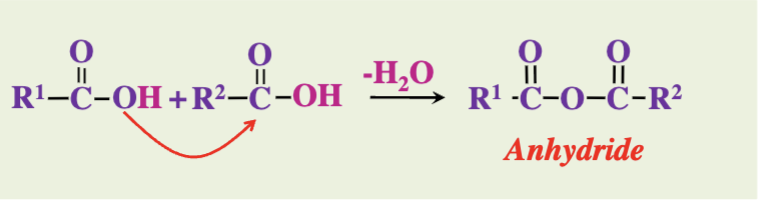
A compound formed from the condensation of two carboxylic acids, resulting in the removal of water.
What kind of reaction leads to the formation of esters and anhydrides?
A condensation reaction, where water is removed.
In ester formation, which functional groups are involved?
In anhydride formation, which functional groups react?
A carboxylic acid (-COOH) and an alcohol (-OH)
Two carboxylic acid groups (-COOH)
What are triacylglycerols (TAGs) made of?
3 fatty acids esterified to a glycerol backbone.
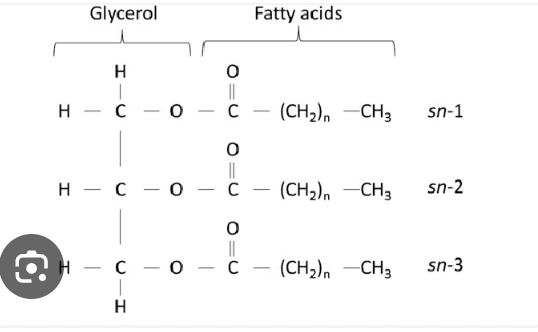
this is the main storage for of fat in animals
Where are TAGs commonly found in the body?
In depot fat (body fat stores), as well as in dietary fats and oils.
Why are TAGs highly hydrophobic?
Because the polar carboxylic acid groups are converted into less polar ester groups (non polar is more hydrophobic)
What affects the melting point of TAGs?
The length and degree of saturation of their fatty acid chains.
simple triacylglycerol
A TAG with the same fatty acid in all three positions on the glycerol.
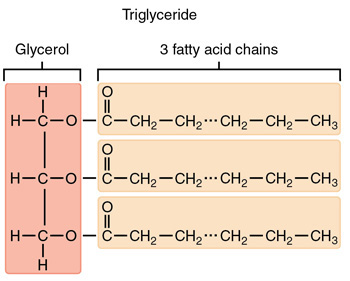
mixed triacylglycerol
A TAG containing two or three different fatty acids.
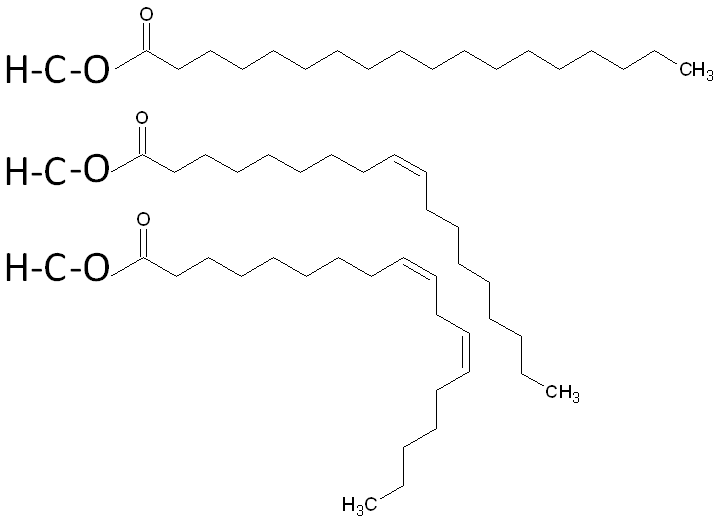
How does chain length and saturation affect the melting point of natural fats?
longer = higher melting point
more saturated = higher melting point
Animal vs plant fat