Lectures 5-6
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Gregor Mendel
worked with garden peas to test family resemblance and genes
true breeding plants
when reproduce all offspring will look like parents (purple x purple = purple)
non-true breeding plants
odd offspring (purple x purple = purple AND white)
the basic cross
bred ture offspring of certain trait with one of different variation of same trait = hybrids
P generation
parent generation (true breeding) (purple and white)
cross fertilize
cross 2 tpes/ variations of a trait
F1 generation
offspring of 1st cross (purple)
self cross
2nd cross, F1s self fertilize
F2 generation
self crossed offspring, color variation (3 purple, 1 white)
dominant trait
captial letter, overriding effect of different variation (will appear visibly)
recessive trait
lowercase letter, masked variation (present at gene level but not visibly seen) (only expressed when genotype is homologous)
F3 generation
1/3 purple breed true, 2/3 purple didn’t
1 element model
parents transmit information (genes) abouut traits to their offspring
2 element model
each individual receives 2 copies (1 from each parent) of each factor (allele) to encode each trait
3 element model
not all factors (alleles) are same, different combinations lead to different traits
4 element model
two alleles dont blend, assemble randomly
5 element model
the presence of an allele doesn’t guarantee it’ll be expressed (can be latent)
homozygote
2 alleles are identical (true breeding)
heterozygote
2 alleles are different (non-true breeding)
genotype
alleles found in individual, AA =/ Aa
phenotype
physical appearance of individual, AA (homozygous) =/ Aa (heterozygous)
phenotype ratio
3:1
genotype ratio
1:2:1 (1 homo dominant, 2 hetero, 1 homo recessive)
Mendels 1st law of heredity
Principle of Segregation - 2 alleles segregate during gamete formation to be rejoined at random during fertilization (1 from each, latent traits)
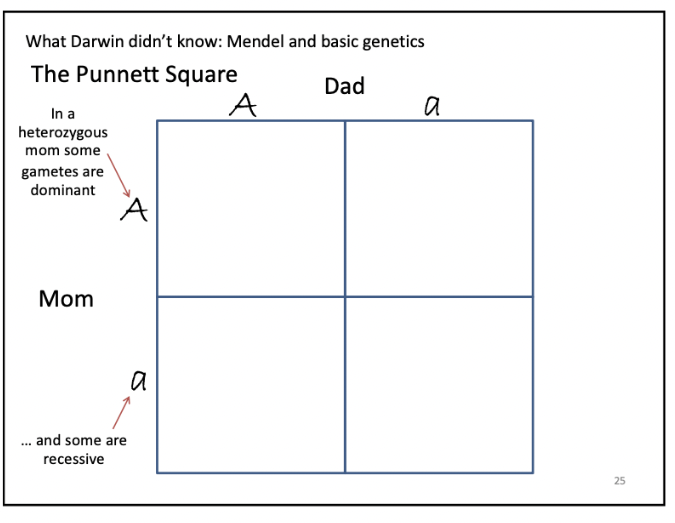
the punnett square
50% mom’s heterozygous gametes dominant/recessive, same for dad
Dihybrid cross
2 traits
dihybrid ratio
9:3:3:1
Mendels 2nd law of herdity
Principle of Independent Assortment - in a dihybrid cross the alleles of each gene assort independently
gene linkage
2 genes linked on same chromosome will be passed down together but will only get offspring with same phenotypes as parents
genes far apart on same chromosome
get segregated during meiosis recombination
polygenic inheritence
phenotype trait attributable to 2 of more genes, quantitative/ continuously varying trait
polygenic inheritence example
height with lots of variation and multiple traits controlling it and disease (difficult)
pleiotropy
simgle gene affects 2 or more characteristics
incomplete dominance
both alleles found in the genotypei
incomplete codominance
a mixture of the alleles in the genotype visible in the phenotype
environmental effects on gene expression
sickle cell anemia and decrease sensitivity of malaria
epistasis
phenotype traits attributable to 2 or more genes that interact (1 modifies/ hides another)
epistasis example
hair color and baldness, fur coat and amount of melanin
codominance example
mice offspring with patches of black and grey fur
number of human chromosomes
46, 23 from mom and 23 from dad
how chromosomes are passed on
cell division that produces gametes
karyotype
complete map set of chromosomes
chromatids
before they replicate, sisters with identical info
centromere
what holds 2 sisters together
chromosomes
paired sister chromatids
homologous pair
same chromosome from mom and dad, same type and genes
why might homologous pair differ
may have different alleles
mitosis phases
interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
interphase
DNA diffuses and replicates
prophase
chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes with identical paired sister chromatids
prometaphase
nuclear envelope breaks, microtubules go to poles/ opposite ends
metaphase
chromosomes line up at equator, condensed and highly coiled (can get best visual)
anaphase
sisters pulled apart, new daughter moves to poles
telophase
cell cleaves in half, daughters enter interphase again separately
Meiosis phases
early prophase , mid prophase , prometaphase, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, telophase 1, prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase 2
early prophase
chromosomes condense
mid prophase
homologous pairs join
prometaphase
pairs cross over
metaphase 1
pairs align at equator
anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes move to poles (sisters dont separate)
telophase 1
cell divides to form sister cells
prophase 2
chromosomes recondense but DNA doesn’t replicate
metaphase 2
centromeres line at equator
anaphase 2
pulled apart and chromosomes move to poles
telophase 2
chromosomes gather into nuclei and cell divides
meiosis products
4 cells with nucleuses with chromosomes
meiosis process
start with 2 DNA, divides 1st into normal amount of DNA then divides again into half as much as normal cell (gametes join)
ploidy
number of copies of chromosomes
haploid
a cell with one copy of each chromosome 1N
diploid
cell with 2 copies of each chromosome 2N
polyploid
more than 2 copies of each chromosome xN
mitosis ploidy
2N to 4N to 2N
meiosis ploidy
2N to 4N to 2N to 1N
crossing over
homologous chromosome pairs (meiosis) have enzymes released that can break and rejoin chromatids
recombination
DNA from non-sister chromatids can be exchange ie. dad chromosome with mom DNA
likeliness of recombination
variable, some might have many or few
recombination leads to
genetic variation (meiosis), reshufflings
gene linkage
in F1 generation, genes are unlinked, 4 gamete combinations are produced (RY,Ry,rY,ry)
all the following are true regarding meiosis except
gametes produced are diploids - are actually haploid
Wilhelm Johannsen
created term gene as unit for inherited traits
Thomas Hunt Morgan
genes rest on chromosomes
George Beadle and Edward Tatum
1 gene codes for 1 enzyme
Oswald Avery, Maclyn McCarty and Colin Macleod
genes are made of DNA
Rosalind Franklin
structure of DNA (helical), Photo 51
the double helix
DNA comprised of 2 intertwined strands of nucleotids
nucleotids fixed along
2 helical backbones made of repeating sugar and phosphate units
nucleotids held together by
hydrogen bonds between nucleotids, paired specifically together
4 nucleotides
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G)
adenine forms
2 hydrogen bonds with thymine
cyotsine forms
3 hydrogen bonds with guanine
how DNA replicates
single parental strand with 2 chains can replicate to 2 daughter strands with exact same information that’s rarely lost
semi econservative replication
produces molecule with both old and new DNA, each molecule contains 1 complete old strand and 1 new one
DNA replication
helix unzips, breaking bonds between paired nucleotids, number of enzzymes bring new nucleotides to the parental chain and form new parent chains
DNA polymerase
match existing nucleotides on parental chain with complementary bases, to form bond between new pairs
the central dogma
portions of DNA get converted into RNA that provides intstructions to cell for production of proteins, who do work of the cell
RNA
single strand of DNA
DNA to RNA
transcription
transcription
works similar to DNA replication
RNA to protein
translation
translation
RNA sequence used to synthesize a polypeptide (protein)