Nutrition 400 Module 2 Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/149
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
1
New cards
Organization of the Human Body
1\.) Chemical Level
2\.) Cell Level
3\.) Tissue Level
4\.) Organ Level
5\.) Organ system level
6\.) Organism level
2\.) Cell Level
3\.) Tissue Level
4\.) Organ Level
5\.) Organ system level
6\.) Organism level
2
New cards
Atom (chemical level)
the smallest portion of which an element can be divided into and still retain properties
protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) make up the middle of the atom while electrons (-) are in the valence shell
protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) make up the middle of the atom while electrons (-) are in the valence shell
3
New cards
Valence shell
first two orbit has 2 valence shells, then every other orbit trys to get 8 electrons to fill the valence shell
4
New cards
Molecule
two or more atoms joined by chemical bonds
example: H2O (water)
example: H2O (water)
5
New cards
complex molecule
Large molecules made up of subunits
example: glycogen
example: glycogen
6
New cards
Molucular formulas
\# of atoms = small numbers after a atom
\# of molecules = big number before the molecules
\# of molecules = big number before the molecules
7
New cards
element
a pure substance made up of only one type of atom
periodic table of elements
periodic table of elements
8
New cards
6 elements that account for 99% of body weight in humans
* oxygen (O), 65% body weight, found in water
* carbon (C) 18% body weight, found in organic molecules
* hydrogen (H), 10% body weight, found in most molecules, including water
* nitrogen (N), 3% body weight, component of proteins
* calcium (Ca), 2% body weight, component of bones, teeth, and body fluids
* phosphorus (P), 1% body weight, found in cell membranes and bone matrix
* carbon (C) 18% body weight, found in organic molecules
* hydrogen (H), 10% body weight, found in most molecules, including water
* nitrogen (N), 3% body weight, component of proteins
* calcium (Ca), 2% body weight, component of bones, teeth, and body fluids
* phosphorus (P), 1% body weight, found in cell membranes and bone matrix
9
New cards
Ions
atoms that have lost or gained an electron (NOT PROTONS)
10
New cards
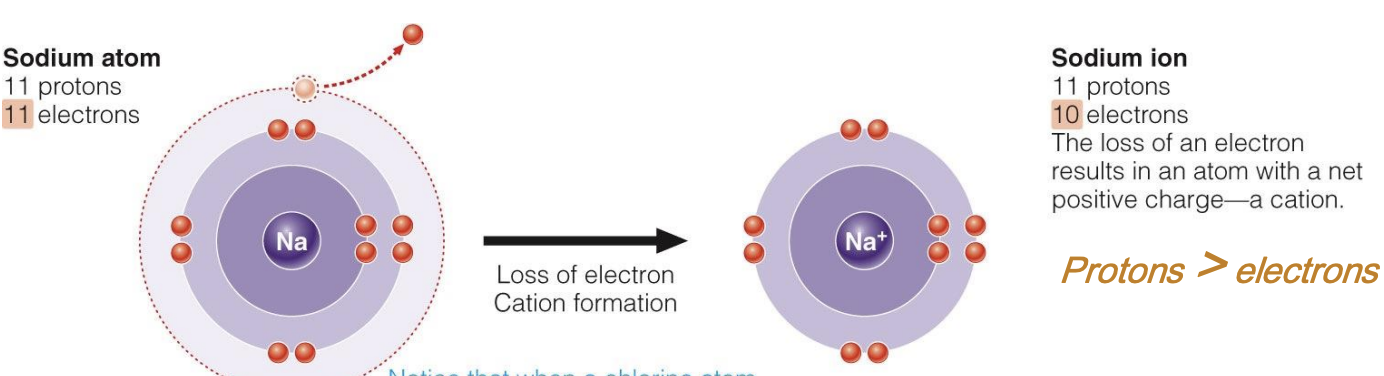
Cation
net positive charge, due to LOSS of electrons
11
New cards
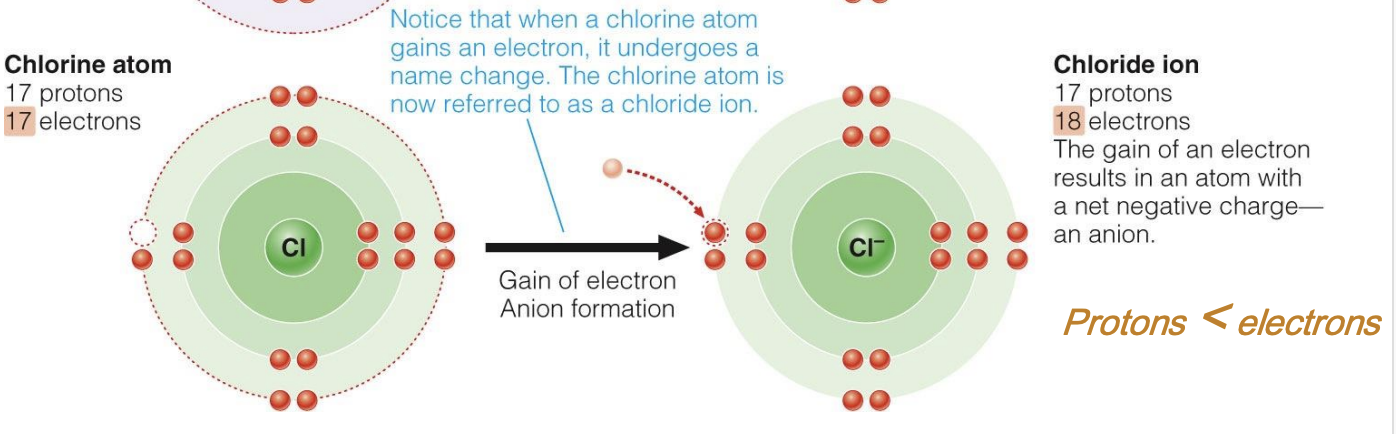
Anion
Net negative charge, due to GAIN of electrons
12
New cards
Formation of Cations
loss of electrons = cation formation
13
New cards
Formation of anion
gain of electron = anion formation
14
New cards
electron transfer
* atoms share electrons
* octet rule
* most atoms prefer 8 electrons in valence shell
* losing/ gaining electrons stabilizes the valence shell
* octet rule
* most atoms prefer 8 electrons in valence shell
* losing/ gaining electrons stabilizes the valence shell
15
New cards
Oxidation reactions
when molecule A transfers its electrons to molecule B, molecule A is oxidized
Oxidation is loss of electrons
Oxidation is loss of electrons
16
New cards
reduction reactions
when molecule B receives electrons from molecule A, Molecule B is reduced.
reduction is gain of electrons
reduction is gain of electrons
17
New cards
free radicals
* free radicals molecules have unpaired electrons, making them unstable and reactive
* in a normal molecules, all electrons are paired
* the free radical steals an electron from another molecule to stabilize itself
* the molecule that lost its electrons has been oxidized creating a new free radical
* this creates a chain reaction; the newly formed free radical oxidizes another molecule by stealing an electron from it
* in a normal molecules, all electrons are paired
* the free radical steals an electron from another molecule to stabilize itself
* the molecule that lost its electrons has been oxidized creating a new free radical
* this creates a chain reaction; the newly formed free radical oxidizes another molecule by stealing an electron from it
18
New cards
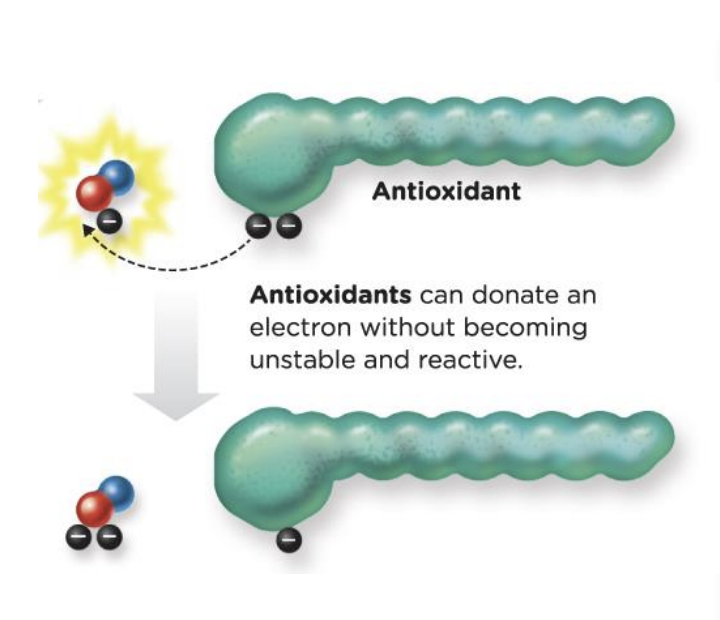
Antioxidants
protective effect: can interrupt the free radical cascade
antioxidants can donate an electron without becoming unstable and reactive
antioxidants can donate an electron without becoming unstable and reactive
19
New cards
Nutrients with antioxidant functions
* water-soluble vitamins
* vitamin C, is an electron donor and functions as a water-soluble antioxidant
* riboflavin, is part of an essential coenzyme that is required by an enzyme that has an antioxidant function and is particularly important in red blood cells
* fat-soluble vitamins
* vitamin E, neutralizes free radicals by donating an electron
* trace minerals
* copper, zinc, manganese, and selenium function as essential components of enzymes that are involved in important antioxidant defense mechanisms that neutralize free radicals
* phytochemical
* beta-carotene and other phytochemical may provide health benefits by their ability to function as antioxidants in our body
* vitamin C, is an electron donor and functions as a water-soluble antioxidant
* riboflavin, is part of an essential coenzyme that is required by an enzyme that has an antioxidant function and is particularly important in red blood cells
* fat-soluble vitamins
* vitamin E, neutralizes free radicals by donating an electron
* trace minerals
* copper, zinc, manganese, and selenium function as essential components of enzymes that are involved in important antioxidant defense mechanisms that neutralize free radicals
* phytochemical
* beta-carotene and other phytochemical may provide health benefits by their ability to function as antioxidants in our body
20
New cards
chemical bonds
* the transfer or sharing of electrons
* atoms → molecules
* examples
* ionic: cations and anions attract each other
* covalent: sharing of electrons
* hydrogen: weak
* atoms → molecules
* examples
* ionic: cations and anions attract each other
* covalent: sharing of electrons
* hydrogen: weak
21
New cards
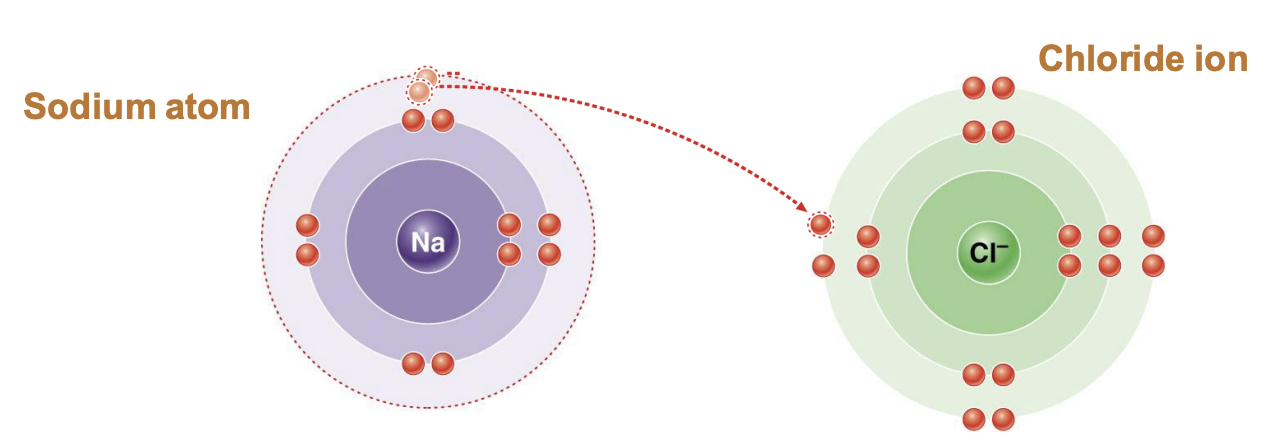
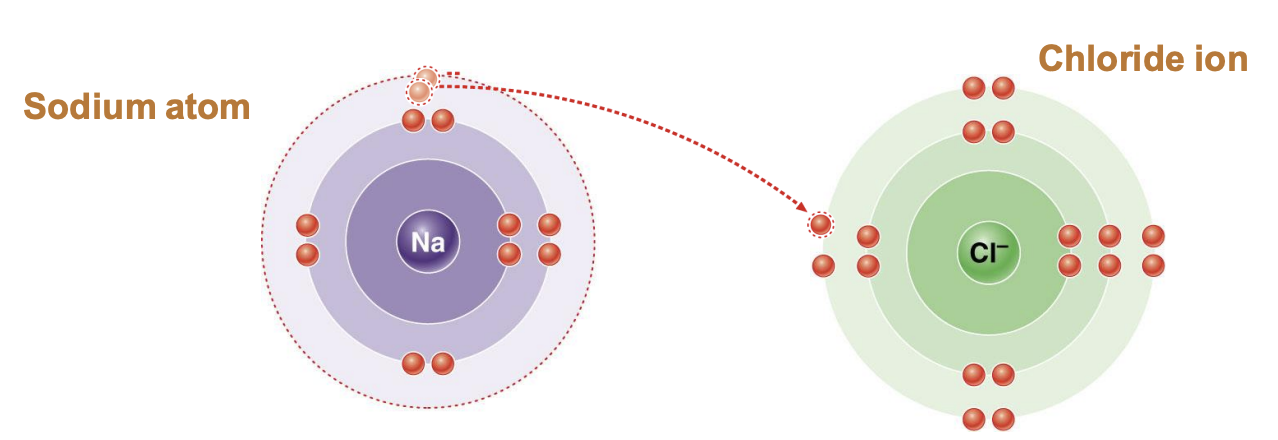
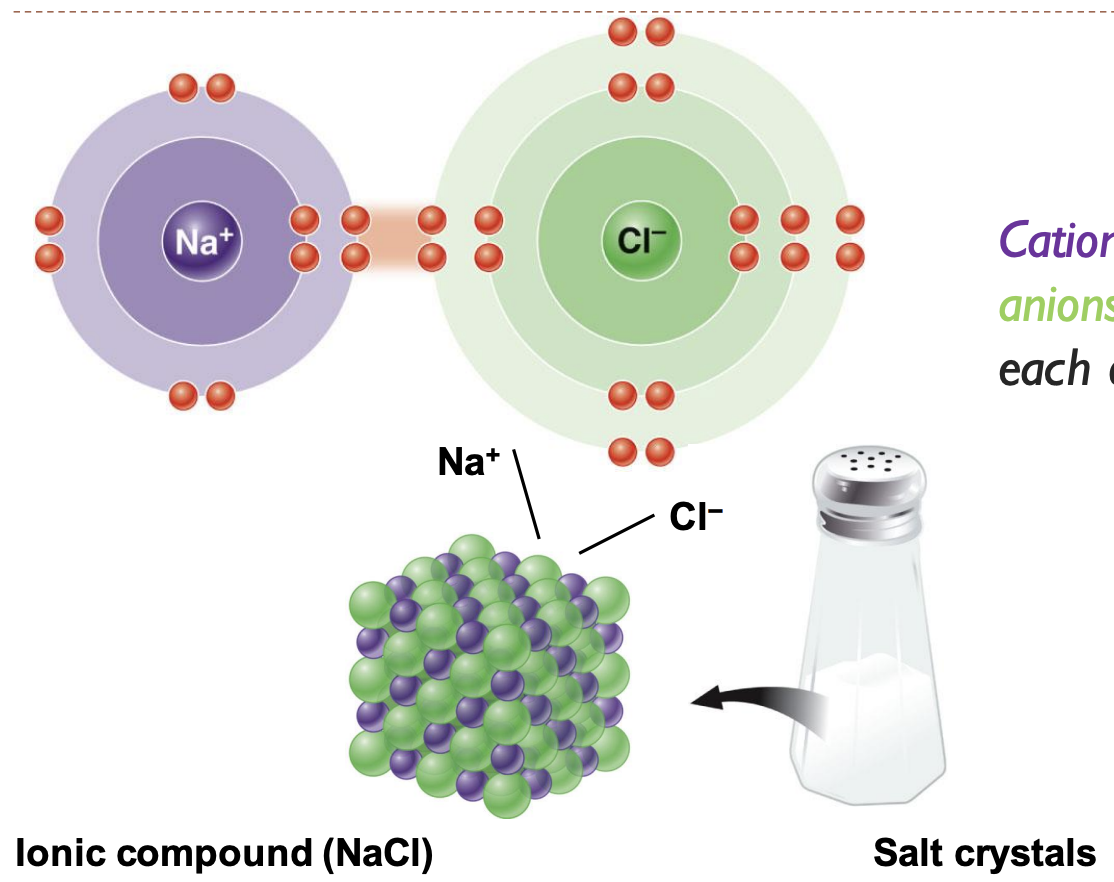
Ionic bond
cations (purple) and anions (green) attract each other like in salt (NaCl)
22
New cards
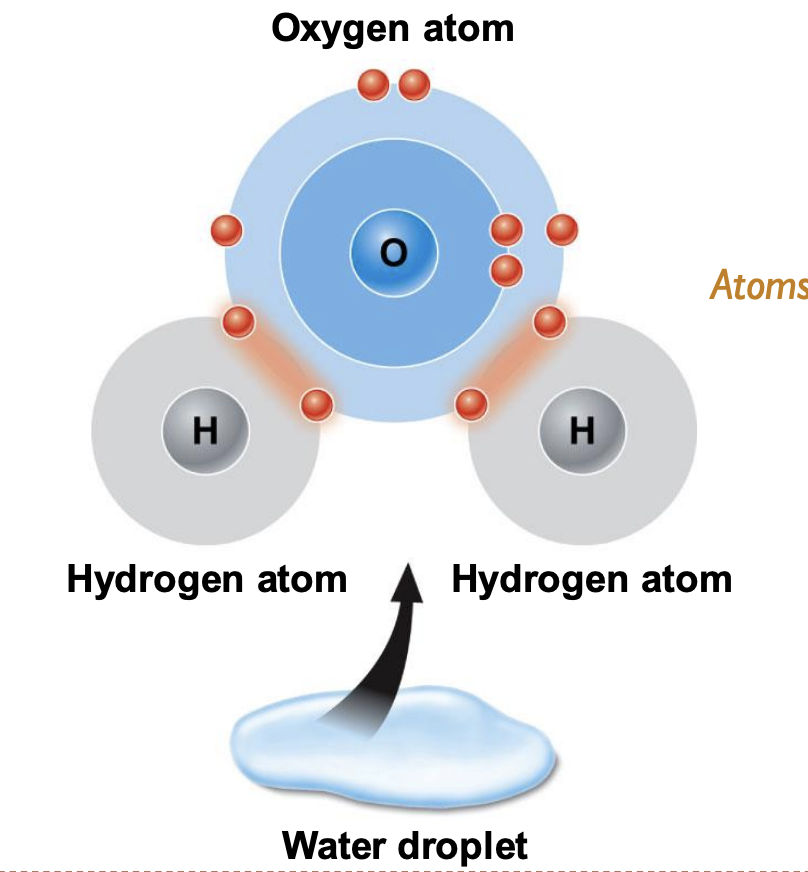
covalent bond
atoms share electrons like in water (H2O)
23
New cards
nonpolar covalent bonds
equal sharing
24
New cards
polar covalent bonds
unequal sharing (+ and - fighting)
25
New cards
Hydrophilic
* polar
* dissolves in water
* dissolves in water
26
New cards
hydrophobic
* nonpolar
* do not dissolve in water
* think phobic (phobia to water)
* do not dissolve in water
* think phobic (phobia to water)
27
New cards
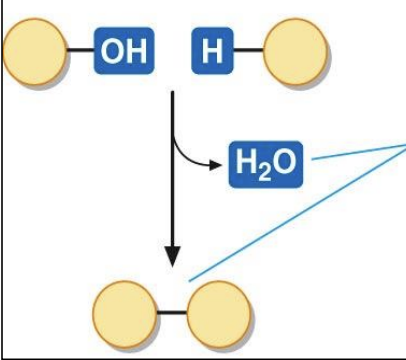
Condensation reactions
* MAKE REACTION
result in the formation of a chemical bond that joins molecules together. when a condensation reaction occurs, a molecule of water is released
result in the formation of a chemical bond that joins molecules together. when a condensation reaction occurs, a molecule of water is released
28
New cards
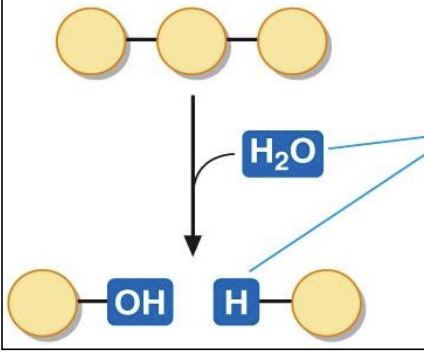
Hydrolysis reaction
* BREAK REACTION
break chemical bonds by the addition of a molecule of water
break chemical bonds by the addition of a molecule of water
29
New cards
pH scale
acidic:
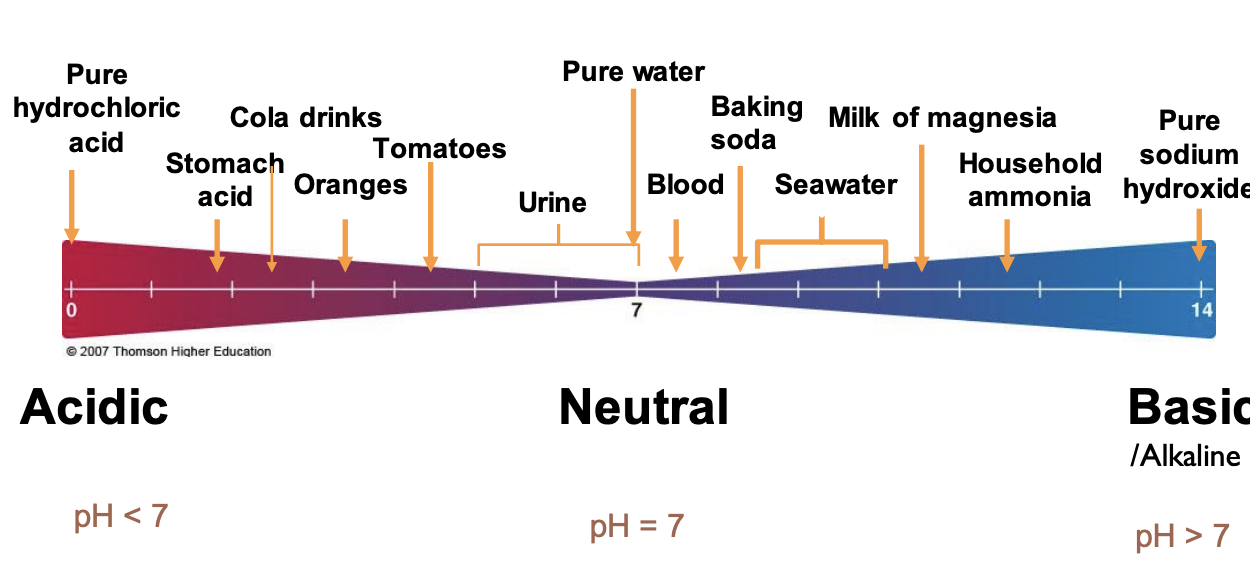
30
New cards
buffering system
* buffer: resists changes in pH
* found in: blood, kidneys, lungs
* prevents acidosis/ alkalosis
* acidosis: high acid
* mild: headache, loss of appetite
* starvation
* diabetes
* alkalosis: high base
* excessive vomiting
* overuse of diuretics/ laxatives
* hyperventilating
* found in: blood, kidneys, lungs
* prevents acidosis/ alkalosis
* acidosis: high acid
* mild: headache, loss of appetite
* starvation
* diabetes
* alkalosis: high base
* excessive vomiting
* overuse of diuretics/ laxatives
* hyperventilating
31
New cards
Homostasis
* state of balance or equilibrium
* controlled by nervous & endocrine systems
* examples
* regulation of blood glucose levels by two major hormones; insulin and glucagon
* controlled by nervous & endocrine systems
* examples
* regulation of blood glucose levels by two major hormones; insulin and glucagon
32
New cards
the cell organelles
cell membrane, smooth ER, rough ER, lysosome, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria
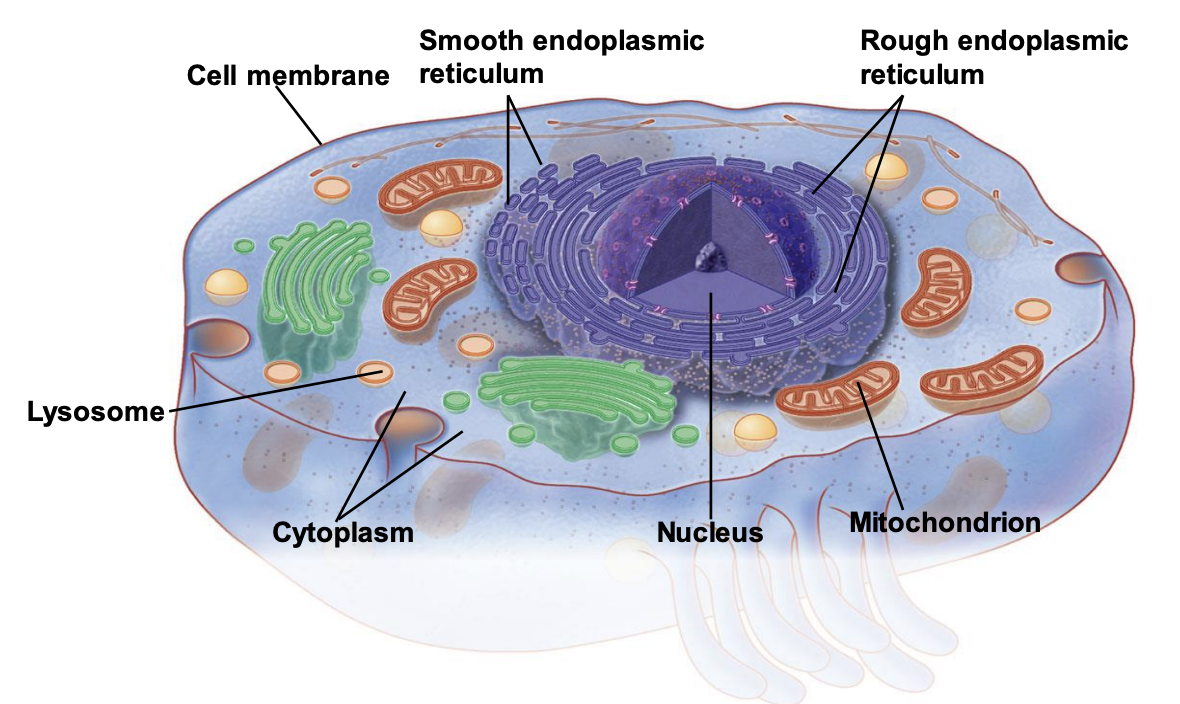
33
New cards
cell membrane
cells are surrounded by a membrane that provides a protective boundary between intracellular and extracellular environments
34
New cards
smooth er
involved in lipid synthesis
do not have ribosomes therefore not involved in protein synthesis
do not have ribosomes therefore not involved in protein synthesis
35
New cards
rough er
contain ribosomes which build and process proteins
36
New cards
lysosome
contain digestive enzymes that breakdown proteins, lipids and nucleic acids
removes and recycles waste products
removes and recycles waste products
37
New cards
cytoplasm
gel-like substance inside cells that conatin the organelles, proteins, electrolytes, and other molecules
38
New cards
nucleus
contains the DNA which provided coded instructions for protein synthesis
39
New cards
mitochondria
produces most of the energy (ATP) of the cells
40
New cards
passive transport mechanisms
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
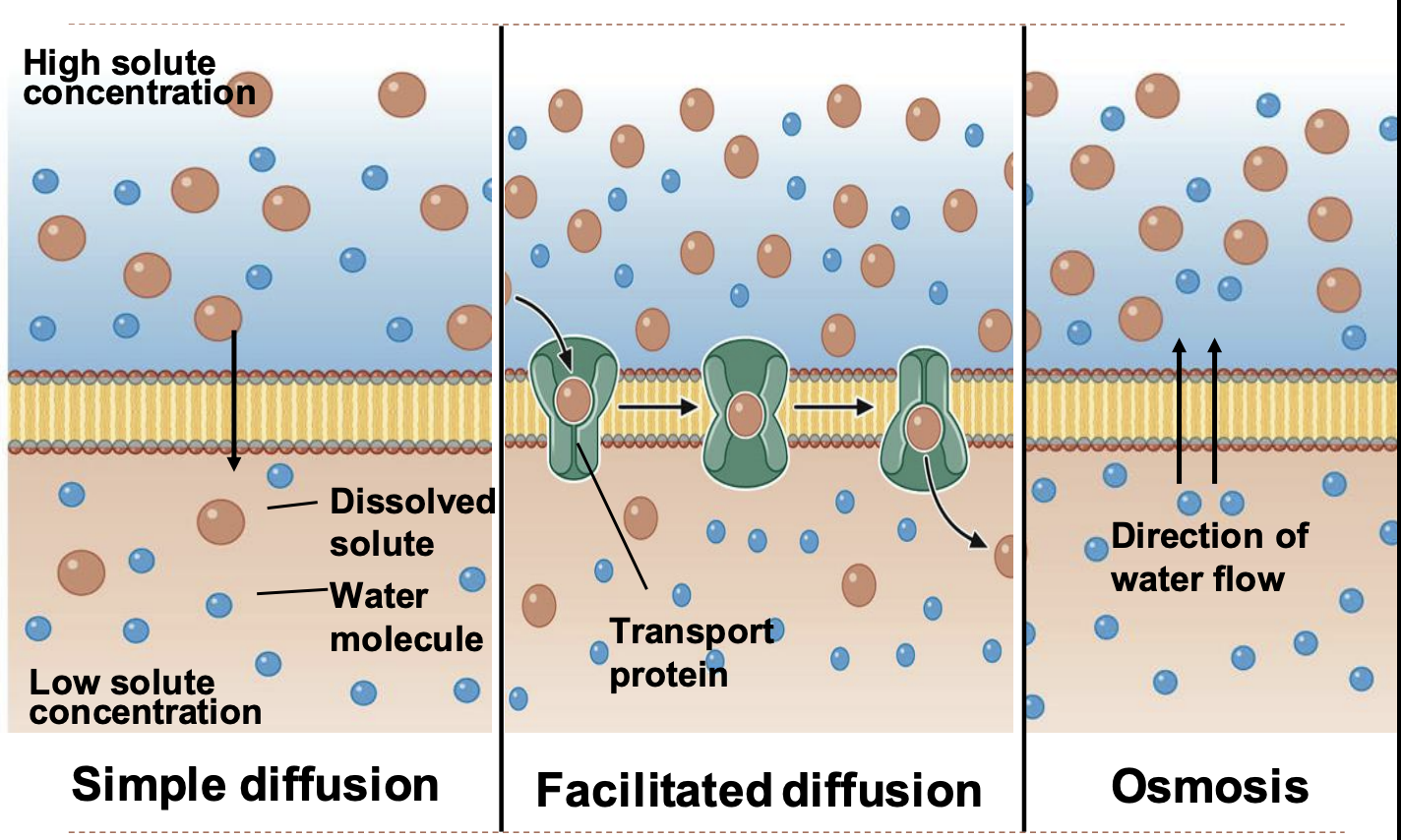
41
New cards
active transport mechanisms
carrier-mediated active transport
exocytosis & endocytosis
exocytosis & endocytosis
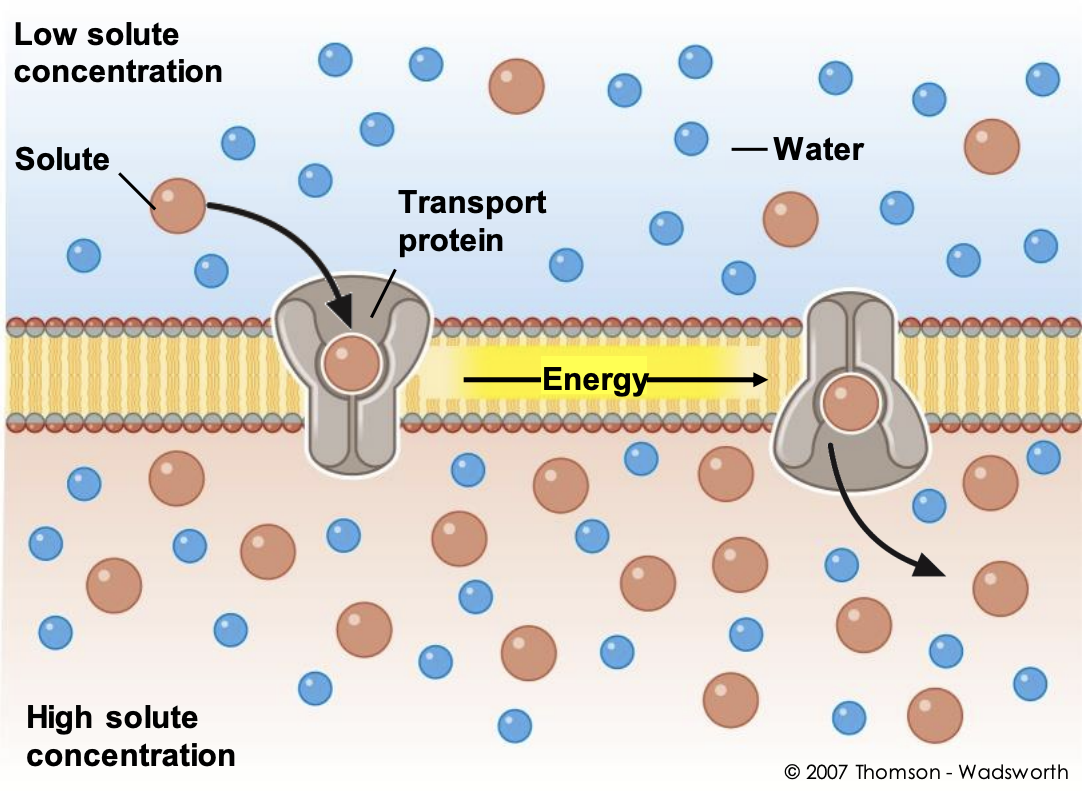
42
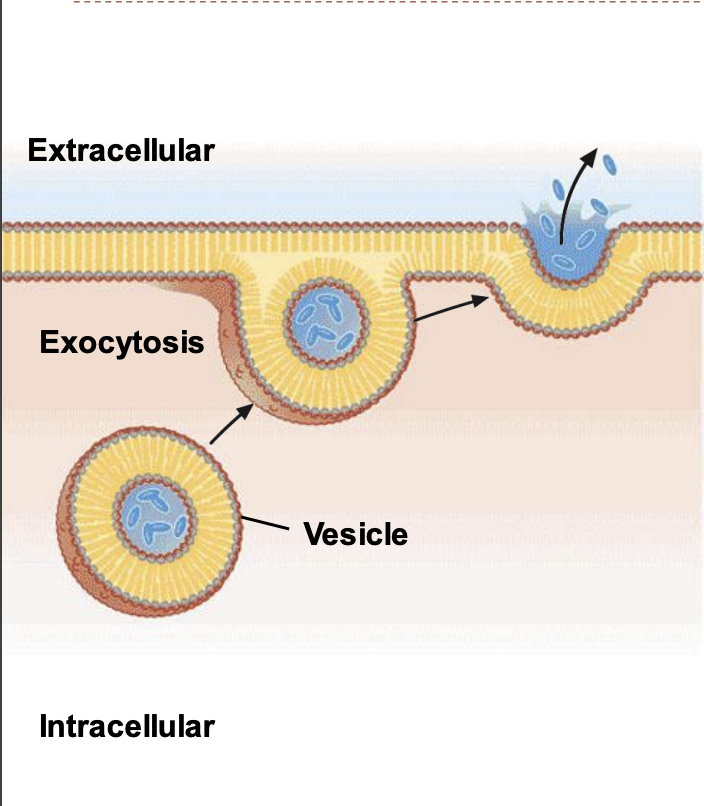
New cards
exocytosis
cells move materials from within the cell into the extracellular fluid. Exocytosis occurs when a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, allowing its contents to be released outside the cell.
43
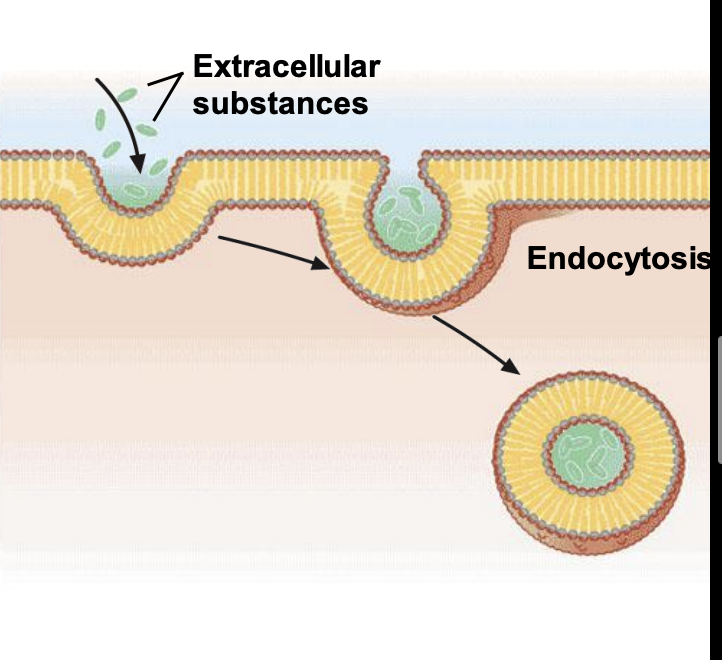
New cards
endocytosis
the process by which cells internalize substances from their external environment. It is how cells get the nutrients they need to grow and develop. Substances internalized by endocytosis include fluids, electrolytes, proteins, and other macromolecules.
44
New cards
humans 4 primary tissue types
epithelial tissue
connective tissue
neutral tissue
muscle tissue
connective tissue
neutral tissue
muscle tissue
45
New cards
epithelial tissue
covers and lines body surfaces, organs, and cavities
46
New cards
connective tissue
provided structure to the body by binding and anchoring body parts
47
New cards
neutral tissue
plays a role in communication by receiving and responding to stimuli
48
New cards
muscle tissue
contracts and shortens when stimulated, playing an important role in movement
49
New cards
Digestive system
* major organs and structures
* mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and salivary glands
* major function
* governs the physical and chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be absorbed into the circulatory system. eliminates solid wastes
* includes organs of gastrointestinal tract, accessory organs
* mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and salivary glands
* major function
* governs the physical and chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be absorbed into the circulatory system. eliminates solid wastes
* includes organs of gastrointestinal tract, accessory organs
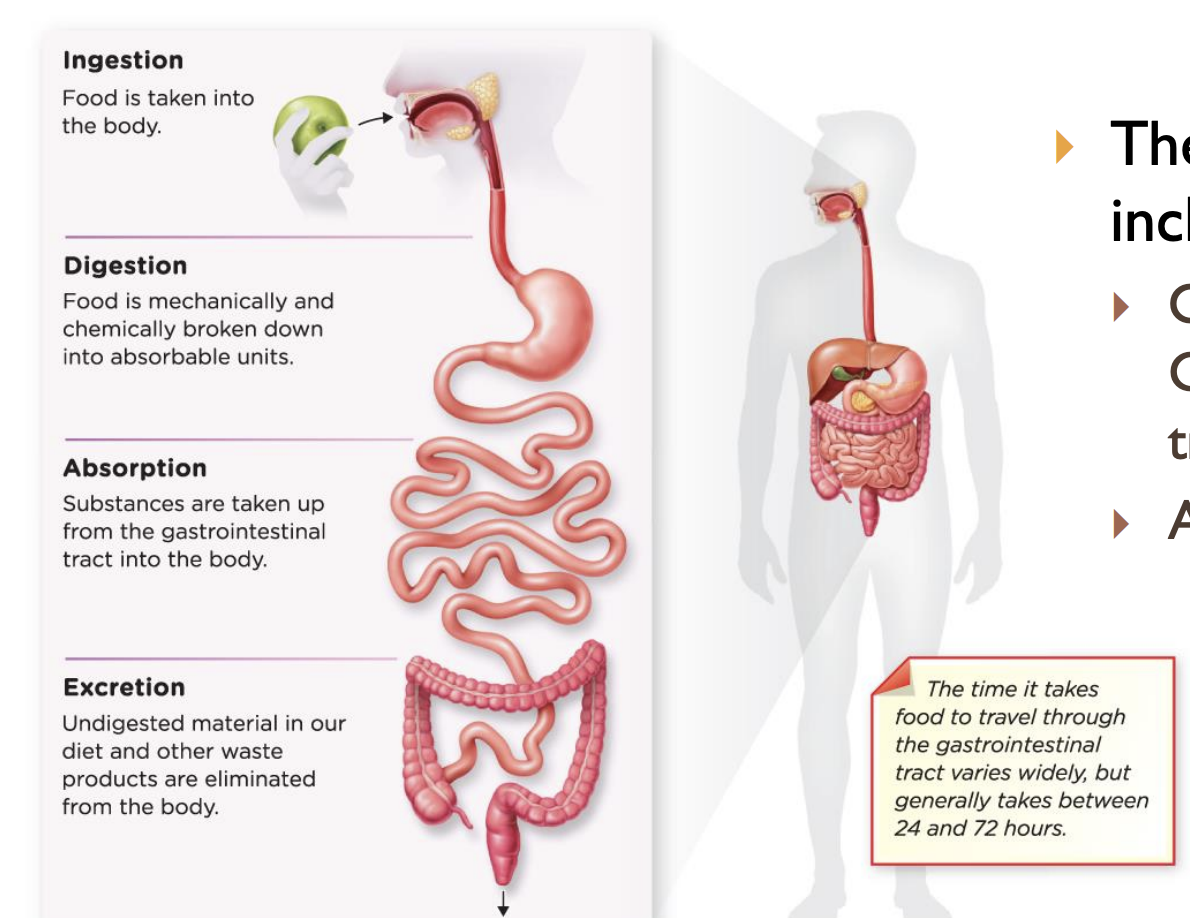
50
New cards
ingestion
food is taken into the body
51
New cards
digestion
food is mechanically and chemically broken down into absorbable units
52
New cards
absorption
substance are taken up from the gastrointestinal tract into the body
53
New cards
excretion
undigested material in our diet and other waste products are eliminated from the body
54
New cards
organs of the GI tract
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine
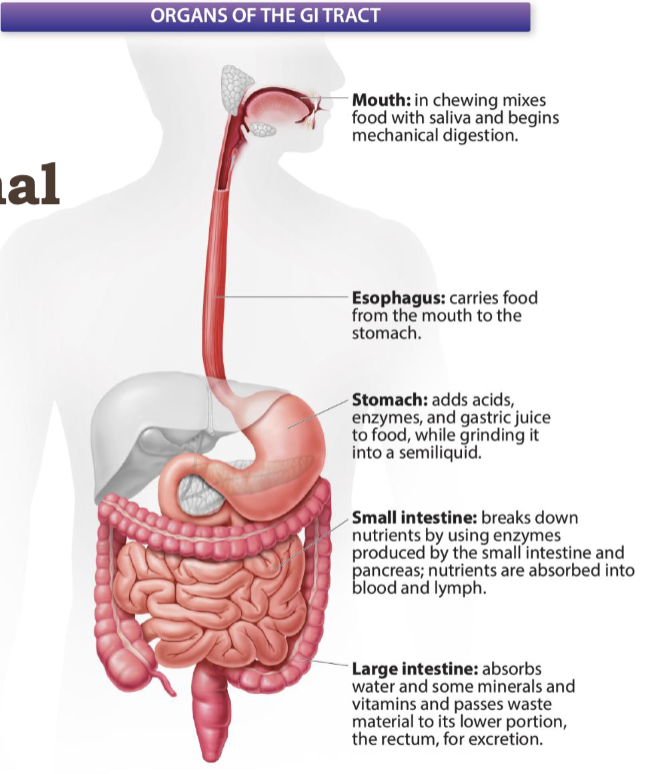
55
New cards
mouth
in chewing mixes food with saliva and begins mechanical digestion
56
New cards
esophagus
carries food from the mouth to the stomach
57
New cards
stomach
adds acids, enzymes, and gastric juices to food, while grinding it into a semiliquid
* major site for mechanical digestion
* major site for mechanical digestion
58
New cards
small intestine
breaks down nutrients by using enzymes produced by the small intestine and pancreas; nutrients are absorbed into blood and lymph
* primary site for digestion of food and absorption of nutrients
\
* primary site for digestion of food and absorption of nutrients
\
59
New cards
large intestine
absorbs water and some minerals and vitamins and passes waste material to its lower portion, the rectum, for excretion
60
New cards
four tissue layers in the GI tract
* serosa
* muscularis
* circular muscle
* longitudinal muscle
* submucosa
* mucosa
* lumen
* muscularis
* circular muscle
* longitudinal muscle
* submucosa
* mucosa
* lumen
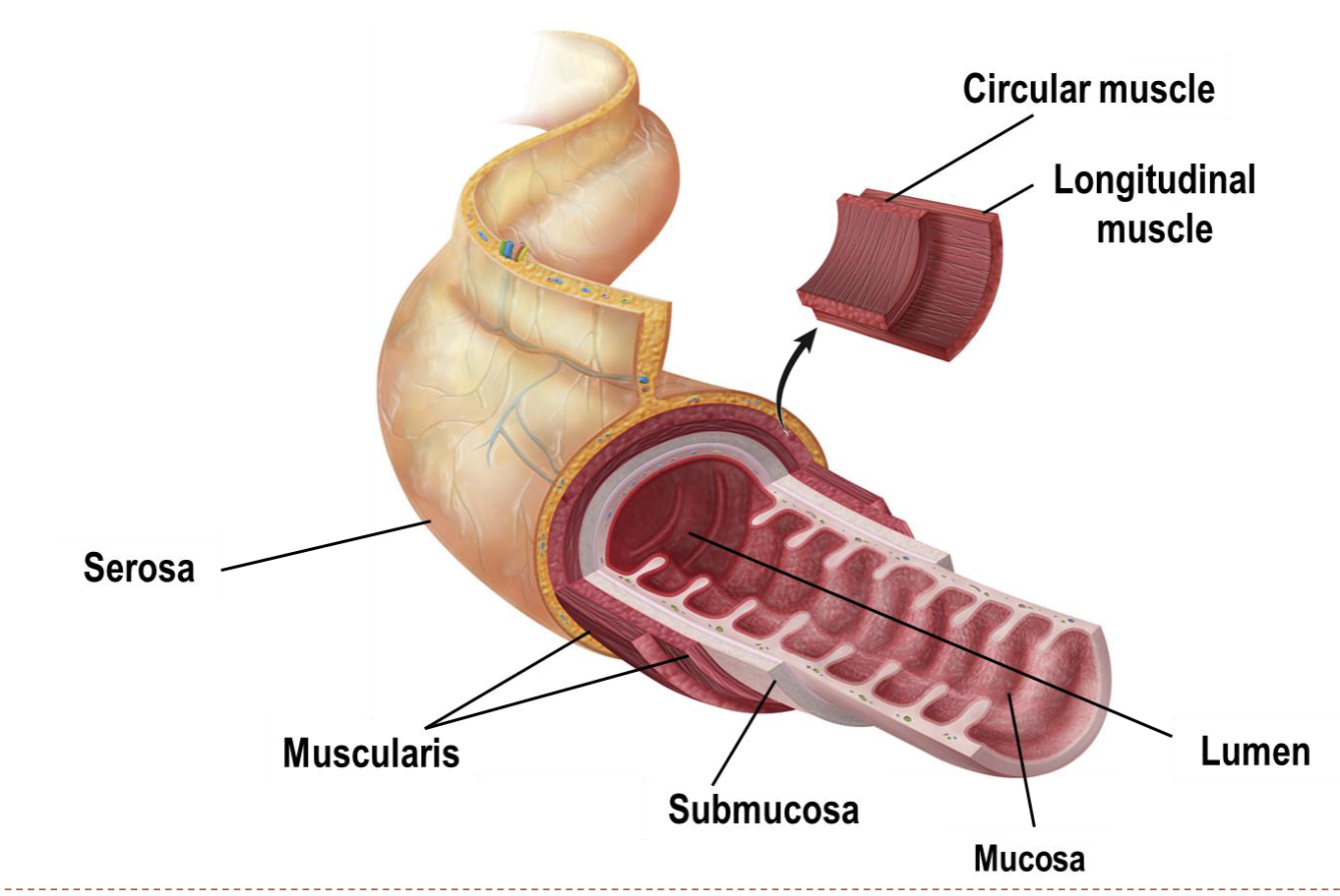
61
New cards
accessory organs and their functions
secrete fluids that aid in digestion
* salivary glands
* secretes saliva that moistens and lubricates food and contains two digestive enzymes
* liver
* produces bile that is required for lipid digestion and absorption
* gallbladder
* stores bile produced in the liver until released into the small intestine
* pancreas
* produces enzymes to digest energy-providing nutrients and released bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid
* salivary glands
* secretes saliva that moistens and lubricates food and contains two digestive enzymes
* liver
* produces bile that is required for lipid digestion and absorption
* gallbladder
* stores bile produced in the liver until released into the small intestine
* pancreas
* produces enzymes to digest energy-providing nutrients and released bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid
62
New cards
Sphincters
regulate the flow of food
* the gastroesophageal sphincter, located between the esophagus and the stomach, relaxes briefly to allow food to enter the stomach
* after the food passes into the stomach, the gastroesophageal sphincter closes to prevent the stomach contents from re-entering the esophagus
* the gastroesophageal sphincter, located between the esophagus and the stomach, relaxes briefly to allow food to enter the stomach
* after the food passes into the stomach, the gastroesophageal sphincter closes to prevent the stomach contents from re-entering the esophagus
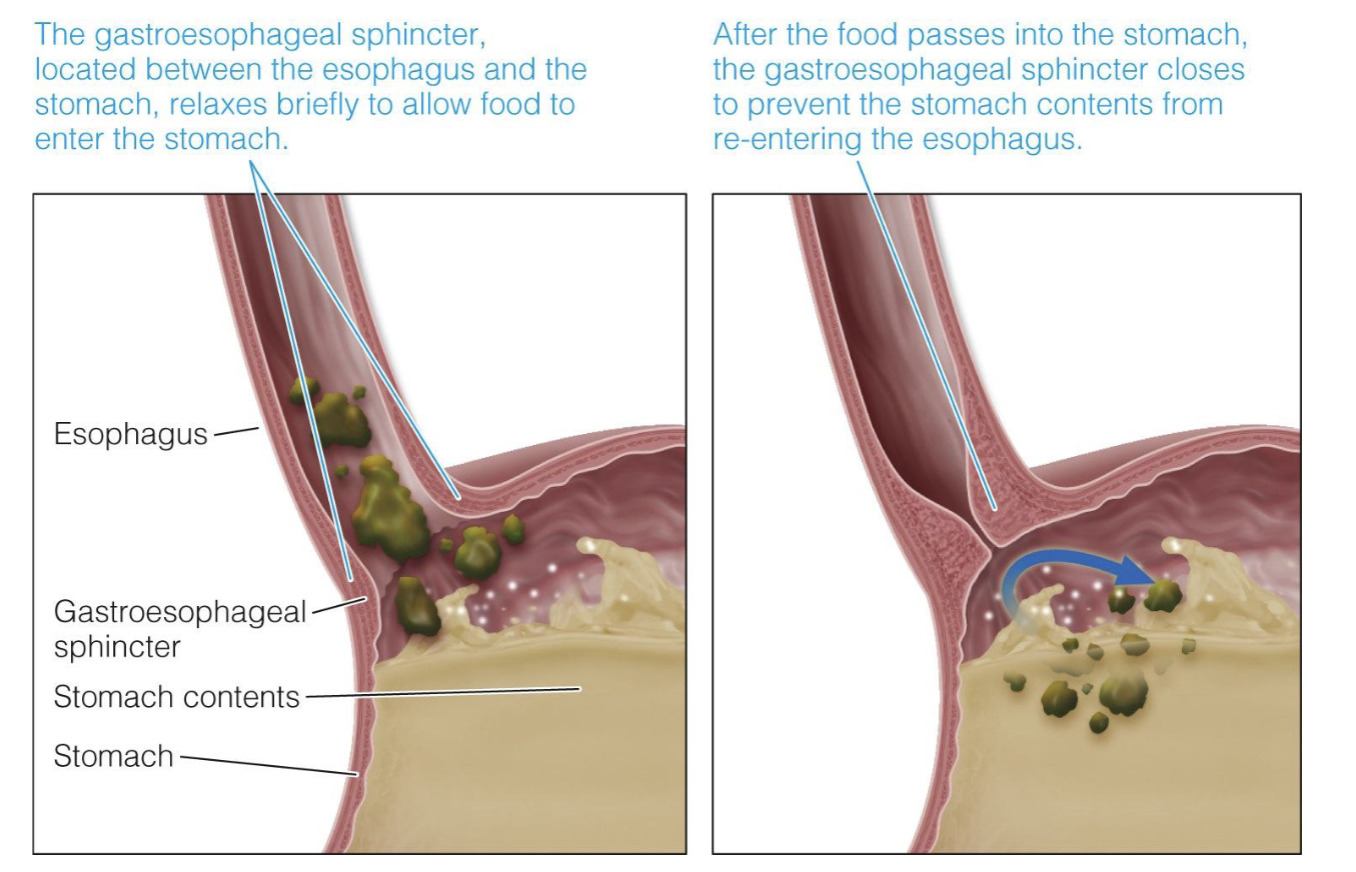
63
New cards
where does food, bolus, chyme, waste take place
* food
* in the mouth
* bolus
* esophagus
* chyme
* stomach, small intestine
* waste
* large intestine
* in the mouth
* bolus
* esophagus
* chyme
* stomach, small intestine
* waste
* large intestine
64
New cards
mechanical digestion
physical break down of food
* mastication
* grinding of food into smaller pieces by the teeth
* peristalsis: propulsion
* rhythmic waves of contractions that move the food particles through the various regions in which mechanical and chemical digestion take place
* segmentation: mixing
* localized contractions of circular muscle of the GI tract
* mastication
* grinding of food into smaller pieces by the teeth
* peristalsis: propulsion
* rhythmic waves of contractions that move the food particles through the various regions in which mechanical and chemical digestion take place
* segmentation: mixing
* localized contractions of circular muscle of the GI tract
65
New cards
chemical digestion
breaks chemical bonds to cleave large molecules into smaller ones
involves enzymes and other substances
* enzymes chemically breakdown components of food
* found throughout our GI tract
* suffix -ase (usually used)
* saliva is part of chemical digestion
involves enzymes and other substances
* enzymes chemically breakdown components of food
* found throughout our GI tract
* suffix -ase (usually used)
* saliva is part of chemical digestion
66
New cards
cephalic phase
early signaling prepares the GI tract for digestion
“wake up” call
“wake up” call
67
New cards
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
happens when gastroesophageal sphincter weakens, the stomach contents flow back into the esophagus. the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus is called gastro-esophageal reflux disease
68
New cards
peptic ulcers
occur when aicd in the digestive tract east away at the inner surface of the stomach or small intestine. the acid can create a painful open sore that may bleed
69
New cards
pancreas
* is an accessory organ
* pancreatic juice
* is an alkaline solution that neutralizes the acidic chyme as it enters the duodenum.
* also contains enzymes that aid in the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins ,and lipids
* pancreatic juice
* is an alkaline solution that neutralizes the acidic chyme as it enters the duodenum.
* also contains enzymes that aid in the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins ,and lipids
70
New cards
Liver and gallbladder
1\.) once bile is made by the liver, some of its transported to the gallbladder where it can be stored for later release
2\.) when the gallbladder contacts, bile is released into the cystic duct. the cystic duct joins the common bile duct
3\.) bile acids in lipid digestion by enabling large lipid globules to disperse in the watery environment of the small intestine
4\.) after aiding in lipid digestion, the bile constituents are reabsorbed from the ileum and returned to the liver via the hepatic portal vein
5\.) the liver uses these constituents to resynthesizes bile
2\.) when the gallbladder contacts, bile is released into the cystic duct. the cystic duct joins the common bile duct
3\.) bile acids in lipid digestion by enabling large lipid globules to disperse in the watery environment of the small intestine
4\.) after aiding in lipid digestion, the bile constituents are reabsorbed from the ileum and returned to the liver via the hepatic portal vein
5\.) the liver uses these constituents to resynthesizes bile
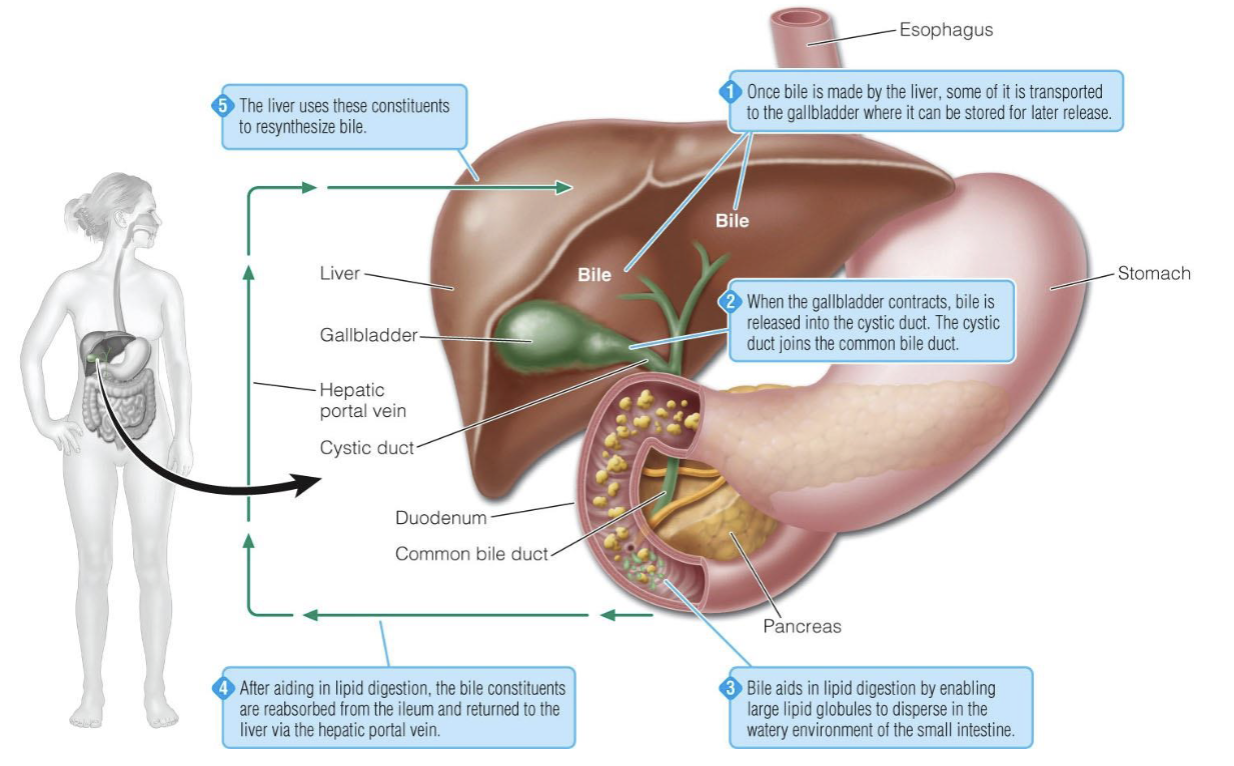
71
New cards
villi of the small intestine
increases the surface area for food absorption and adding digestive secretions
72
New cards
microvilli of the small intestine
absorbs nutrients and protects the body from intestinal bacteria
73
New cards
celiac disease
* autoimmune disease
* inflammatory response to gluten
* wheat, rye, barley
* villi damaged; poor nutrient absorption
* inflammatory response to gluten
* wheat, rye, barley
* villi damaged; poor nutrient absorption
74
New cards
delivering nutrients to the body via circulatory and lymphatic system
* circulatory system (blood vessels)
* carbohydrates
* amino acids
* minerals
* water-soluble vitamins
* lymphatic system
* mosts fats some vitamins
\
* carbohydrates
* amino acids
* minerals
* water-soluble vitamins
* lymphatic system
* mosts fats some vitamins
\
75
New cards
gut microbiome
* benefits
* retrieves some energy from undigested carbohydrates
* improves health of mucosa in the gut
* promotes immune system health
* enhances mineral absorption
* synthesizes vitamin K, folate, biotin
* displaces pathogenic (bad) bacteria
* reduces cancer risk
* probiotics and prebiotics
* retrieves some energy from undigested carbohydrates
* improves health of mucosa in the gut
* promotes immune system health
* enhances mineral absorption
* synthesizes vitamin K, folate, biotin
* displaces pathogenic (bad) bacteria
* reduces cancer risk
* probiotics and prebiotics
76
New cards
inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
* chronic autoimmune disease
* causes inflammation which can permanently harm the intestines
* examples
* ulcerative colitis
* chron’s disease
* causes inflammation which can permanently harm the intestines
* examples
* ulcerative colitis
* chron’s disease
77
New cards
irritable bowel syndrome
* group of symptoms including abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and other discomfort
* function disorder → does not lead to serious disease
* does not cause inflammation
* effects up to 20% of adults in the US
* function disorder → does not lead to serious disease
* does not cause inflammation
* effects up to 20% of adults in the US
78
New cards
carbohydrates
main source of energy for the body (4 kcal/g)
* composition
* carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O)
* composed of one or more sugar (saccharide) units
* functions in food
* source of fiber
* adds sweetness and flavor
* found sources
* starches and grains
* fruit
* dairy
* sweets/ desserts
* functions in the body
* source of energy for all cells in the body
* indispensable source of energy for the brain, red blood cells, and muscles during intense exercise
* important for intestinal health
* reduces the use of protein for energy
\
* composition
* carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O)
* composed of one or more sugar (saccharide) units
* functions in food
* source of fiber
* adds sweetness and flavor
* found sources
* starches and grains
* fruit
* dairy
* sweets/ desserts
* functions in the body
* source of energy for all cells in the body
* indispensable source of energy for the brain, red blood cells, and muscles during intense exercise
* important for intestinal health
* reduces the use of protein for energy
\
79
New cards
simple carbohydrates
* Monosaccharides (1 sugar unit)
* glucose
* circulates in the blood stream. its found in fruits, vegetables, and honey
* frutose
* found in fruits vegetables, and honey
* galactose
* one of the monosaccharides that make up milk sugar
* disaccharides (2 sugar units)
* lactose
* often called “milk sugar” as it is found in onlu milk, yogurt, and other dairy products
* sucrose
* otherwise known as “table sugar” it is found in fruits and vegetables
* maltose
* formed in large amounts as a product of starch digestion; however very little is found in the foods we eat
* glucose
* circulates in the blood stream. its found in fruits, vegetables, and honey
* frutose
* found in fruits vegetables, and honey
* galactose
* one of the monosaccharides that make up milk sugar
* disaccharides (2 sugar units)
* lactose
* often called “milk sugar” as it is found in onlu milk, yogurt, and other dairy products
* sucrose
* otherwise known as “table sugar” it is found in fruits and vegetables
* maltose
* formed in large amounts as a product of starch digestion; however very little is found in the foods we eat
80
New cards
complex carbohydrates
* oligosaccharides (3-10 sugar units)
* raffinose
* stachyose
* polysaccharides (>10 sugar units)
* glycogen (digestible polysaccharides)
* major storage form of carbohydrate in animals
* found in liver, muscle
* structure
* highly branched
* readily available sites for enzyme action
* starch (digestible polysaccharides)
* major storage form of carbohydrate in plants
* 2 types of plant starch:
* amylose: is a straight chain polymer
* amylopectin: is branched
* dietary fiber (indigestible polysaccharides)
* diverse group of polysaccharides found in plants (within the cell wall)
* may be straight chains of glucose or branched chains composed of a variety of sugars
* abundant in legumes, nuts, whole grains, vegetables, and some berries
\
* raffinose
* stachyose
* polysaccharides (>10 sugar units)
* glycogen (digestible polysaccharides)
* major storage form of carbohydrate in animals
* found in liver, muscle
* structure
* highly branched
* readily available sites for enzyme action
* starch (digestible polysaccharides)
* major storage form of carbohydrate in plants
* 2 types of plant starch:
* amylose: is a straight chain polymer
* amylopectin: is branched
* dietary fiber (indigestible polysaccharides)
* diverse group of polysaccharides found in plants (within the cell wall)
* may be straight chains of glucose or branched chains composed of a variety of sugars
* abundant in legumes, nuts, whole grains, vegetables, and some berries
\
81
New cards
potential health benefits of dietary fiber (indigestible polysaccharides)
* soluble fiber
* low CVD risk
* promotes satiety and low obesity risk
* slows BG rise following CHO ingestion
* insoluble fiber
* low risk of Type 2 diabetes
* low constipation occurrence
* high fiber intake may lower risk of some cancers
* low CVD risk
* promotes satiety and low obesity risk
* slows BG rise following CHO ingestion
* insoluble fiber
* low risk of Type 2 diabetes
* low constipation occurrence
* high fiber intake may lower risk of some cancers
82
New cards
diverticular disease
* results when small, protruding pouches called diverticula form along the wall of the large intestine
* characterized by the formation of out pouching along ten wall of the large intestine
* high fiber diet and active lifestyle has protective effect
* characterized by the formation of out pouching along ten wall of the large intestine
* high fiber diet and active lifestyle has protective effect
83
New cards
anatomy of a whole grain
* **endosperm** contains the highest amount of starch and protein and its all that remains when a grain is refined
* **bran** contains the majority of dietary fiber and a significant amount of B vitamins and minerals
* **germ** the embryo of the seed that germinates and grows and contains essential fatty acids and a number of B vitamins and minerals
* GERM AND BRAN
* vast majority of vitamins and minerals and phytochemical are found in the **germ and bran**
* **germ and bran** are removed when processing wheat to produce **refined grains**
* **bran** contains the majority of dietary fiber and a significant amount of B vitamins and minerals
* **germ** the embryo of the seed that germinates and grows and contains essential fatty acids and a number of B vitamins and minerals
* GERM AND BRAN
* vast majority of vitamins and minerals and phytochemical are found in the **germ and bran**
* **germ and bran** are removed when processing wheat to produce **refined grains**
84
New cards
fortification
* nutrients are:
* **absent** originally
* **added** to prevent deficiencies in a community
* **absent** originally
* **added** to prevent deficiencies in a community
85
New cards
enriched
* nutrients are:
* **present** originally
* lost during processing
* **put back in!** to maintain nutrient profile
* 5 nutrients in the U.S. requires to be added back in after processing is:
* iron
* thiamin
* riboflavin
* niacin
* folate
* **present** originally
* lost during processing
* **put back in!** to maintain nutrient profile
* 5 nutrients in the U.S. requires to be added back in after processing is:
* iron
* thiamin
* riboflavin
* niacin
* folate
86
New cards
how much carbohydrates do we need?
* 2020 dietary guidelines for Americans
* consume at least half of all grains as whole grains. increase whole grain intake by replacing refined grains with whole grains
* health and medicine division recommendations (DRIs)
* RDA: 130 g/day
* AMDR: 45%-65% of total calories
* 2,000 kcal/day diet: 225-325 g/day
* 2,500 kcal/day diet: 281-406 g/day
* consume at least half of all grains as whole grains. increase whole grain intake by replacing refined grains with whole grains
* health and medicine division recommendations (DRIs)
* RDA: 130 g/day
* AMDR: 45%-65% of total calories
* 2,000 kcal/day diet: 225-325 g/day
* 2,500 kcal/day diet: 281-406 g/day
87
New cards
added sugars in the diet
goal:
88
New cards
low carbohydrates diets
* < 100 g CHO/ day
* unlimited meats, high-fat foods
* low glycogen synthesis
* water & body protein loss
* short-term vs long-term effects
* unlimited meats, high-fat foods
* low glycogen synthesis
* water & body protein loss
* short-term vs long-term effects
89
New cards
carbohydrate digestion
dietary carbohydrates (salivary amylase) → polysaccharides, dextrins, sucrose, lactose, maltose (pancreatic amylase) → → monosaccharides: glucose, galactose, fructose (active transport) → monosaccharides in blood stream
90
New cards
digestion of carbs in the mouth
* mastication
* salivary amylase
* acts on alpha -(1,4) linkages
* salivary amylase
* acts on alpha -(1,4) linkages
91
New cards
activity in the stomach for carbohydrates
* salivary amylase in inactivated by gastric acid
* starch chemical digestion stops
* starch chemical digestion stops
92
New cards
digestion in the small intestine for carbohydrates
polysaccharides (pancreatic amylase) → disaccharides (disaccharidases) → monosaccharides
* the digestion of disaccharides takes place on the surface of the brush border of the small intestine
* intestinal disaccharidases hydrolyze disaccharides. the resulting monosaccharides are transported into enterocytes
* the digestion of disaccharides takes place on the surface of the brush border of the small intestine
* intestinal disaccharidases hydrolyze disaccharides. the resulting monosaccharides are transported into enterocytes
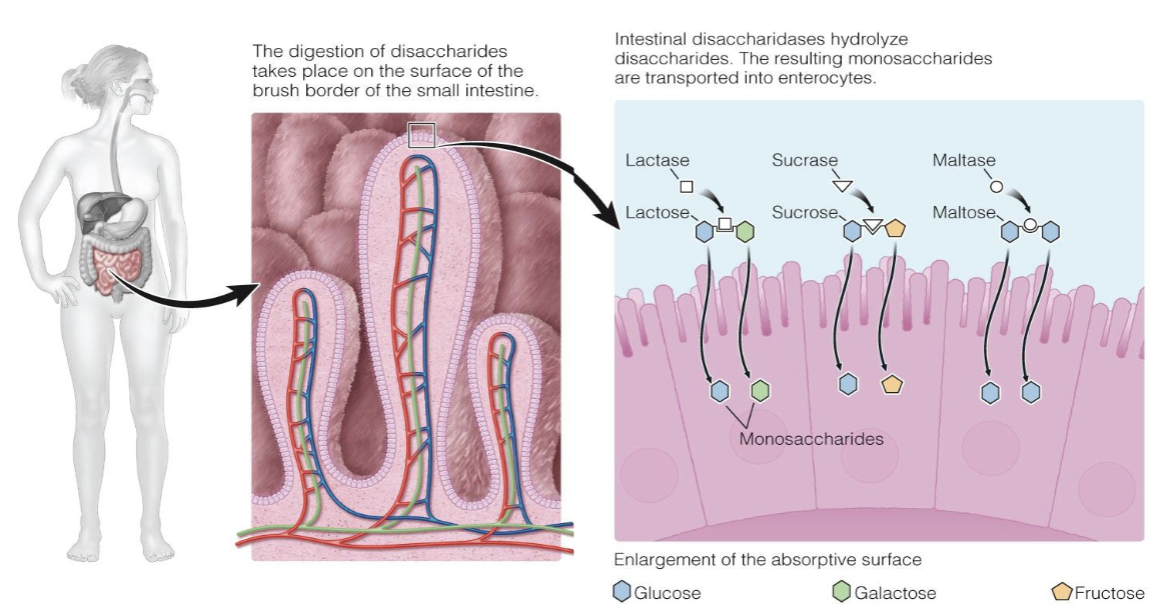
93
New cards
absorption in the small intestine for carbohydrates
glucose absorption occurs in the small intestine by active transport via the sodium glucose co transporter. galactose, fructose and some glucose absorption is completed by the Glut5 transporter by facilitated diffusion
94
New cards
lactose intolerance
cause: lactose deficiency
symptoms: nausea, bloating, abnormal discomfort, diarrhea
treatment:
* lactose dairy products or lactase pills
* add calcium and vitamin D rich foods or supplements
symptoms: nausea, bloating, abnormal discomfort, diarrhea
treatment:
* lactose dairy products or lactase pills
* add calcium and vitamin D rich foods or supplements
95
New cards
3 fates of glucose
* immediate energy source for all cells
* concerted into glycogen (glycogenesis)
* limited source of stored carbohydrate in the liver
* converted into fat
* adipose tissue (unlimited storage capacity)
* concerted into glycogen (glycogenesis)
* limited source of stored carbohydrate in the liver
* converted into fat
* adipose tissue (unlimited storage capacity)
96
New cards
insulin
regulates glucose uptake from the blood
97
New cards
glucagon
regulates release of glucose into the blood
98
New cards
lipid basics
* supply energy (9 kcal/g)
* C, **H**, O
* oils vs fats
* water insoluble (non polar = hydrophic
* diverse function and structure
* energy, insulation, fat soluble, vitamins, cell membranes, essential fatty acids, satiety & palatability
* types of lipids
* fatty acids
* triglycerides
* sterols
* phospholipids
* C, **H**, O
* oils vs fats
* water insoluble (non polar = hydrophic
* diverse function and structure
* energy, insulation, fat soluble, vitamins, cell membranes, essential fatty acids, satiety & palatability
* types of lipids
* fatty acids
* triglycerides
* sterols
* phospholipids
99
New cards
fatty acids
* carbon chain with hydrogen atoms attached
* methyl (CH3) & carboxylic acid (COOH) groups
* differ in chain length and saturation
* determines their function and role in health and disease
* chain length
* short chain < 8 carbons
* medium chain = 8-12 carbons
* long chain > 12 carbons
* degree of saturation
* no double bonds (saturated)
* solid at room temp
* one double bond (unsaturated)
* liquid at room temp
* 2 or more double bonds (unsaturated)
* liquid at room temp
* methyl (CH3) & carboxylic acid (COOH) groups
* differ in chain length and saturation
* determines their function and role in health and disease
* chain length
* short chain < 8 carbons
* medium chain = 8-12 carbons
* long chain > 12 carbons
* degree of saturation
* no double bonds (saturated)
* solid at room temp
* one double bond (unsaturated)
* liquid at room temp
* 2 or more double bonds (unsaturated)
* liquid at room temp
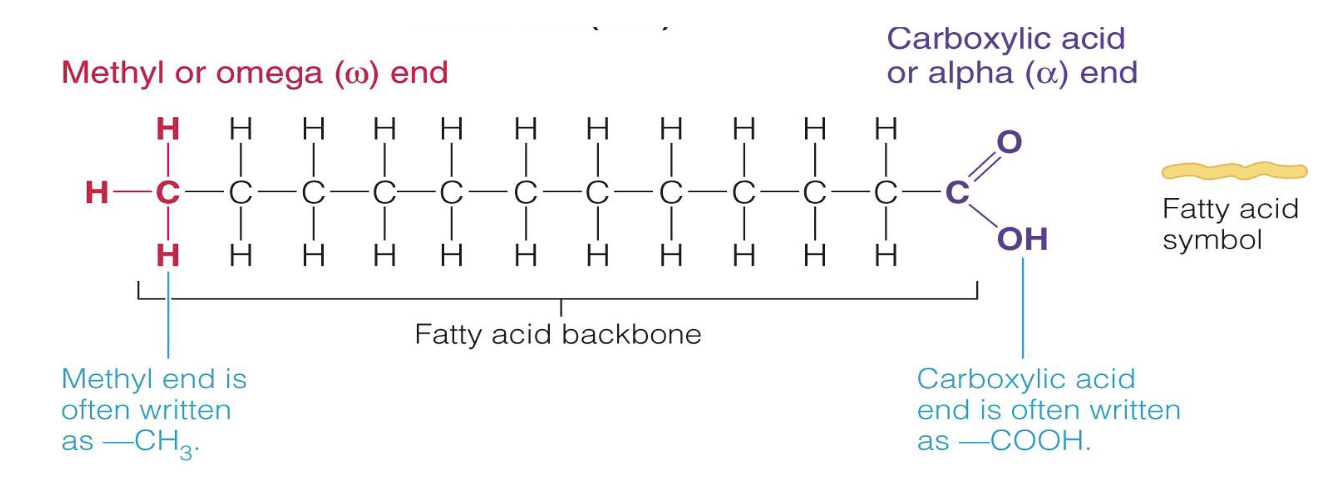
100
New cards
essential fatty acids
omega 3- fatty acids (Linoleic acid)
omega-6 fatty acid (Linoleic acid)
omega-6 fatty acid (Linoleic acid)