Chapter 5 - IAS 38 Intangible Assets
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Intangible Asset
an identifiable non-monetary asset without physical substance. It is a resource that is controlled by the entity as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected
Value of Intangibles
Often the provide market advantage.
More to do with increasing the company’s future worth.
Can easily be destroyed by excessive carelessness and a bad reputation.
Definite intangibles
Contact based with an agreed upon expiration date - limited lifespan
Indefinite intangibles
Do not have a limiting factors to their useful life. these assets are not amortised as there is no foreseeable limit to the benefit, or cash flow generated from them.
Recognition criteria
Probable that any future economic benefit associated with the asset will flow to, or from the entity
Cost, or value that can be measured reliably
Economic benefit
Probability of future economic benefits from intangible assets may be based in reasonable and supportable assumptions. there is an exceptionally high likelihood of gaining benefit from the asset.
Cost
Main criterion for recognition is that we should be able to reliably measure the cost of the asset. in the same way as we would measure a tangible asset.
Includes the price a company pays plus any amounts incurred to get the asset into working order.
Goodwill
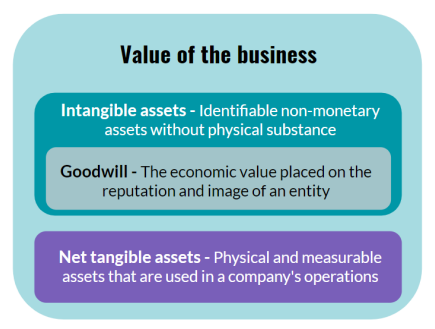
Purchased Goodwill
is Measured at the consideration paid at acquisition, less the fair value of the net assets of the acquired entity
Internally generated goodwill
Incurs expenses, increasing the possibility of the future economic benefit. Is never considered as an intangible asset. Any expenditure incurred is directly expensed
Research and development
It is important that research are identified separately from development as they are recorded differently.
Research phase
Are expensed when incurred , the likelihood of future benefit is uncertain - if research and development cannot be properly differentiated, whole amount must then be expensed.
Development phase
IAS 38 - an intangible asset should be recognised if an entity demonstrates all of the following:
technical Feasibility of completing the intangible asset
Intention to complete the asset
Ability to use or sell
Probable that the asset will generate future economic benefit
technical, financial and other resources to complete the project
Measure the development cost
In-process research and development
a Project acquired during a merger or acquisition is recognised as an asset at cost. additions to the project will be subject to the main recognition criteria.
Measurement of intangible assets
The Cost model.
The revaluation model.
Cost Model
Carried at cost less accumulated amortisation and impairment losses - valued at historical cost.
Revaluation model
Intangible assets being carried at re-valued amounts less any subsequent amortisation and impairment losses.
Based on fair market value and must be determined by an active market.
If no active market can be found - only then the cost model can be used.
If an active market can found - Same logic as the rules for revaluing property, plant and equipment are followed.
If the re-valued amount is higher than the original cost, then the added amount is recognised in other comprehensive income as ‘revaluation surplus’
Useful life
Definite intangible assets amortise over its life
Indefinite intangible assets with infinite nature, should not be amortised at all.
Accounting for amortisation
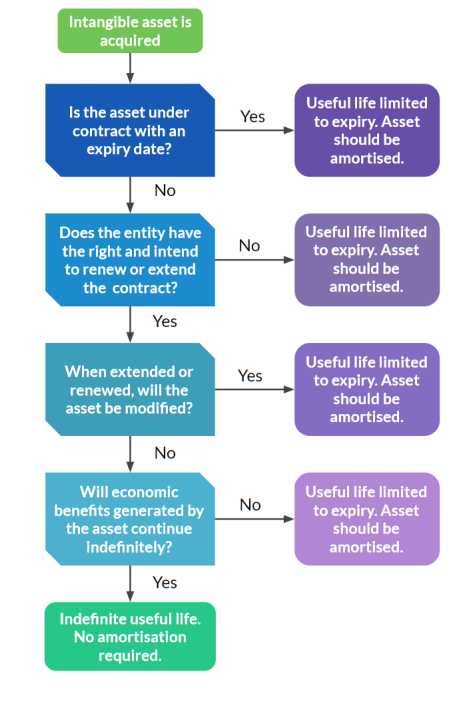
Amortisation
Is the systematic reduction of the value of an intangible asset over its useful life.
Straight-line amortisation method should be chosen when consumption pattern cannot be determined.
Impairment IAS 36
What was previously a valuable intangible asset no longer has as much value. this process of reduction in value of an asset is known as impairment.
Requires an entity to regularly check for impairment of its intangible assets.
Carrying amount
Is important that this is not overstated or inflated.
Once it exceeds its fair market value or recoverable amount, that intangible asset is deemed to be impaired.
Impairment losses are recognised as an expense
De-recognition
No longer any future economic benefits to be expected it needs to be written off.
Any gains or losses arising from the disposal recorded as income or expenses.
Asset held for sale and discontinued operations
Re-classified as an asset held for sale and discontinued operations. amortisation of the asset stops immediately at this point.
Acquisition deal transactions
consideration paid at acquisition less fair value of the net assets of the acquired entity.