P2 - Electricity
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Define electrical current
the rate of flow of electrical charge
Define component
Something that transfers electrical energy to another form
How is an ammeter connected?
In series
What does an ammeter measure?
Current (amps)
What does a voltmeter measure?
Potential difference (v)
How is a voltmeter connected?
In parallel to the component
What is the unit for charge?
Coulombs
Potential difference=
current x resistance
Current rule in series
Same current flows through all components
PD rule in series
PD is shared between components
PD rule in parallel
The supply PD is equal to the PDs across each component in each loop
Current rule in parallel
Total current supplied is the sum of the currents in each separate branch of the circuit
Define resistance
a property of components in a circuit that opposes the current
What are the variables affecting resistance?
Material of wire
Temperature
Area of wire cross section/diameter
Length of wire
Resistance rule in series
As the number of resistors increases, the total resistance increases too
Resistance rule in parallel
As the number of resistors increase, the total resistance of the circuit decreases because there are more possible pathways for the electrons to get through
Graph for filament bulb PD against current
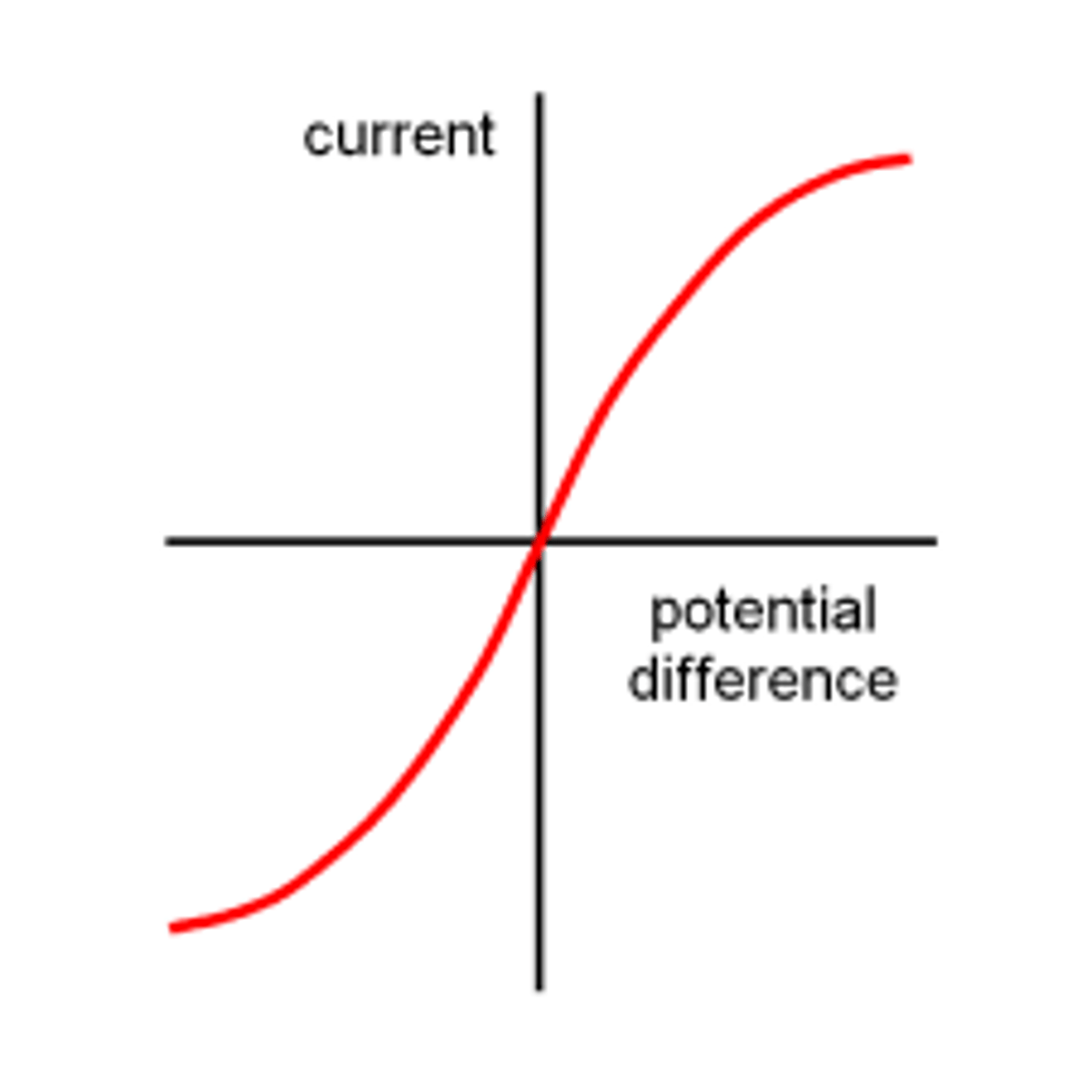
Graph for ohmic/fixed resistor PD against current
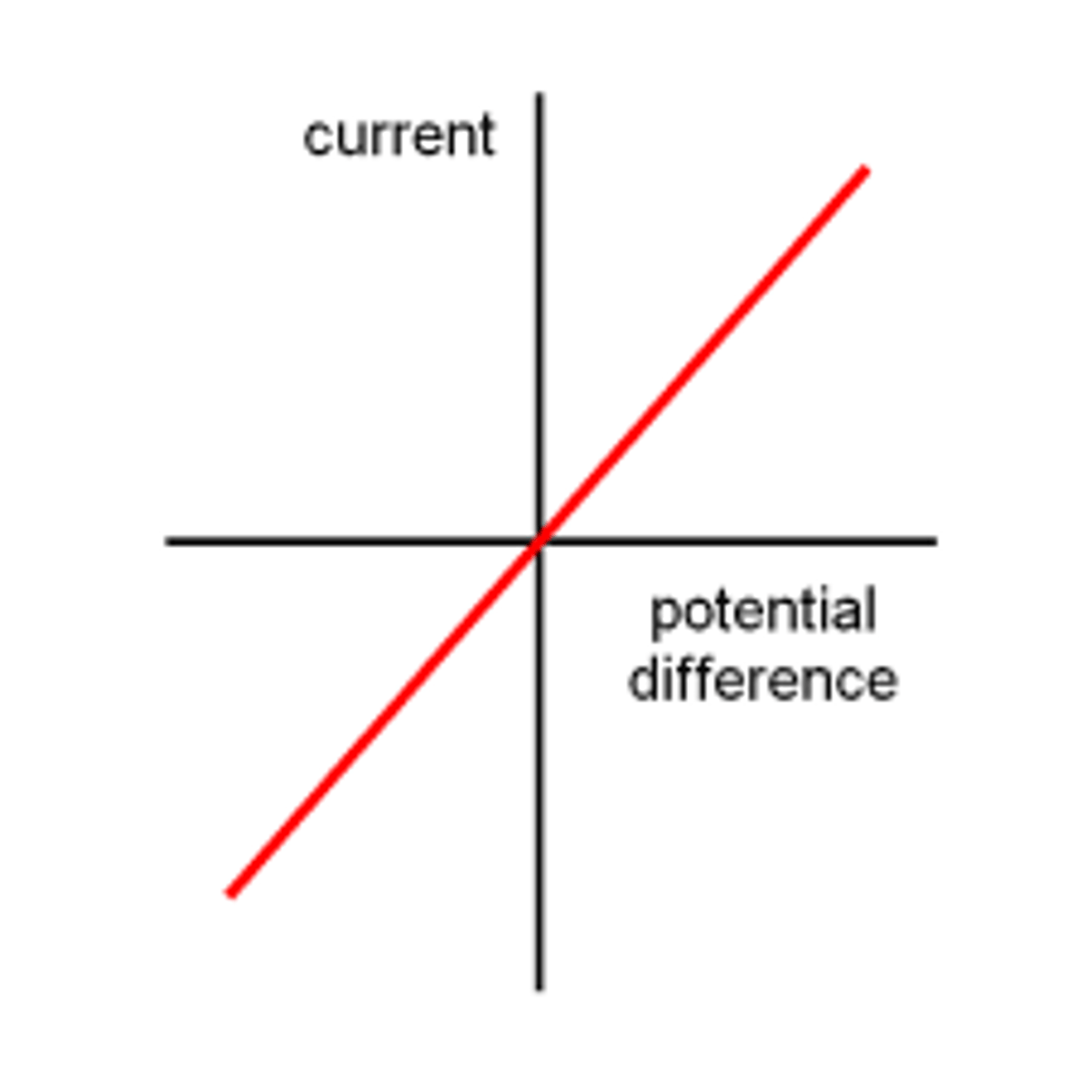
Graph for diode PD against current
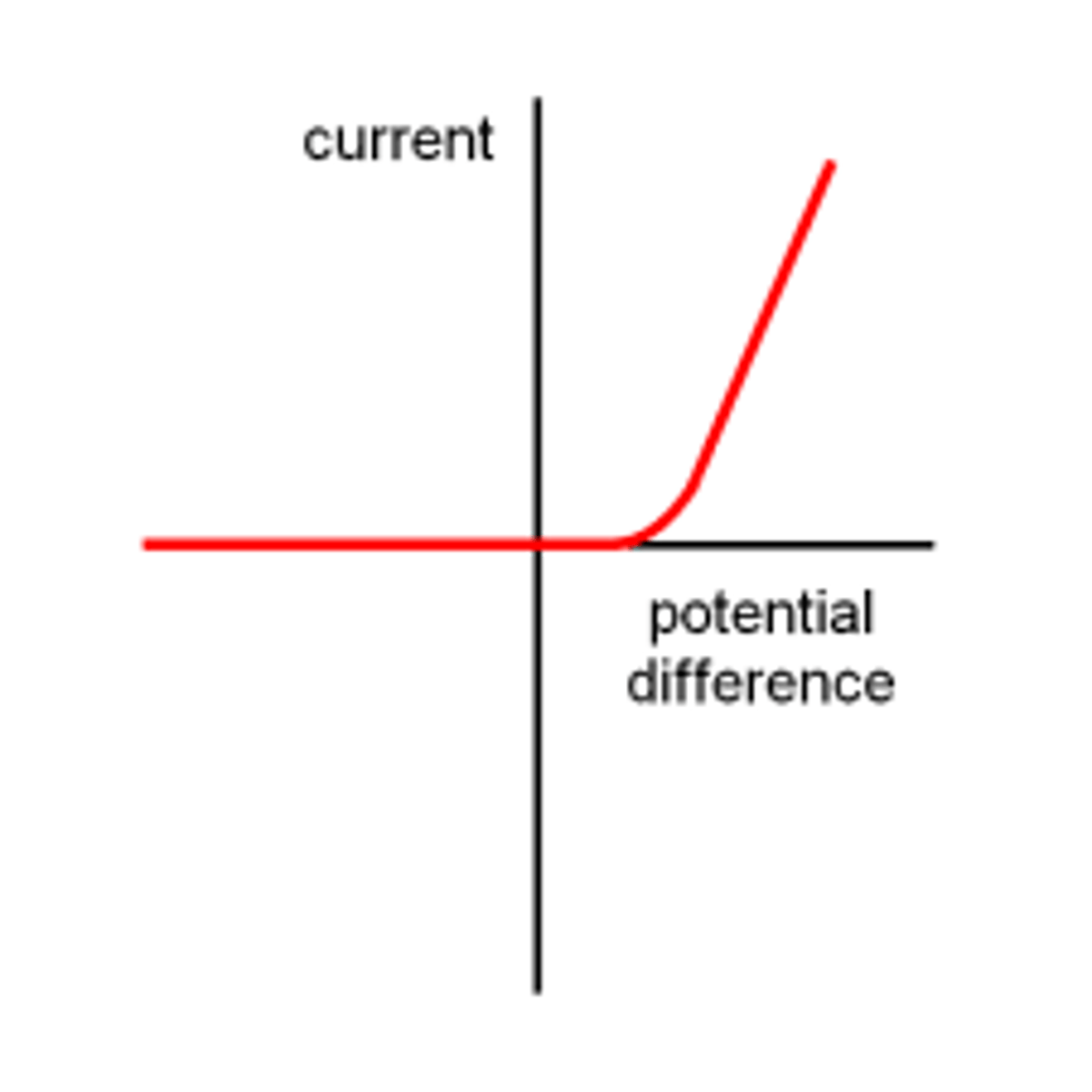
In a diode, what is the current rule
Current can only flow in one direction
In an ohmic resistor, what can be said about the relationship between current and potential difference?
Directly proportional
What happens to bulbs as we add more in series?
They get dimmer
What happens to bulbs as we add more in parallel?
They stay the same brightness
Which direction does current flow in a circuit?
From the positive terminal to the negative terminal
A resistor whose resistance decreases when temperature increases is a:
thermistor
A resistor which cannot vary the amount of resistance it provides is a:
fixed resistor
In which type of resistor does the resistance vary with light intensity?
light dependent resistor
The resistance of a thermistor decreases when the temperature _______
increases
The current flow in a thermistor is greatest when the temperature is
brighter
Diode
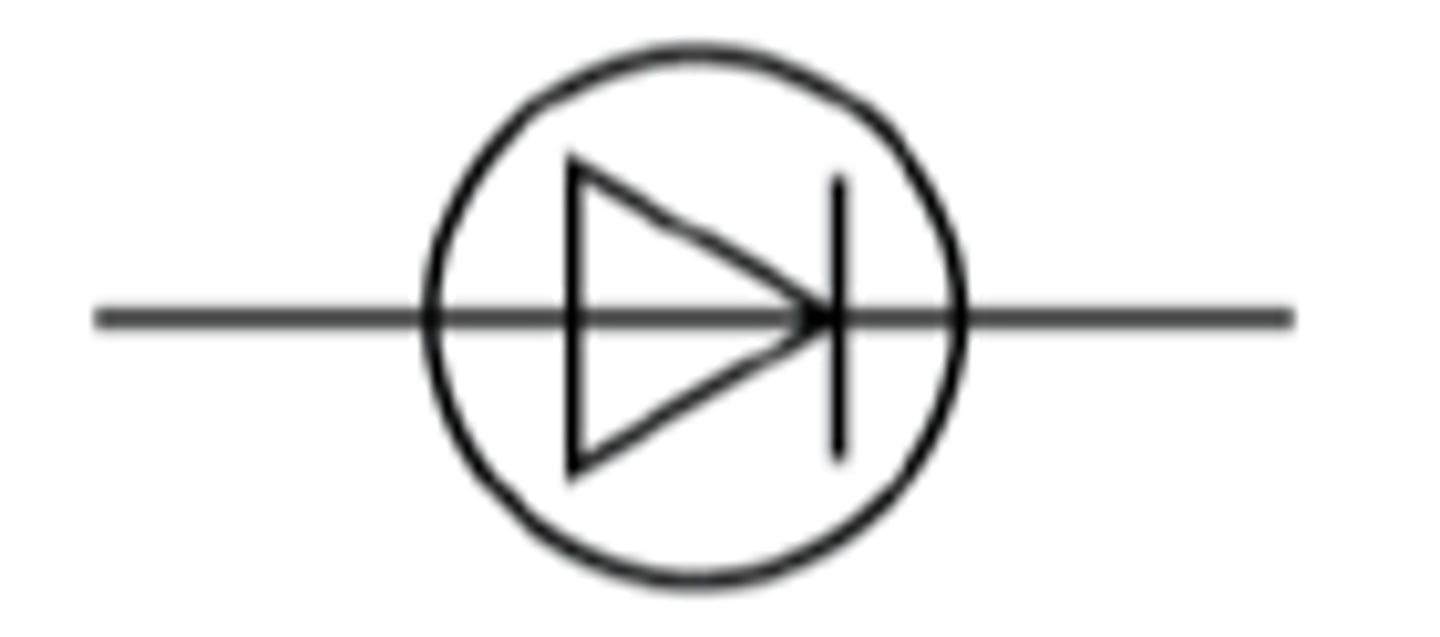
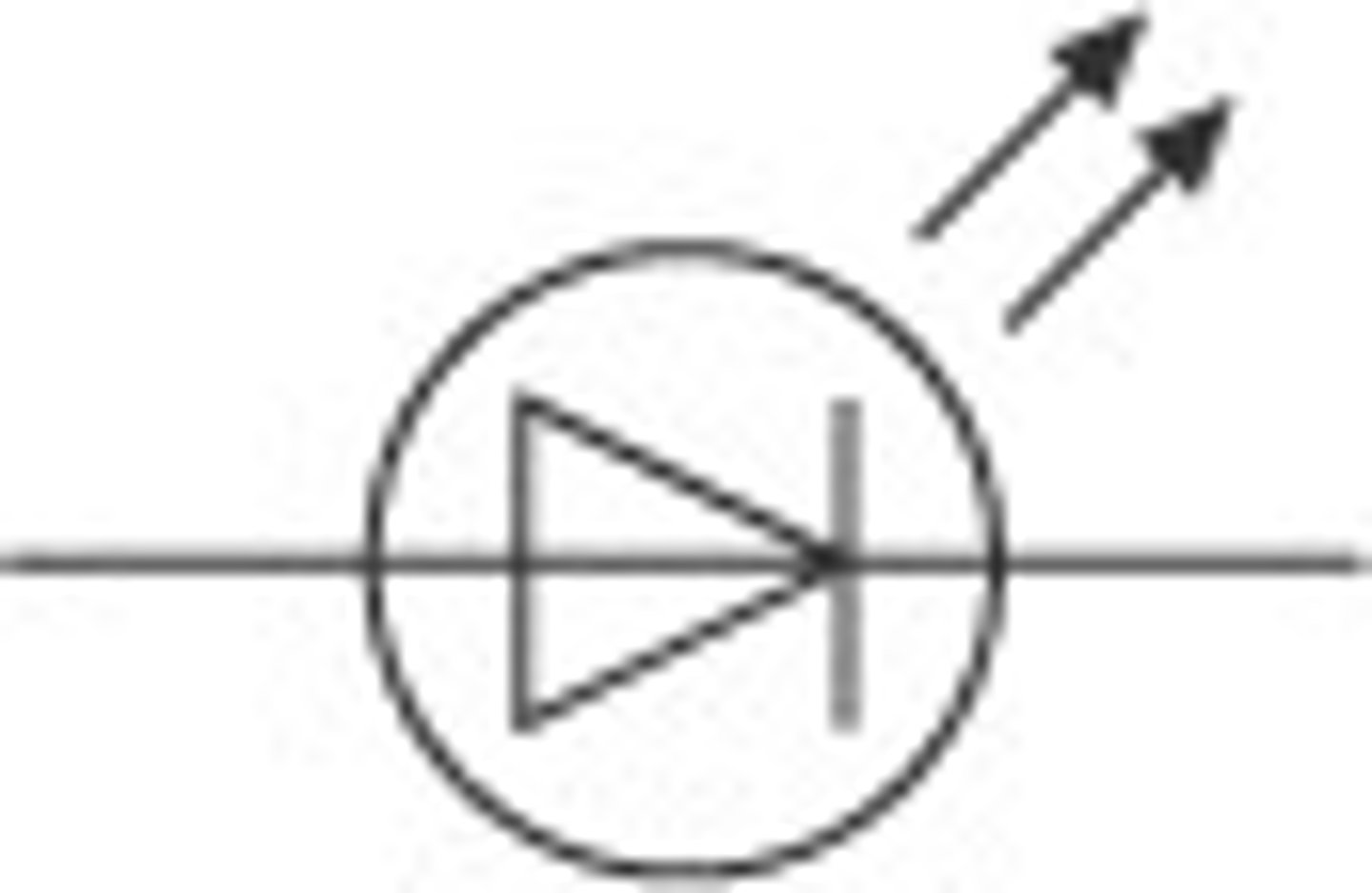
Light emitting diode
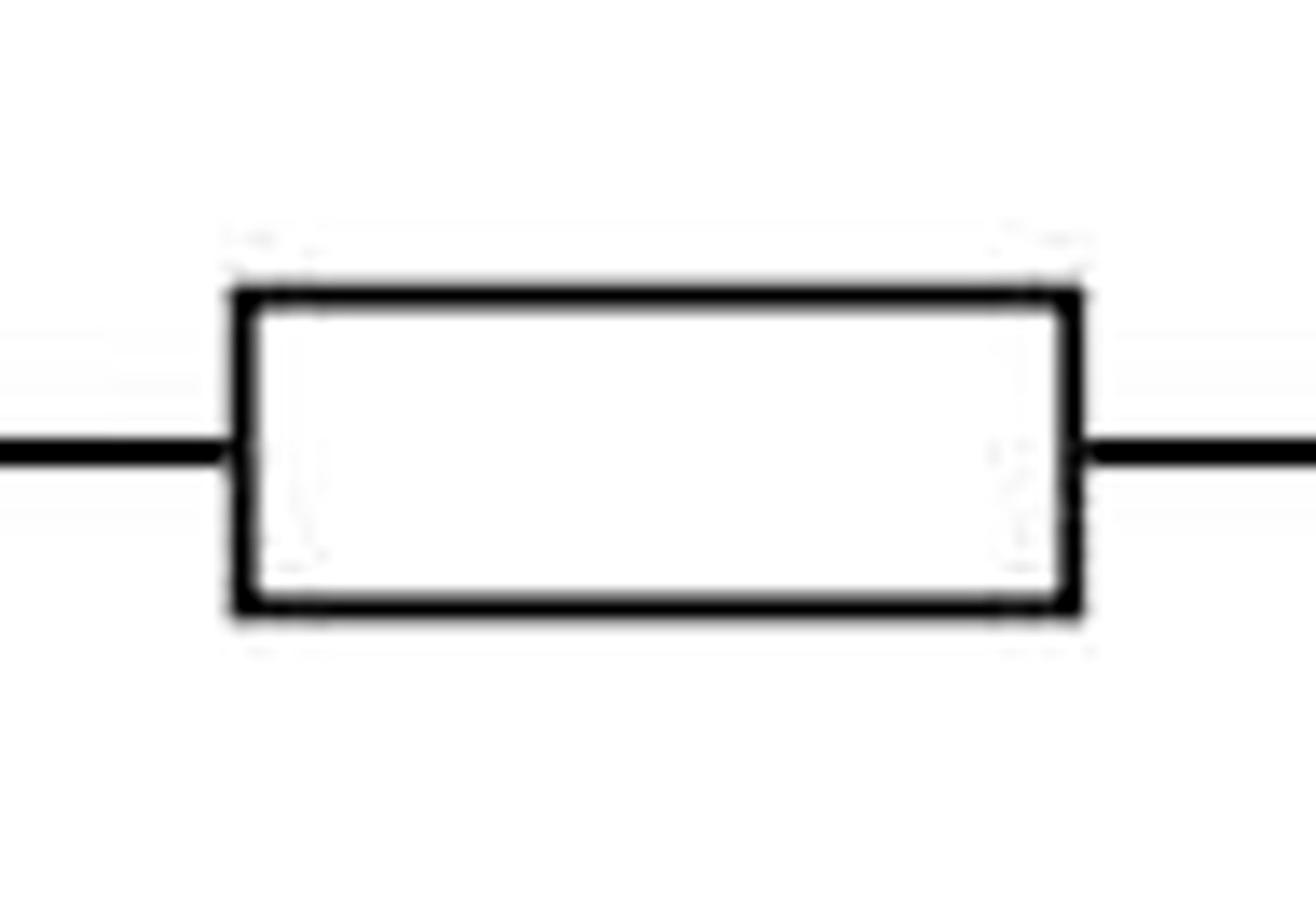
Fuse

Fixed resistor
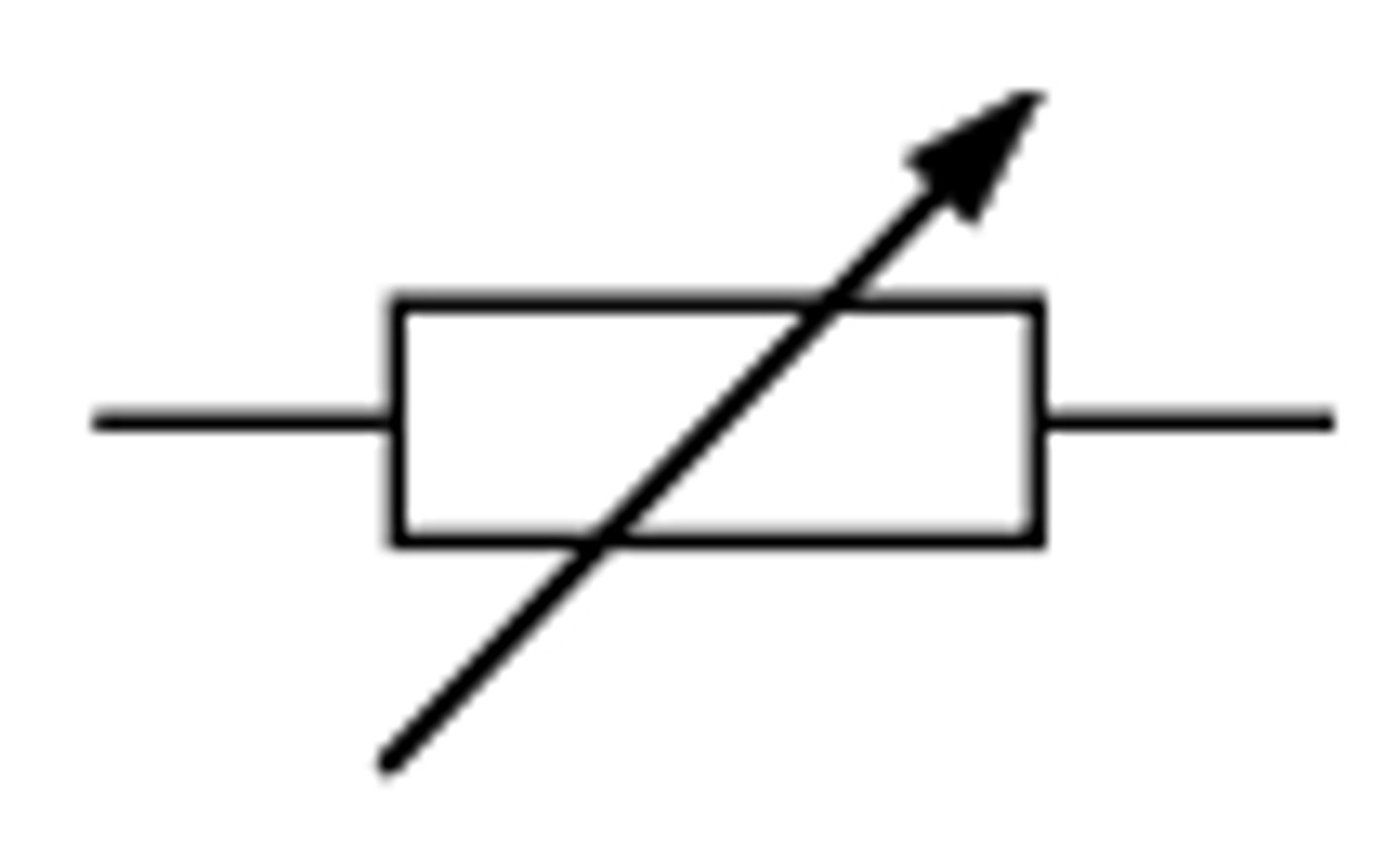
Variable resistor
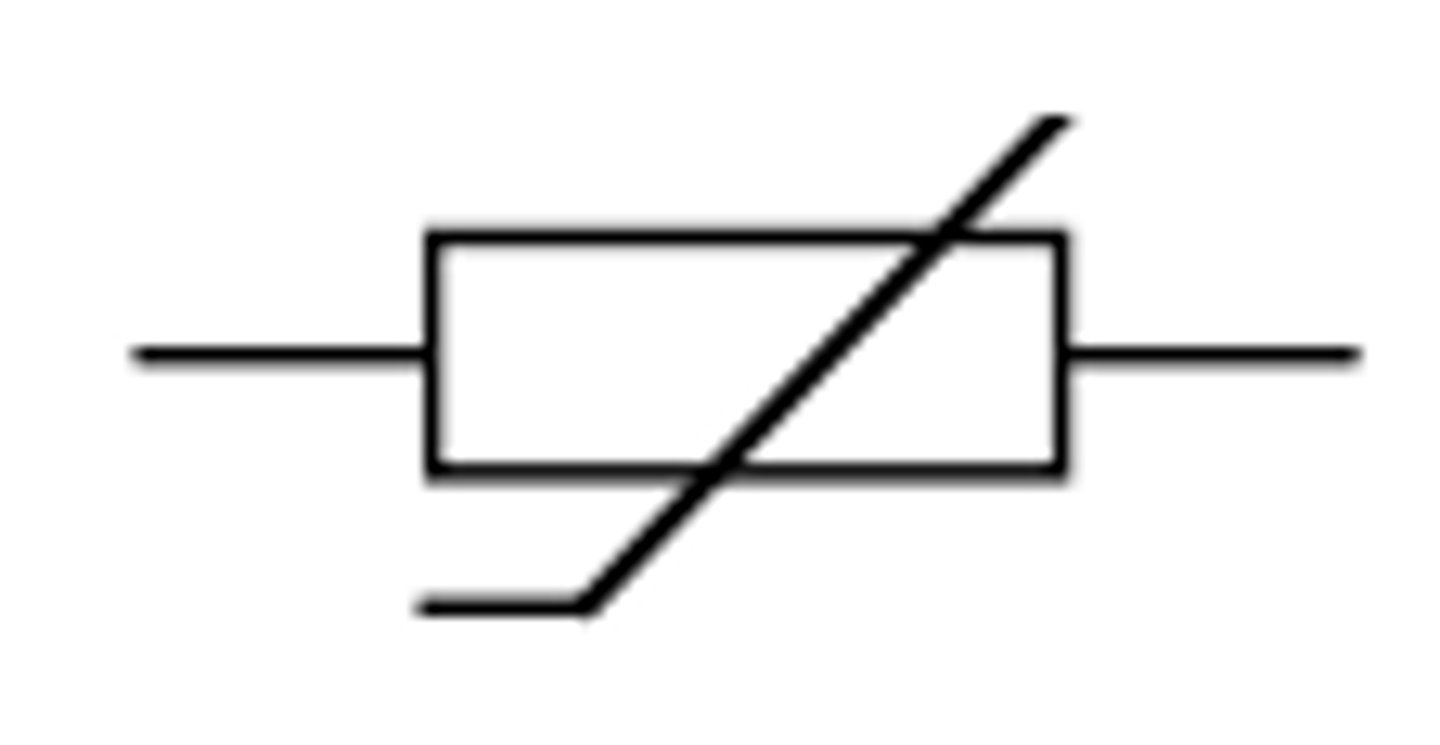
Light dependent resistor

Thermistor
Letter used for charge
Q
Letter used for current
I
Charge (Q) =
current (I) x time (t)
Energy transferred (e) = power x
time
Energy transferred (e) = charge (Q) x
potential difference (V)
(for p2) power =
potential difference (V) x current (I)
In series, potential difference is...
shared across all components
In series, current is...
the same everywhere
In series, the total resistance is...
the sum of the resistance of each component
In series, components with a greater resistance will have a...
higher voltage
In parallel, the potential difference is...
the same everywhere
In parallel, current is...
shared between loops
Loops that have a greater resistance will take a...
lower share of the current
As more loops added in parallel, the total resistance will...
decrease
Power = resistance x
current^2
What are the stages of energy distribution?
Power station -> step-up transformer -> pylon cables -> step-down transformer -> consumer
What do power stations do to cope with surges?
Operate at below maximum output, have lots of spare capacity
Why must current be kept low?
High currents through wires cause high temperatures due to resistance, meaning energy is lost as heat
What do step up transformers do?
Increase the voltage to around 400 000 V
What do step down transformers do?
Decrease the voltage to around 230 V
Is UK mains AC or DC?
AC
What is the frequency of the UK mains supply?
50 Hz (50 cycles per second)
What is the voltage of the UK mains supply?
230 V
Is the current in a cell/battery AC or DC?
DC
Which type of current periodically reverses its direction?
AC
What is the pd of the live wire?
(+-) 230V AC
What is the pd of the neutral wire?
0V
What is the pd of the earth wire?
0V (unless there is a fault)
What colour is the earth wire?
green and yellow
What colour is the live wire?
brown
What colour is the neutral wire?
blue
What does the earth wire do?
Provides an alternate pathway for current to flow away from the casing of the appliance if the live wire is touching it
What is a surge?
a sudden increase in current
What are disadvantages of a fuse that don't exist in a circuit breaker?
A fuse cannot be repaired once broken and needs to be replaced but a circuit breaker is just tripped
What four ways help prevent electric shocks?
Earthing,
Double insulation,
Fuse,
Circuit Breaker
Define static electricity
A build up of charge on insulating materials
What causes a spark?
If two objects have been rubbed together and one has built up lots of negative charge so it has a potential difference between it and an earthed object, causing electrons to jump across the gap
What is an earthed object?
Has 0V
Why does static electricity not build up on conducting materials?
The electrons can just flow back so no charge is built up
When two materials are rubbed together, which particles are transferred?
electrons
What are the rules for drawing field lines
Positive go outward, negative go inward, at perpendicular angles to the surface
Why can sparks travel in air which is normally an insulator?
Air is ionised to positive ions by very charged particles so it can conduct electricity