Pediatric Dermatology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Acne Vulgaris
inflammation of pilosebaceous glands causing inflammatory papules/pustules
S/S: open (blackheads); closed (whiteheads), comedones <5mm, cystic nodules >5mm
Dx:
-Mild - small amount papules/pustules w/o scarring; Tx: Topical Retinoids
-Moderate - comedones + larger amounts papules/pustules; Tx: topical retinoid/antibiotic + Doxycycline PO (macrolide if <8yo), oral contraceptives
-Severe - nodular or cystic acne; Tx: oral isotretinoin (risk managed)
Alopecia Areata
Nonscarring autoimmune condition that destroys the hair follicle causing smooth, discrete, circular patches of complete hair loss (painless/non-pruritic)
- Scalp is most common site
S/S: patchy hair loss, exclamation point hairs, ± nail pitting
Dx: clinical, Punch biopsy (definitive)
Tx: Topical corticosteroids, switch to systemic if refractory
- JAK inhibitor if severe
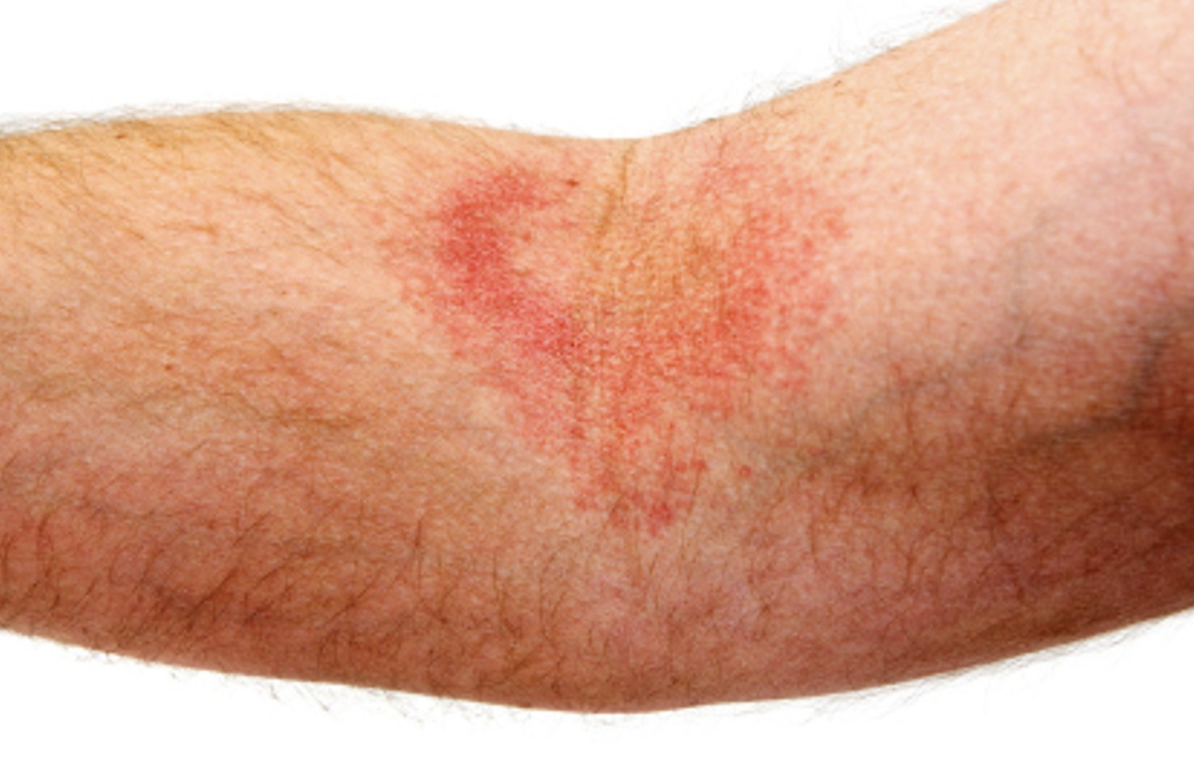
Contact Dermatitis
inflammation of skin due to direct contact with irritant/allergen
most commonly: cleaners, solvents, alloys, poison oak/ivy
S/S: erythematous papules/vesicles with oozing, weeping, pruritis 12-48 hours after exposure
Dx: clinical, patch testing if cause unknown
Tx: remove irritants, topical steroids (oral if severe), alternative Tacrolimus
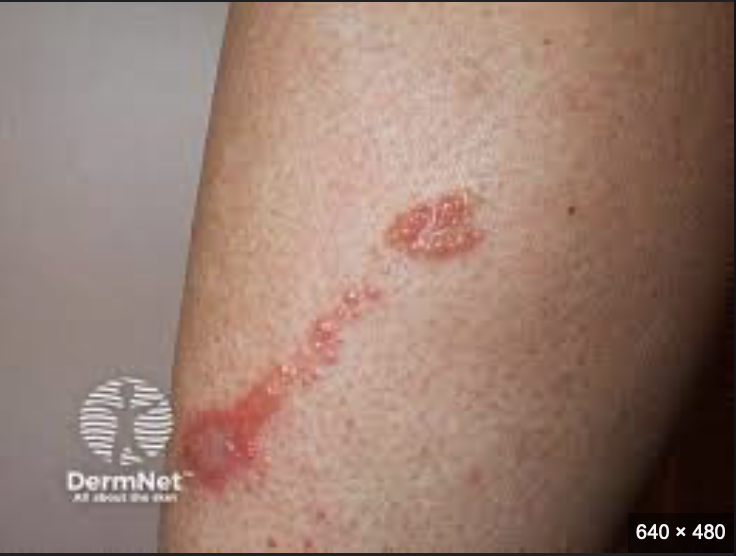
Rhus allergy
most common form of allergic contact dermatitis involving lesions that begin as erythematous macules that become papules or plaques
-initial blisters form 7-10 days after exposure
-subsequent outbreaks the rash may appear within hours to two days
- Look for linear streaks
- Plant oil can be on anything (including pets; leads to repeated exposures)
Prevention:
- Avoid plants with three leaves
Tx:
-medium to strong potency topical steroids (short-course)
-oral antihistamines for pruritus
-oatmeal baths
-Use a barrier (clothing, OTC products that bind resin)
Diaper Dermatitis
skin inflammation due to prolonged contact with urine/feces, may have superimposed candida infection
S/S: erythematous papules, maceration, superficial erosions, spares skin folds
Dx: clinical diagnosis
Tx: frequent diaper changes, barrier cream; topical steroids if persistent
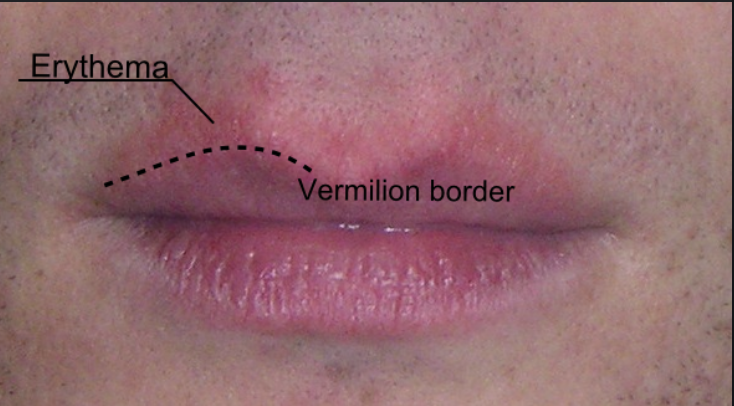
Perioral Dermatitis
Inflammation affecting the skin around the mouth, most commonly due to chronic topical steroid use
S/S: inflamed small papules/papulopustules or scaling around mouth that spares vermillion border
Dx: clinical diagnosis
Tx: discontinue steroid, topical pimecrolinus, doxycycline if severe (erythromycin young children)
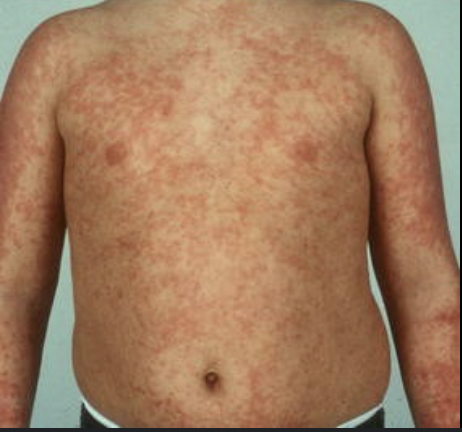
Drug Eruptions
Type IV T-mediated hypersensitivity reaction after initiation of drug treatment
most common: penicillin, sulfas, NSAIDs, clindamycin
S/S: generalized morbilliform rash of bright macule/papules that coalesce into plaques; ± fever, pruritis, mild eosinophilia
Dx: clinical diagnosis
Tx: discontinue offending agent, oral antihistamines, topical/oral steroids if severe
Erythema Multiforme
Reactive type IV hypersensitivity response to infection/medication exposure
S/S: target lesions with dusky center, negative Nikolsky sign, ± mucosal membrane involvement
Dx: clinical, can direct immunofluorescence
Tx: remove offending drug, topical steroids, oral antihistamines
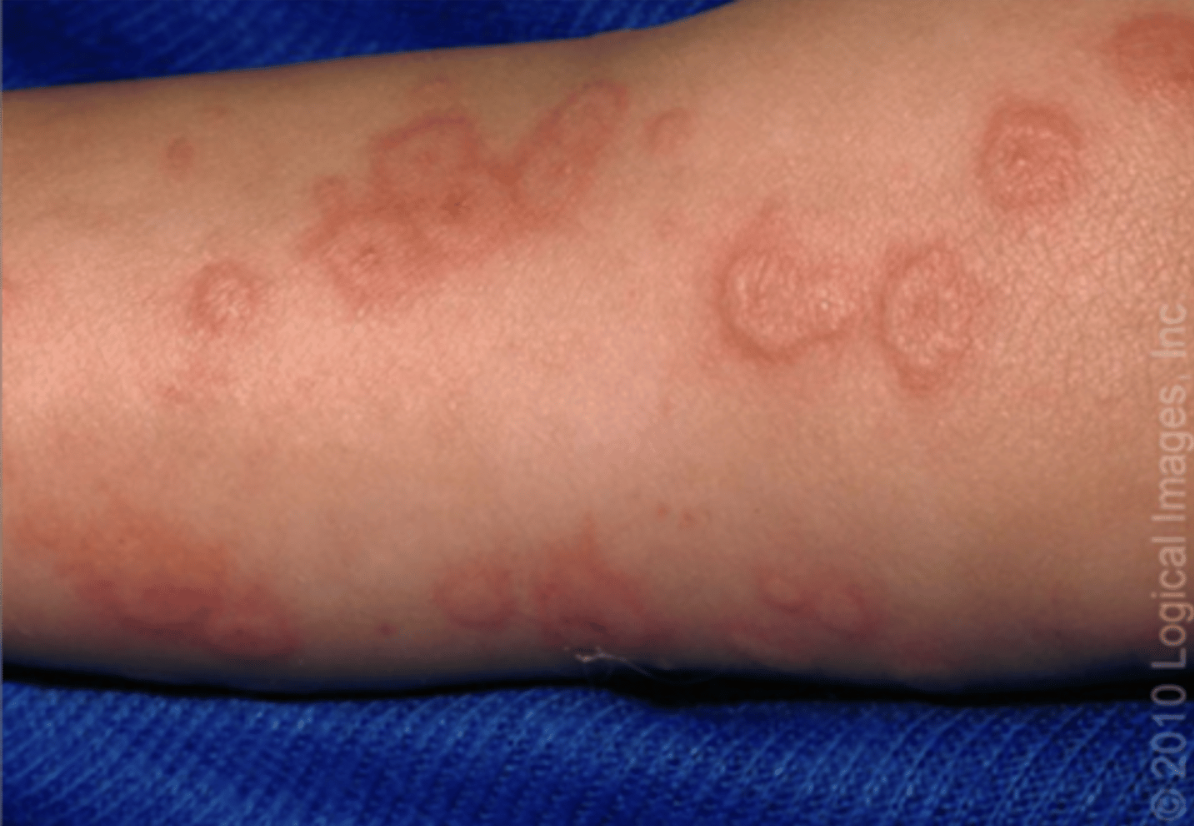
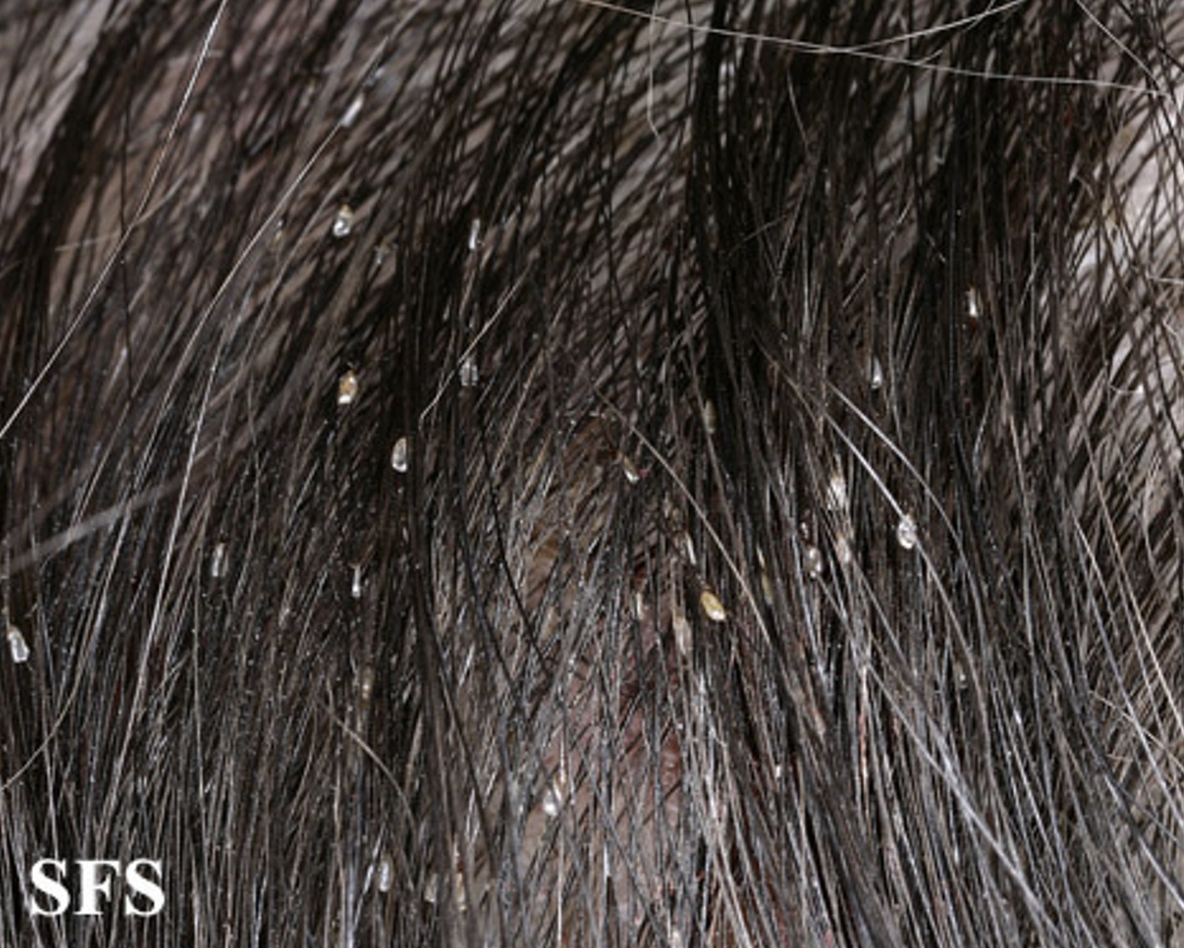
Lice
pediculus humanus capitis; parasitic insects that live on the hair shaft and cause itching
SSx:
- Intense Itching (especially occipital area)
- Papular urticaria near lice bites
- Nits: white, oval-shaped egg near the hair shaft (diagnostic to condition)
Tx: Topical Permethrin 1% cream + fine-tooth comb to remove the nits
-Launder bedding and clothing in hot water and high heat
-Place pillow/toys (that cannot be laundered) in air-tight plastic bags for 2 weeks
-Entire house must be treated
Scabies
skin infection due to the mite Sarcoptes scabiei
S/S: intensely pruritic worse at night, after hot shower, linear burrows on palms and soles of feet
Dx: mineral oil microscopy of skin scrapings
Tx: Permethrin 5% topical cream
Tinea capitis/pedis/cruis/corporis
Superficial fungal infection of head / feet / groin / body
S/S: pruritic, scaly, erythematous, scalloping, +/- central clearing, macerating if moist, alopecia on hair-bearing skin
Dx: clinical, KOH prop, Woods lamp
Tx: topical antifungals, oral Griseofulvin for capitis
Lichen Planus
Cell mediated inflammatory mucocutaneous papulosquamous dermatitis
S/S: purple, polygonal, planar, pruritic, papules or plaques with fine scales
Dx: Wickham striae: fine white lines on skin lesions or oral mucosa is diagnostic feature, consider punch biopsy
Tx: high potency topical corticosteroids with occlusive dressings, antihistamines for pruritis
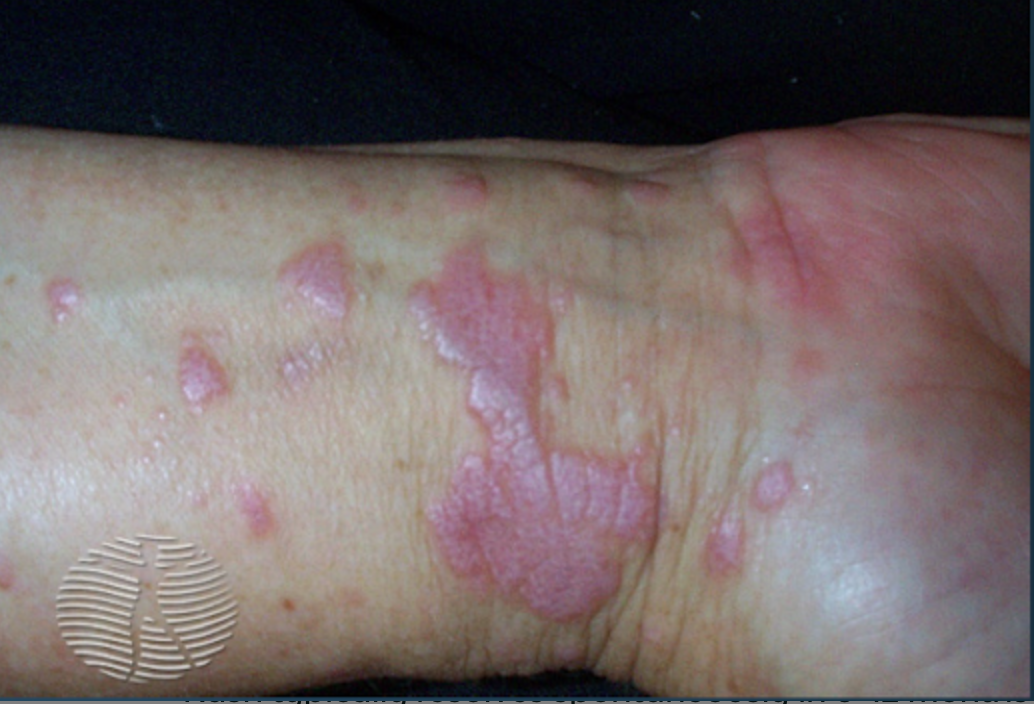
Pityriasis Rosea
Rash associated with viral infection, commonly herpesvirus 6/7
S/S: salmon colored herald patch progressing to papules with outer scaling in Christmas tree distribution + pruritis
Dx: clinical diagnosis
Tx: self-limiting, topical steroids or oral antihistamines for itching
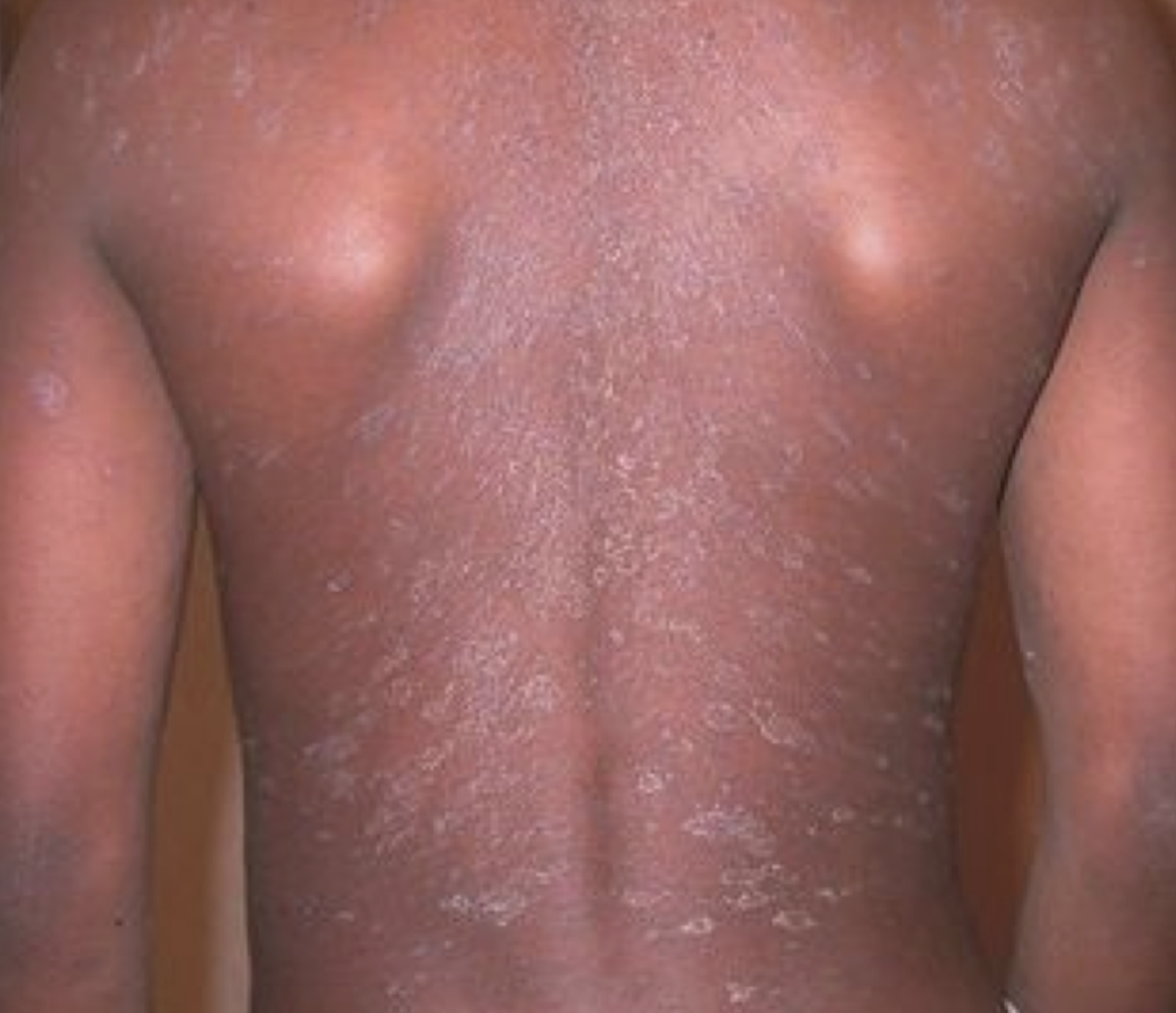
Verruca vulgaris
A small, fleshy bump on the skin or mucous membrane caused by HPV infection
S/S: firm hyperkeratotic papules with thrombosed capillaries (plantar) or small flat topped flesh colored papules (flat warts- plana *in picture)
Dx: clinical diagnosis
Tx: self-resolving ~2 years; topical salicylic acid; cryotherapy
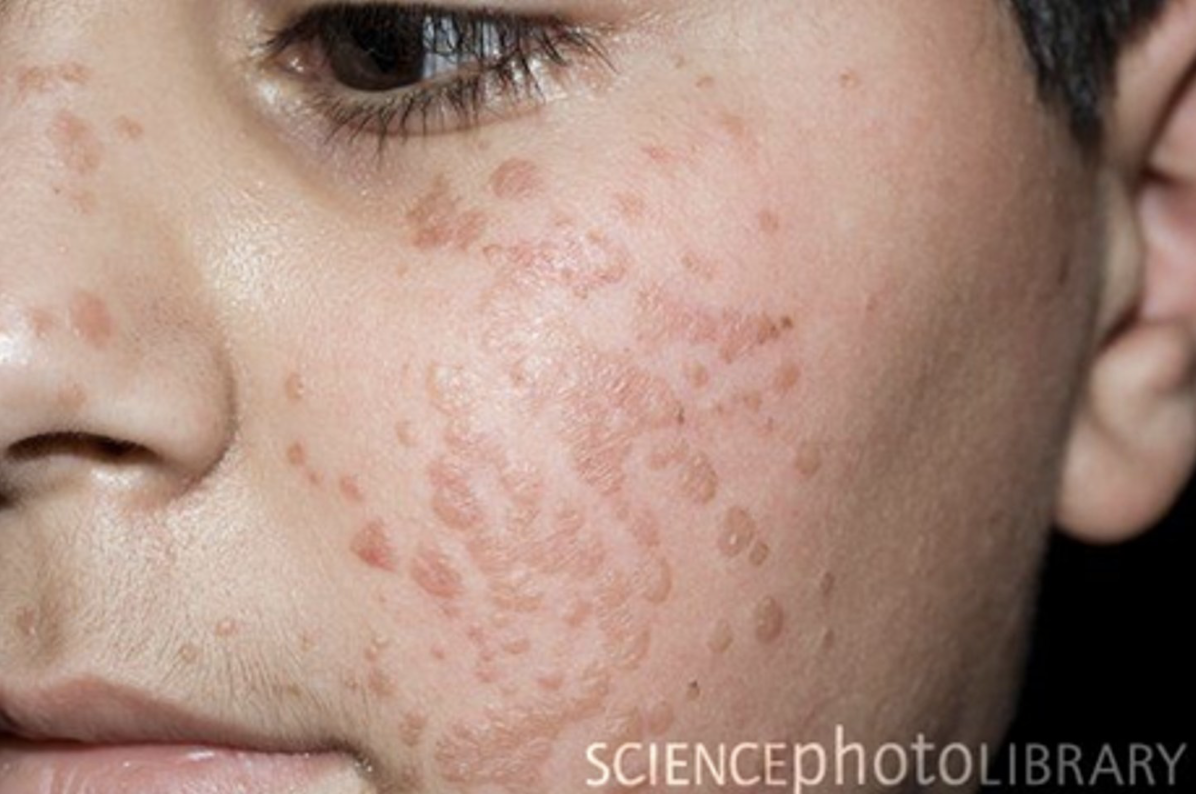
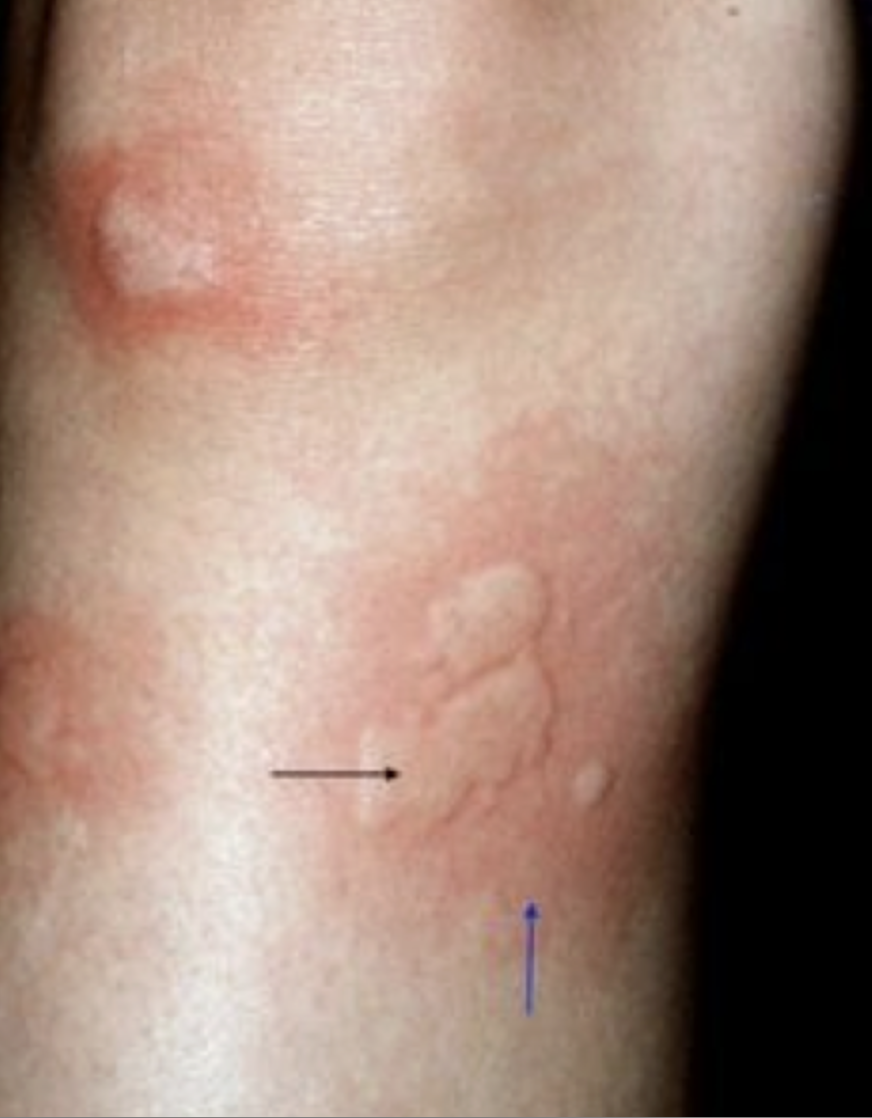
Urticaria
Type I (IgE) hypersensitivity reaction causing localized superficial edema and redness of skin
triggers: foods, stress, hot/cold temp, insect bites
S/S: acute onset blancable raised red plaques (wheals) + intense pruritis
Dx: clinical diagnosis
Tx: oral 2nd generation antihistamines (H1 blockers), avoid known triggers/meds, oral steroids (more severe)
Atopic dermatitis
rash due to defective skin barrier causing itching and inflammation
Atopic triad: asthma, allergic rhinitis, eczema
S/S: pruritis, dry skin, scaly plaques in flexor creases (face/neck/extensor in infants from crawling)
Dx: clinical diagnosis
Tx: soak and seal, avoid triggers (heat, soap, detergents), topical steroids for acute flare, antihistamines, Tacrolimus if severe