Orthopedics & Physical Therapy
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
long bones
thigh, lower leg, upper arm, lower arm, & digits
short bones
wrists and ankles
flat bones
inside the scapulae, ribs, and pelvic bones
irregular bones
patella and vertebrae
periosteum
fibrous membrane covering the outside of bone tissue
cartilage
smooth, elastic connective tissue that covers the ends of bones
osteoblasts
a precursor cell in bone formation
endosteum
membrane lining the inner portion and marrow cavity of the bone
hematopoiesis
formation of blood cells
epiphysis
the rounded end of a long
diaphysis
the main or midsection of a long bone
proximal
situated toward the point of origin or attachment
distal
situated away from the point of origin or attachment
fibrous joints
found in the sutures of the skull and made of fibrous tissue; these joints exhibit synarthrosis (no movement)
cartilaginous joints
found in the pubic symphysis b/w the pelvic bones and b/w the vertebral bodies of the spine; this type of joint exhibits amphiarthrosis (slight movement)
synovial joints
found in the neck, shoulders, arms, hands, hips, legs, and feet; experience diarthrosis (freely moveable)
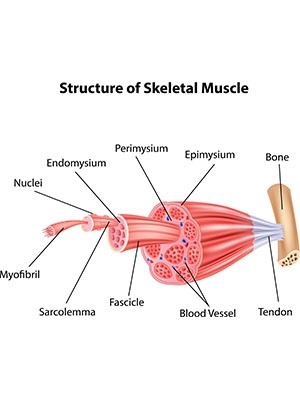
skeletal muscle
is attached to bones and responsible for the movement of the body; contracts voluntarily
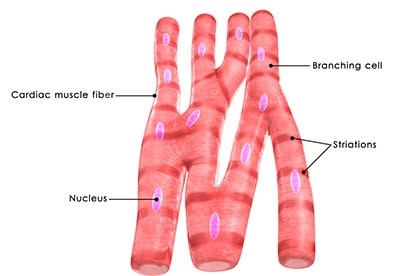
cardiac muscle
lines the walls of the heart; contracts involuntarily
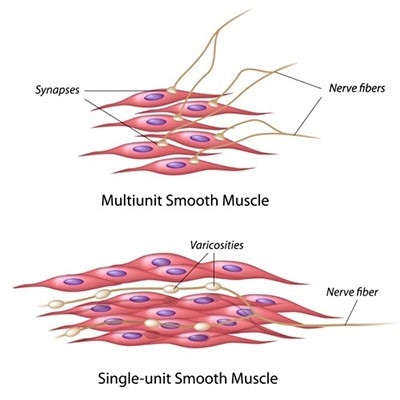
smooth muscle
lines the walls of blood vessels, respiratory tree, and hollow organs; contracts involuntarily
kyphosis
outward curve of the spine usually in the thoracic region creating a hump on the back
scoliosis
lateral curve of the spine causing one hip or shoulder to be higher than the other
lordosis
an inward curvature to the lower spine and results in a swayback
muscular dystrophy
progressive, degenerative weakening of the muscles
osteoarthritis
gradual onset of joint pain with edema and decreasing range of motion caused by degeneration of the joint tissues
rheumatoid arthritis
progressive autoimmune system disease resulting in deformed, painful joints
bursitis
inflammation of the bursae in synovial tissue of the joint resulting in pain and limited range of motion in the joint
osteoporosis
a disorder in which calcium needed for body functioning is taken from the bones causing the bones to become brittle and at risk for fracture
carpal tunnel syndrome
chronic burning or aching pain in muscles and the soft tissue of the joint
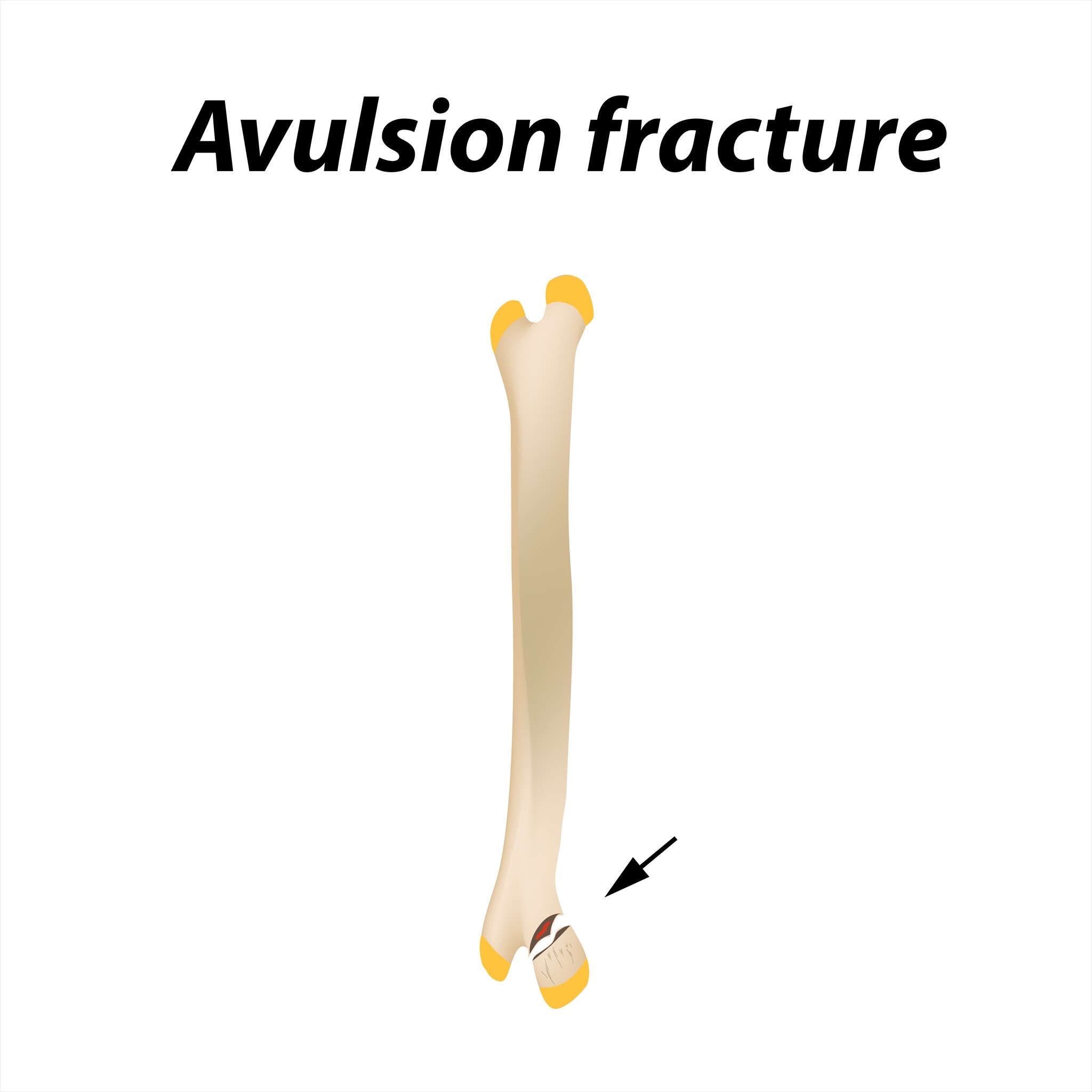
avulsion fracture
fragment of a fractured bone is torn away with the muscle or ligament
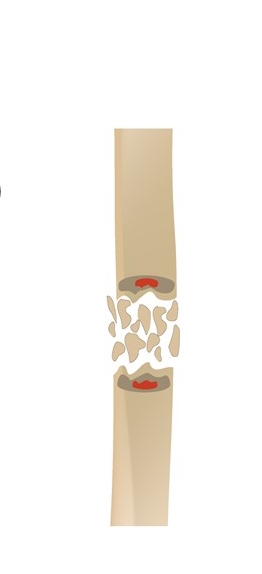
comminuted fracture
crushing or splintering of the bone
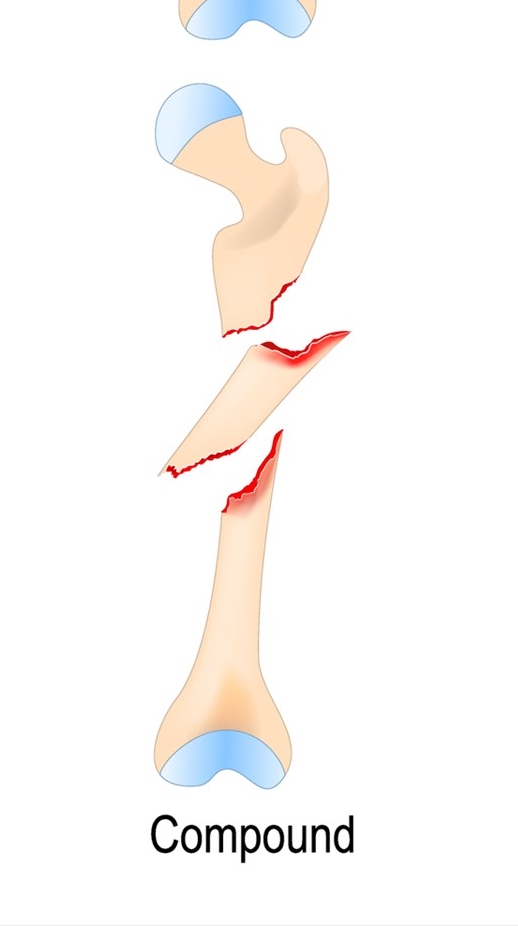
compound fracture
open wounds over the ends of the fractured bones; often an end of the bone is visible
compression
collapse of the bone due to pressure exerted on it
depression
fragments or portions of bone pressed down in the skull and into the brain and surrounding tissue
displaced fracture
bone ends out alignment
greenstick fracture
bone partially bent and partially broken, like a twig or branch of a tree
impacted fracture
one end of a fractured bone driven or wedged into the other end of the same bone
longitudinal fracture
fracture parallel with the long axis of the bone, usually running along part of the length of the bone
nondisplaced fracture
bone ends remain in alignment
oblique fracture
a type of broken bone where the break runs diagonally across the bone at an angle
pathological fracture
a broken bone caused by a pre-existing disease that has weakened the bone, making it more susceptible to fracture under normal stress
simple fracture
a break that does not compromise the skin
spiral fracture
fracture follows a helical pattern, twisting around the axis of the bone
transverse fracture
fracture crosses the bone at 90 degree angle to the bone’s axis
lyme disease
a bacterial infection transmitted by the bite of ticks, can lead to arthritis
osteomyelitis
an inflammation or swelling of bone tissue that is usually the result of an infection
sprain
a stretching or tearing of ligaments
strain
when a muscle or tendon is stretched too far, sometimes leading to a “pulled muscle”
dislocation
occurs when w bone is forced out of its normal position in a joint
tendon problems
issues with the strong, rope-like connective tissues that attach muscles to bones
cartilage problems
issues with the tough, flexible tissue that cushions the ends of bones in joints
amputation
a surgical procedure where a part of the body, such as a limb, is removed