Bone test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/156
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
1
New cards
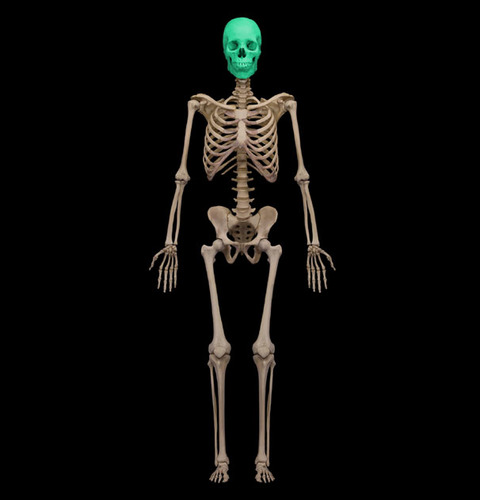
Cranium
2
New cards
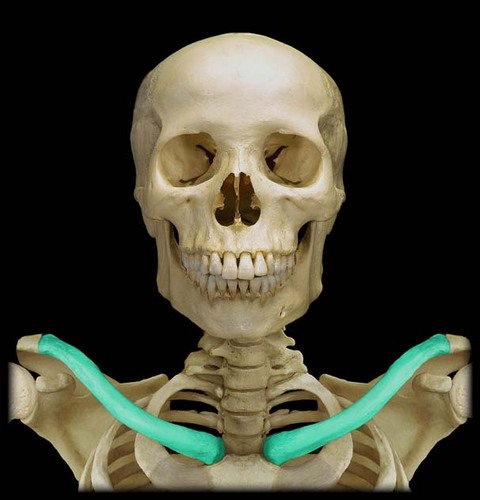
Clavicle
act as a brace when we hold our arms out, anchors muscles, and attaches to the sternum medially and the scapula laterally
3
New cards
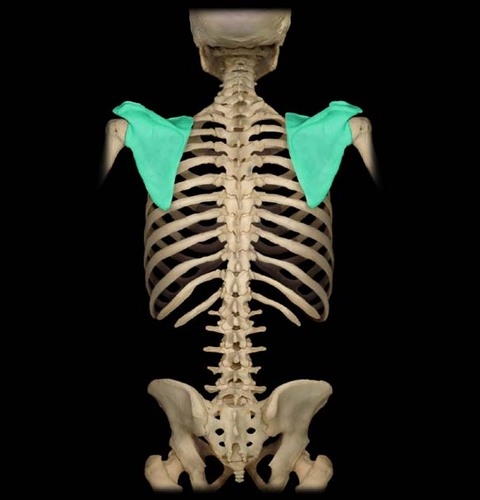
Scapula
attaches to the rib cage and vertebral column by the muscle, allows for more mobility and flexibility, and allows the arms to move laterally
4
New cards
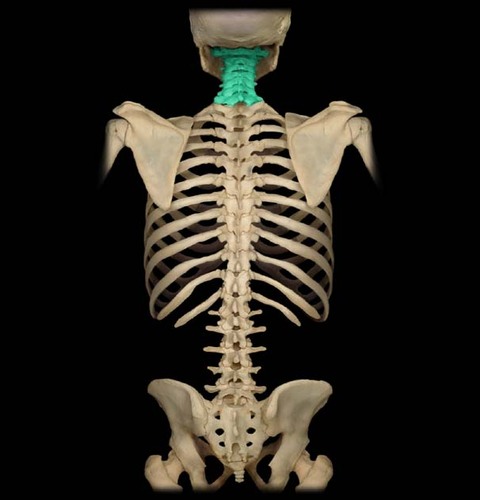
Cervical vertebrae
5
New cards
True ribs
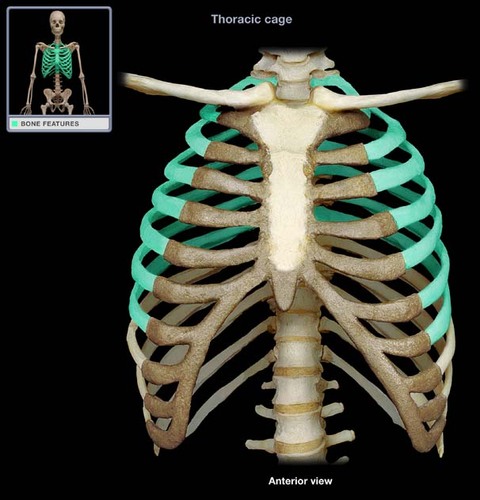
6
New cards
False ribs
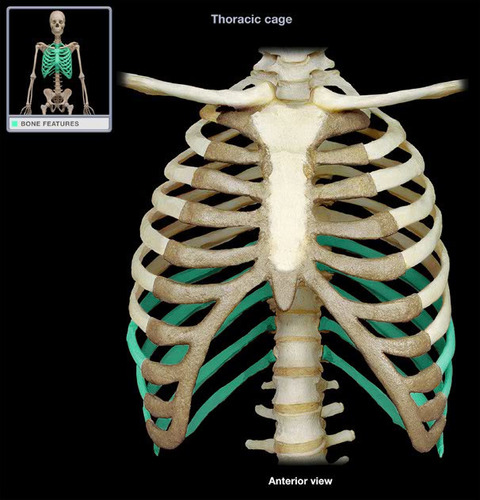
7
New cards
Humerus
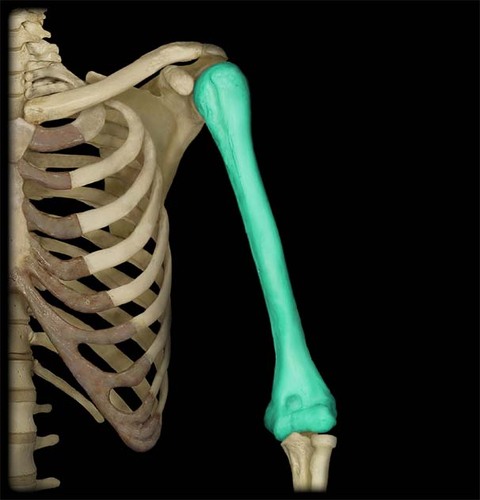
8
New cards
Radius
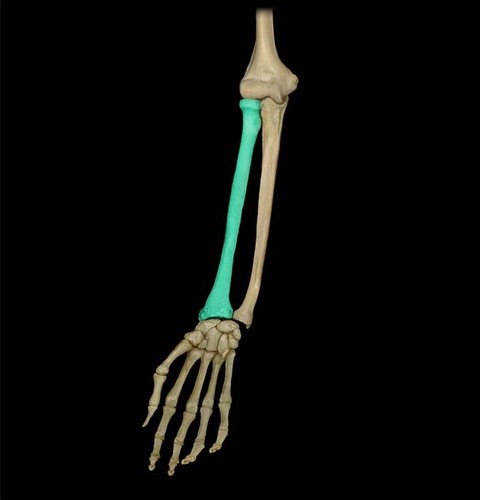
9
New cards
Ulna
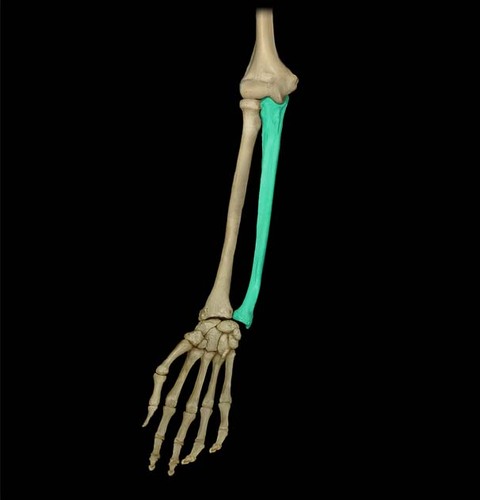
10
New cards
Sternum
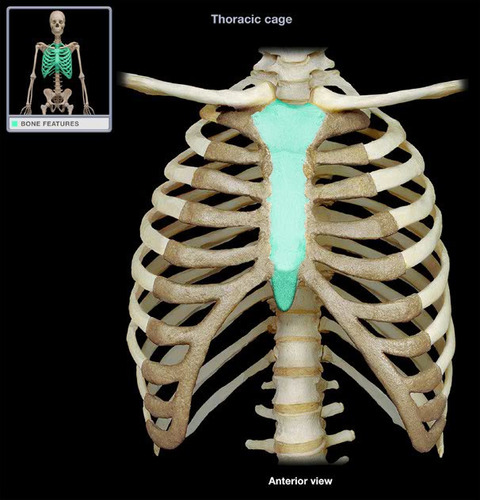
11
New cards
Ilium
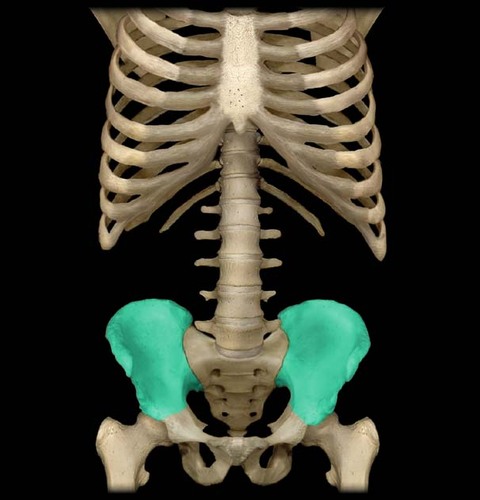
12
New cards
Sacrum
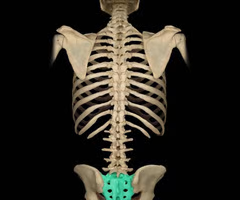
13
New cards
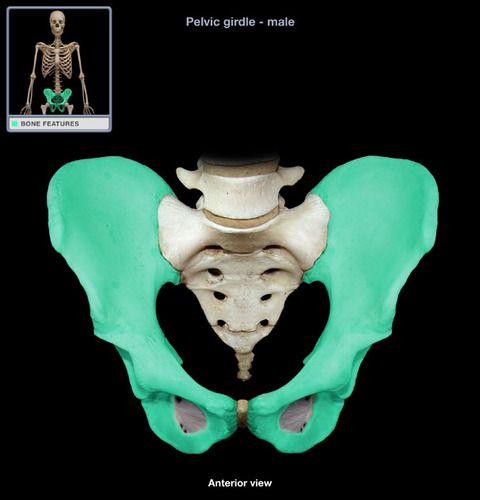
Coxal
14
New cards
Pubis
15
New cards
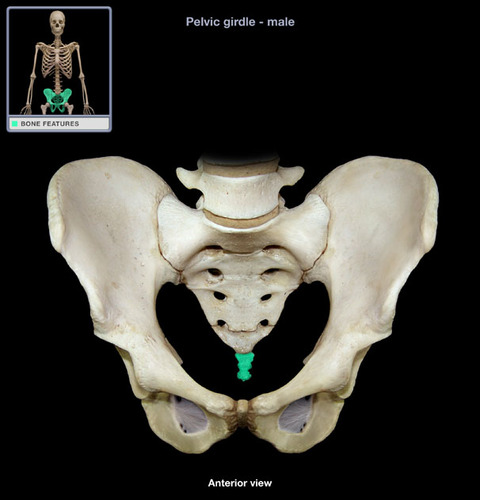
Coccyx
16
New cards
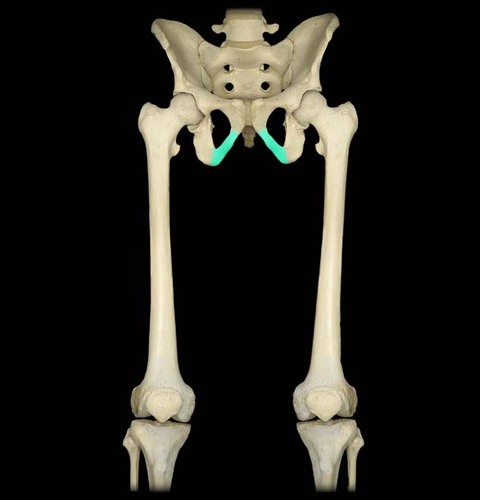
Pubic arch
17
New cards
Ischium
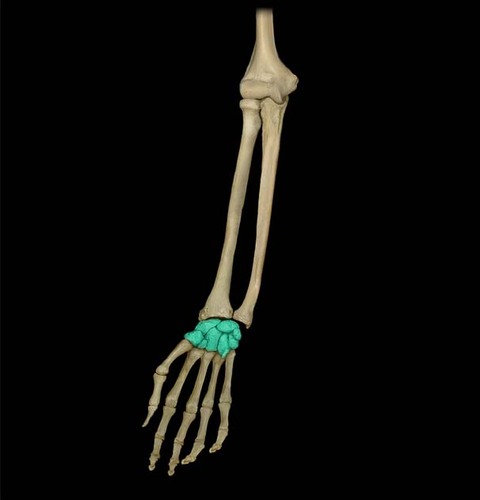
18
New cards
Carpals
19
New cards
Metacarpals
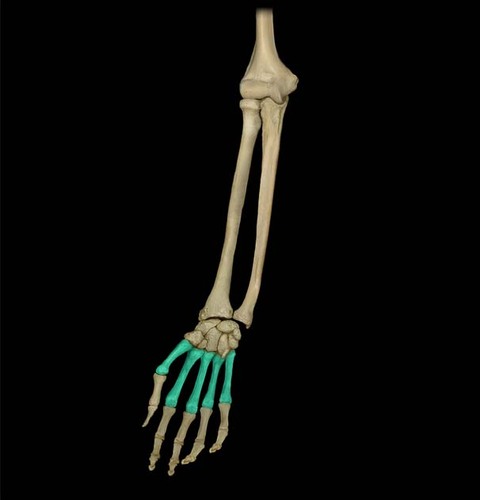
20
New cards
Phalanges
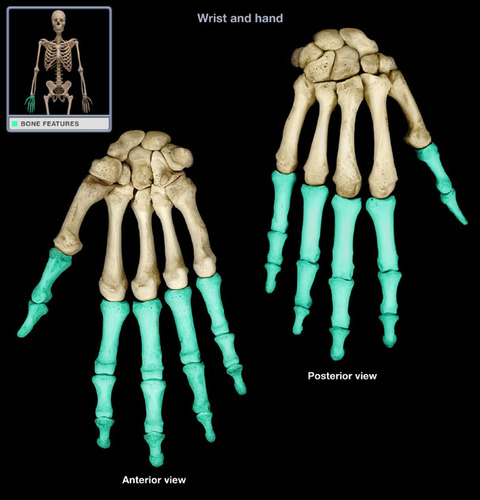
21
New cards
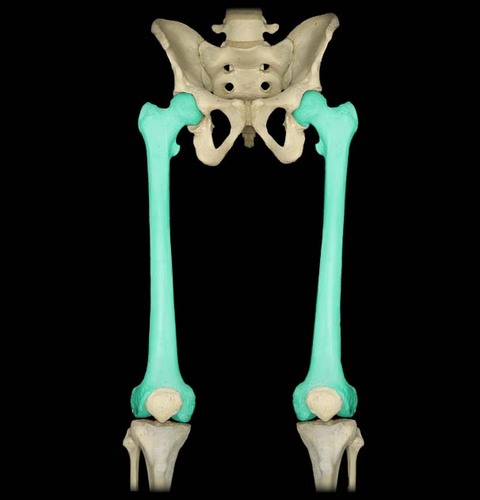
Femur
22
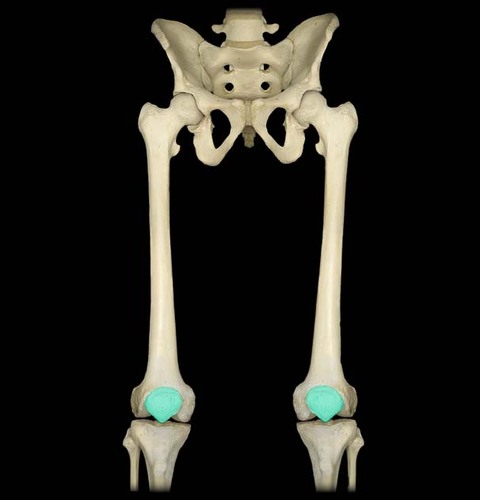
New cards
Patella
23
New cards
Tibia
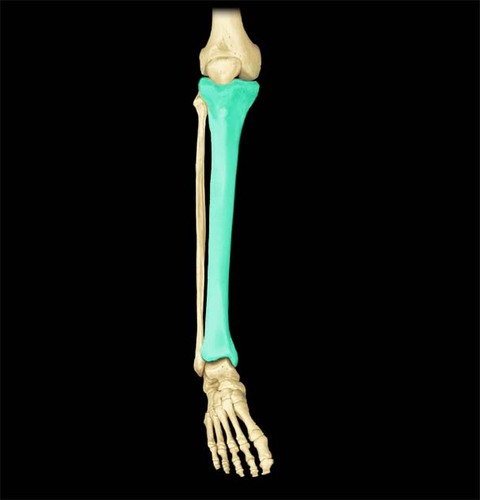
24
New cards
Fibula
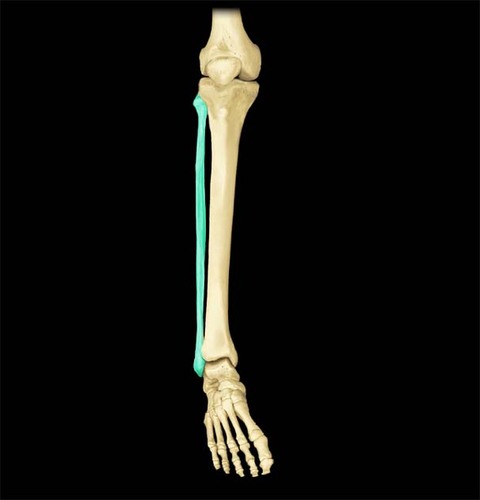
25
New cards
Tarsals
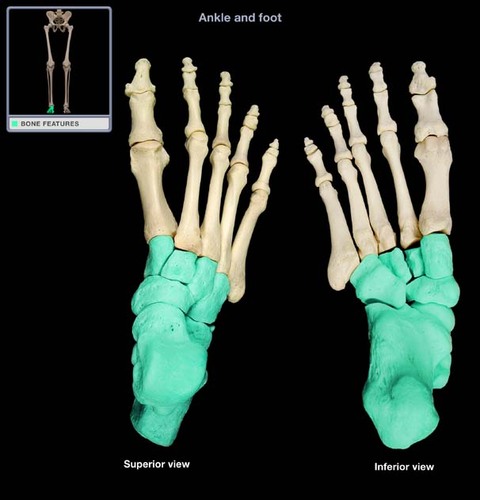
26
New cards
Metatarsals
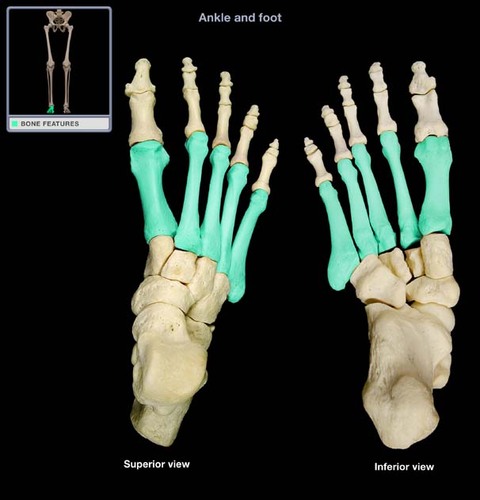
27
New cards
Axil skeleton
center of the body
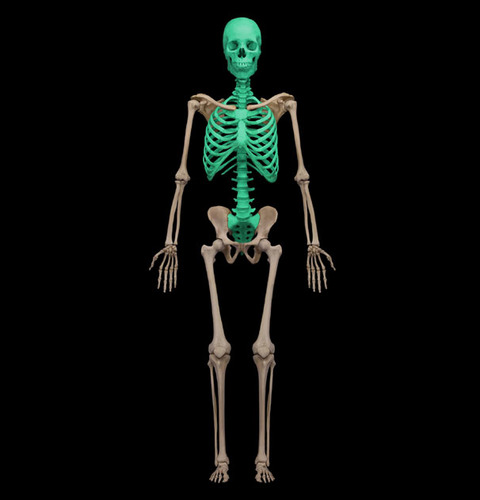
28
New cards
Appendicular skeleton
appendages
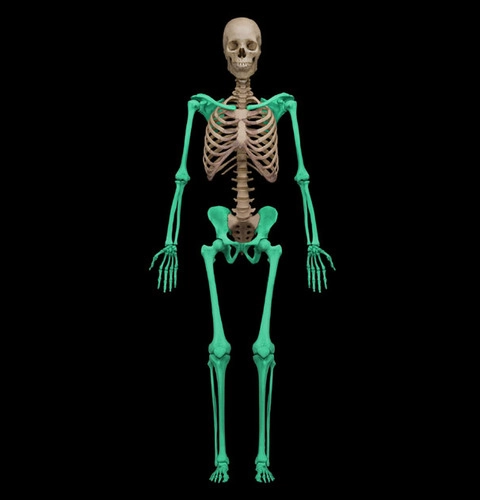
29
New cards
Calcaneus bone
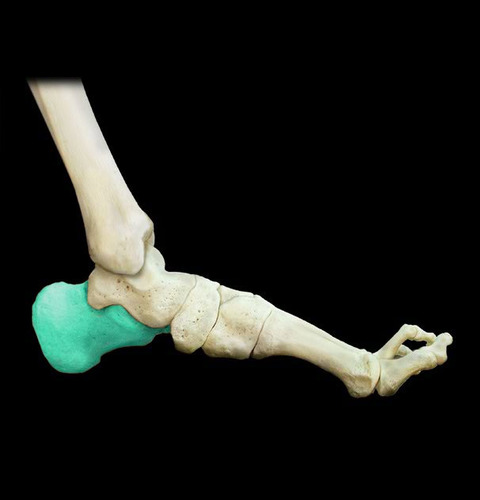
30
New cards
Talus bone
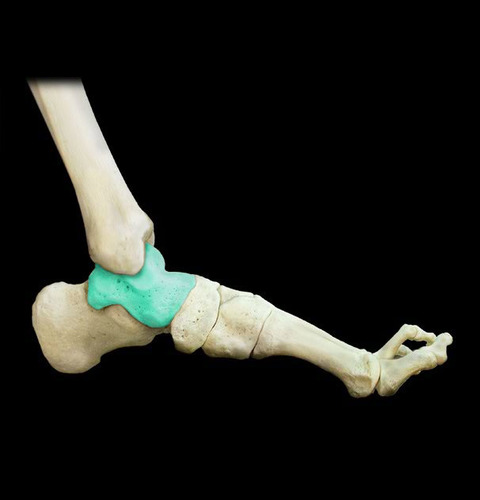
31
New cards
Zygomatic bone
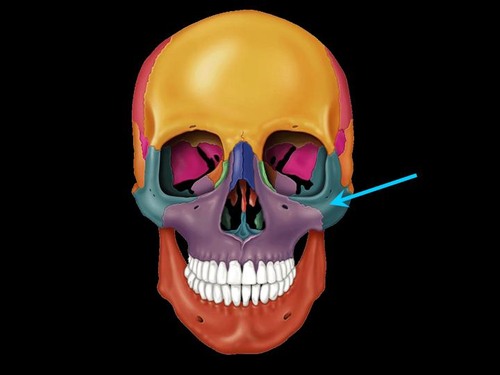
32
New cards
Parietal bones
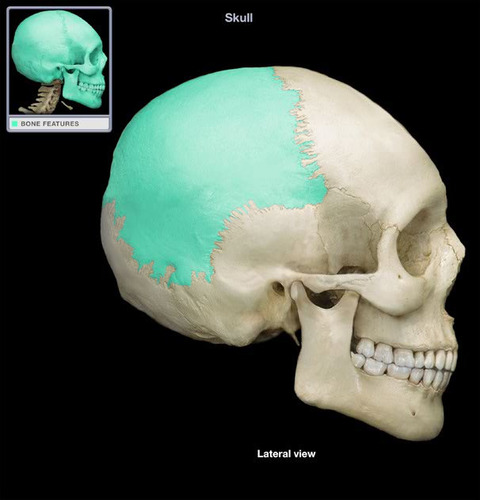
33
New cards
Ethmoid bone
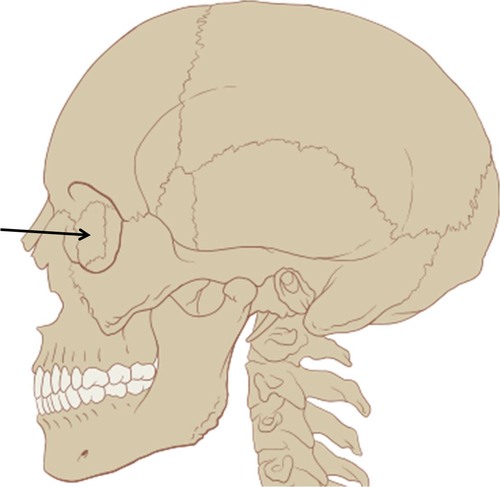
34
New cards
Lacrimal bone
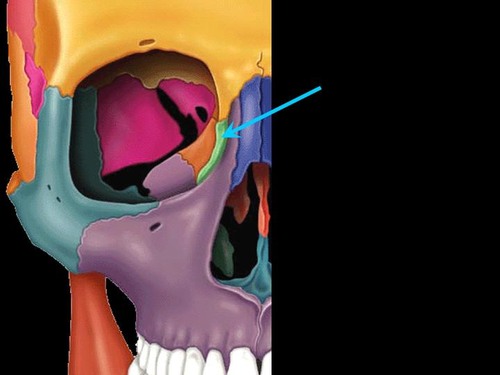
35
New cards
Nasal bones
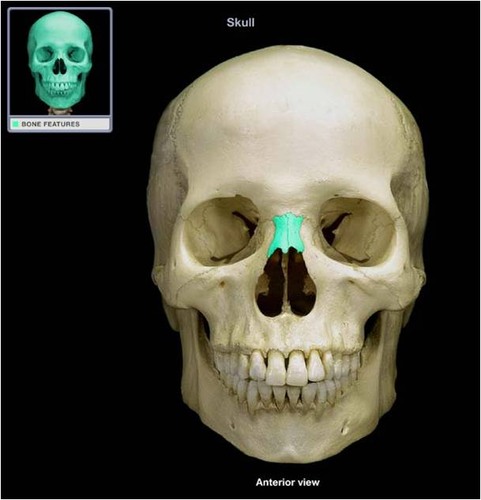
36
New cards
Frontal bones
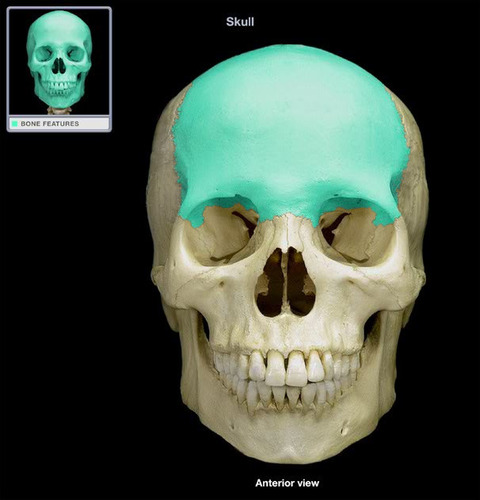
37
New cards
Maxillary bones
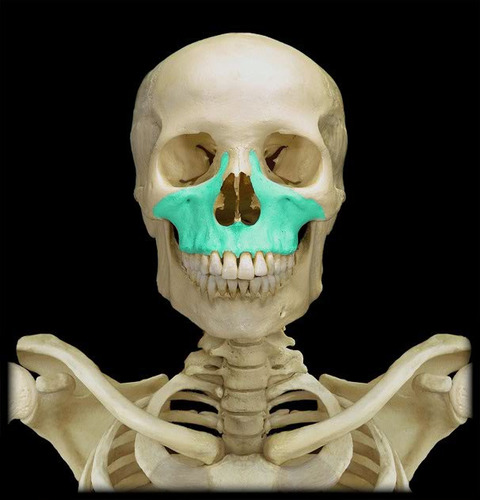
38
New cards
Occipital bones
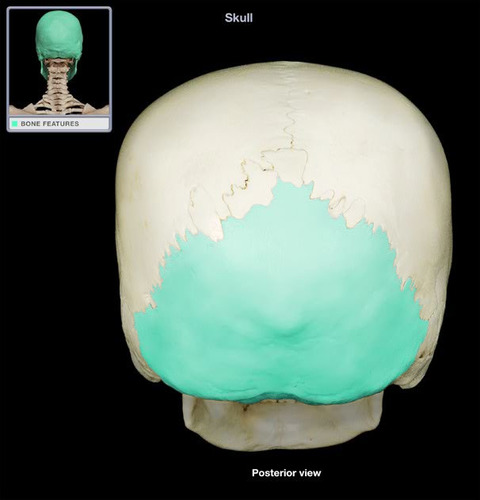
39
New cards
Mandible
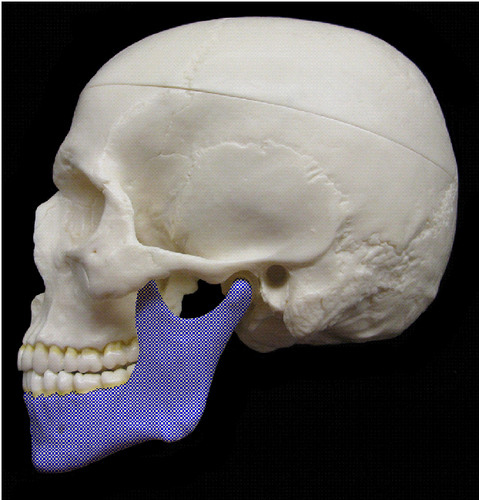
40
New cards
Temporal bones
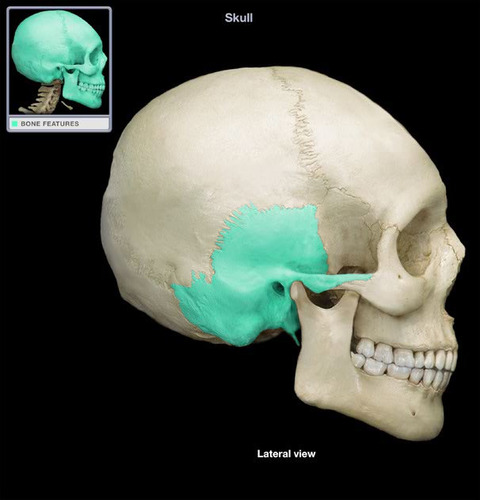
41
New cards
Thoracic vertebrae
42
New cards
Lumbar vertebrae
43
New cards
Sacral vertebrae
44
New cards
Cartilage
flexible connective tissue
45
New cards
Ligaments
short bands of tough, yet flexible, dense connective tissue that can connect 2 bones and stabilize joints
46
New cards
Tendons
Cords of dense connective tissue, connect muscle to bone
47
New cards
Joints
articulations or junctions between 2 or more bones and include all other components, aid in movement and flexibility
48
New cards
Thumb
is opposable, has a special joint with metacarpal 1 and 2 phalanges
49
New cards
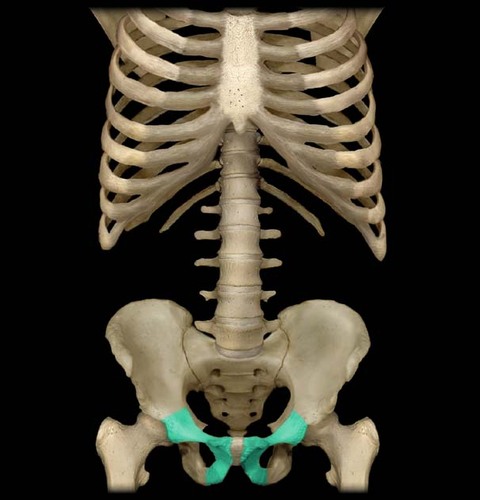
Pelvic girdle
50
New cards
Pectoral girdle
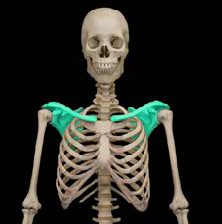
51
New cards
Thoracic cage
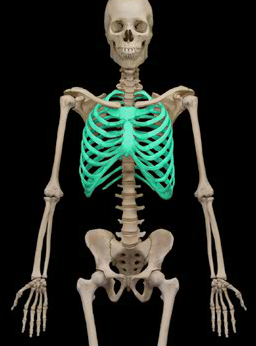
52
New cards
Proximal epiphysis
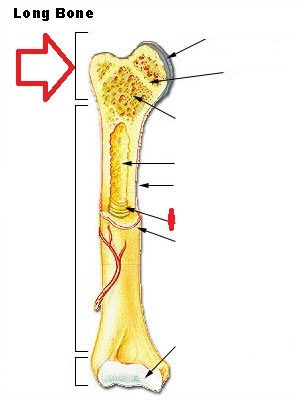
53
New cards
Spongy bone
small needle-like pieces of bone and open space, in most bones, makes blood cells and stores fat, lessens bone weight
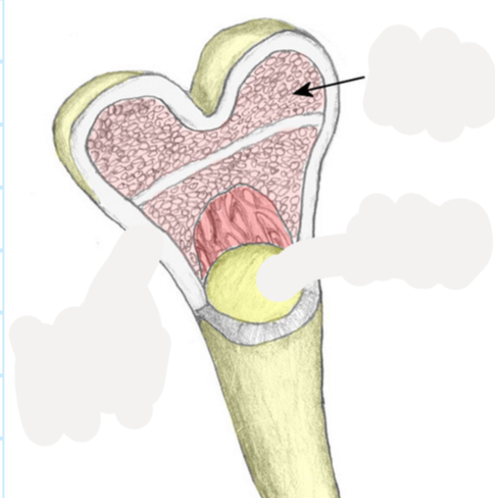
54
New cards
Epiphyseal line
where the plate used to be once it is fused by osseous tissue, in adults after growth is finished
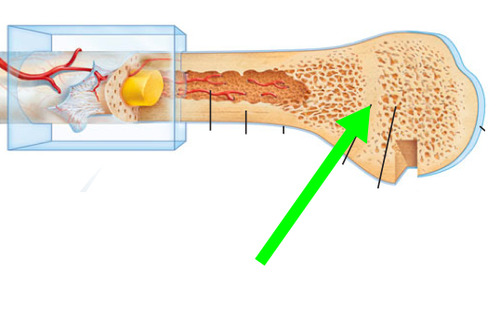
55
New cards
Periosteum
fibrous connective tissue, covers shaft of long bones
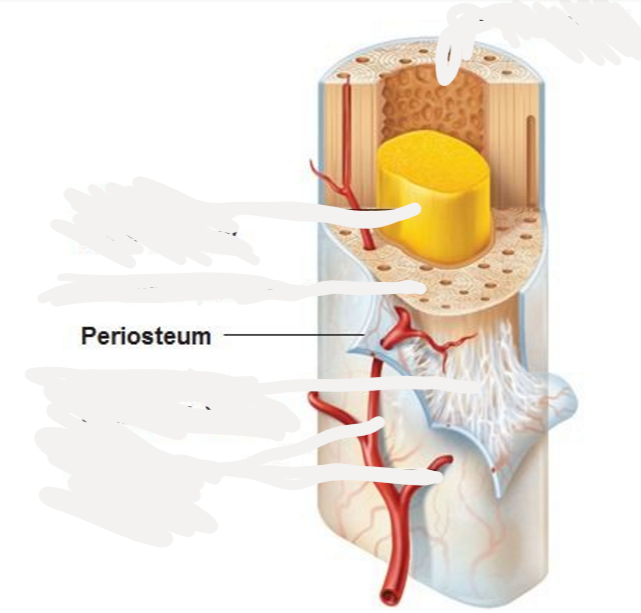
56
New cards
Compact bone
dense, smooth, and homogeneous, in all bones, hard external layer of bones, surrounds the medullary cavity, provides protection and strength
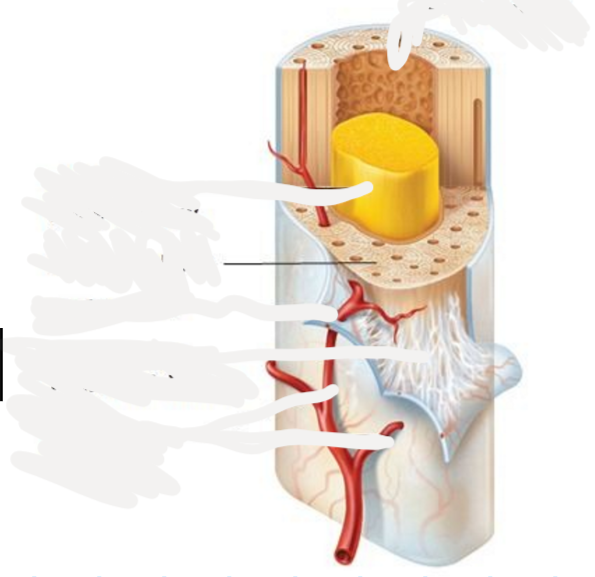
57
New cards
Medullary cavity
full of yellow marrow, cavity in the shaft of a long bone, stores adipose tissue
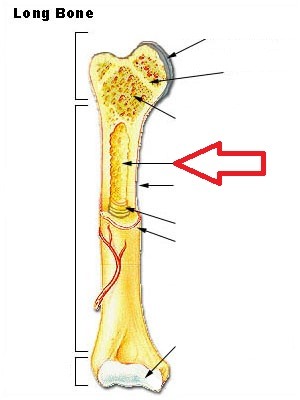
58
New cards
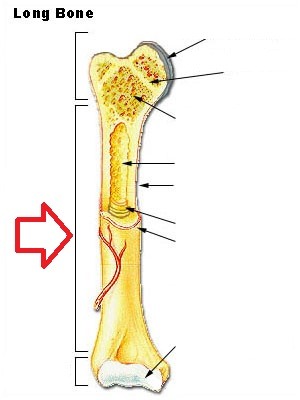
Diaphysis
made entirely of compact bone
59
New cards
Distal epiphysis
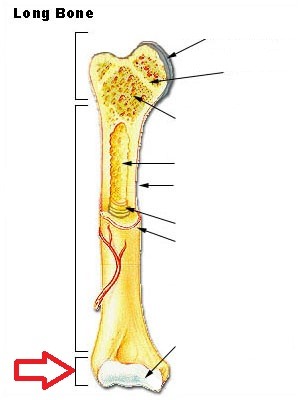
60
New cards
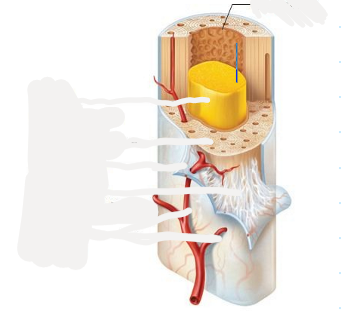
Endosteum
membrane lining the inner surface of the long bone bony wall, helps bones grow, repair, and remodel
61
New cards
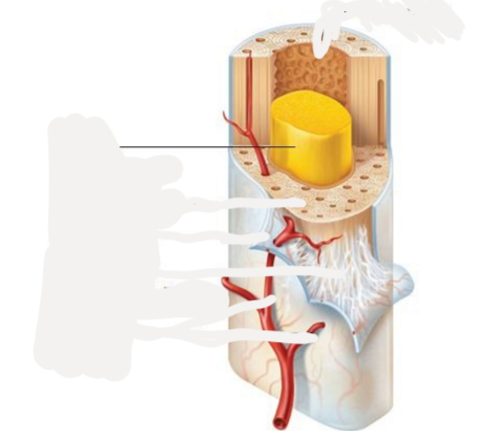
Yellow bone marrow
inner cavity of long bones, made of adipose tissue, in children forms blood cells
62
New cards
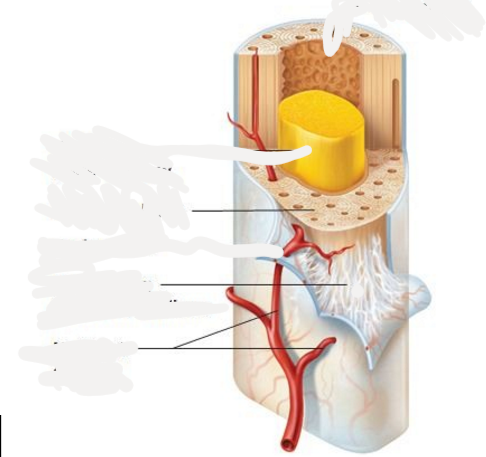
Perforating (sharpey's) fibers
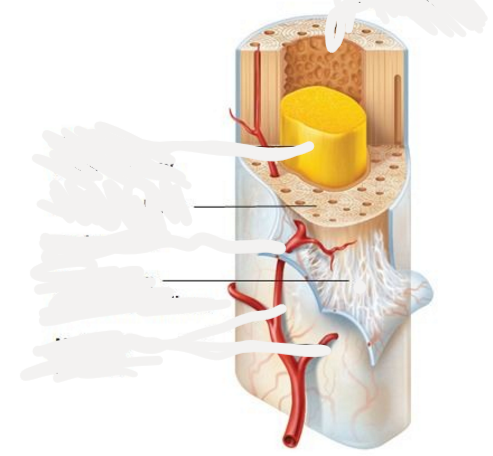
63
New cards
Nutrient arteries
narrow cavity of long bones through nutrient canals, forms the central arteries
64
New cards
Articular cartilage
covers the epiphyses of long bones, made of glassy hyaline cartilage, provides a smooth surface that decreases friction at joints
65
New cards
Epiphyses
ends of long bones, a thin layer of compact bone, encloses spongy bone, allows long bone to move in joints
66
New cards
Diaphysis
the shaft on the of the bone that makes up the majority of the long bones
67
New cards
Red bone marrow
in cavities in spongy bone of flat bones and epiphyses of some long bones, contain blood stem cells that can become red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets
68
New cards
Nerves in the bone
found along blood vessels, in periosteum, volkmann's canals, marrow, osteochondral, growth plate, and synovial membrane, connection to the nervous system, spatial orientation pain temperature and painful stimuli
69
New cards
Organic matrix
gives the bones strength and flexibility, calcium and collagen
70
New cards
Nutrient route through a bone
periosteum, osteon, central canal, lamellae, lacum, osteocyte
71
New cards
Canaliculi
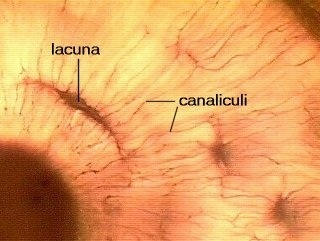
72
New cards
Central canal
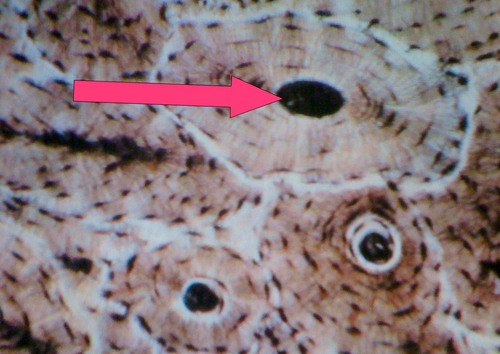
73
New cards
Lacuna
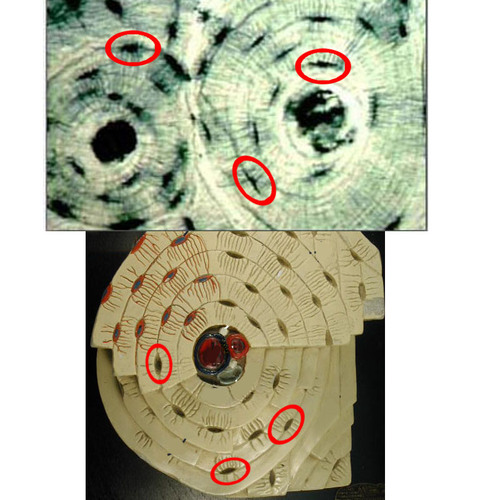
74
New cards
Phalanges (T)
75
New cards
Connective tissue
the majority is bone (osseous) tissue but cartilage and dense connective tissue cover the bone’s external surface
76
New cards
Nervous tissue
tissue in bone, has nerves
77
New cards
Epithelial tissue
in the bone blood vessels, provides nourishment
78
New cards
Muscle tissue
skeletal muscle tissue, attached to the bone
79
New cards
Skeleton
a framework holding up the entire body, protects the most vital organs, bones used as levers to produce movements, stores minerals and energy, forms hormones and blood cells
80
New cards
Hematopoiesis
blood cell formation, occurs in the red bone marrow of certain bones
81
New cards
Nutrients in bones
calcium and phosphate (released into the blood when needed), energy stored in the form of fat in yellow bone marrow
82
New cards
Long bones
longer than they are wide, tend to have a long shaft with either end being a bit wider, arm bones, hand bones, leg bones, and footbones
83
New cards
Short bones
more cube-shaped, tend to be as wide as they are long, provide support and stability with little movement, carpals and tarsals
84
New cards
sesamoid bone
a type of short bone, patella, a special type of short bone, means to be shaped like a sesame seed, embedded within tendons
85
New cards
Flat bones
thin and flat, often with a little curve, have a large surface area for attaching to muscles, sternum, shoulder blades, ribs, and cranial bones
86
New cards
Irregular bones
every other bone, have a highly specialized shape and structure, coxal and vertebrae
87
New cards
Structure of bone
dense and smooth layer of compact (cortical) bone tissue on the outside surrounding the more porous spongy bone tissue on the inside, bones usually have distinct markings due to ligaments and muscles
88
New cards
Compact bone
made up of osteons, lamella with tiny slats and collagen, and haversian canals
89
New cards
Osteons
the basic structural unit, long cylinders that act as tiny weight-bearing pillars in the bone
90
New cards
Lamella
hollow tubes grouped together to make compact bone, filled with tiny salts and collagen fibers that allow the bone to resist torsion and stress, the salt is hard, the collagen is rubbery and durable
91
New cards
Haversian canal
runs through the middle of each osteon and contains small blood vessels for nourishment and nerve fibers for signaling
92
New cards
Spongy bone
less organized than compact bone, no osteons, have trabeculae
93
New cards
Trabeculae
in spongey bone, tiny bone struts that are key for helping the bone to resist stress: also where bone marrow is
94
New cards
Projections
a type of bone marking, where muscles and ligaments attach
95
New cards
Surfaces
a type of bone marking, forms joints
96
New cards
Depressions and openings
a bone marking, for blood vessels and nerves to run through
97
New cards
Osteocytes
maintain healthy bone structure, housed in the lacunae- gaps between the lamellae, monitor and maintain quality in response to stimuli
98
New cards
Osteoblasts
build and construct bones by calcifying bone as it forms
99
New cards
Osteoclasts
critical in the regeneration of the bone through bone remodeling by absorbing bone tissue wherever it is not needed or is degenerating
100
New cards
Ossification (osteogenesis)
the process of bone tissue formation, the key to forming your skeleton as an embryo, essential for bone growth from childhood up to early adulthood, used for bone remodeling and repair later in life, articular cartilage and epiphyseal plates don't go through this