Criminology quiz 1
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Criminology is based on…
Theory
Criminology is the process of…
Making laws, breaking laws, and of reacting towards the breaking of laws
Criminology is
The scientific study of crime, causes, and control
What is a theory?
A set of propositions that describe casual relationships between variables
What is an integral part of the research process
A theory
A theory is not___ but___
Deterministic; probabilistic
What is a Macro level theory?
Theories that are broad in scope and explain social structure and its effects
What is a micro level theory?
A theory that focuses on the interactions and behaviors of individuals and small groups, examining how personal relationships and everyday interactions shape social phenomena
What are the seven criteria for a good theory?
Empirical validity, probabilistic concept of causality, legal consistency, scope, parsimony, testability, empirical falsification
What is empirical validity?
The theory can proven with other research
What is the probabilistic of concept of causality?
Correlation doesn’t equal causation
What is legal consistency?
When laws are applied equally and without unjustifiable differentiation
What is the scope?
The extent of relevant information.
What is parsimony?
Use of the simplest theory that fits the data
What is crime as a whole?
Crime occurs over a social construct, occurs over a time a place, contains the elasticity of evil, and is subject to change based on shifting landscapes
What is the elasticity of evil?
What's considered evil today might not be considered evil tomorrow
What are the 4 ways to view crime?
Legalistically, politically, socially, psychologically
What is crime legalistically?
Any act that violates the law committed without defense/excuse and is penalized by the state
What is crime politically?
Any act against someone in a position of power
What is crime socially?
Any antisocial act that is an offense against human relationships
What is crime psychologically?
A problem behavior that makes living in society difficult for norm abiding citizens
What are the drawbacks of defining crime individually (socially, politically, legalistically, psychologically)?
Doesn't recognize the origin of crime/law, can be used unfairly, difficult to maintain order, limited in scope and doesn't reflect harm done
Why do we need theories?
Usefulness (creates our framework for understanding), policy implications (informed decision making)
What are the three questions criminologists want to know?
Why crime occurs, why is it increasing/decreasing, who commits it and why
What are the three major data sources?
Official statistics, victimization survey data, self-reported data
What is an example of an official statistics data source?
The uniform crime report (UCR)
What are the two types of systems in the UCR?
1, summary reporting system (srs), 2. National incident based reporting system (nibrs)
Is the SRS or NIBRs retired?
SRS
Why is NIBRS better than SRS?
1. More specific, 2. Collects more information, 3. Helps give context to crime, 4. More flexible
What is an example of a victimization survey data?
The national crime victimization survey (NCVS)
What does the summary reporting system ( SRS) do?
It only reports the largest crime
What is the national crime victimization survey (NCVS)?
The nation's primary source of information on criminal victimization, 2. Only involves crimes of people 12+, 3. Samples 240,000 people in 150,000 houses, 4. Is based on interviews
What is self-reported data?
Data provided by individuals about their own offenses/crimes committed, 2. Used for less serious offenses (e.g. drug use)
What is the number of offenses per 100,000 formula?
What is the number of offenses per 100,000 = # of offenses / population of the jurisdiction
What are the two types of theories that explain problems?
1. unit theories, 2. metatheories
What do unit theories do?
They emphasize a particular problem and make testable assertions about that problem
What are metatheories?
Rarely testable theories and are ways of interpreting reality
What are the 5 theories on why crime rates have been declining?
Increased incarceration, 2. legalization of abortion, 3. Unleading of gasoline, 4. Improved policing strategies, 5. social and economic factors
What are the origins of modern criminology?
Classical school, 2. Positivist school
What was the belief of the classical school of criminology (the enlightenment/1700s)?
Criminality is caused by free will, crime is a choice
Does classical school focus on the actor or the act?
The act
What did the positivist school of criminology think (mid 1800s - 1900)?
Crime is caused by uncontrollable factors, it uses the scientific method to study crime
Does the positivist school focus on the actor or the act?
The actor
______ of punishments is more effective in preventing crime than ____
Certainty; severity
Punishments should be proportional to …
the crime's impact on Society
What is specific deterrence?
Punishing offenders for their crimes deters those specific offenders from further crime
What is general deterrence?
Punishing some offenders deters people in the general population from crime
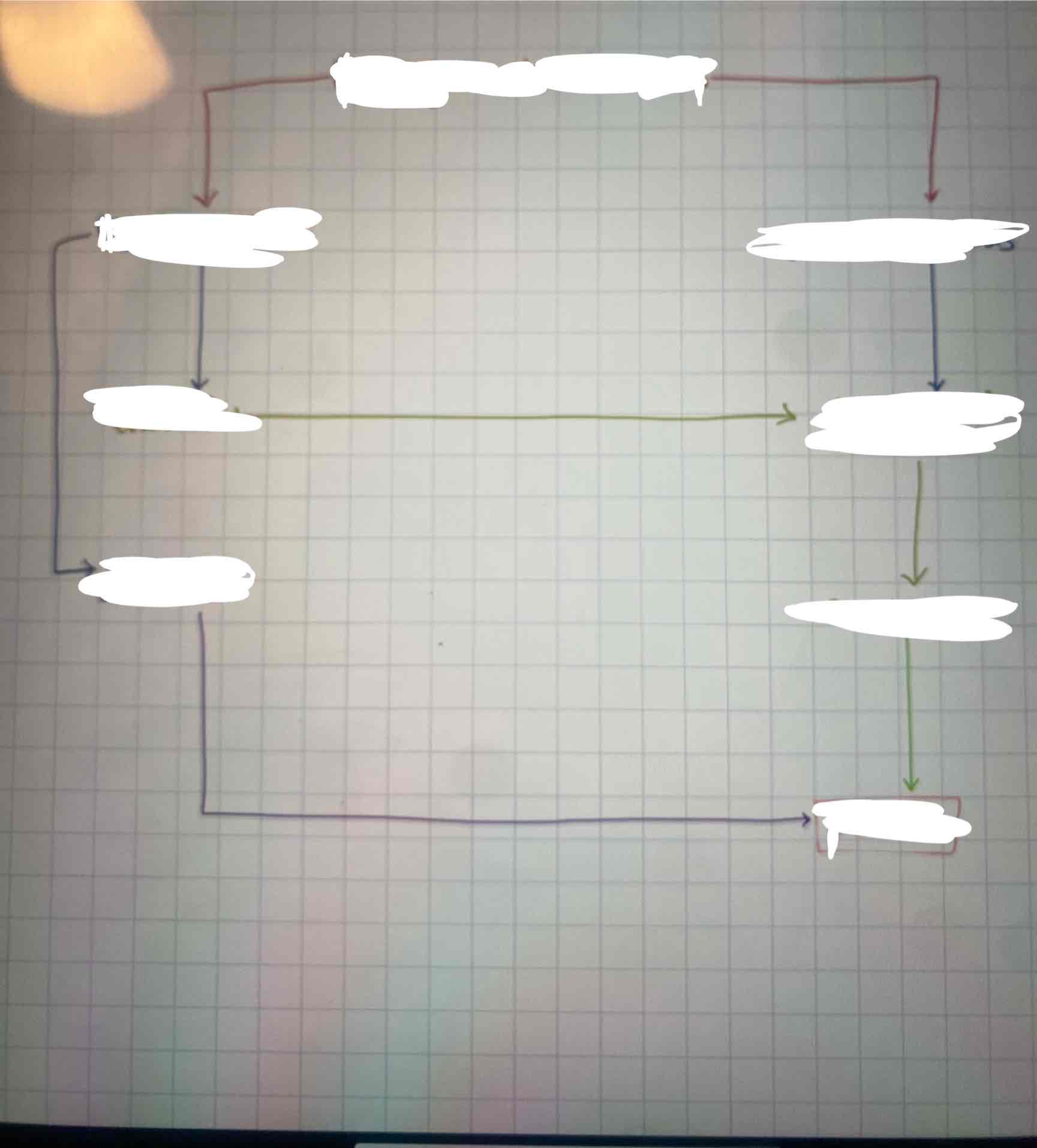
Fill in the blanks:
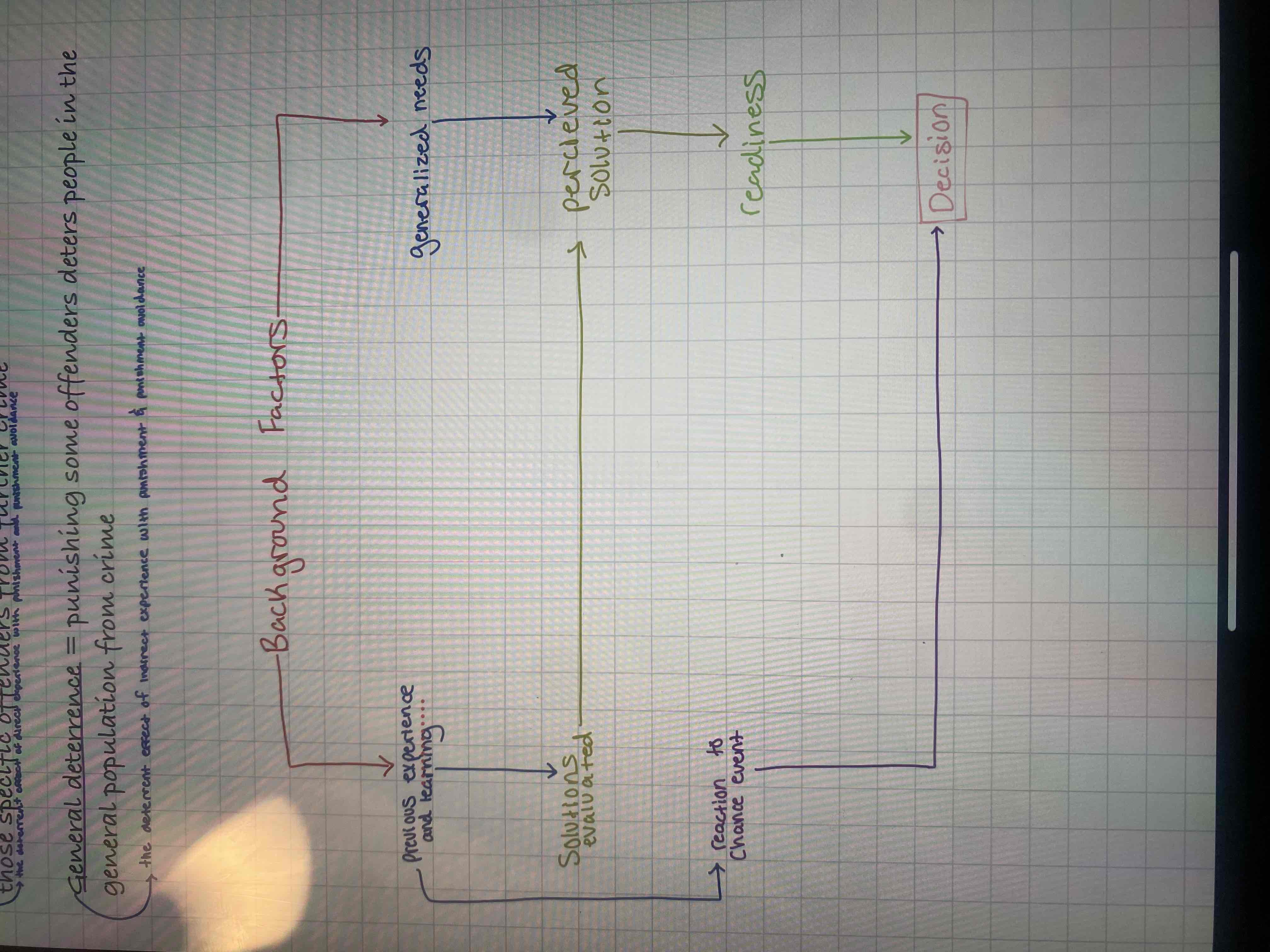
What 4 types of experiences affects people's perceptions of the certainty of punishment and thereby influences crime?
Direct experience with punishment (specific deterrence)
Indirect experience with punishment (generaI deterrence)
Direct experience with punishment avoidance
Indirect experience with punishment avoidance
How was criminal justice in medieval times (400 AD -1500 AD)?
Localized (operating under lords/nobles), 2. Punishment for revenge
What are the 4 goals of punishment?
retribution
incapacitation
rehabilitation
deterrence
What is retribution?
Revenge
What is incapacitation?
Rendering an individual incapable of committing future crimes
What is rehabilitation?
Changing the criminal's behavior
What is deterrence?
Stopping others from committing the same crime
What was the age enlightenment (1700s) about?
Moved away from supernatural explanations of crime , 2. Proposed that people are rational and choose to commit crimes when benefits>costs 3. The classical school of criminology
What is the model of man?
It humans have these 3 qualities, then crime is the freely chosen result of the rational decision that the benefits of the crime outweigh the costs
What are the 3 qualities of the model of man?
Free will
Hedonistic
Rational
Define hedonistic:
People persue things that give them pleasure
What did Cesar beccaria advocate for in "on crimes and punishment (1764)”?
for punishment to deter crime, rather than be for retribution
punishment protects the social contract and must fit the crime
he focused on the guilty act (actus reus)
What is the social contract?
Mutual respect and dignity among citizens and between the individual and the state
In order to deter crime, punishment should be…
Swift
Certain
Severe / fair
What is a certain punishment?
How often people were people were sent to prison for a specific crime
What is a severe crime?
The average number of months they served for the crime
What are the limits of deterrence?
Penalties learned after arrest (can't be weighted against benefits before )
Punishment is far from certain
Rationality
Some people have little to lose
What happened to deterrence theory over the years?
Experienced a resurgence in the 1970s and had a major influence on criminal justice policies
Many states implemented "three strikes and you're out" laws
The prison population soared during this period
What is the "three strikes and your law?
At/after your third offense you would go to jail for 25 - life
What is recidivism?
A tendendency of a convicted criminal to reoffend
What was happening in the 60s?
increase in crime and civil disobedience
the "war on drugs"
"nothing works" in rehabilitation by Robert martinson
What is rational choice theory?
an extension of deterrence theory
developed by Clarke and Cornish in 1986
builds on classical Criminology
different crimes require different decision-making models
What 3 things cause bounded/ limited rationality which leads to a sub-optimal decision to commit crime?
Cognitive limitation, information imperfection, and time constraint
Why do people continue to commit crimes?
Increased professionalism
Changes in life style and values( adapting to a life of crime)
Changes in peer groups (friends with more criminals)
No perceived "way out" of criminal behavior
Why do people stop committing crimes?
Big life events (e.g. Child, marriage, injury, job offer)
Something goes wrong while committing a crime
Maturity
External support
What is routine theory?
Certain changes in the modern world have provided motivated offenders more opportunities to commit crime
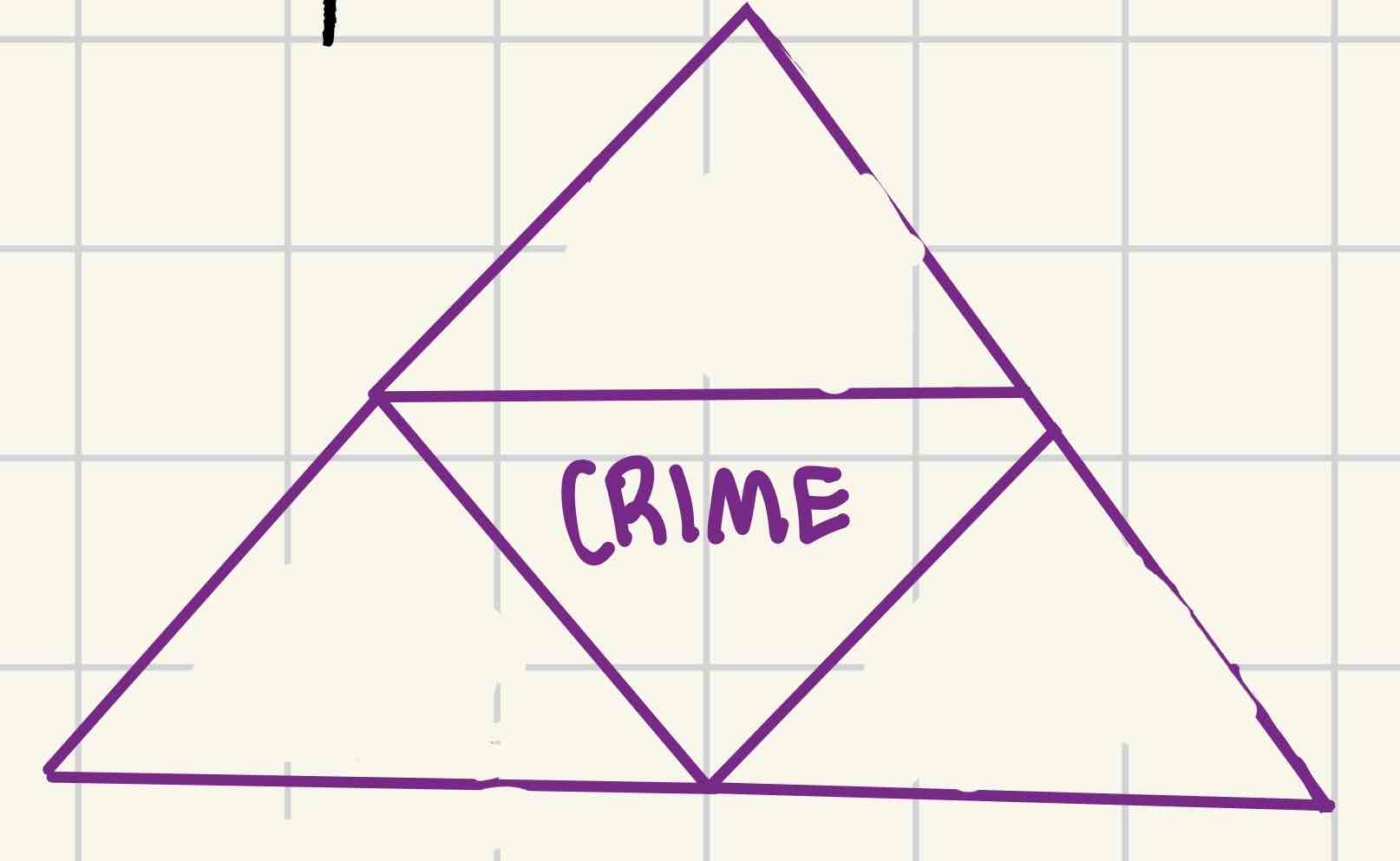
What are the three parts of the crime triangle in rational theory?
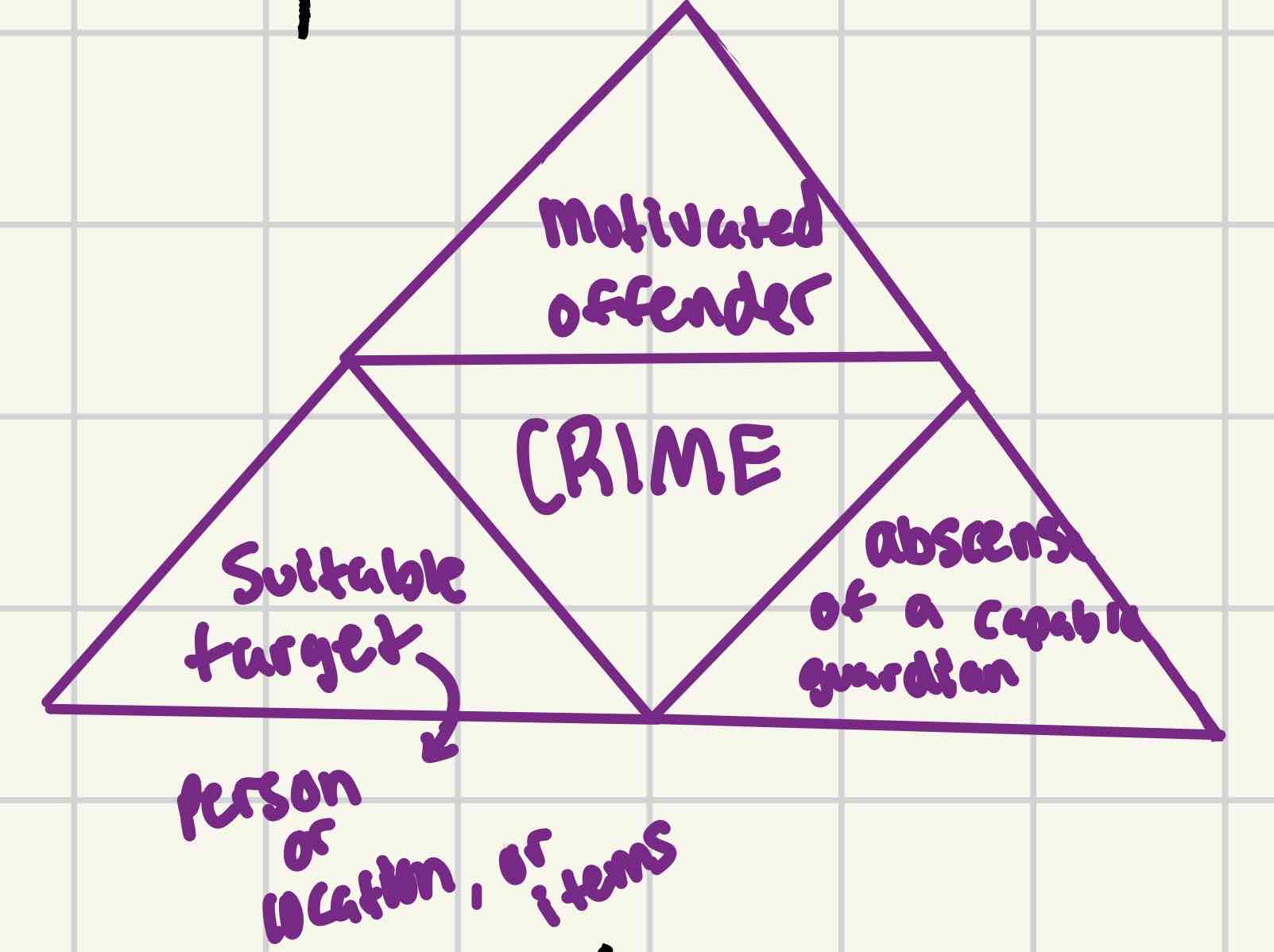
What are police talking about when they examine a "motivated offender'?
how societal structures create conditions for motivations to be acted upon
What makes suitable targets?
vulnerability, attractiveness
• value, visibility, accessibility, and inertia
What is situational crime prevention?
a police strategy That focuses on reducing opportunities for crime
What were the effects of MartinSon's report?
Politics and social tides shifted
More focus on deterrence
Less focus on rehabilitation
What did Cesar Beccarua do?
He wrote on crime and punishment, was against torture/death penalty
What did Martin son write?
Nothing works (about rehabilitalion)
Classical school of criminology focuses on_____ but rational choice theory focuses on_____.
Law; economic theory