Waste water management/ Portable water
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
why does waste water require treatment before being released into the environment
it contains organic matter which is harmful to plants and the environment(it includes fats, oils greases and synthetic products
sewage and agricutral waste water contains?
-organic matter
-harmful microbes
-pesticides/fertilsers
industrial waste water contains
-organic mater
-harmful microbes
1st stage of sewage treatment
1)Screening:
-metal grid
-steeps large solid objects and grit removed
2nd stage of sewage treatment
2)Sedimentation:
-sludge(solid sediments-contains human waste) pushed towards centre of tank and settle at the bottom
-sludge pumped to storage tank
-the sludge is anaerobically digested by bacteria
3rd stage of sewage treatment
3)Aerobic digestion:
-effluent watery liquid-pee) flows to the aerated tank
-this liquid contains organic matter and harmful microorganisms which us broken down aerobically by bacteria
4th stage of sewage treatment
4)Final treatment
-useful bacteria settle to bottom recycled
-waste water is now safe to release into the environment
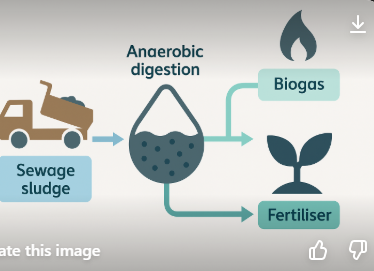
Treating sludge
Once Anaerobic digestion by bacteria it can be used as fertilizer or as biofuel
-as u heat it up, more bio gas is produced(35-55) —> bio gas is a renewable resource
water purification
Process of removing undesirable chemicals and contaminants from water like dissolved solid
how to portable water produced
-choosing an appropriate source of fresh water(reservoir)
From freshwater (like rivers, lakes):
Filtration (remove solids)
Sterilisation (kill microbes) — by chlorine, UV light, or ozone.
From seawater (where freshwater is scarce):
Desalination by distillation or reverse osmosis (both very expensive and energy-intensive).
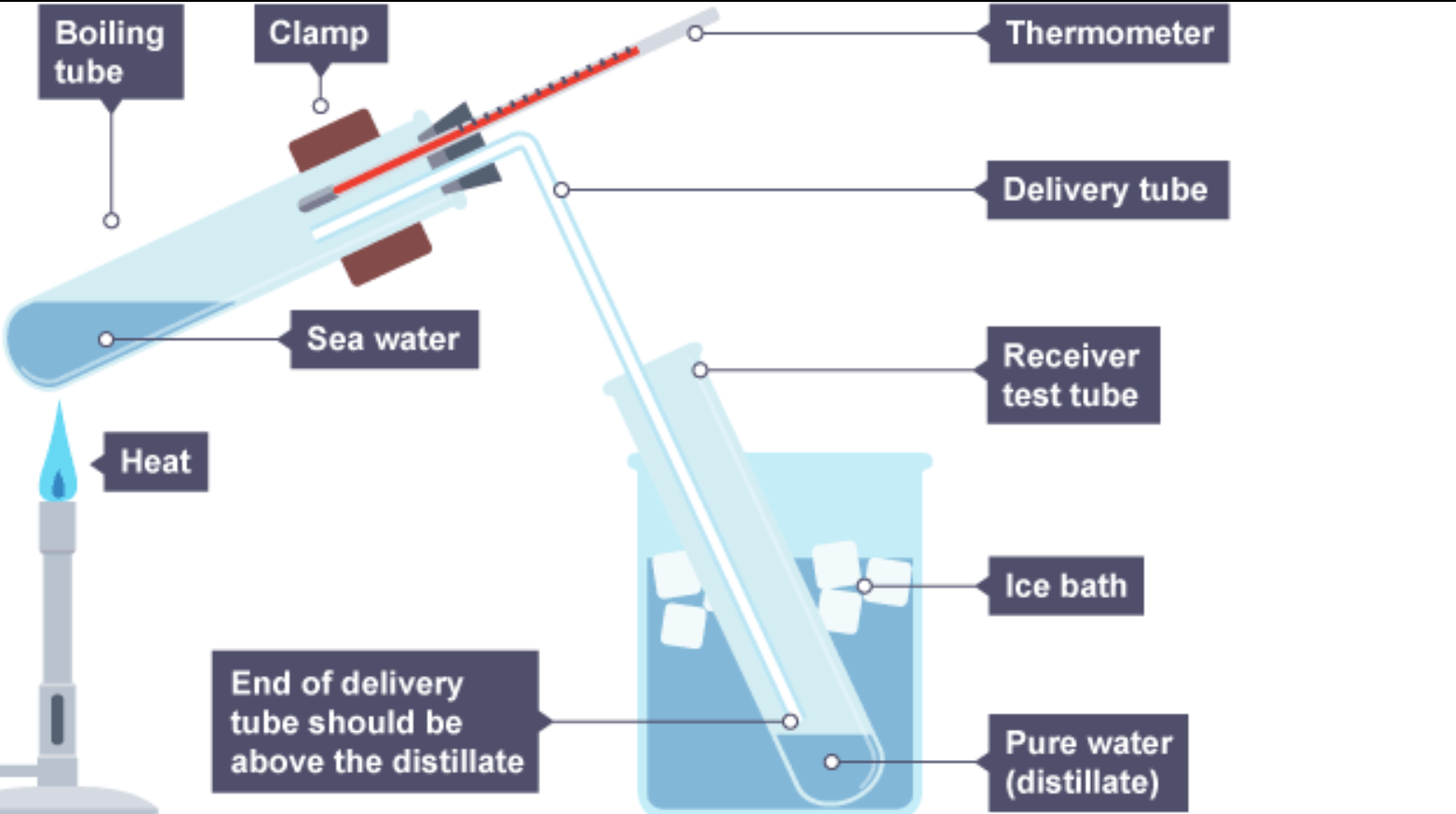
Distillation
A process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points
water is heated and evaporated, then condensed into pure water (leaving salts behind - removes salts and microbes).
reverse osmosis
A desalination process that involves forcing water through a semi-permeable membrane (blocks out salts, microorganisms and waste).
What are two problems with desalination?
High energy cost.
Expensive equipment.
Why is potable water not considered pure water?
Because it contains small, safe amounts of dissolved substances, unlike pure water which is conatins no minerals
pure water is
How would you distill water (RQ)?
Heat the water until it boils.
The water evaporates (turns into steam), leaving dissolved salts and impurities behind.
The steam travels through a cooling tube (condenser) where it cools and condenses back into liquid water.
The pure distilled water is collected in a separate container.
How is waste water produced?
Waste water is produced from domestic, industrial, and agricultural activities, primarily from water used for drinking, cooking, bathing, and processing.
explain the uses of sewage slurry
Fertiliser, biogas for (renewable)energy, improving soil in land restoration.
What factors help justify the choice of potable water supply in different scenarios?
💧 Availability – Freshwater sources, seawater, rainwater
⚡ Energy use – Desalination = high energy, filtration = low energy
💷 Cost – Cheaper methods preferred where possible
🏥 Safety – Must meet potable standards (safe for drinking)
♻ Sustainability – Recycled water/rainwater may be best in some areas
🗒 Choose the supply based on local conditions, infrastructure, and resources.