globalisation
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
geography paper 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
what is globalisation?
the interdependence and interconnection of countries across the world.
the rate of globalisation is increasing, creating new opportunities for people + businesses - creating winners, but also creating losers due to widening inequality, the environmental impact, exploitation etc.
economic globalisation
TNCs trade products internationally + use outsourcing and offshoring to lower costs
industries relocate to developing countries to save money on labour - brings economic growth
trade blocs (e.g EU, NAFTA, ASEAN) create economic integration between states + promote development
cultural globalisation
exposure to international media (tv, social media) - recognition of other cultures
international travel - experience other cultures
greater awareness + understanding of world events due to education + news
westernisation - spread of western culture e.g. mcdonalds seen internationally
political globalisation
governments form connections via trade deals + blocs
western democracies influence global political ideas - e.g. market economies in former communist states
deregulation policies allow markets to grow internationally
IGOs harmonise national economies and political relations e.g the United Nations
social globalisation
international immigration creates multicultural societies where people share + adopt cultures e.g. cultural restaurants
social networking has revolutionized human connections on an international scale
global NGOs and charities aid in improving education and health worldwide
globalisation throughout history - transport examples
steam power - 1800s, britain’s steam technology allowed them to move their goods and armies quickly, dominating continents such as Asia and Africa
jet aircraft - efficient aircraft allows faster transport of goods + increasing competition between affordable airlines (ryanair, easyjet) allows more people to travel
containerisation - over 200 million container movements every year - important to the global economy.
globalisation throughout history - technology examples
telegraph - 1860s, allowed for instant communication worldwide, revolutionary for businesses
telephones - very popular, particularly among youth = better global communication
broadband + fibre optics - 1990s, transfers data very quickly via cables along the ocean floor
gps - satellites allow goods to be tracked across the world + gps is essential for modern cars
internet - approximately 67.5% of people have access to internet + social media is also influential in the rapid spread of news, knowledge, and opinions
advantages of trade blocs
larger potential market = larger potential revenue
as businesses cater for more demand (by increasing the volume of production), other businesses can benefit - providing raw materials, skilled workers and outsourcing opportunities = positive feedback loop
trade of essential materials
disadvantages of trade blocs
countries within major trade blocs are only focused on themselves
countries within trade blocs are not treated fairly e.g mexico was considered lesser than us or canada within NAFTA (north american free trade agreement)
trade restrictions
tariffs - tax for importing/exporting goods e.g. trump’s executive orders: 25% tariffs on goods from mexico + canada, 15% on goods from china
non-tariff barriers - such as quotas (fixed number of goods) or requirements
bans on products from specific countries - e.g. barbie banned in saudi arabia
ethical responses to globalisation - to combat unsustainability + consumer societies
localism - buy local to decrease food miles + support local businesses = less carbon emissions so is overall more sustainable
transition towns - grassroots movement to promote local sourcing + self-sufficiency - preparing for an era post-fossil fuel usage, avoiding products such as oil. examples include totnes, devon = community driven + local charity = renewable
bristol pound (local currencies) - largest alternative to gbp in the uk, encourages buying from local + independent businesses → leads to a positive local multiplier effect
fair trade/ethical consumption - reduce inequalities of global trade, improving working conditions, reduce environmental degradation
recycling - managing resource consumption, helps to reduce eco. footprint, government sets targets for recycling to local councils + fines to organisations that don’t follow
case study: north korea - switched off countries (political)
1953: korea splits + north korea came under “soviet sponsored communist control” - with the founder adopting a policy of diplomatic + economic self-reliance to stop outsider/western influence.
however, now relies on chinese aid to feed population due to economic issues (lack of trade) + resource mismanagement = cut off from global economy
case study: sahel region - switched off countries (geographical)
landlocked, relies on poor quality roads + passage through neighboring countries to access coast = high transport costs which deters FDI + foreign markets, harsh desert climate so leads to desertification, poor infrastructure + low literacy levels = unattractive for offshoring , low income + subsidence farming, high levels of corruption
examples of countries in this region include chad, mali, niger, burkina faso etc
case study: china’s open door policy - special economic zones
received foreign direct investment when china was a communist country, but struggled to improve agriculture + industry.
death of mao marked china’s change from a planned economy to a mixed one with an increasingly open market environment
xiaoping (new leader) wanted to encourage FDI to secure the policy, and open 4 sez’s in 1980 e.g. shenzhen
all sez’s aimed to attract capital/business from external chinese communities
economic growth was rapid, by 2013, china has overtaken the usa to become the world’s biggest goods trading nation - however this wasn’t sustained = slowdown of china’s economy
KOF index
measures globalisation of countries based on political, social + economic factors on a scale of 1-100:
political (39%) - membership of igos + trade blocs, number of foreign embassies, participation in international treaties
economic (37%) - long distance flow of goods, services, capital + flows of fdi
social (24%) - personal contact through international phone calls + tourist numbers, information flow through number of internet users per 1000, cultural proximity e.g. number of mcdonalds
AT kearney index
measure of globalised cities, based on:
economic integration - imports + exports, fdi
personal contact - telephone traffic, travel + tourism, remittance
technological activity - internet users + hosts, secure servers
political engagement - membership of igos, signatories to international treaties, number of embassies
simple measures of globalisation (considers one factor)
gni - value of goods + services (also considers overseas earnings)
ppp (purchasing power parity) - expenditure of a population + reflects the cost of living
income per capita - mean average income per person
gdp - total value of goods + services (doesn’t consider overseas/informal earnings) + measured in usd → varies due to fluctuating exchange rates
composite measures of globalisation
economic sector balance - considers primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary sectors + describes the composition of a country’s industry
gender inequality index - considers female participation = treatment within society e.g. reproductive health (adolescent birth rates, maternal mortality ratio), empowerment (parliamentary seats held by women), and employment
human development index - measure of social development e.g. life expectancy, wealth, education
environmental tensions as a result of globalisation
jumbo ski resort - first nations: resort had been in the making for 30 years + was constantly tied up in legal battles due to the region being sacred to the indigenous ktunaxa first nations + home to the grizzly bear. the area has high elevation, plentiful snowfall + accessibilty so ideal + attractive for skiing industry. government + stakeholders (e.g. patagonia - clothing brand) were against the idea due to the area’s “incredible mix of environmental and cultural value) - “keep jumbo wild” campaign against the development, ensuring sustainability
palm oil - indigenous population in the amazon: indigenous + traditional communities say palm oil plantations are polluting their water sources, poisoning their soil, e.g. high, but legal, levels of agrochemical residue found in these communities, + driving away fish + game → impact on their lives - first raised as an issue in 2012, but palm oil is important within the food industry, e.g. unilever + nestle, therefore difficult to compromise on. sustainable policy aimed to guarantee the supply of biofuel while protecting the environment by banning deforestation in native forested areas
rising food (by 2050, food demand is likely to double + high consumption of meat = water stress), water (agriculture, industry + growing populations), energy insecurity (continued use of fossil fuels is inevitable) + biodiversity is under threat + globalisation has exacerbated climate change
transnational corporations
tncs are companies that operate across multiple countries - usually have their headquarters (usually in hics - europe, usa, japan and some in china), production + sales in different countries → crucial for globalisation. tncs provide raw products, manufactured goods, services or information (exists across sectors) → make products, create jobs, invest in countries + can contribute to culture. some may have a political influence e.g. put pressure for countries to create sezs + reduce taxes for the tnc to invest. tncs are very influential to a country’s level of globalisation + interconnectivity (some have larger revenues than entire countries) → furthermore, in 2016, top 200 tncs = 25% of the world’s economic activity but only hired 1% of the population. but, some tncs may exploit the environment + population to maximise profits + efficiency.
tncs create links between countries + with other companies - benefits tnc + expands the company
links through fdi - investing in countries benefits them by creating jobs + growing the economy
links through integration - horizontal (taking ownership of part of the supply chain e.g. buying a factory) or vertical (taking ownership of another company in a similar industry → e.g. food industry as larger companies own smaller ones)
impacts of tncs - increasingly known to consumers = bad reputation for some tncs
natural disasters e.g. tohoku 2011 - can disrupt supply chains which can affect production + tank profit - a tncs need for interdependence + global logistics can have major implications for global markets
collapse of the rana plaza factory in bangladesh 2013 (1134 people killed) impacted garment tncs → faced intense scrutiny over exploitation of workers + unsafe working conditions + a loss of profit + production
products made for consumers, such as phones, use global supply chains to spend less money on manufacturing. tncs may often invest in the source of raw materials in order to save money in the supply chain e.g. investing in fruit plantations to lower the cost + remove the middle man
outsourcing
tncs that provide tertiary industry products/services will often outsource tasks to other companies to save money + time. tncs like apple outsource their manufacturing process to maximise profit.
offshoring
companies that make manufactured products will often have their factories in lics due to lower labour costs, reduced taxes, weaker workers’ rights + weaker environment regulations. this creates ethical issues with tncs exploiting poorer citizens to maximise their products
glocalisation
adaptation of goods + services by a tnc to meet local needs or tastes → increases customers within a select region e.g. halal mcdonalds in muslim countries + generally changing menus to appease global customers, netflix personalising their shows for global views e.g. “trending in india today”
global shift
the shift of industry from the west to asian countries e.g. china, vietnam + bangladesh. this has lead to deindustrialisation in the west - since the 1960s = loss of jobs → originally relocating to china + now bangladesh for the lower labour costs, reduced taxes, weaker workers’ rights + weaker environment regulations = cheaper to manufacture here then import, rather than manufacturing locally.
winners of the global shift: creates jobs, infrastructure investment, education, poverty reduction + training, health sector improved + more products for consumers.
losers of the global shift: loss of land, unplanned settlements e.g. brazil favelas + mumbai slums, environmental + resource pressure → air/water pollution, land degradation, over-exploitation of resources + loss of biodiversity.
outsourcing services to india
many indians can speak fluent english - “the business language of the world” → indian government invested in infrastructure such as broadband capacity to attract high tech companies
benefits | costs |
workers receive middle class wages which has meant an increase in disposable income | many workers believe that they are being exploited, with long shifts + still lower wages than developed countries |
this means more customers + spending for businesses = positive multiplier effect | employees are often demotivated due to the repetitivity of their work |
people running the companies where services are outsourced to have seen increasing profits | the inequality between the richest + the poorest is increasing as the poorest are not well educated + cannot benefit from outsourcing jobs |
outsourcing of manufacturing to china
in 1990s, cities such as shenzhen + dongguan offered investors a large pool of cheap labour for manufacturing and other secondary employment → outsourcing to china has increased, but sweatshops (accelerated china’s globalised status) are becoming less popular in china → cheaper labour in bangladesh + vietnam + bad reputation of chinese products. instead, technological outsourcing opportunities move to china with offers of higher wages.
benefits | costs |
new production methods + techniques brought by tncs have now been adopted by local companies = local economic development | many employees have been exploited with unsafe working conditions → chemicals, long hours, limited human rights, relaxed health + safety regulations. |
locals, especially in rural areas + would be subsidence farming, now earn real wages | environmental degradation → polluted rivers with arsenic + lead (and other chemicals) + air pollution with particulates → increases asthma suffers + pollution related fatalities |
case study: detroit - deindustrialisation
located in the rustbelt, usa - heavy manufacturing, mainly expansion of the automobile industry → 1950 - 1.85mil moved to detroit to work in this industry (ford, general motors + chrysler) + 1910-1970 millions of african americans migrated to detroit for these jobs = racial tension. when mechanisation occurred in the 1970s, resulting in huge job losses + an energy crisis + an economic recession in the 1980s + growing foreign competition = plummet in profit, as detroit relied on this industry. faces many social + environmental issues - dereliction, depopulation, crime + high unemployment, contamination.
today, this has resulted in deindustrialisation + rust-sunbelt migration = mass abandonment of homes → entire streets are completely boarded up. 31.5% of residents live in poverty + an 8% unemployment rate (yet this fluctuates - 21.4% in 2020 + similar in 2010) + declining school enrollment rates (51,600 in 2023 but 53,000 in 2021). 252 murders recorded in 2023 + an average of 41 per 100k residents → global average 6.1 + struggling to stop brain drain
however, many deindustrialised usa cities (minneapolis, boston, philadelphia) have been able to recover since → but the establishment of these motor companies may have held detroit back as workers had little reason to pursue a higher education, as these companies provided higher wages. poor urban planning + lack of investment + deindustrialisation → poor perception → reinforces crime + poor quality of life
deindustrialisation
relocation/outsource their manufacturing to asia → social + economic impacts:
dereliction - many textile companies located in uk northern cities closed → area they occupied became abandoned + derelict
contamination - other area suffered from abandoned chemical + industrial waste, infiltrating the soil + local waterways
as companies move away, rates of unemployment increase → depopulation, as residents migrate to find new jobs → deprivation of inner city areas will increase = rise in crime
rural-urban migration - seek better employment opportunities or better standard of living (as perceived of uban cities)
rural pull factors:
employment opportunities - large businesses + tncs provide a wide range of jobs + opportunity to be promoted to better roles with higher wages.
services - better access to services in urban cities, as distance needed to travel is reduced + there is more likely to be specialised facilities in the city than in rural areas e.g. education, healthcare, government embassies + offices
infrastructure - transport links (roads, railways, buses) are faster + more reliable in urban areas + less congestion + better internet + broadband connection in urban areas + streetlights → feel safer
however, these pull factors aren’t certain → may not experience a better quality of life
rural push factors:
poverty - people can’t earn enough (seasonal or declining industry e.g. farming) + few job opportunities = high poverty + deprivation
conflict e.g. ukraine, syria, gaza, darfur - scarcity of resources which can can cause conflict between groups as they fight for resources (water, agricultural land or natural resources + wealth)
land reform - may be difficult for locals (especially native, indigenous communities) to prove they own land → tncs can claim the land instead
agricultural modernisation - mechanisation → less people required on farms = rise in unemployment, which forces economic migration on the unemployed
climate + natural disasters - occurrence of droughts or crop failures can force migration in search of food or water, regions impacted by natural disasters may feel pressured to move to avoid economic loss or fatalities
challenges faced by growing cities
strain on services like education + healthcare
overcrowding + development of slums
rising crime rates
poor sanitation e.g. open sewers
lack of green space
high levels of congestion
case study: lagos - megacities
current population around 17mil → expecting to reach 25mil by 2035. most of the population have undertaken rural-urban migration for better economic opportunities + a higher standard of living - from across nigeria as income is 4x higher than rural nigeria + rapidly growing job industries e.g. construction, technology + services = jobs for skilled + unskilled.
however, this rapid growth has lead to a high population density with unstructured urban infrastructure with poor quality roads + limited access to services due to urban sprawl, environmental pollution + traffic congestion (5mil+ cars + industry uses incineration + no city wide waste disposal), piracy (impacts quality of services), high living costs, and a rise in crime.
there is a significant inequality gap between the cbd (with tncs such as dutch shell oil) vs slums on the outskirts → makoko slums - 14.6% are unemployed, only 7% own their land, only 10%have homes with a bath, kitchen + toilet → spread of disease e.g. malaria + 8.5% of population live in poverty (1.3mil).
rising sea levels costs lagos $4bil annually + predicted to be flooded by 2050, while receiving 2000mm of tropical rainfall each year. 50% of girls have not attended basic education level of school (due to expensive fees but also family choice - instead child marriage + early childrearing, genderbased violence)
international migration
elite migrants - generally skilled or wealthy people, with the ability to move to global hubs (london, paris, new york) e.g. russian oligarchs with investor visas + purchase properties in london → some believe this has escalated uk house prices - but others believe the “trickle down theory” → business + tax paid will eventually improve london as a whole
economic international migrants - many cities like riyadh, dubai, london, new york attract workers with low pay + specific skills e.g. construction → fills skill gaps + can advance a country’s development but can create issues such as a rise in illegal immigrants
international migration - benefits vs costs
benefits | costs | |
source country | migrants send back remittances which can aid in development + reduce poverty without government intervention, migrants become skilled → can return to set up their own businesses, encouraging local economic growth + employment opportunities, reduced service spending for government as population decline | brain drain as skilled workers leave, migrants tend to be young so elderly are left behind + can be isolated, decline in services due to low customer numbers, which can lead to the negative multiplier effect → reduces businesses + services, potential dereliction of agricultural land |
host country | can help fill skills gaps, working migrants contribute to the economy (paying taxes + buying services), increase cultural/demographic diversity, young migrants can balance an aging population or increase a dwindling population over time, businesses have a larger pool of employees + customers | rise of far right organisations - hate crime and racial tensions if lack of understanding between migrants + original population, strain on services (education + healthcare) due to an increasing population, house price inflation due to higher demand |
culture
cultural imperialism + government control over religion has been necessary, in the past, for successful imperial control but globalisation → emerging global culture
culture include: language, traditions, religion, food → influenced by media, migration, tncs + businesses + social media BUT in recent years, there has been large change to cultures + ideologies for developed/developing nations.
e.g. traditional asian diets are low in meat, but western influence has increased meat consumption → increases obesity + methane emissions to global warming
but there are also positive changes to culture → western paralympics has increased job opportunities for the disabled across the globe
cultural erosion
communities suddenly exposed to a new culture face sudden cultural diffusion, especially young people → can cause conflict, due to the value of culture to some communities e.g. the welsh not - discouraged welsh speaking in schools → culturally eroded the welsh language from the root. cultural erosion also includes loss of tradition, e.g. the loss of tribal life in papua new guinea - now wear t-shirts.
however, the spread of a western culture brings new awareness to marginalised groups e.g. paralympics 2016 - emerging/developing countries recognised their disabled communities more.
resisting cultural erosion
france - attempted to limit globalisation by restrict foreign language media + stopping religious cultural change by banning niqab/burkas + other religious symbols in public places
china - censorship of foreign media prevents information that critiques their government → cannot access bbc, facebook or search controversies (tiananmen square)
iran - early 2000s, the government banned barbie dolls as they were deemed inappropriate for the islamic state → halting westernisation
widening inequality gap
absolute poverty has decreased (but is still high) + average income has risen since the 1950s → but in the poorest parts of africa, this is slow → increase of wealth in europe + usa = widening gap between the rich + the poor. africa’s inequality gap is very significant - south africa vs sao tome + principe
gini coefficient measures inequality on a scale of 0-100 - 0 is perfect inequality while 100 is perfect equality - currently, south africa (63) has the highest while kyrgyzstan (26) has the lowest
globalisation as a creator of conflict
far right parties + organisations are becoming more popular with growing support - in europe, partially due to expansion of the eu in 2004 which increased the flow of migrants to 8 eastern european countries → e.g. germany accepts the most migrants (out of all eu countries) but there is a rise in support for Patriotic Europeans against the Islamisation of the West (PEGIDA). as of now, 6 eu countries (italy, finland, slovakia, hungary, croatia + czech republic) have hard right parties in government.
globalisation has not eased environmental or political tension between nations e.g. river nile + colorado river
protecting cultural identity
despite cultural diffusion + erosion, some cultures + indigenous communities have strengthened their identity as tourists are attracted to experience their culture + witness their traditional lifestyle e.g. papua new guinea. indigenous/nomadic groups have grouped together to support eachother + maintain their traditional lifestyles e.g. first nations continue to prosper
the issues with ethical responses to globalisation
localism: buying goods from local providers can be expensive - not affordable lifestyle for many. while carbon emissions are reduced, the intense resource consumption needed to grow crops locally may offset the benefits = growing tropical fruit in england requires lots of energy to create ideal conditions = not worth it
transition towns: very few communities actually doing anything, it doesn’t help the rest of the population, puts less into the economy
bristol pound: put a strain on the local economy by confusing wealth with money - makes areas poorer. growth of cashless payment + cryptocurrency impacted the success, with the bristol pound removed fro circulation in 2021.
fair trade: leads to higher prices for consumers (due to better wages of farmers) + excludes the poorest farmers as you have to pay to join fair trade programs
recycling: inequality in recycling efforts, 2⁄3 of uk households = unsure of which bins to use. some houses recycle 67% of waste, others only 20% = unequal
consumerism
consumerism is the idea that increasing the consumption of goods + services purchased is a desirable goal, and that a person’s well being + happiness depend fundamentally on obtaining consumer goods + material possessions. but why is this an issue?
consumerism portrays the ideology that the public should be allowed to have and want whatever → creates issues when considering how ethically a good is produced, making people unaware of the problems consumerism creates:
exploitation of workers - has seen a massive increase as globalisation has accelerated, as tncs want to maximise profits so workers face poor working conditions + little pay - 2021, 27.6 million people were doing forced labour, and around 1 in 4 of these were children
environmental issues - urban sprawl, pollution, resource depletion + insufficient waste disposal
throw-away societies - people think less about the longevity of a product, and opt to throw things away when its no longer needed
social, environmental + political tensions caused by globalisation
post-accession migration - movement of people from the eight post-communism, central + eastern european countries (joined eu in 2004) - including czechia, estonia, hungary, latvia
enclaves - a portion of territory surrounded by a larger territory who inhabitants are culturally or ethnically distinct
diaspora - the dispersion/spread of a people from their homeland
ethnoscapes - human migration - flow of people across boundaries
immigration policies - the way in which a government controls who can arrive + settle in their country - via rules + regulations
protectionism - government policies that restrict international trade to help domestic industries
censorship - the suppressio of speech + public communications → conducted by governments, private institutions + other controlling bodies
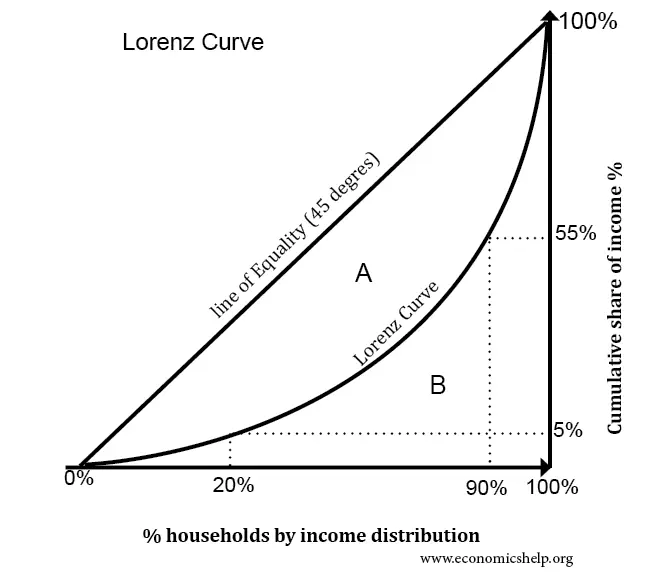
lorenz curve
shows the distribution of wealth within an economy
case study: mumbai - megacities
2025 - home to 22million, having doubled in size since 1970, leading to issues related to its rapid growth, with significant levels of unplanned settlements - largest named dharavi, with limited access to services, specifically water, power + sanitation. water is only provided for 2 hours per day, so many queue up for their share. mumbai is ranked the 4th most polluted megacity in 2018, + mass rural-urban migration has occurred for many to earn higher wages.