Govt. Intervention
1/15
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
why do we need govt intervention? (3)
if a business neglects other people like workers (w less wage), overcharging, damaged env, pressurizing work
govt sets up legal systems to prevent it
if they do it too much tho, it’ll discourage enterprise, reduce foreign investment = reduces national income growth, job creation, decrease tax revenue & consumer choice
how do you deal w/ externalities (2)
basically, businesses cut down trees, etc to make space for buildings, etc
basically → negative and external costsbut if they set up a recycling operation, they benefit the environment
→ reduces external and positive costs
→ taxes can be included + pollution permits
whats regulation of competition? (1/4)
they promote PREVENTING competition: anti-competitive practice to prevent competition
1. encourage growth of small firms = more comp if they join = they get low taxes, sometimes govt provides fund
2. low barrier 2 entry: barriers r removed = more comp
3. introducing ANTI comp legislation: prevents:
eliminates practice n reduces comp
promotes and sustains comp in markets
protects consumer interests
freedom of trade
how do they limit monopoly power? (2/4)
if they exist, they need to be monitored, otherwise w/o it they can exploit consumers
how do they protect consumer interests? (3/4)
people want good quality, and at a fair price with good service. w/o intervention, firms might exploit it using anti-comp.
- they increase prices, price fixing
- restricting consumer choice by sharing the market
- raising barrier to entry (spending lots of money on ads)
what else does consumer legislation cover? (4/4)
it covers consumer issues and aims to protect from practices mentioned before, prevents businesses from making false product claims, and stuff that doesnt pass food safety protocol, not fit for purpose.
if they break the law they have to pay the fine and compensate.
what are the fair trade issues covered by legislation? (8)
quality
production safety
prices
information
promotion
consumer rights
trading and age restrictions
payment methods
what is the sale of goods act 1979?
states that products sold must have good quality and fit for purpose
whats the food safety act 1990?
this law states that food should be fit for human consumption and comply w/ safety standards
how does the govt control merges and takeovers?
they monitor them to make the markets stay competitive
may be blocked or allowed to go ahead if conditions are met
what are subsidaries?
companies that are half-owned by another company
whats minimum wage?
amount paid per hour (legally entitled to pay)
how does the govt intervene in a labor market?
they set a minimum wage so employers cant pay less
employers get a penalty if they pay less
workers are then entitled to have money owed repaid at the current rates
what are the reasons to why they would intervene?
to raise income
they benefit women, ethnic households, low-income families
low inc people are entitled to claim welfare benefits, if income rises tho, they cant
it saves the govt money + when it rises ppl pay more taxhigh wage = motivates = boosts economy
employer justifies high wages by investing in training n’ machinery
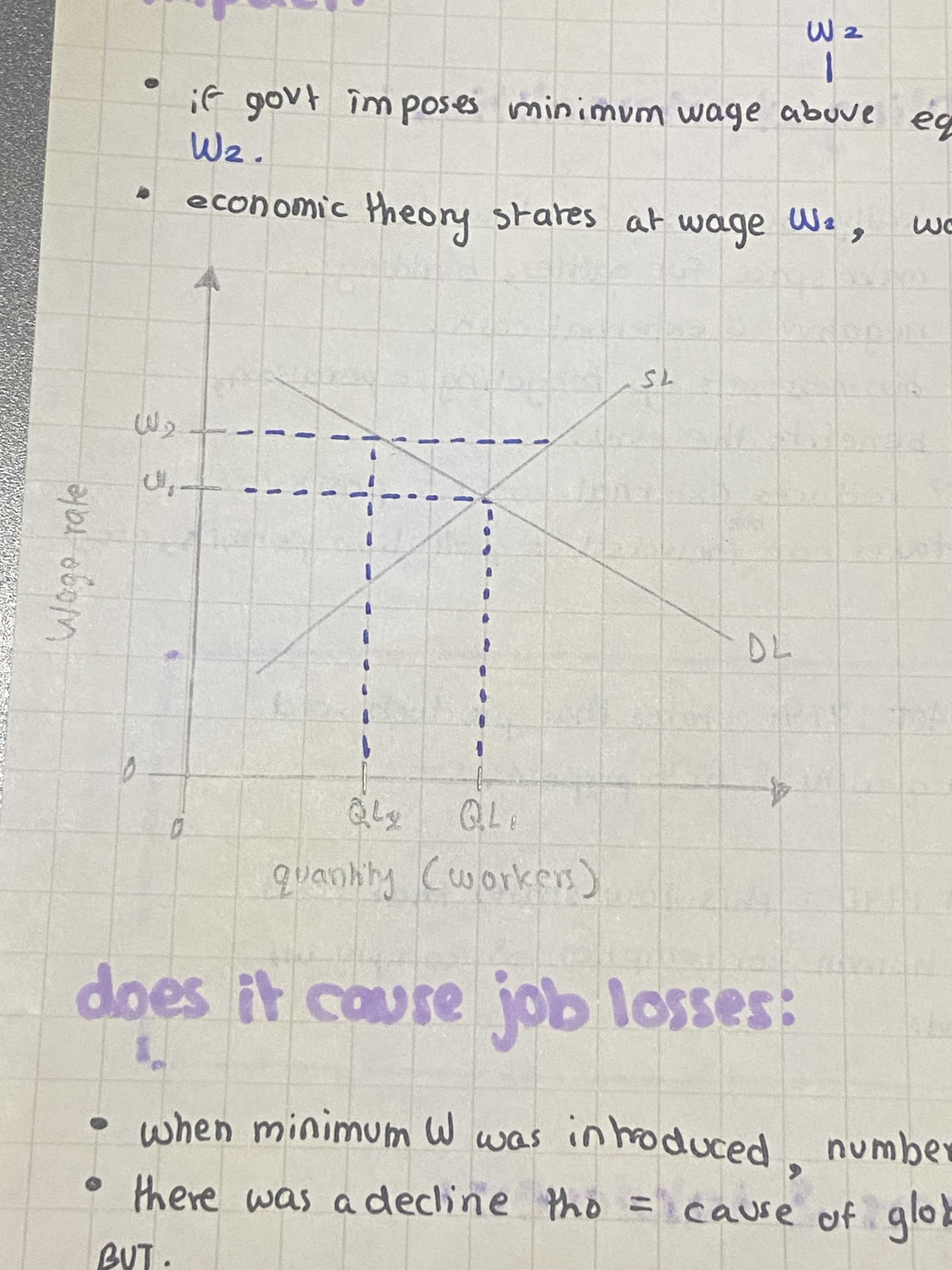
whats the impact? (graph)
→ basically, govt imposes minimum wage ABOVE (W2) equilibrium wage (W1)
→ law states that workers will get atleast W2
economic theory states that at wage W2, workers employed falls from QL1 to QL2 = job loss from minimum wage
how does it cause job losses? (3)
when MW was introduced, number of ppl employed went up
there was a decline tho, cause of global financial crisis
BUT,
- it didn’t reduce employment when MW increased, labor market (low wage) actually performed better
demand for labor increases in US and UK as those economies grow strongly