Pediatrics (Exam 1) - Genetic Disorders
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
marfan syndrome inheritance
autosomal dominant
3 systems involved in marfan syndrome
skeletal, opthalmologic, cardiac
Caused by a pathologic variant in a single gene, FBN1 (a connective tissue protein gene)
marfan syndrome
Marfan's Syndrome (Ophthalmologic):
-Early and severe _______
-Dislocation of the ______
-Hypoplastic _____
-Increased risk of retinal ________
myopia, lens, iris, detachment
Marfan's Syndrome (Cardiac):
-_______ insufficiency
-Progressive ________ of the aortic root
aortic, dilation
Marfan's Syndrome (Skeletal):
•Tall, thin body habitus
•_________ fingers and toes
•________ excavatum or carinatum
•Scoliosis
•Pes _______
•Joint __________
long, pectus, planus, laxity
Ghent criteria used for diagnosis of Marfan’s:
-Positive _______ history + __ other characteristic
OR
-Systemic score ≥ ____ points
family, 1, 7
Marfan syndrome scoring:
•Relates to wrist/thumb _______
•Elbow ________
•Pectus deformity
•Arm ________
•Spinal deformity
•________ characteristics
•Significant _______
•Mitral valve ___________
flexibility, extension, span, facial, myopia, prolapse
neurofibromatosis inheritance pattern
autosomal dominant
Spontaneous mutations account for 30-50% of cases caused by a pathologic mutation in the, NF1 gene (neurofibromin protein, a tumor suppressor gene)
neurofibromatosis
Also known as von Recklinghausen disease
neurofibromatosis
Life expectancy for patients with NF1 may be reduced by _________
10-15yrs
S/Sx:
•Café au lait macules
•Axillary freckling
•Cutaneous neurofibromas
•Lisch nodules
neurofibromatosis
Concerning if there are more than _____ Café au lait macules that are >____ mm in diameter in a prepubertal child
6, 5
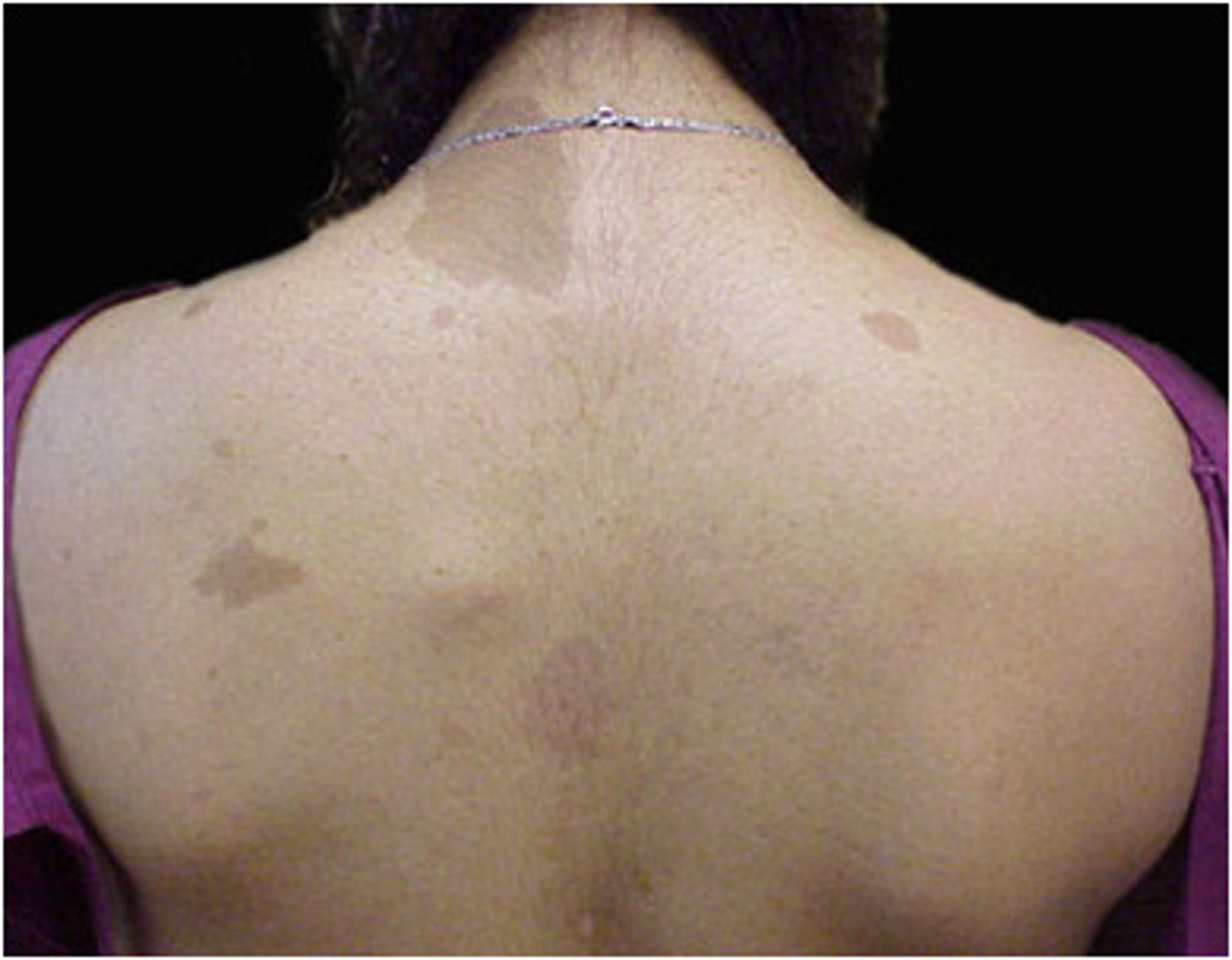
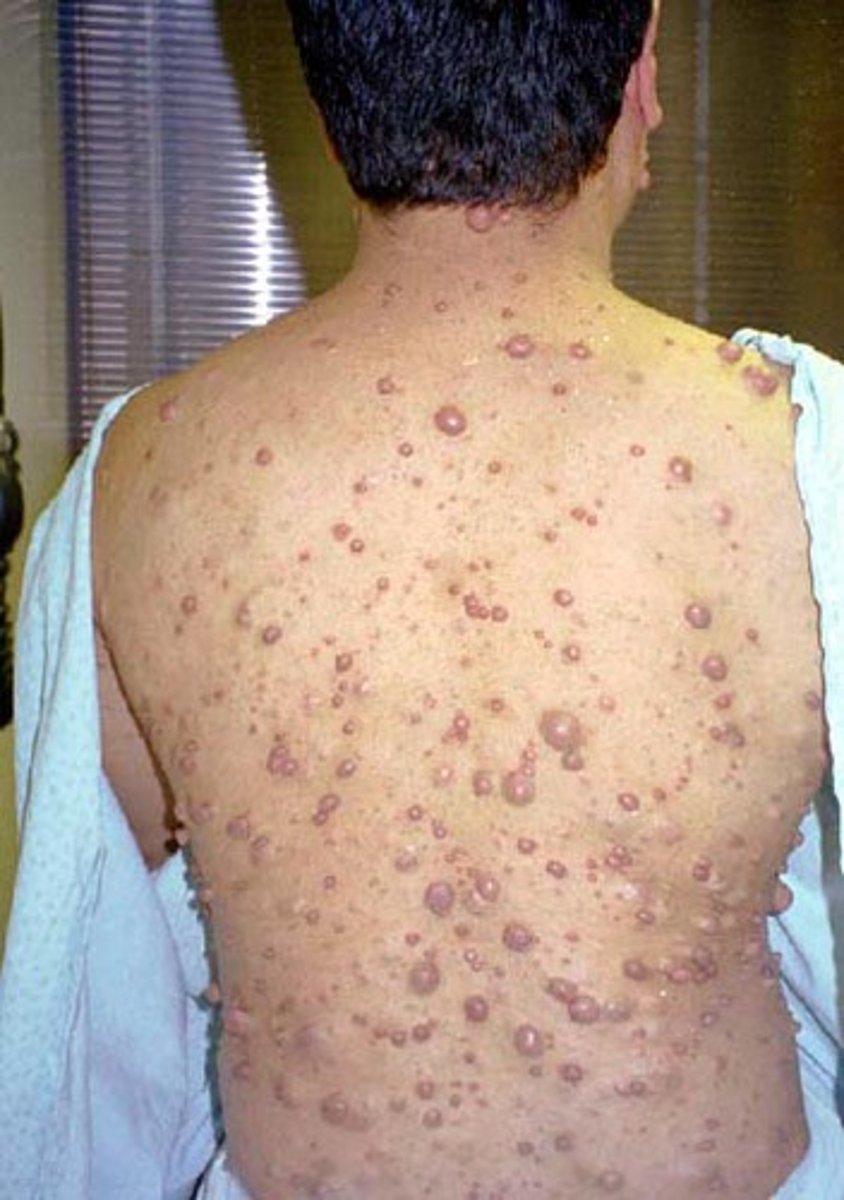
•Small discreet soft lesions within the dermis and epidermis
•Usually asymptomatic
•Mostly cosmetic concerns
cutaneous neurofibromas
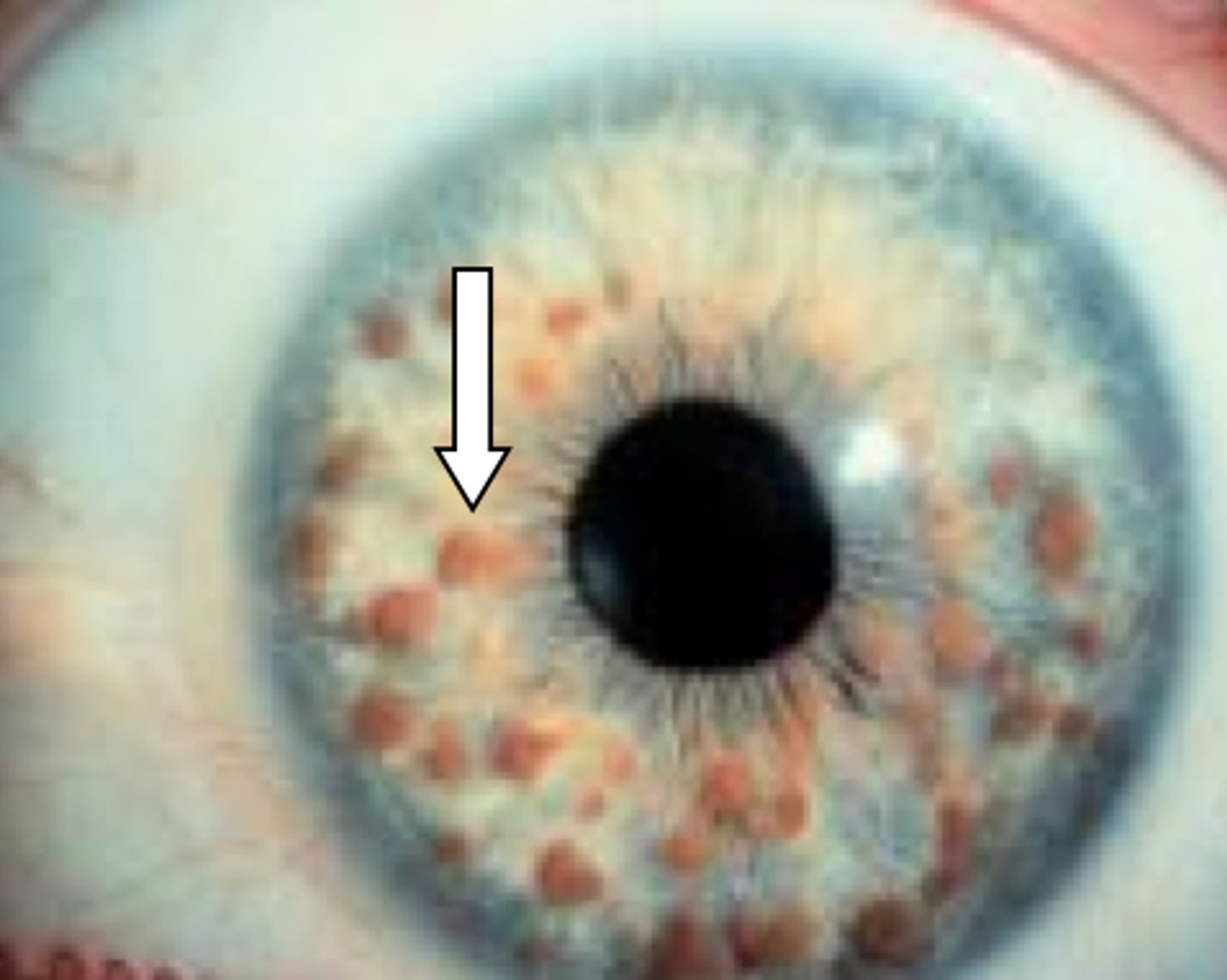
distinctive for neurofibromatosis, iris hamartomas; benign, disappear in adulthood
lisch nodules
MCC of death in neurofibromatosis
malignancy
Complications
Learning disabilities
Scoliosis
Seizures
Cerebral vascular abnormalities
Other tumors, such as optic nerve gliomas
neurofibromatosis
47, XX, + 21 or 47, XY, + 21
trisomy 21 (down syndrome)
Most common chromosomal abnormality in liveborn infants
trisomy 21 (down syndrome)
Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome):
•95% due to _____________
•3% due to Robertsonian ___________ (merger of 2 chromosomes, often 13, 14, 15, 21, 22)
•2% due to ____________
nondisjunction, translocations, mosaicism
Downs syndrome pts are at higher risk for :
•Congenital heart disease (40%), ie: _______
•Hypothyroidism
•Atlantoaxial instability
•Higher rate of ________
•Polycythemia
•Increased risk for ________
•Cataracts
•GI anomalies, ie: __________
•Increased risk of _________ by age 35 y/o
vsd, infection, ALL, hirschsprung, alzheimer's
Recognizable characteristics in the neonatal period
•Facial features
•Hypotonia
•Short broad hands
•Single transverse palmar crease
•Wide gap between the first and second toes
trisomy 21 (down syndrome)
down syndrome appearance:
•__________: Flattened occiput
•__________ midface
•__________ nasal bridge
•________ ear with over-folded helix
•Neck folds due to _________ skin
brachycephaly, hypoplastic, flattened, small, redundant
down syndrome appearance:
•Upslanting palpebral ________
•____________ folds
•Open mouth with _________ tongue
fissures, epicanthal, protruding
47, XX, + 18 or 47, XY, + 18
trisomy 18
Also called Edward's syndrome
trisomy 18
2nd most common autosomal trisomy
trisomy 18
Trisomy 13 and 18:
•Male : Female = _____ who survive
•Only 12% reach the ____ birthday
•_______ for gestational age
1:4, first, small
trisomy 18 is caused by _______________
nondisjunction
S/Sx:
•Hypertonia
•Prominent occiput
•Micrognathia
•Low-set, malformed ears
•Short sternum
•Rocker bottom feet
•Hypoplastic nails
•2nd and 5th digits overlap the 3rd and 4th in clenched fists
trisomy 18
47, XX, + 13 or 47, XY, + 13
trisomy 13
Also called Patau's syndrome
trisomy 13
3rd most common trisomy
trisomy 13
Caused by nondisjunction or Robertsonian translocations (chromosomes 13 and 14)
trisomy 13
S/Sx:
•Midline facial defects (cleft lip/palate)
•Midline central nervous system anomalies
•Sloping forehead
•Small, low-set, malformed ears
•Polydactyly
•Genital deformities
•Congenital heart disease
•aplasia cutis congenita
trisomy 13
Punched out scalp lesion over the occiput pathognomonic for trisomy 13
aplasia cutis congenita
Most common genetic cause of hypogonadism and infertility in men
klinefelter syndrome
47, XXY or 46, XY (if mosaicism)
klinefelter syndrome
Extra X chromosome and poor sperm viability causes infertility with no physical evidence in infancy or childhood
klinefelter syndrome
S/Sx:
Males are phenotypically normal until adolescence
In adolescence
•Genitals remain infantile in size
•Failure to develop facial hair, deep voice, and libido
In adulthood
•Gynecomastia may develop
•Tall, long limbs
•Osteopenia
•Osteoporosis
klinefelter syndrome
-Sex chromosome abnormality
-45, X --> women
-Nondisjunction , post-conceptional
turner syndrome
The only monosomy that survives to birth
turner syndrome
Responsible for up to 10% of first trimester losses of pregnancy
turner syndrome
S/Sx:
•Low set ears
•Triangular face
•Flattened nasal bridge
•Epicanthal folds
•Webbing of the neck
•Shield-like chest; wide internipple distance
•Puffy hands and feet
turner syndrome
S/Sx:
•Congenital heart defects
•horseshoe kidney
•Short stature
•Hypothyroidism
•Infertility
•streak gonads and estrogen deficiency
turner syndrome
Turner syndrome may be diagnosed in:
•Infancy, if _________ is more evident
•Childhood, due to _______ stature
•Adolescence, due to failure to develop _________ sexual characteristics
•Adulthood, due to __________
phenotype, short, secondary, infertility
Paternal uniparental disomy
angelman syndrome
Caused by Chromosome Deletion in maternal chromosome 15 in the 15q11 region
angelman syndrome
•Partner to Prader-Willi Syndrome (opposite deletion)
•Both result in moderate to severe intellectual disability
•Both begin with failure to thrive
angelman syndrome
S/Sx:
•Absence of speech
•Ataxic movements of the arms and legs
•Short stature
•infertile
•Maxillary hypoplasia
•Microbrachycephaly
•Seizure disorder with inappropriate laughter
angelman syndrome
Maternal uniparental disomy
prader willi syndrome
Caused by Chromosome Deletion in paternal chromosome 15 in the 15q11 region
prader willi syndrome
S/Sx:
•Fetal and infantile hypotonia
•Poor initial weight gain, feeding concerns
•Postnatal obesity with insatiable appetite
•Developmental delay
•Almond-shaped eyes
•Hypogonadism
•Small hands and feet
prader willi syndrome
Failed expression of FMRP (the protein product of the FMR1 gene)
fragile X syndrome
Most common cause of inherited intellectual disability
fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome Affects _____ and ___________ development in the early embryonic period.
CNS, testes/ovary
S/Sx:
•Macrocephaly
•Long, wide, protruding ears
•Long face
•Prominent jaw
•Flattened nasal bridge
•Velvety skin
•Hyperextensible joints
•Mitral valve prolapse
•Macro-orchidism
fragile X syndrome
S/Sx:
•Learning disabilities
•Physical features less common
•Mood disorders
•Schizoid personality
•Disturbances of affect, socialization, communication
fragile X syndrome in females
S/Sx:
•Severe-borderline cognitive impairment
•Delayed speech
•Short attention span
•Hyperactivity
fragile X syndrome in males
Deletion in the short arm of chromosome 5
cri du chat
S/Sx:
•Catlike cry due to tracheal hypoplasia
•Low birth weight
•Failure to thrive
•Hypotonia
•Developmental delays
•Microcephaly
•Craniofacial dysmorphism
cri du chat
Deletion in chromosome 7
williams syndrome
S/Sx:
•Supravalvular aortic stenosis
•Growth delay and short stature
•Moderate intellectual disability but strong personal social skills—gregarious personality
•Potential for autism spectrum disorder and unusual musical ability
•Hypercalcemia
williams syndrome
S/Sx:
"Elfin facies"
•Flared eyebrows
•Blue irides
•Full periorbital and oral regions
•Depressed nasal bridge
williams syndrome
Most common cause of preventable intellectual disability
fetal alcohol syndrome
S/Sx:
•In utero and post natal growth restriction
•Microcephaly
•Intellectual disability
•Dysmorphic facial appearance
•Skeletal and cardiac abnormalities
fetal alcohol syndrome
S/Sx:
•Problems with coordination
•Attention deficit
•Hyperactivity
•Impulsivity
•Learning disorders
•Behavior disorders
fetal alcohol syndrome