HLTH 335 Test 1
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What was learned from the slime activity
Recipes = Theories
Can be messy
Many similar theories = Slightly different outcome
Sometimes we use the wrong steps
The recipe did not work
Sometimes behaviour change does not work on the first try
Sometimes the recipe (theory) just is not the right one for the individual you are trying to
change
Run out of an ingredient
Sometimes people are at their capacity for regulating their behaviour. They are on empty and it is not the right time to make a change
What's a theory?
A set of interrelated concepts, definitions, and propositions that presents a systematic view of events or situations by specifying relations among variables in order to explain and predict events or situations.
Why use theory to guide intervention?
Summarizes the cumulative knowledge of how to change behaviour in different populations, behaviours, and contexts
Target meaningful determinants of change
Understand why the intervention worked (or not)
Tests theory
Top 9 List: What makes a quality theory
clarity of constructs - 'Has the case been made for the independence of constructs from each other?'
clarity of relationships between constructs - 'Are the relationships between constructs clearly specified?'
measurability - 'Is an explicit methodology for measuring the constructs given?'
testability - 'Has the theory been specified in such a way that it can be tested?'
being explanatory - 'Has the theory been used to explain/ account for a set of observations? (statistically or logically)
describing causality - 'Has the theory been used to describe mechanisms of change?'
achieving parsimony - 'Has the case for parsimony been made?' (vili)
generalisablity - 'Have generalisations been investigated across': (a) behaviours? (b) populations? (c) contexts?'
Having an evidence base
Social Cognitive Theory
Social Cognitive Theory (SCT) emphasizes self-efficacy beliefs as central to motivation, well-being, and personal achievement.
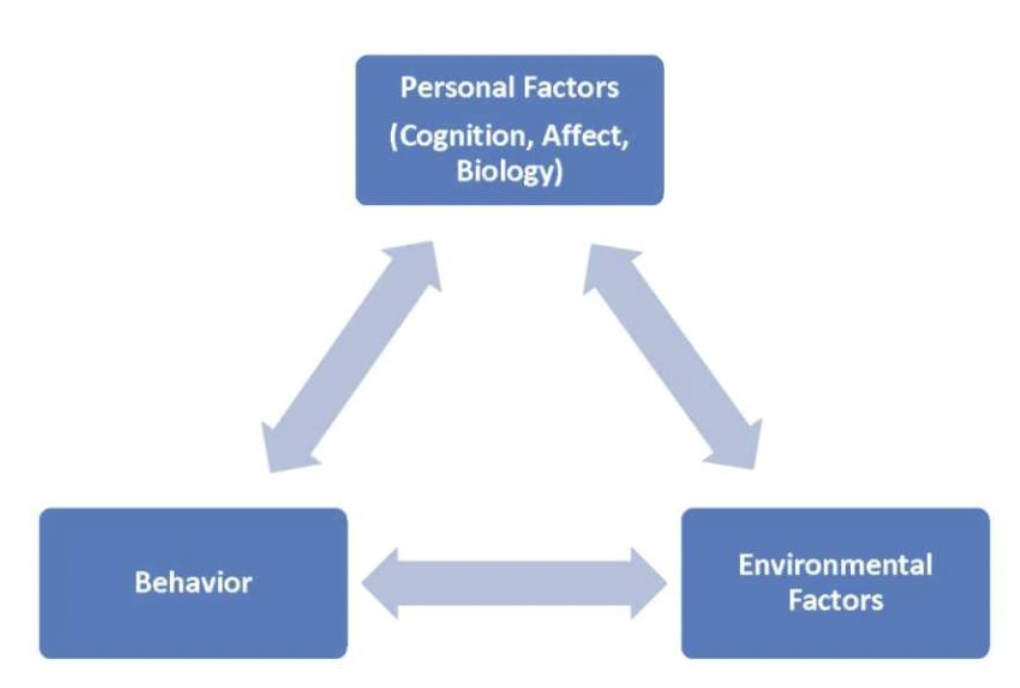
SCT: Reciprocal Determinism
Behaviours are determined by the interaction between personal factors, environmental factors and the behaviour itself
How does Self Efficacy lead to behaviour change?
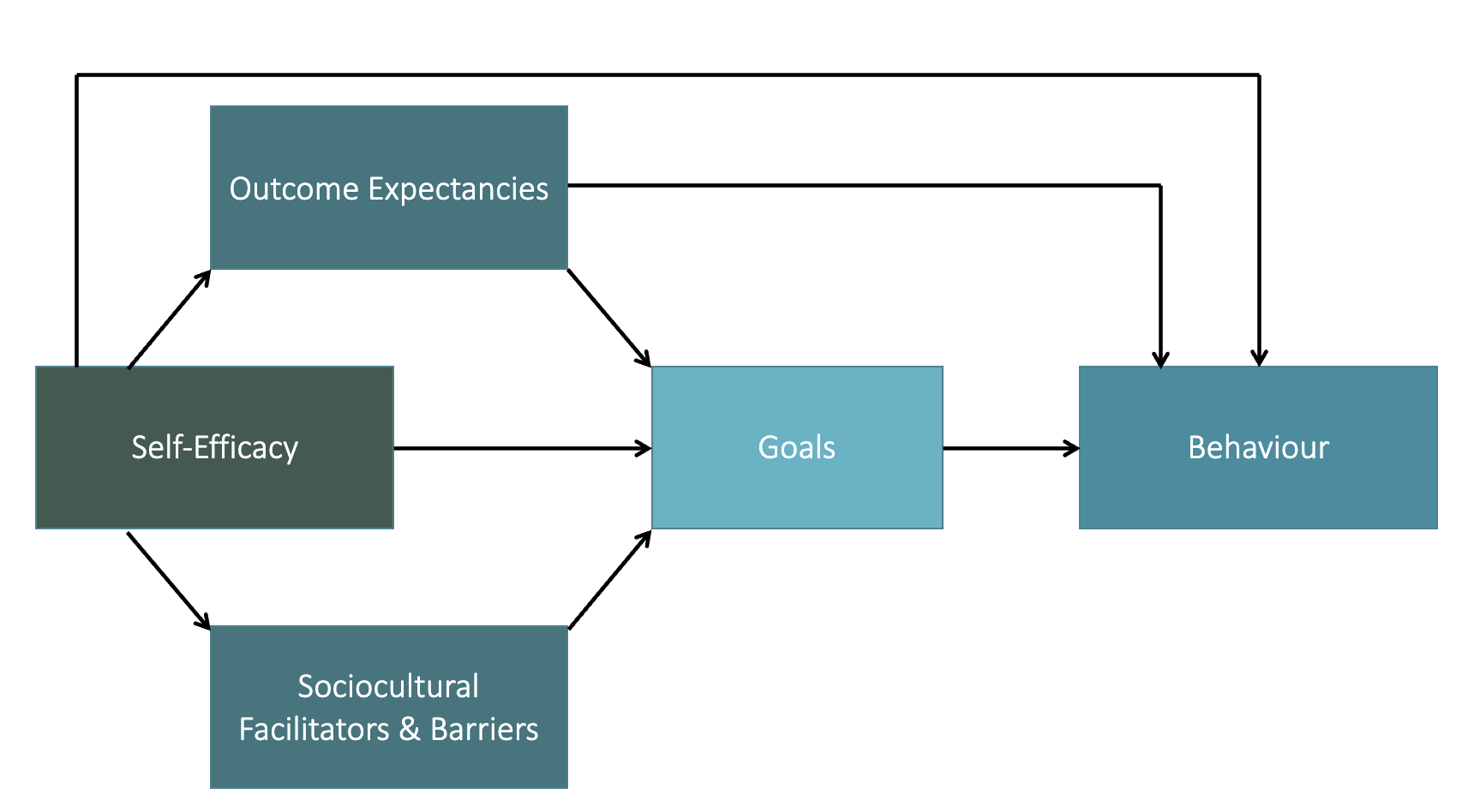
Perceived Self-Efficacy
Beliefs in one's capacity to organise and execute the courses of action required to produce given attainments
Affects the courses of actions people choose to pursue, how much effort is put forth in a given endeavour, ..., and the level of accomplishment they realise
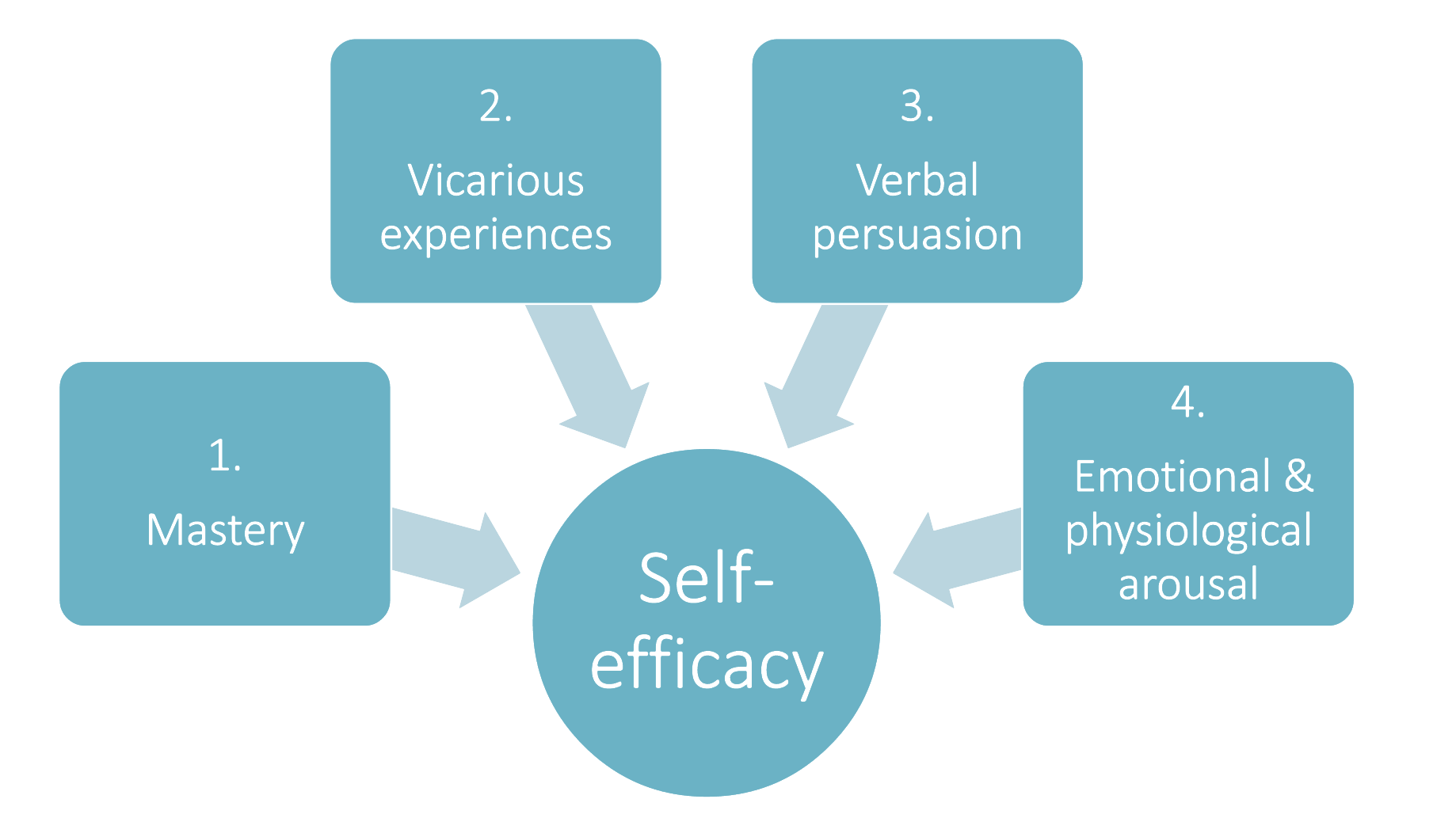
Modifiable Factors of Self Efficacy
Mastery experience
Past performance success and failure for similar behaviours influence self-efficacy.
Vicarious experience
Modelled behaviours are associated with the development and change in self-efficacy.
Social persuasion
Verbal and non-verbal feedback from significant, knowledgeable others.
Physiological and affective states
Physical and emotional cues associated with performance and behaviour.
Task Self Efficacy
Can you do a behaviour?
Self-Regulatory Self Efficacy
Can you self-regulate ("organize") yourself to make the behaviour possible?
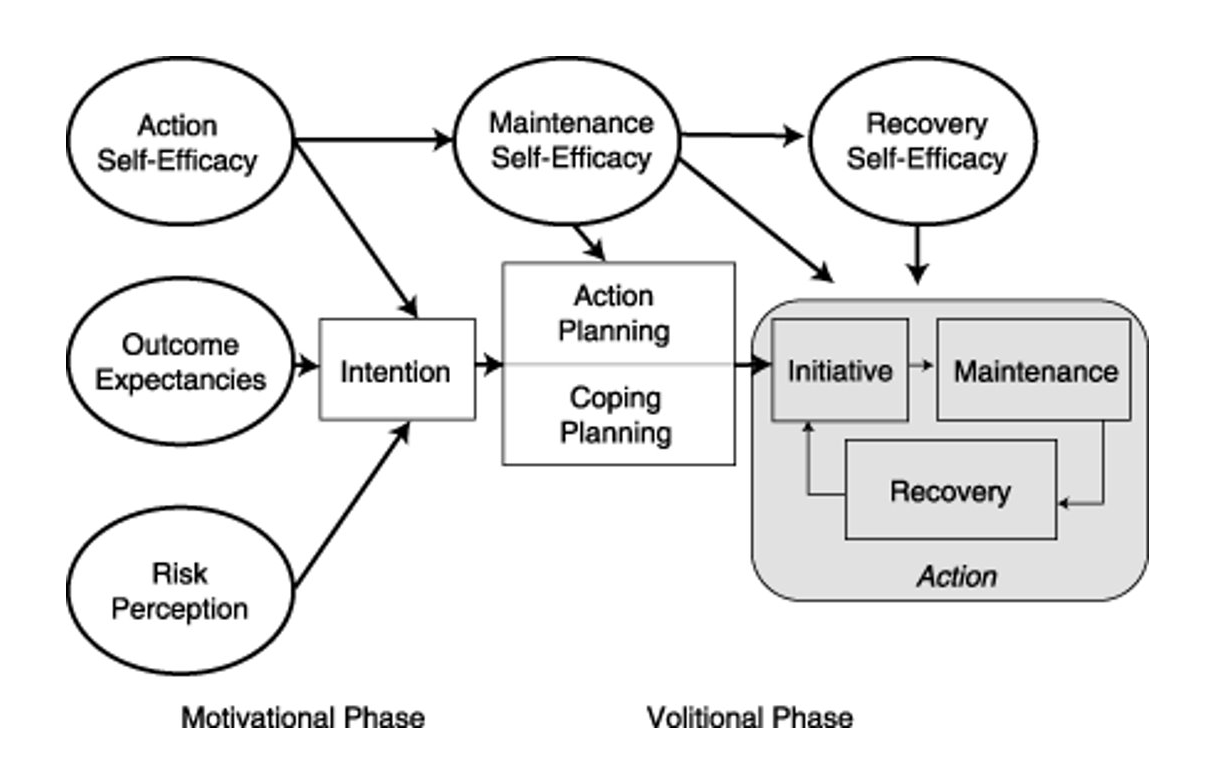
Health Action Process Approach
Intentions = goals, their intent to engage in a behaviour
Intention is influenced by
outcome expectancies (perceived likelihood that engagement will give way to particular results)
action self-efficacy (competence, confidence and ability to do an activity),
risk perception (general perceptions of health/social risk)
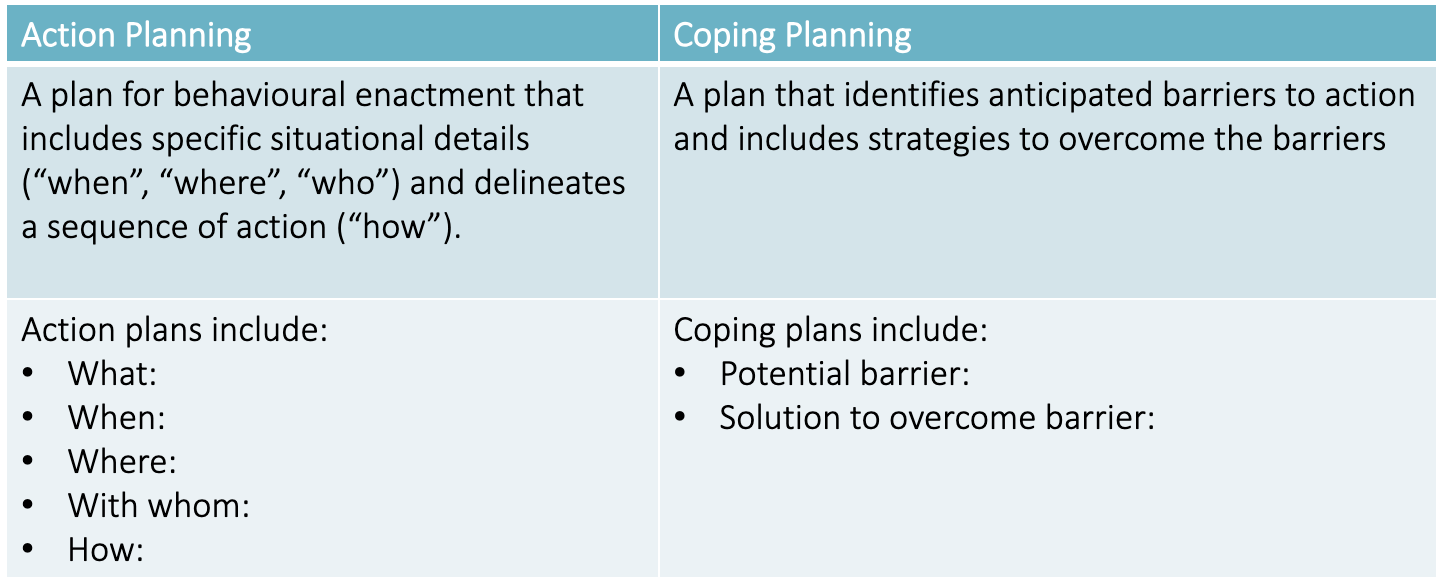
Action Plan vs Coping Plan
Maintenance Self Efficacy
Confidence in ability to do task despite barriers
Self-Determination Theory
Self-determination theory is a global theory of human motivation and development
The focus of the SDT framework is the extent to which behaviours are undertaken freely, as opposed to being controlled by some external agent (e.g., coach, physician) or contingency (e.g., rewards, deadlines).
SDT asserts that people are naturally endowed with innate tendencies for personal growth and development that flourish when social environments provide optimal conditions.
3 Psychological Needs of SDT
Individuals have three fundamental psychological needs, and fulfilling them promotes the internalization of behaviour regulation towards more autonomous motives.
These psychological needs are:
Competence: Feeling effective and capable when facing challenging tasks.
Autonomy: Feeling ownership over behaviour, with actions stemming from a sense of choice and internal control.
Relatedness: Experiencing meaningful connections with others
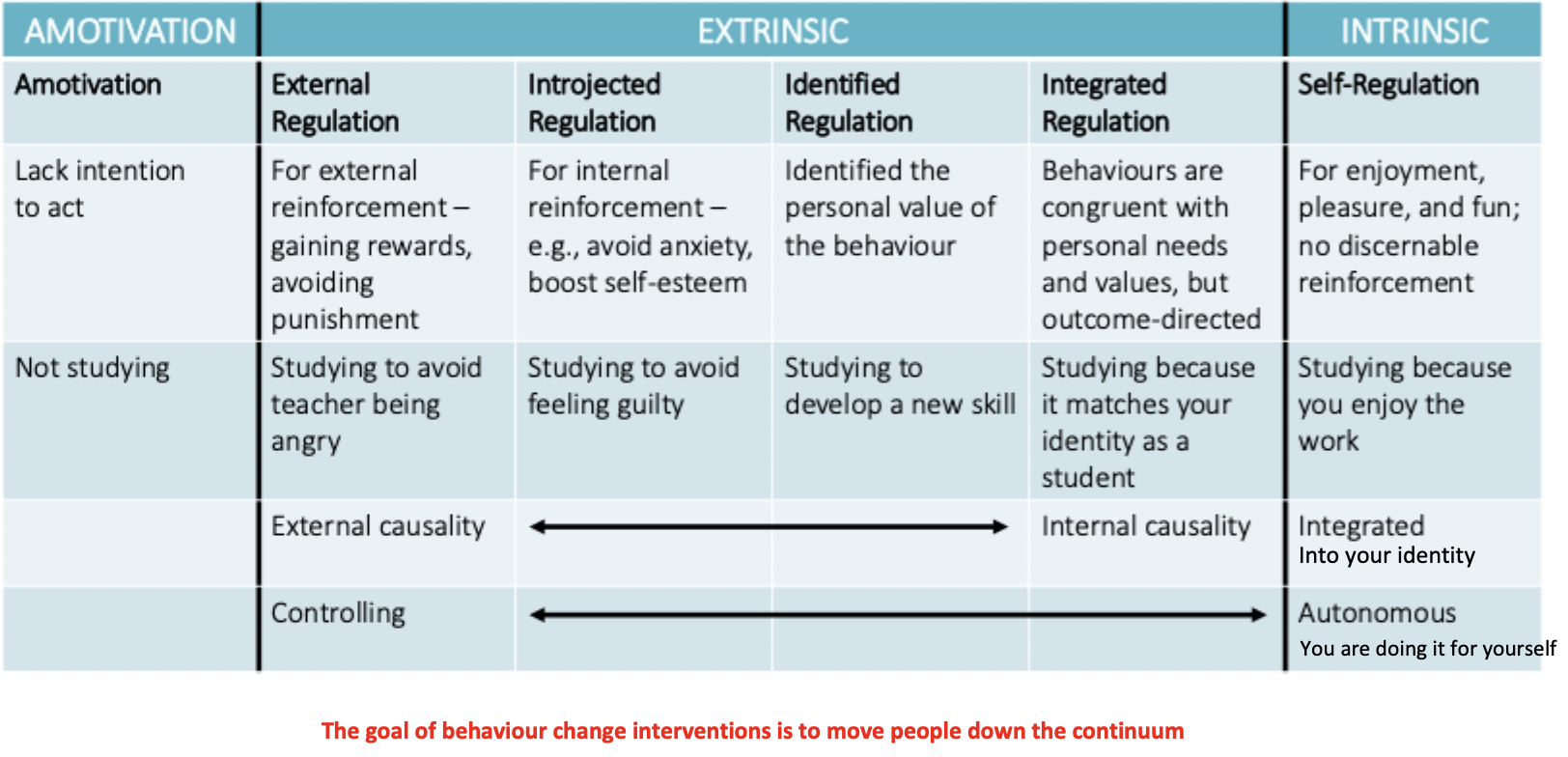
Intrinsic Motivation
Doing of an activity for its inherent satisfactions rather than for some separable consequence. When intrinsically motivated a person is moved to act for the fun or challenge entailed rather than because of external prods, pressures, or rewards.
Extrinsic Motivation
Doing something because it leads to a separable outcome
Four forms of extrinsic motivation
External regulation: Least self-determined, driven by external demands or contingencies.
Introjected regulation: Motivated by avoiding negative emotions or maintaining self-worth.
Identified regulation: Linked to personally valued goals, even if the activity itself may not be enjoyable.
Integrated regulation: Motivated by the activity's alignment with one's identity.
Motivation Continuum