econ macro test
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
macro objectives
1) low unemployment
2) low & stable rate of inflation
3) Economic growth
4) Equity in distribution of income
self correcting gap
inflationary:
Wages rise
Price levels rise
Sras decreases
deflationary:
Wages lower
Price levels lower
Sras increase
cyclical unemployment
Job losses that occur when an economic downturn reduces demand, leading to a decrease in labor demand and, consequently, layoff
cyclical unemployment solutions
demand management policies (monetary / fiscal)
fiscal: better
Increase Government Spending: Invest in infrastructure = create jobs and stimulate economic activity.
Lowering taxes = increases income & investment = boosts spending & demand
Monetary: not ideal
Lowering interest rates = increase borrowing and spending
Effectiveness is limited when interest rates are already low or in a liquidity trap
Structural unemployment
permanent fall in demand for a particular skill and therefore a mismatch between supply and demand for a certain type of labor skills
structural unemployment solutions
Market-based / interventionist
interventionist: education & training programs, subsidies to individuals (reallocation / firms (training)
market-based: move to different areas, personal skill development
Frictional unemployment
temporary and voluntary unemployment that occurs when individuals are between jobs or entering the workforce for the first time, taking time to find a position that matches their skills and preferences
frictional unemployment solutions
Market-based / interventionist
interventionist: job training programs, unemployment benefits
market based: improve flow of information, career counseling
Seasonal unemployment
When people working certain jobs are only needed during certain times of the year
seasonal unemployment solutions
Market-based / interventionist
Interventionist: subsidies for off-season industries, training program
Market based: encourage seasonal contracts, improve flow of information
inflation
persistent increase in APL of the economy
effect of inflation
Reduced Purchasing Power
Increased Cost of Living
Increased Costs
Price Adjustments
Reduced Economic Growth
higher interest rates
inflation solutions
best: contractionary monetary policy (but any other policy will work)
—> central bank raise interest rates = borrowing more expensive = decrease AD component
worst: supply side (because inflation is a short run problem)
deflation
persistent fall in the APL in economy
demand pull inflation
Happens due to an increase in component of AD
cost push inflation
Increased costs of production
Decrease in SRAS
fiscal policy
set of government policies relating to expenditure & taxation that influences aggregate demand in an economy
fiscal policy advantages / disadvantages
advantages
long-term economic growth (when investing in infrastructure)
Ability to target sectors of the economy (because gov can control what to tax)
income redistribution
Dealing with rapid and escalating inflation (because gov hold power to directly influence)
disadvantages
Time Lags (takes time to get used to)
Political Pressure (electoral cycles, ideological differences)
Sustainable debt (when govs run budget deficits to fund expansionary fiscal policy it can become national debt)
for expansionary fiscal only:
Crowding-out Effect (increase gov spending = increase AD = higher prices = fall in investment) —> contractionary side effects
monetary policy
the use of interest rates and the money supply to influence the level of aggregate demand and economic activity in a country
how monetary policy works
expansionary:
lowering interest rates = reduce cost of borrowing money = increase in consumer spending & investment
Increasing money supply = lower interest rates
monetary policy advantages / disadvantages
advantages:
fast to implement
No political intervention
No “crowding out”
Reversibility
disadvantages:
Time lags (takes time to have effect)
Ineffectiveness when interest rates are low
Low consumer and business confidence = wont effect consumer spending and investment
market based supply side policies
policies that aim to increase LRAS with minimal gov intervention to foster economic efficiency
DEREGULATION: reducing regulations on operations which may increase their costs of production
PRIVATIZATION: sale of government-owned firms to the private sector (privatized firms operate more efficiently)
POLICIES THAT INCREASE COMPETITION: Policies to increase competition (competition encourages greater efficiency (such as enforcing strict anti-monopoly laws)
TRADE LIBERALIZATION: increase competition to encourage more free trade and lead firms to be more efficient
supply side policies
policies that are designed to increase the LRAS in the economy by increasing the quantity / quality of FOP
market based supply side policy advantages / disadvantages
advantages:
Reduces government burden
Improved efficiency & productivity (encouraged by increase competition)
Promotes individual and business incentives
disadvantages
Reduction of income taxes may have opposite effects = not incentivize more work
reduce income tax = more income = people choose to work less
Reduction in taxes = increase income inequality
Income tax: benefits higher wage earners more
Corporate tax: benefit wealthy shareholders
Deregulation may negatively affect the environment, worker safety, health, and working conditions
Privatization may not have the desired effects (firms dont succeed)
Time lags
interventionist supply side policies
policies that aim to increase LRAS with active gov intervention to foster economic growth
Investment in human capital: government provided training programs
Research and development: offering tax incentives and guaranteeing intellectual property rights, such as patents and copyrights
Provision and maintenance of infrastructure
Direct support for businesses/industrial policies
interventionist supply side policy advantages / disadvantages
advantages:
Target specific areas
Positive externalities
improve standard of living
disadvantages
gov / national debt
Time lags
Policies depend on ideology of gov
Controversies from funding specific programs
progressive tax
income increases, increasing tax rate
regressive tax
income increases, decreasing tax rate
proportional tax
income increases, constant tax rate
Direct taxes
taxes paid directly to the government
Indirect taxes
taxes on spending on goods and services
policies to reduce inequality
progressive tax
interventionist: Investing in human capital, increase min wage, targeted gov spending
progressive taxation for reducing inequality advantages / disadvantages
advantages:
More equitable (fair) for lower income individuals to pay a lower tax rate
(since they need the money more than higher income individuals)
Provides the government with funds to finance its expenditures
improves inequality directly by closing the gap
reduced burden on low income
Disadvantages:
less incentive to work harder (because higher income = more taxes)
discourage businesses from operating in a specific place and cause them to move to a place with lower tax rates
less incentive to invest = decrease ecnomic growth
gdp
the total value of all final goods and services produced within a country over a year, regardless of who owns the factors of production
gni (gross national income)
total income received by the nationals of a country, equal to the value of all final goods and services produced by the country’s nationals regardless where they’re located.
purchasing power parity
method of currency conversion that accounts for differences in price levels between countries
unemployment
People of working age who are without work, available for work, and actively seeking employment
AD
total demand for all final g&s within an economy over a period of time at different APL
AS
total output of g&s produced in an economy over a period of time at different APL
sras
total output of g&s produced in an economy at different APL in the short run, when resource prices are fixed.
lras
total output of g&s produced n an economy at different APL when all resource prices, are flexible, and the economy is producing at full employment of resources.
labor force
People who are eligible to work and actively looking for work
inflationary / deflationary gap
inflationary: Equilibrium is at a level of output greater than the full employment level of output due to excess AD
deflationary: Equilibrium is at a level of output lower than the full employment level of output due to shortage of AD
stagflation
period of falling output and rising prices
hidden unemployment
People who are not considered unemployed but are not fully employed
disinflation
decreasing rate of inflation
cpi
a measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services
economic growth
increase in real GDP over time
demand management policies
policies used by governments and central banks to influence the level of AD in an economy to achieve macroeconomic objectives
interest rate
price of borrowing money
base rate
interest rate set by the central bank
equity
fairness
equality
same amount of something
income
money received by owners of FOP
wealth
money, assets, or things of value that people own
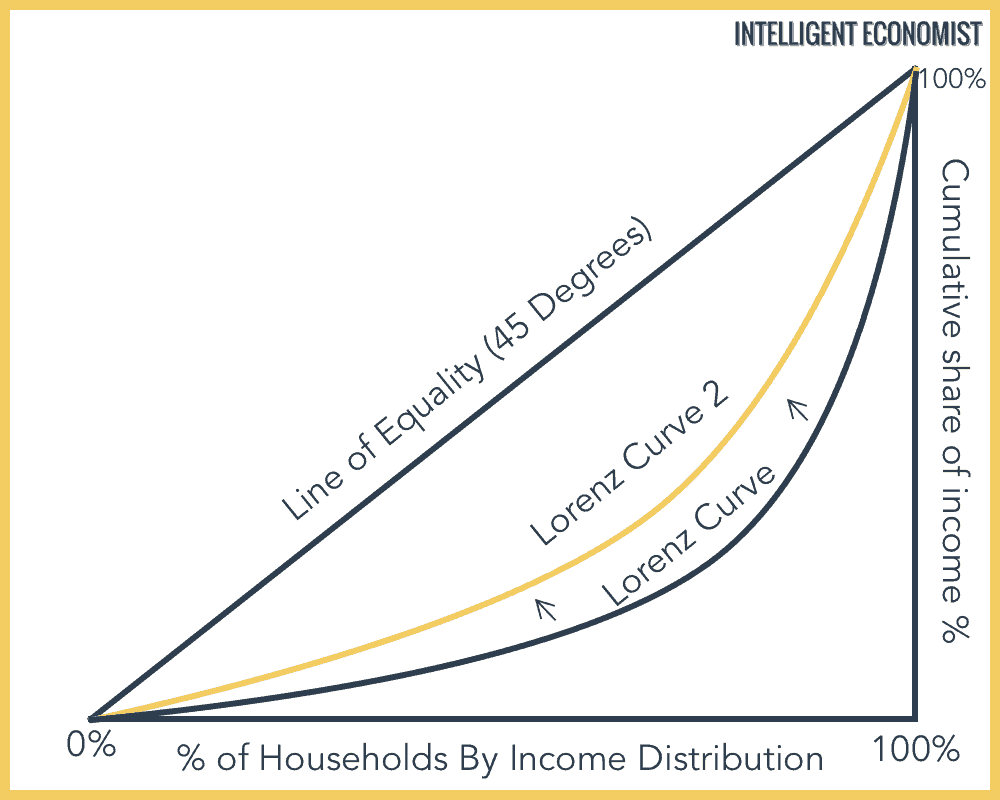
types of inequalities
ECONOMIC INEQUALITY: Degree people differ in their ability to satisfy their economic needs
INCOME INEQUALITY: differences in how income is distributed in a population
WEALTH INEQUALITY: differences in the amount of wealth people own
gini coefficient
numerical measure of income / wealth inequality within a population
poverty
inability to satisfy minimum consumption needs
absolute poverty
when a person/household does not have enough income to meet basic human needs
relative poverty
an individual or household's income is lower than the median income of their population
Multidimensional poverty index (MPI)
Measures poverty in three dimensions: (Health, Education, Living standards)
Values are from 0 to 1
Countries are poor = people are deprived in at least ⅓ of the indicators
see what areas contribute to poverty
transfer payments
payment made by gov to individuals that redistribute income away from certain groups & towards other groups
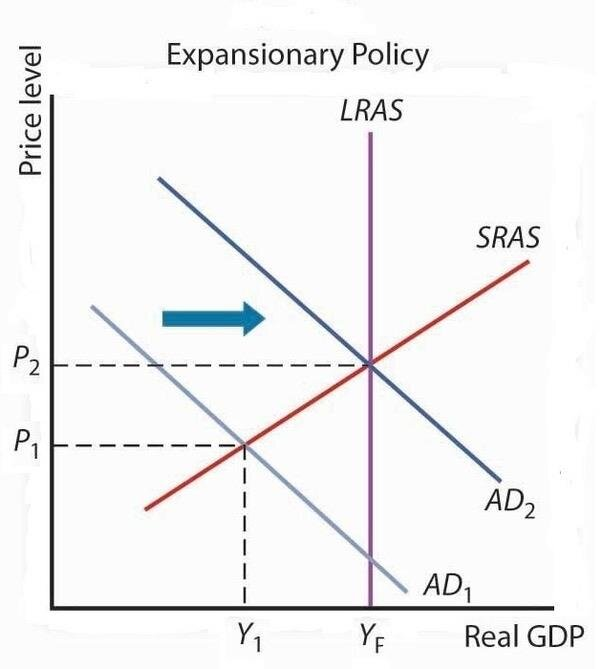
keynesian diagram
Active gov intervention is necessary to stimulate AD and correct economic downturns
new classical diagram
Limited gov intervention needed because markets self-correct
business cycle
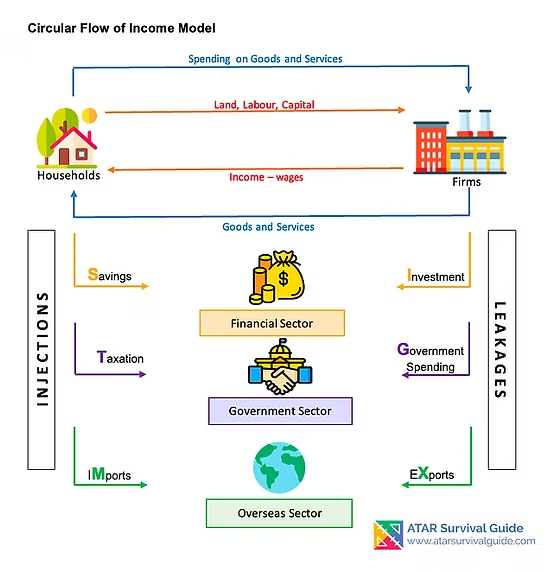
circular flow of income model
labor market
used to describe unemployment content
sticky wages
when nominal wages are slow to adjust in response to changes in economic conditions
sras diagram
lras diagram
can be new classical or keynesian
lorenz curve