lecture 11 deep time how old is old
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Niagara Gorge
The limestones, shales, sandstones and dolostone are now exposed as distinct layers in the falls and along the in the _______ are interpreted as marine sediments produced in a shallow water platform region with variable water depth
uniformitarianism (James Hutton 1726-1797)
The principle of ________ states that physical processes we observe operating today also operated in the past, at roughly comparable rates, so the present is the key to the past
Geochronology
Cretaceous (145-66 MYA) –Sections of the supercontinent Pnagea drifted apart; widespread chalk deposition
Jurassic (201-145 MYA) - Warm, wet climate that gave rise to lush vegetation and abundant life; Age of the dinosaurs.
Triassic (252-201MYA– The start of start of the diversification of life outside of the oceans
Permian (298.9-352 MYA)– The great mass extinction, Earth's crustal plates formed a single, massive continent called Pangaea; reptiles replaced amphibians; and marine organisms lived in the large ocean, Panthalassa.
Pennsylvanian (323.2 million to 298.9 MYA) –Advance and retreat of shallow seas; swamps formation near the equator
Mississippian (359-323 MYA) –Earth in a greenhouse climate state with warm temperatures
Devonian (419-359 MYA)-Diversity and abundance of fish species 85% global coverage of ocean; warm climate; glaciation and lowering of sea level resulted in amass extinction at the end of the period
Silurian (448.3-419 MYA)–flooded continents with shallow seas, emergence of vascular plants and mound-type coral reefs
Ordovician (485–444 MYA) –Evolution of early vertebrates; oceans dominated by molluscs and arthropods
Geological maps
________ indicate the rock unit or recent deposit forms the ground at a given place
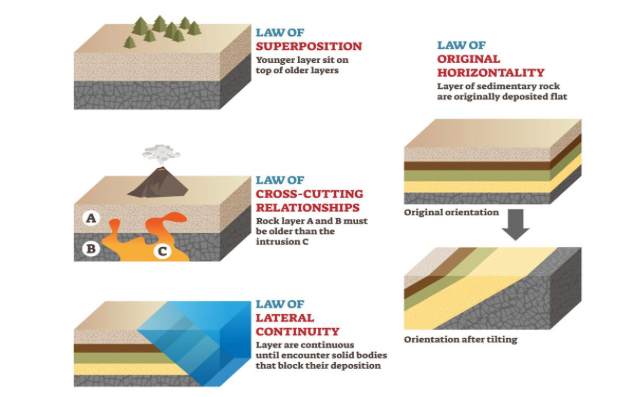
Stenos Laws
In 1669, Niels Stensen (1638-1686) also Latinized as Nicolaus Stenoformulated several basic rules that helped him make sense of the rocks of Tuscany and the various objects contained within them
Areas that were once deep oceans hundreds of millions of years ago are now mountainous or desert regions.
Principles of relative dating
Original Horizontality
•Lateral Continuity
•Superposition
•Cross Cutting Relationships
•Inclusions
•Faunal Succession
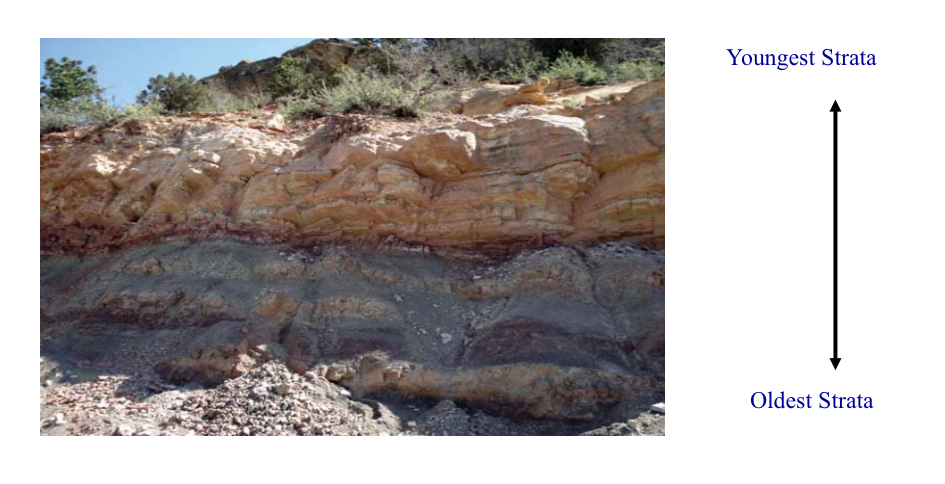
Principle of Superposition
By convention, the oldest layers are deposited from oldest at the bottom to youngest at top.

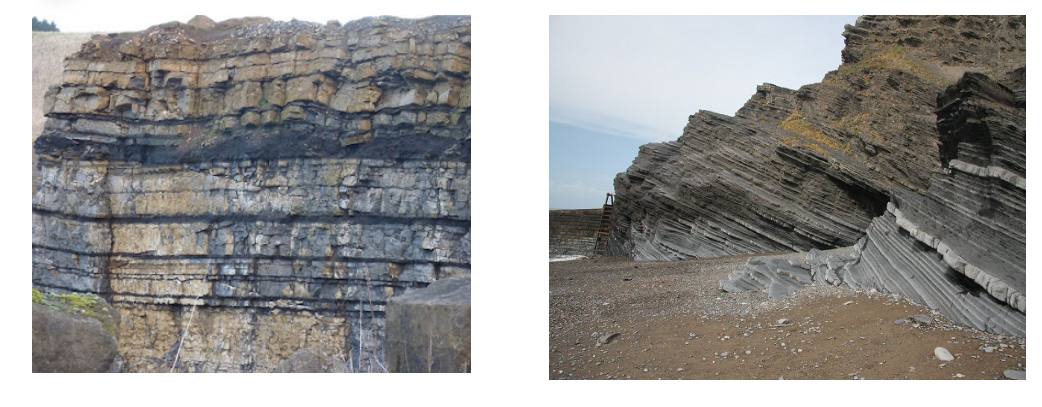
Principle of Original Horizontality
Initially, sedimentary rocks are deposited horizontally before they undergo geologic deformation or tilting

Principle of lateral continuity
Strata extend laterally until they thin pr pinch out at the sides of a basin. Any breaks in the bed may be due to erosion
Principle of inclusions
rock containing an inclusion (fragment of another rock) must be younger than the inclusion. For example, a conglomerate containing pebbles of basalt is younger than the basalt, and a sill containing fragments of sandstone must be younger than the sandstone.
Principle of Faunal Succession
Fossils in sedimentary rocks can also be correlated . These layers can also be given an absolute date by bracketing them between igneous rocks dated radiometrically– see blue stars.