Microscope Anatomy & Endocrine System: Lab Review for Biology
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
What is the function of the ocular lenses in a microscope?
They magnify the image by a factor of 10 and are the lenses you look through.

What is the total magnification when using the scanning lens?
40X (4X magnification of the lens multiplied by 10X of the ocular lens).
Which objective lens should be used with the coarse adjustment knob?
The scanning lens.
What is the total magnification of the low power lens?
100X (10X magnification of the lens multiplied by 10X of the ocular lens).
What is the total magnification of the high power lens?
400X (40X magnification of the lens multiplied by 10X of the ocular lens).
What is the purpose of the nosepiece on a microscope?
It holds and allows rotation of the objective lenses.
What should you do before placing a slide on the stage?
Lower the stage to its lowest position using the coarse adjust knob.
How should you carry a microscope?
By holding both the arm and the base.
What is the role of the stage clips on a microscope?
They secure the slide in place on the stage.
What is the function of the Abbe condenser?
It intensifies the light coming from the light source to improve contrast.
What adjustment knob is used for fine focusing?
The fine adjust knob.
What happens to the light intensity as you increase magnification?
The light may appear to dim as magnification increases.
What is the purpose of the coarse adjustment knob?
It moves the objective lenses up and down to focus, but should only be used with the scanning lens.
What should you do after focusing with the coarse adjust knob?
Use the fine adjust knob to perfect the focus.
What is the first step in focusing a microscope?
Use the coarse adjust knob with the scanning lens to get a rough focus.
What is the role of the arm in a microscope?
It connects the body of the microscope to the base and is used for transport.
What is the function of the stage adjusting knobs?
They move the stage forwards/backwards and left/right.
What should you do to line up the specimen on the slide before viewing?
Position the slide so the specimen is in the pool of light.
What is the difference between the coarse adjustment knob and the fine adjustment knob?
The coarse adjustment knob is larger and used for initial focusing, while the fine adjustment knob is smaller and used for precise focusing.
What type of lens is not used in the lab according to the notes?
The oil immersion lens.
What should be done after switching from scanning power to low power?
Move the nosepiece and click the low power lens into position.
What is the base of the microscope?
The bottom part that supports the microscope.
What is the procedure for switching from scanning power to low power on a microscope?
Move the nosepiece to click the low power lens into position and use the fine adjust to bring the image back to clarity.
What does it mean that microscopes are parfocal?
It means that when you focus at one magnification, the image stays mostly in focus as you move to the next level.
What should you do to maintain the structure in the center of your field of view when switching magnifications?
Always center the structures you are looking at before switching from scanning to low power.
What indicates that you are focused at the level of the slide when adjusting the stage?
If the image in your field of view moves when you move the stage, you are focused at the level of the slide.
How can you tell if you are focused on oil or debris on the objective lens?
If you can move the stage but the field of view stays the same, you are focused on oil/debris.
What is the primary function of the endocrine system?
To release hormones into the bloodstream.
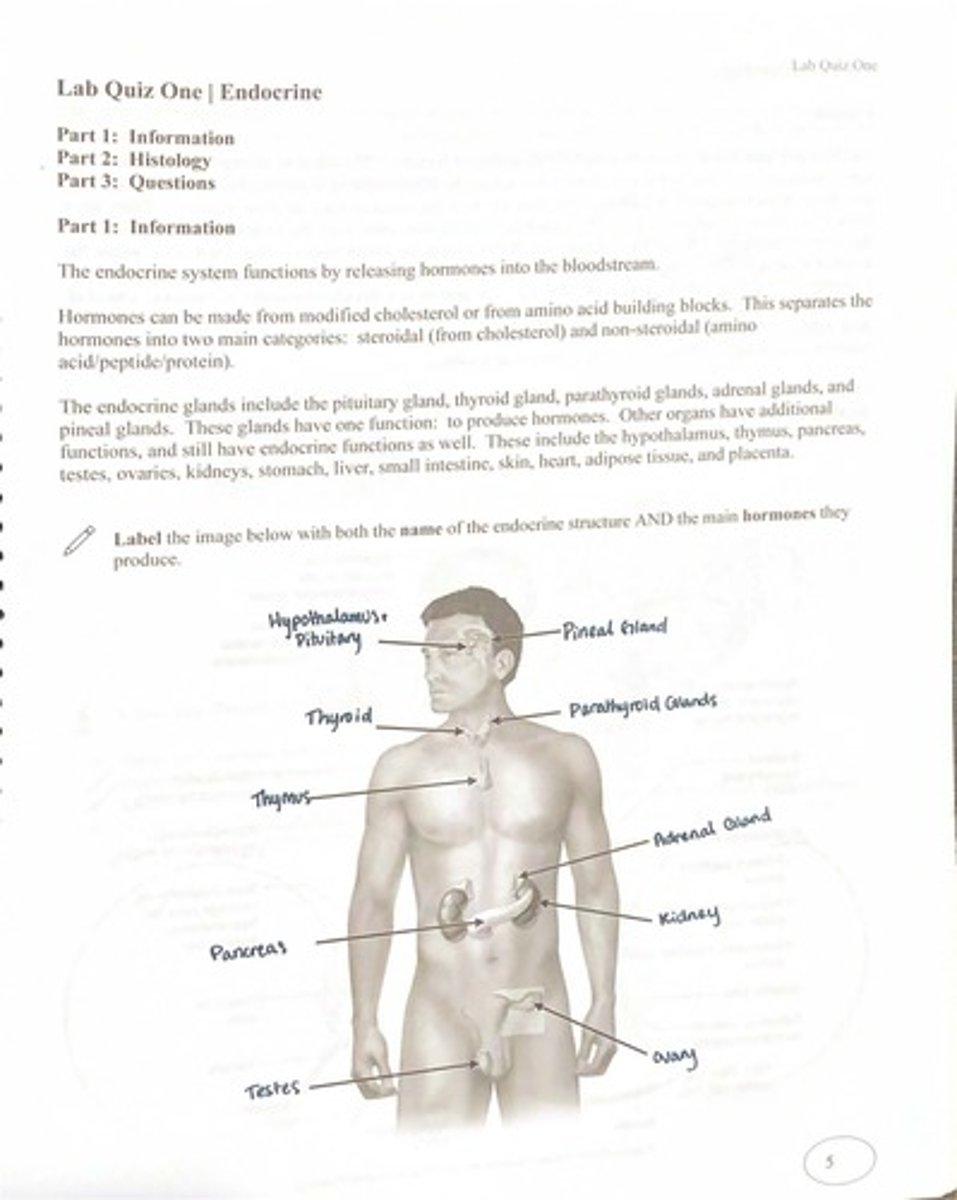
What are the two main categories of hormones based on their composition?
Steroidal hormones (from modified cholesterol) and non-steroidal hormones (from amino acid/peptide/protein).
Name three endocrine glands mentioned in the notes.
Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands.
Which organs have additional functions but also have endocrine functions?
Hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas, testes, ovaries, kidneys, stomach, liver, small intestine, skin, heart, adipose tissue, and placenta.
What is the hypophyseal portal?
A direct circulatory pathway between the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary.
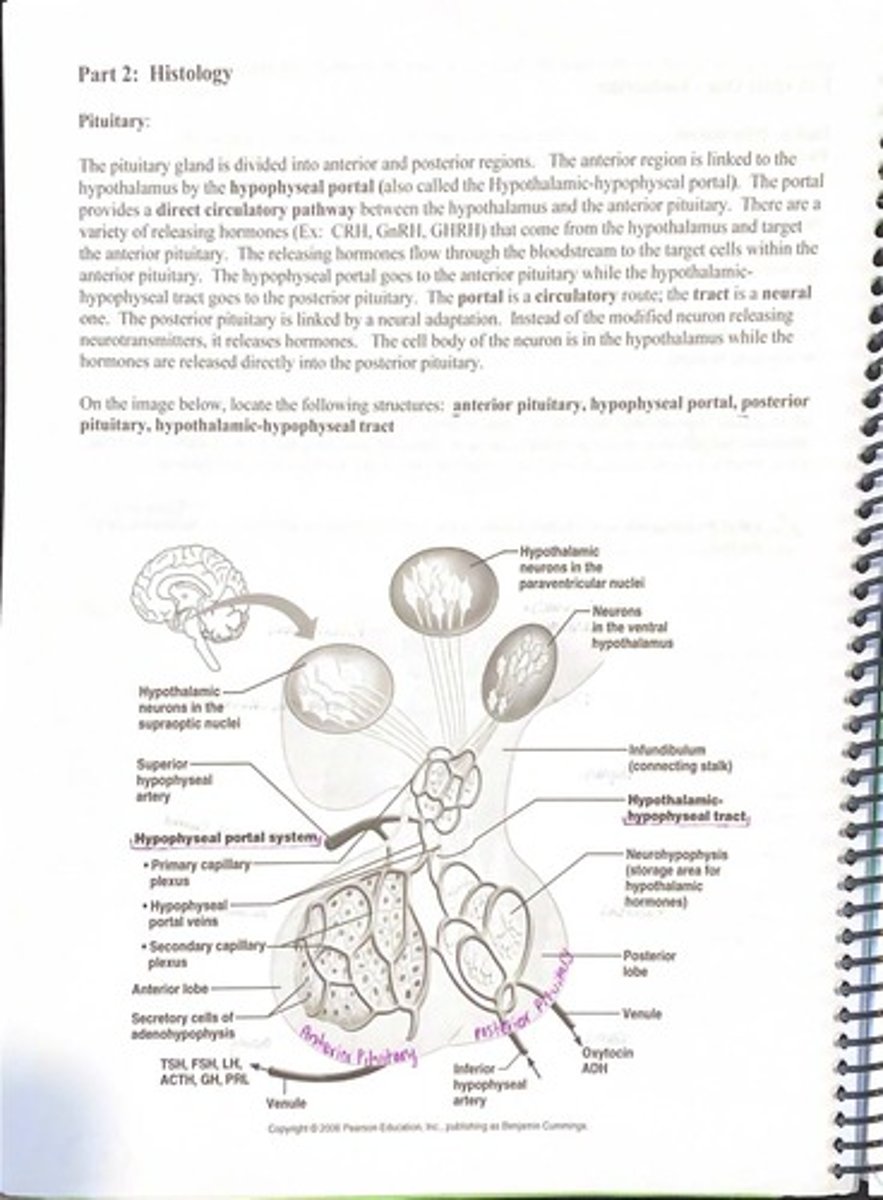
What type of hormones flow through the hypophyseal portal to the anterior pituitary?
Releasing hormones such as CRH, GnRH, and GHRH.
How is the posterior pituitary linked to the hypothalamus?
By a neural adaptation where hormones are released directly into the posterior pituitary.
What hormones are stored in the posterior pituitary?
Oxytocin and ADH (antidiuretic hormone).
What is the difference between the hypophyseal portal and the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract?
The portal is a circulatory route to the anterior pituitary, while the tract is a neural route to the posterior pituitary.
What are the main hormones produced by the anterior pituitary?
TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, GH, and PRL.
What is the role of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract?
To connect the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary via neural pathways.
What is the anterior pituitary also known as?
Adenohypophysis.
What is the function of the anterior pituitary?
To secrete hormones that regulate various physiological processes.
What is the primary capillary-plexus in the hypophyseal portal system?
It is the network of capillaries that receives releasing hormones from the hypothalamus.
What is the secondary capillary-plexus in the hypophyseal portal system?
It is the network of capillaries in the anterior pituitary where hormones are delivered to target cells.
What is the infundibulum?
The connecting stalk between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland.
What is the neurohypophysis?
The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, which serves as a storage area for hypothalamic hormones.
What is the function of the hypothalamic neurons in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei?
They are involved in the production of hormones released into the posterior pituitary.
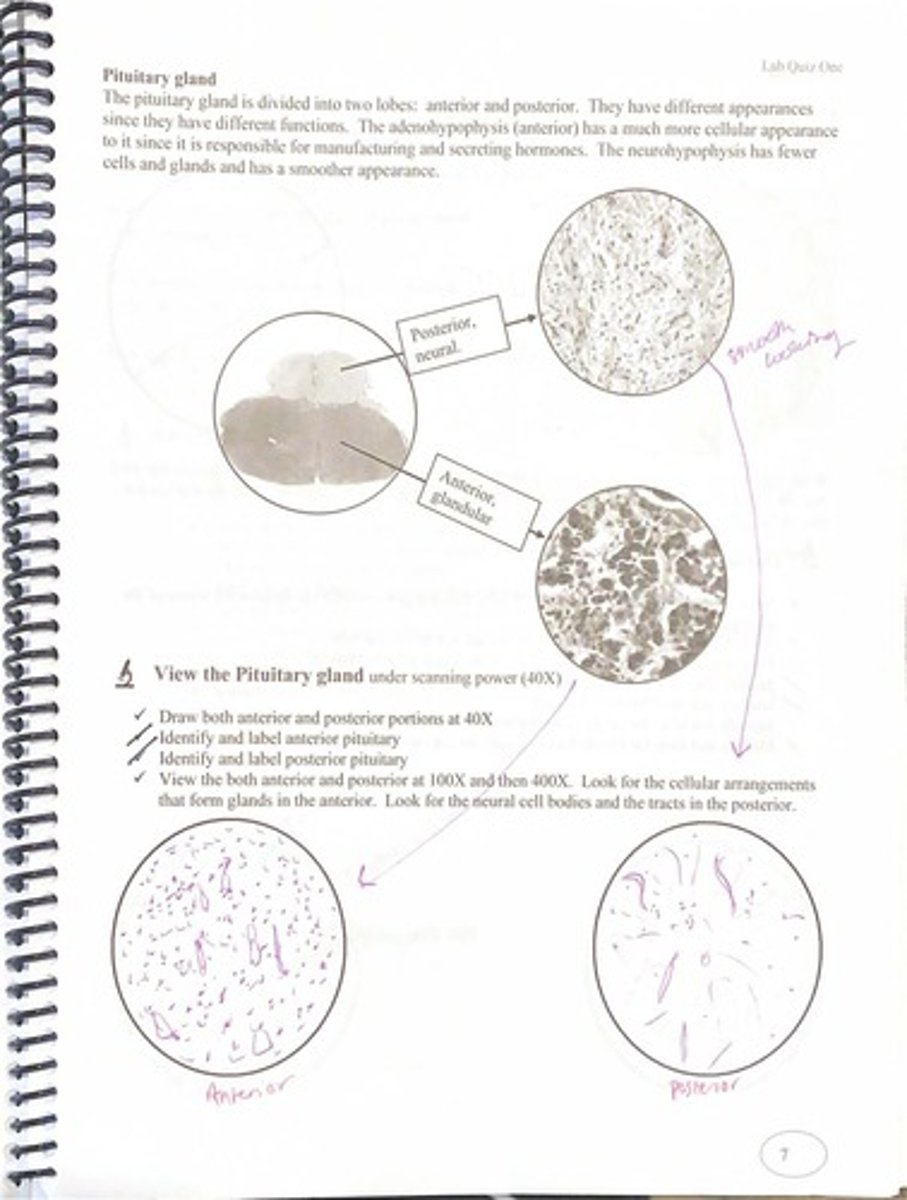
What are the two lobes of the pituitary gland?
Anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis).
What is the primary function of the anterior pituitary gland?
Manufacturing and secreting hormones.
How does the appearance of the anterior pituitary differ from the posterior pituitary?
The anterior pituitary has a more cellular appearance, while the posterior pituitary is smoother with fewer cells.
What structures should be identified in the pituitary gland under 40X magnification?
Anterior pituitary and posterior pituitary.
What is the primary function of the thyroid gland?
To produce thyroid hormones through follicles and extrafollicular cells.
What are the components of a thyroid follicle?
Follicle cavity, follicular cells, and colloid.
What types of cells are found in the parathyroid glands?
Chief cells and oxyphil cells.
What hormone is produced by the chief cells of the parathyroid gland?
Parathyroid hormone.
Where are the parathyroid glands located?
On the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
What distinguishes the appearance of parathyroid chief cells from oxyphil cells?
Chief cells are smaller and darker, while oxyphil cells are larger and lighter staining.
What are the two regions of the adrenal glands?
Cortex (outer region) and medulla (inner region).
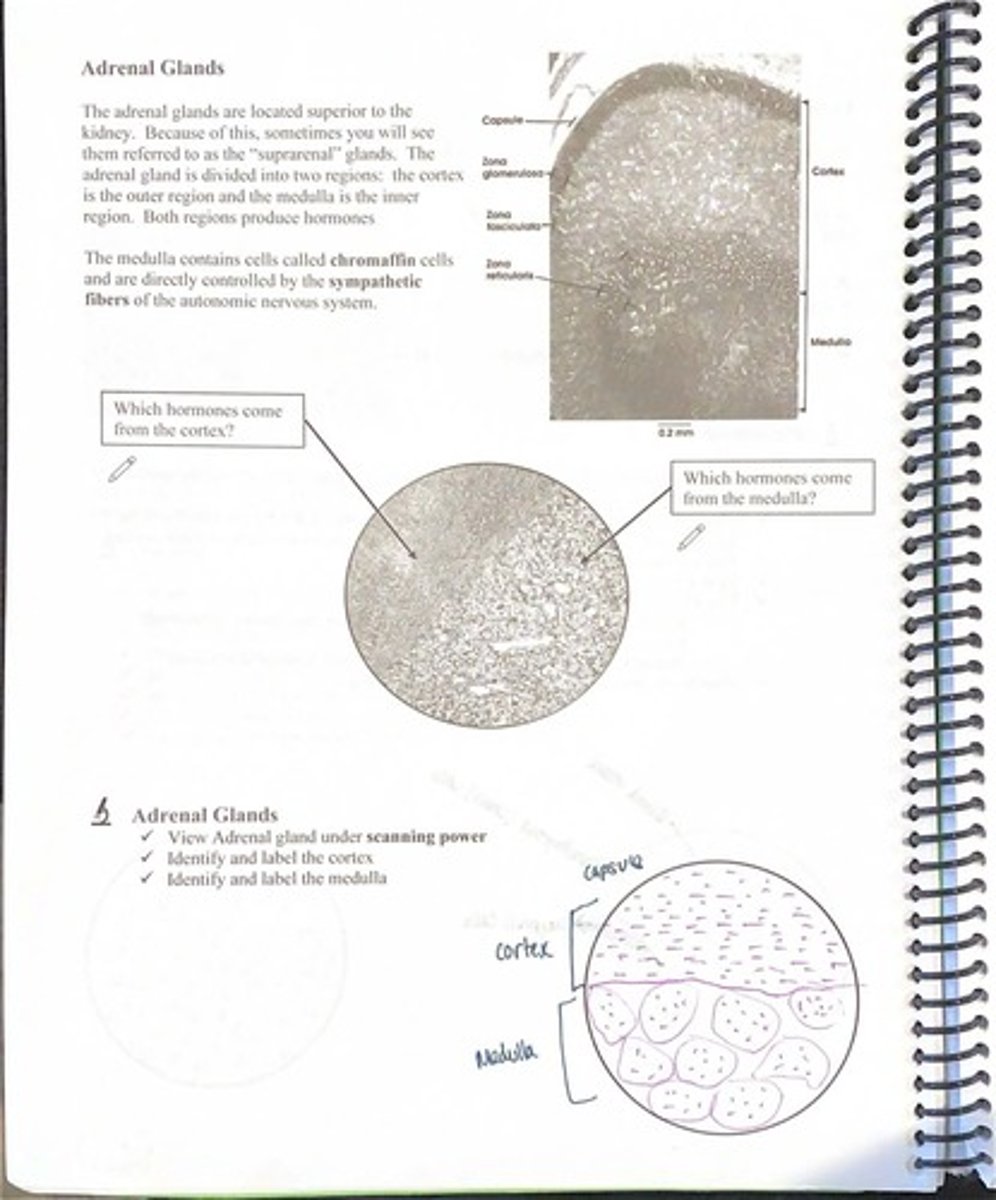
What type of cells are found in the adrenal medulla?
Chromaffin cells.
How are the adrenal medulla cells controlled?
By sympathetic fibers of the autonomic nervous system.
What happens to the thymus as we age?
Its function decreases and it eventually changes to fatty or fibrous tissue.
What is the function of the thymus in the lymphatic system?
It is where lymphocytes learn to function.
What hormone does the thymus produce?
Thymosin.
What should be observed in the thyroid gland under 40X and 100X magnification?
The layout of the structures, including follicles and extrafollicular cells.
What should be identified in the adrenal gland under scanning power?
The cortex and medulla.
What is the significance of the thymus in infants and children?
Its function is elevated during this period.
What is the appearance of the thyroid follicles?
They consist of cuboidal cells surrounding a cavity filled with colloid.
What is the primary role of the adrenal cortex?
To produce various hormones.
What is the structure of the thymus?
Divided into lobes and lobules.
What is the relationship between the thyroid and parathyroid glands?
The parathyroid glands are embedded within the thyroid gland.
What should be looked for when viewing the thyroid/parathyroid slide?
Follicles of the thyroid and patches of more cellular parathyroid tissue.
What is the primary function of the thymus?
The thymus is where lymphocytes (white blood cells) learn to function.
How is the thymus organized structurally?
The thymus is divided into lobes, which are further divided into lobules containing follicles.
What are the two main regions of a thymic follicle?
Cortex and medulla.
What is the role of thymocytes in the thymus?
Thymocytes start their education in the cortex and can become T-cells or Natural Killer cells.
What distinguishes the cortex from the medulla in the thymus?
The cortex stains darker and contains many lymphoid cells, while the medulla stains lighter and contains Hassall's corpuscles.
What are the testes responsible for?
The production of sperm and testosterone.
What structures within the testes are responsible for sperm production?
Seminiferous tubules.
What type of cells are found between the seminiferous tubules and what is their function?
Interstitial cells (Cells of Leydig) release testosterone.
What is spermatogenesis?
The process of sperm cell creation within the seminiferous tubules.
What are the two main regions of the ovaries?
Cortex and medulla.
What develops in the ovarian cortex?
The egg/oocyte.
What are the different types of cells surrounding the oocyte in the ovaries?
Follicular cells (single layer) and granulosa cells (multiple layers).
What is the function of the ovarian follicles?
They are responsible for the production of estrogen.
What are the key structures found in the ovarian cortex?
Different stages of follicles.
What is the role of the medulla in the ovaries?
The medulla is the inner region that does not contain follicles.
What is the zona pellucida?
A glycoprotein layer surrounding the oocyte.
What is the corona radiata?
A layer of granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte.
What is the theca folliculi?
Connective tissue surrounding the follicle with blood vessels.
What is the significance of Hassall's corpuscles in the thymus?
They are structures found in the medulla that may play a role in the education of thymocytes.
How can you identify the seminiferous tubules under a microscope?
They appear as many circular structures within the testes.
What are spermatogonia?
Spermatogenic cells located in the epithelium of the seminiferous tubules.
What are the five cell types in the anterior pituitary?
Somatotropes, lactotropes, corticotropes, thyrotropes, gonadotropes.
What hormones are released from the anterior pituitary?
Growth hormone, prolactin, adrenocorticotropic hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone.
What are the functions of the hormones released from the anterior pituitary?
HGH: growth and metabolism; TSH: controls metabolism via thyroid gland; ACTH: manages stress and energy through adrenal glands; FSH and LH: reproduction by acting on the gonads; Prolactin: lactation.
What are the differences between the anterior and posterior pituitary?
Anterior: synthesizes and releases its own hormones, larger; Posterior: stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus, smaller.
Which hormones are released from the posterior pituitary?
Oxytocin and Antidiuretic Hormone (Vasopressin).
Where are the posterior pituitary hormones made?
In the hypothalamus.
What are the functions of the posterior pituitary hormones?
ADH: regulates water balance and blood pressure by increasing water absorption in the kidney; Oxytocin: stimulates uterine contractions during labor and milk let-down reflex.
Which hormones are produced at the thyroid follicles?
Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4).
Which thyroid hormone is extrafollicular?
Calcitonin.
What are the functions of the thyroid hormones?
Regulate body metabolism, growth, development, energy, and heat production.