Merged flashcards for ESD
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
polymorph
non-toxic and fully biodegradable polymer, comes in small plastic granules. if heated to 62C the granules fuses to make it moldable, then shaped by hand and is solid when cooled. good for prototyping or making repairs
thermochromic pigments
reacts to heat by changing colour at different temps. used in room and pediatric thermometers, spray paints, childrens cutlery
photochromic pigments
reacts to uv to change color. longer exposed, darker it becomes. caused by reaction of light sensitive particles in pigments. used in nail polish, vehicle spray paint, clothing, beach products
photochromic particles
used in sunglasses (silver halides).
quantum tunneling composite
conductor or insulator. electrical resistance varies on pressure or stress applied. more pressure = conductive particles move closer = less resistance. billions of conductive nanoparticles held in a polymer without touching. no pressure = insulator. used in touch-sensitive pads for phones and computers, keyboards, wearable tech
modern material
materials developed with a specific application in mind. developed by inventing new or improved manufacturing processes
graphene
ultra-thin, transparent layer of graphite just 1 atom thick and 200x stronger than steel. light, strong, flexible, strechable, great conductor of heat & electricity. no developed uses but potential to be used in aerospace, medical, electronic and energy industries
cornstarch polymers
plastics made from vegetable starches, fully biodegradable, non-toxic when composted. used for disposable food and drink containers, bottles, pens
metal foams
metals (e.g. aluminium) that contain many gas-filled spaces which make the material lightweight, while still stiff, tough, and strong under compression. uses are bone implants, lightweight car parts
titanium
extremely corrosion-resistant, high strength-to-weight ratio. pure t. does not react with the body and is used in medical, artificial joints, dental implants, orthopedic applications
fibre optic
optical fibres that allow digital info to travel as pulses of light along thin glass strands at very high speed. carries more info than copper, does not suffer from electromagnetic interference (distorts signal). inner glass core little thicker than human hair, transmits light by reflecting it off the wall of the cladding. used in telephone cables, internet communications & cable tv signals
liquid crystal displays (LCDs)
nanoengineered materials
materials engineered into very small particles or structures on the nano scale (1-100 × 10^-9m). often shows new properties
applications of nanoengineered materials
sunscreen (nanoparticles absorb UV rays)
carbon fibre structures (stiffened using silica nanoparticles)
lithium-ion battery (electrodes based on nanoparticle tech)
flexible solar cells (uses nanoparticle tech)
self-cleaning glass (used in construction, uses nanoparticles)
composite materials
made up from two or more different materials bonded together
glass reinforced plastic (grp)
also known as fibreglass, glass fibres coated in thermosetting plastic resin. stronger and tougher than the plastic by it self, heat-resistant, easy to mold into complex shapes. used in boats, kayaks, surfboards, PCBs
carbonfibre reinforced plastic (crp)
carbon fibres coated in thermosetting plastic resin. lighter, tougher, stronger than grp, but more expensive. uses are protective helmets, racing cars, sports equipment, laptops
technical textiles
enhanced fabrics designed to be purely functional
kevlar
synthetic fibre that can be woven into a very strong fabric that is resistant to abrasion (scraping). useful in bulletproof vests, protective clothing for motorcyclists
nomex
fabric of synthetic fibres that have fire resistance built into them instead of the fbaric being treated with flame retardance. (fire-resistance cannot be washed or worn away) used in firefighters’ and racing drivers’ overalls
What is the process of all mechanisms?
Input, Process, Output
What are the types of movement in mechanisms?
Linear, Reciprocating, Rotary, Oscillating
What does a linear mechanism do?
Straight line, one direction
What does a reciprocating mechanism do?
Straight line, forwards and backwards movement
What does a rotary mechanism do?
circular movement
What does a oscillating mechanism do?
circular forwards and backwards movement
What is the three parts of a lever?
Effort load Fulcrum
What is the ‘effort’ part of a lever?
The power you put into a lever
What is the ‘Load‘ part of a lever?
The weight of the object moved
What is the ‘fulcrum‘ part of a lever?
The point at which the lever turns or pivots
What is the first class of a lever system
E F L
What is the second class of a lever system
F L E
What is the third class of a lever system
F E L
The formula of mechanical advantage
MA = Load / Effort
The formula of velocity ratio
VR = distant effort moves / distant load moves
What is the type of linkage that goes back and forth
Reverse motion linkage
What is the type of linkage that turns 90 degrees in direction
Bell crank

What is this cam?
Eccentric cam

What is this cam?
Ratchet/snail cam
What is this cam?
Pear cam
What is a pulley?
A wheel with a groove around its edge in which a belt, rope or chain can sit
What is the formula for Speed Ratio
SR = Diameter of driver pulley / Diameter of driven pulley
What are the two parts of a pully (gears)
Driver pully and Driven Pulley

What is this type of gear?
Bevel gear
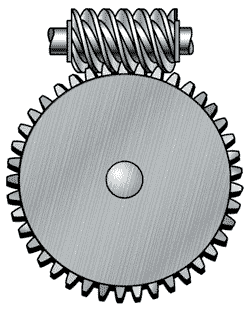
What is this type of gear?
Worm gear

What is this type of gear?
Rack and pinion gear
What is a smart material?
one which changes its properties in response to a change in environment, reacting to stimuli
What are smart alloy?
A group of alloys which have super elasticity and have Shape memories
What is a nitinol made of?
an alloy made of nickel and titanium
What is a feature of nitinol?
it is biocompatible and a smart alloy with shape memory characteristics.
What are Shape-memory Plastics (SMPs)?
These can be used to sense temperature change because they change shape when a certain temperature is reached.
What is a polymorph?
What can super elasticity do?
undergoes large strains and spring back to their original shape (normal metal alloys are permanently deformed)
What is a medical application for nitinol?
used in arterial stents to widen restricted arteries. the mesh stent is compressed and placed inside the artery. it is then warmed which expands to its original shape, pushing against the artery walls, allowing improved blood flow
What is a polymorph?
non-toxic and fully biodegradable polymer, comes in small plastic granules. if heated to 62C the granules fuses to make it moldable, then shaped by hand and is solid when cooled. good for prototyping or making repairs