HUMANBIOLOGY_CHAPTEREIGHT
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
asexual reproduction
form of reproduction in which offspring arise from only one parent
apoptosis
programmed cell death that is a normal part of development
chromosome
a continuous molecule of DNA wrapped around protein in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell; also, the genetic material of a prokaryotic cell
DNA polymerase
enzyme that adds new DNA nucleotides and corrects mismatched base pairs in DNA replication
chromatin
collective term for all of the DNA and its associated proteins in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell
cell cycle
sequence of events that occur in an actively dividing cell
interphase
stage preceding mitosis or meiosis, when the cell carries out its functions, replicates its DNA, and grows
mitosis
division of genetic material that yields two genetically identical nuclei
cytokinesis
distribution of cytoplasm into daughter cells in cell division
malignant tumor
mass of abnormal cells that has the potential to invade adjacent tissues and spread throughout the body
metastasis
transfer of cancer cells from a tumor to other sites in the body
Some method of cell division is necessary for every organism to ______
reproduce
In asexual reproduction, the offspring are genetically ______ to each other.
identical
Because apoptosis is an intentional act on the part of the cell, it is sometimes referred to as "______ cell death."
programmed
A single molecule of DNA and its associated proteins is called a ______.
chromosome
What is the role of the enzyme DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
add complementary DNA nucleotides.
Before cell division can occur, what molecule must be replicated so it can carry instructions to new cells?
DNA
Regulated cell death that is a necessary part of development is called
apoptosis
During a section of the cell cycle collectively called ______, the cell is not dividing, but protein synthesis, cell growth, DNA replication, and basic cell functions are occurring.
interphase
A cell's genetic material is contained in one or more ______.
chromosomes
The daughter cells of mitosis have half as many chromosomes as the parent cell.
False
What enzyme adds complementary bases to exposed single strands of DNA during DNA replication?
DNA polymerase.
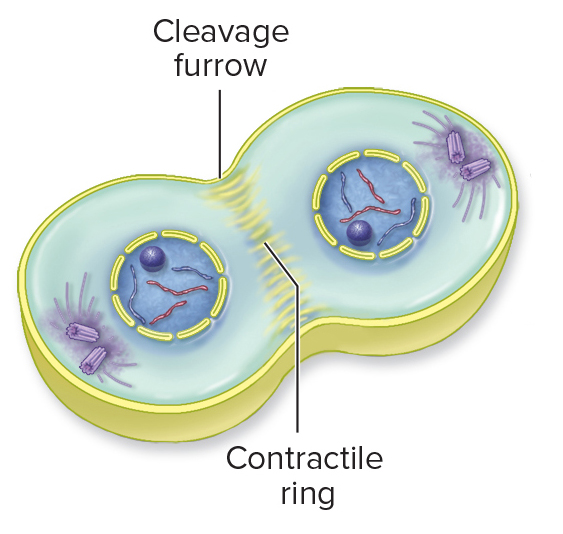
What cellular event is occurring in this picture?
cytokinesis
Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of ______, which is composed of uncondensed DNA and associated proteins.
chromatin
The ______ describes the events that occur in a eukaryotic cell from cell division, including division of the genetic material and the cytoplasm, through the interval of cell activity before the next cell division.
cell cycle
Several internal ______ in the cell cycle ensure that a cell does not enter into the next phase of the cell cycle before completing the previous phase.
checkpoints
The phase of the cell cycle called interphase is a time of inactivity and rest for the cell after mitosis.
False
A malignant tumor is one that ______.
invades the surrounding tissue
Which of the following best describes the overall process of mitosis?
The type of cell division that separates chromosomes and produces two daughter cells with identical nuclei.
Following mitosis, what process splits the organelles, cytoplasm, duplicated nuclei, and macromolecules into two daughter cells?
Cytokinesis
What type of cells may divide constantly throughout their life?
stem cells