Dairy Herd Fertility Parameters
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What rates are used to measure herd fertility?
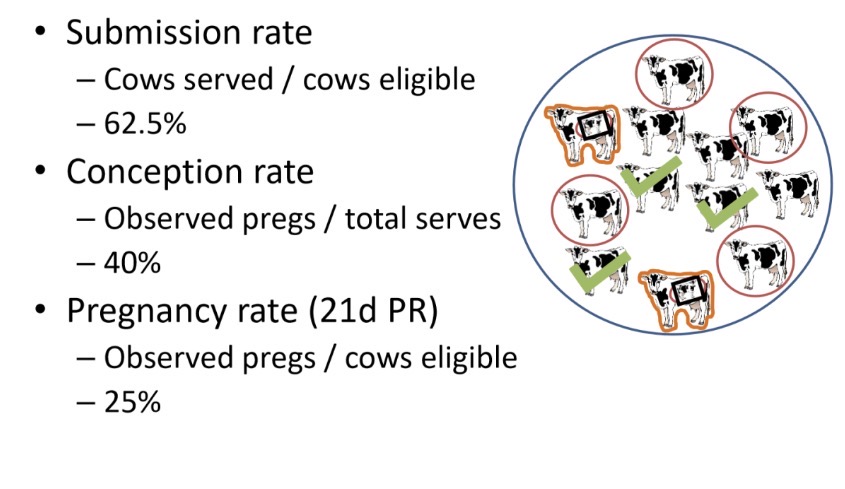
Submission rate (SR)- effectiveness of putting semen in cows
Conception rate (CR)- effectiveness of semen + egg = calf
Combined= Pregnancy rate (PR) or 21d PR
Which of the 3 is the most accurate measure of herd fertility
21d PR is the most accurate measure of herd fertility
How do you calculate submission rate?
In any 21 day window:

What cows are actually eligible?
Cows that are:
passed the voluntary wait period (50-60 d)
Complete uterine involution and return to cyclicity
Not yet pregnant
For breeding
In any 21 day window
If you are still struggling to visualize submission rate, he shows an example over a few slides in the PowerPoint. It’s helpful but not worth making flashcards over
How do you calculate conception rate?

Again, there is a visual example if needed, but it is a pretty simple concept imo (no hate fr)
How do you calculate 21 day pregnancy rate?
In any 21 day window:

Ugh fine ill ask you a math example for 21d pr…..
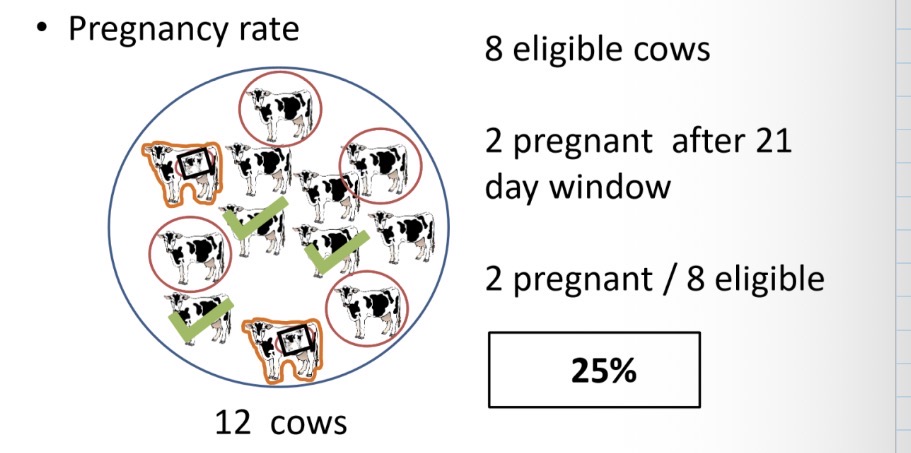
If there are 8 eligible cows and 2 are pregnant after the 21 day window, what is the 21d pr?
25% you melon
Why can submission rate and conception rate alone be misleading in herd fertility?
I mean look at this example. Only 3/12 got pregnant but submission rate and conception rate are much higher values and are misleading when only 25% of ur eligible cows actually got pregnant
What are other ways you can measure fertility performance?
Why are these also not accurate representations of herd fertility?
calving interval- describes overall fertility
Only shows how fertility rates were… 9 months ago
Calving- first service (Heat detection evaluation)
Another value that is usually well above the realistic fertility performance
Calving to conception interval- only cows that conceived
Another value that is usually well above the realistic fertility performance
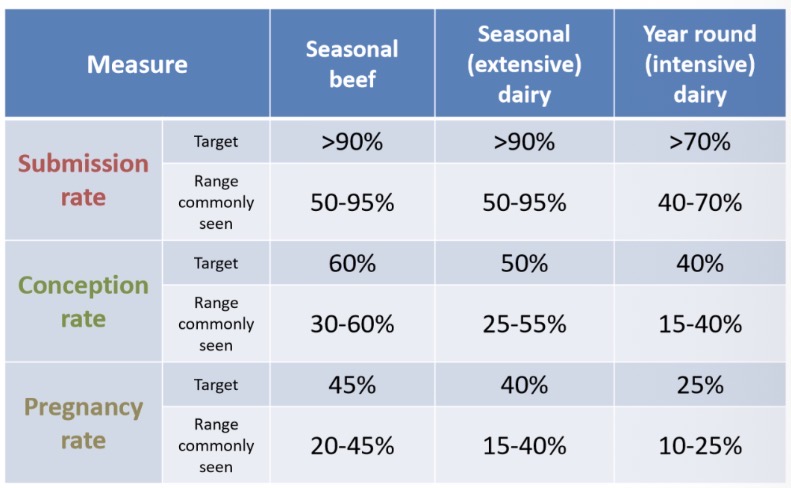
What are SR, CR, and PR targets for:
Seasonal beef?
Seasonal (extensive) dairy?
Seasonal (intensive) dairy?
This PowerPoint got too many slides so stop ur screenshot hating fr
Why is high PR a good thing on a farm?
Well yeah obviously it helps make the farmer money, but what is an indirect reason?
There is a positive correlation between milk yield and pregnancy rates.
Good fertility = more peaks = more time above profit line = more money again (indirectly tho 😉)
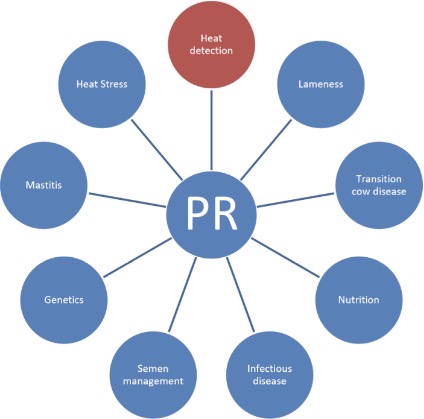
What are the factors limiting fertility performance!!!!
Heat detection
Lameness
Transition cow disease
Nutrition
Infectious disease
Semen management
Genetics
Mastitis
Heat (as in high temperature, not estrus) stress
How is estrus usually detected?
Usually by observing signs of estrus from a cow.
How should estrus be detected?
A combination of observing estrus expression annddddd
using technology to assist in detection of estrus behavior that could usually be missed (late at night or when no one is around)
How do you calculate the efficiency/accuracy of heat detection?
Sensitivity- % cows served that were actually in heat
Specificity- % cows not served that were not in heat
How do you know heat detection is “poorly sensitive”? What about “poorly specific”?
Low sensitivity = increased false negatives = increased cows missed
Low SR because:
cows not served but cycling
Pregnancy detection negative (means a heat was missed in those 30 days)
Low specificity = increased false positives = increased cows served when not in heat
Low CR because:
AI cows that were not in heat (poor detection)
What is an inter-service interval? How long should it last?
One cow served twice in a row
should be 21 (18-24) days apart (cycle length of the cow)
What would a service interval at ______ indicate?
2-17 days
25-35 days
36-48 days
>48 days
These are relatively simple answers so don’t think too hard
2-17 days- one of the two heat detections were wrong
25-35 days- a heat was missed
36-48 days- lots of animals missed, low sensitivity
>48 days- lots of animals missed, low sensitivity
What percentage of Inter-service intervals should be between 18-24 days on a “good” farm?
At least 60%
Remember this!
Improving heat detection improves fertility


How does lameness affect fertility rate?
when researched, cows that experienced lameness before 70 DIM (days in milk) showed a lower SR, CR, and PR. try and keep cows not lame!

What are transition cow diseases?
any problem at calving
What are some examples of transition cow diseases?
Any of these are labeled as a clinical incidence:
milk fever
dystocia
twins
metritis
ketosis
retained fetal membranes (RFM)
left displaced abomasum
How do you calculate the incidence of post-partum diseases?
this is like any other incidence rate, take whatever disease and divide it by the number of calvings, for example:
number of RFM
number of calvings
This kinda goes without saying but…..
controlling transition diseases improves fertility!

I am going to not go into too much detail, he didnt really in the powerpoint because he said a later lecture was covering it more
what are some nutrient causes that affect fertility?
Negative energy balance (NEB)
Macro-minerals
protein excess
trace elements/vitamins
When would a cow most likely experience an NEB?

what about NEB causes infertility?
the cow goes into a transition period which causes mobilization of excess body fat, releasing high plasma non esterified fatty acid (NEFA) and high plasma ketone bodies (K), these negatively affect the follicle in some way (sorry bros i just know it negatively affects it)
How do macro-minerals cause infertility?
milk fever or hypocalcemia at calving causes:
porr appetite → NEB
RFM
immuno suppression
All of this leads to lower SR/CR… and 21d PR
How does acidosis and high plasma urea cause infertility?
the high dietary crude protein that causes acidosis and high plasma urea (which is measurable in blood, urine, and milk) causes changes in the uterine environment and affects embryos quality and viability, lowering CR
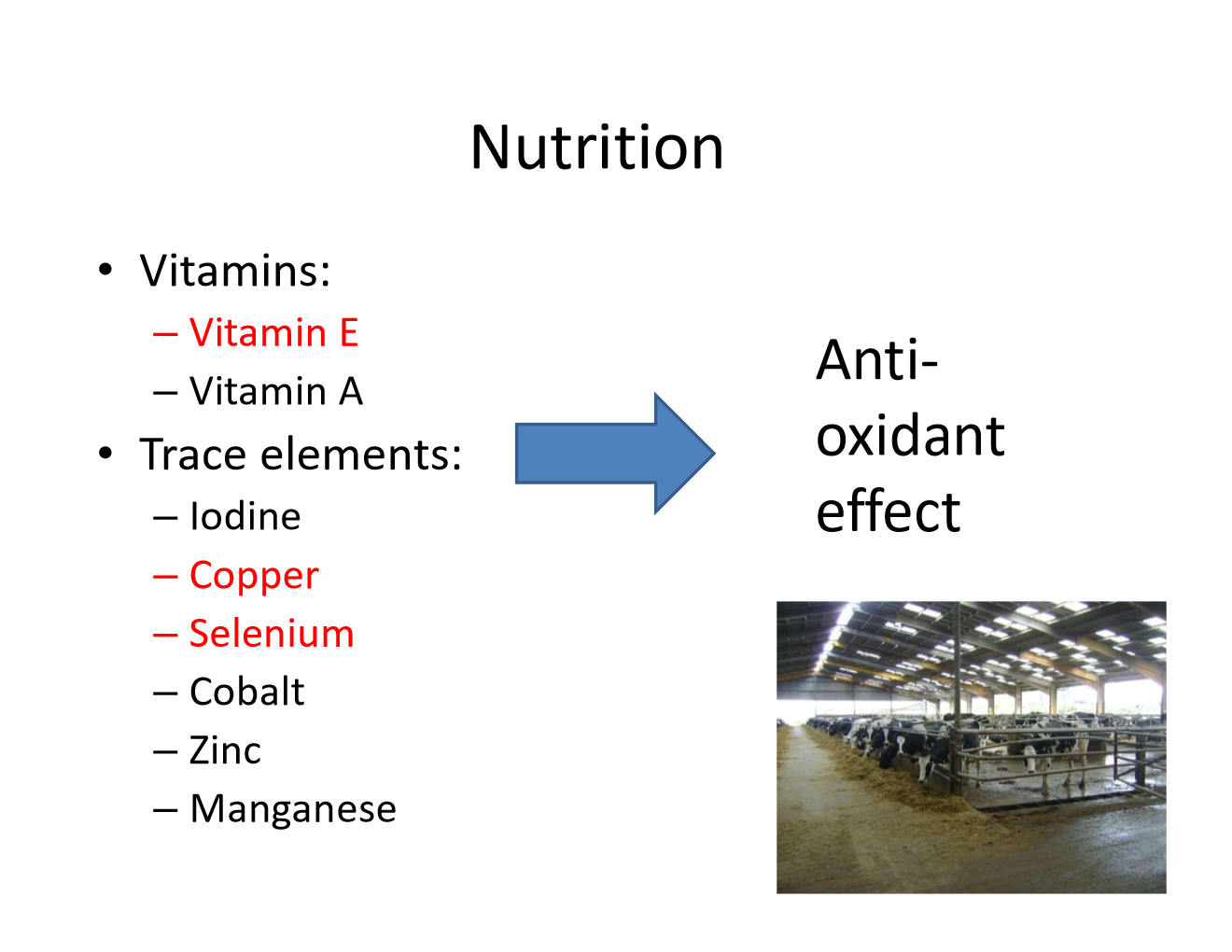
Why are elements important in fertility?
Because of their antioxidant effect! (except for the ones in red, still important tho!)

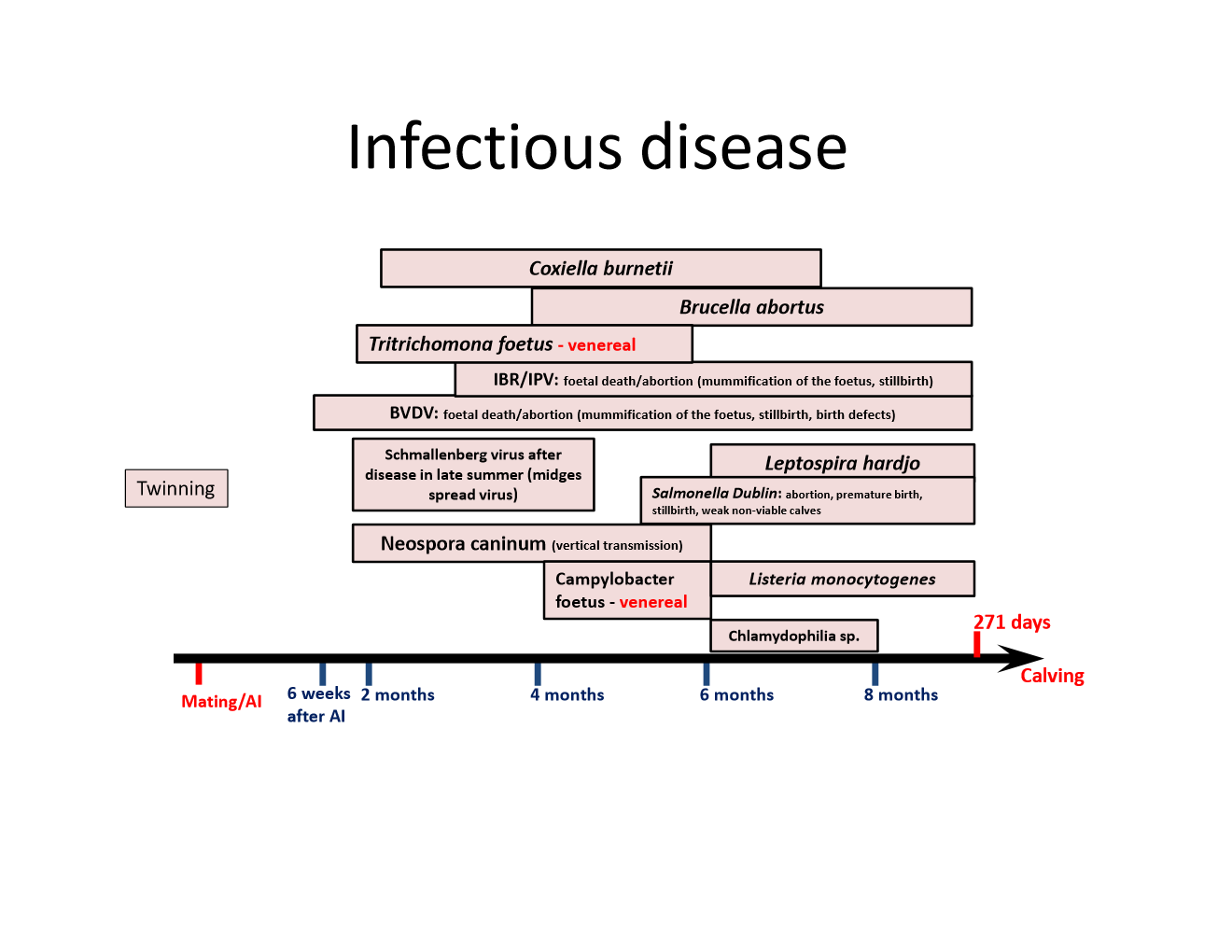
what are some infectious diseases that cause infertility? when do each of them occur in cow pregnancy?
What are some indirect effects of infectious disease?
for example, BVD:
increases calves disease (d+, pneumonia, navel ill, etc)
causing lower replacement rate (birth to first calving)

What factors of semen management affect infertility the most?
Semen handling, AI technique, and breeding policy (sexed semen)
How does sexed semen improve fertility in a dairy herd?
Directly, it negatively affects fertility, causing a decrease in CR. But indirectly, it also allows for:
easier calving
Genetic gains
Increased herd size
Reducing bull calf numbers

How does genetics affect fertility?
Using genomics allows for:
higher-reliability genomic proof for female young stock
same for young bulls
greater diversity when picking replacement heifers
serving genetically superior animals while putting the rest to beef (basically, can sell less-superior genetics)

How does mastitis affect fertility?
mastitis causes:
inflammation
incr temp
pain
Leading to:
lower SR, CR, and 21d PR

How does heat stress affect fertility?
it bad