Principles of Gas Exchange
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what is gas exchange
O2 uptake into and CO2 elimination from blood
occurs by simple diffusion
rate of diffusion
rate of diffusion α A x ΔP
A=surface area
ΔP= pressure gradient
factors affecting diffusion
surface area
pressure gradient
thickness of membrane
physicochemical properties
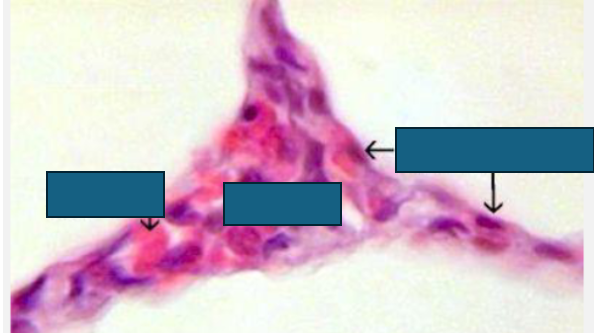
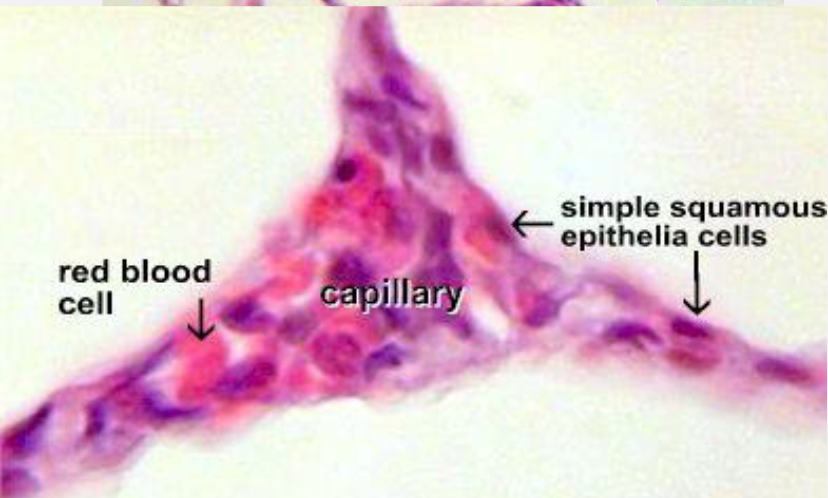
membrane of alveolus
pressure gradient
difference in partial pressure of respective gases in alveolus and the blood
partial pressure→ pressure it would exert if it was the only gas in the container
universal gas equation
pV=nRT
dalton’s law of partial pressure
partial pressure of gas in gas mixture= total pressure x fractional concentration of gas
partial pressure of oxygen in alveoli
lower than atmospheric pressure:
inspired air humidified in upper airway
in alveoli→ oxygen taken up, CO2 added
body consumes more O2 molecules than it produces CO2 molecules (1.25x more O2)→ due to respiratory quotient
effect of humidification
at 37C saturated vapour pressure ≈ 6.3kPa
in fully humidified air at 37C partial pressure of oxygen= (101.3-6.3) x 0.21=19.95kPa
effect of CO2
typical value of alveolar partial pressure of CO2 is 5kPa
if one CO2 was produced for every O2 consumed= ppO2 would be (19.95-5)=14.95kPa
however, 1.25x more O2 than CO2 so ppO2 in alveoli→ 13.7 kPa
how does carbon dioxide and oxygen move into/out of blood
simple diffusion through fluids
what primarily affects partial pressure of gases in fluids
solubility of gas in fluid
less soluble→ more remains out of solution and is free to pass out of solution to create partial pressure
carbon dioxide solubility compared to O2
CO2 is approx. 24 times more soluble in water than oxygen
theoretical rate of diffusion of O2 and CO2
more soluble and therefore higher diffusing capacity
in theory, CO2 transfer much more efficient than O2 transfer
effect of higher diffusing capacity of CO2
alveoli/ capillary gap equilibrates quicker
partial pressures of O2 and CO2 of healthy person at rest
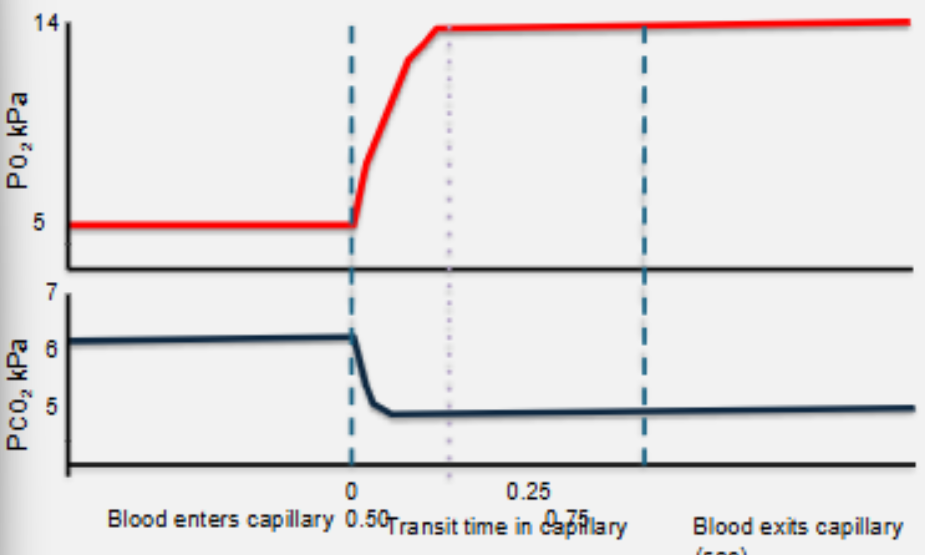
partial pressures of O2 and CO2 of healthy person during exercise
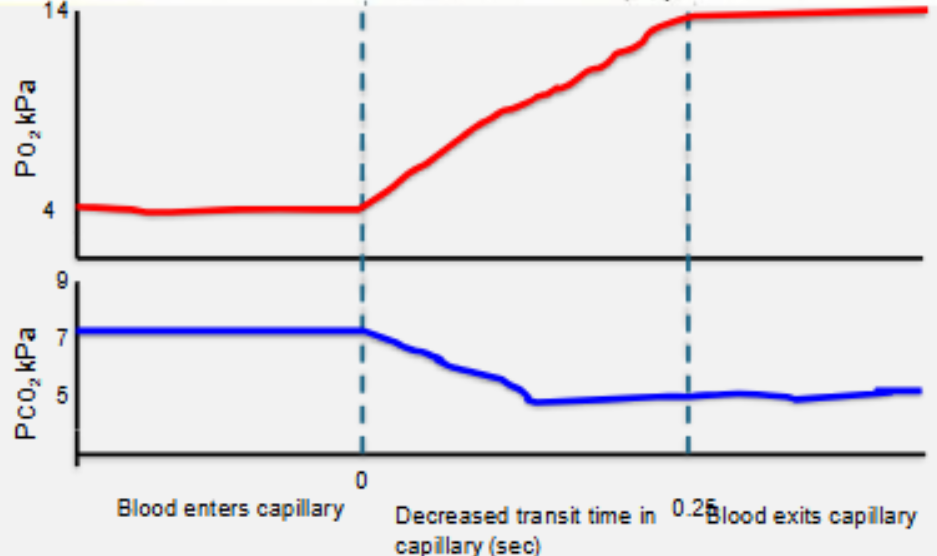
partial pressures of O2 and CO2 of patient with pulmonary fibrosis during exercise
results in type 1 respiratory failure (hypoxia)
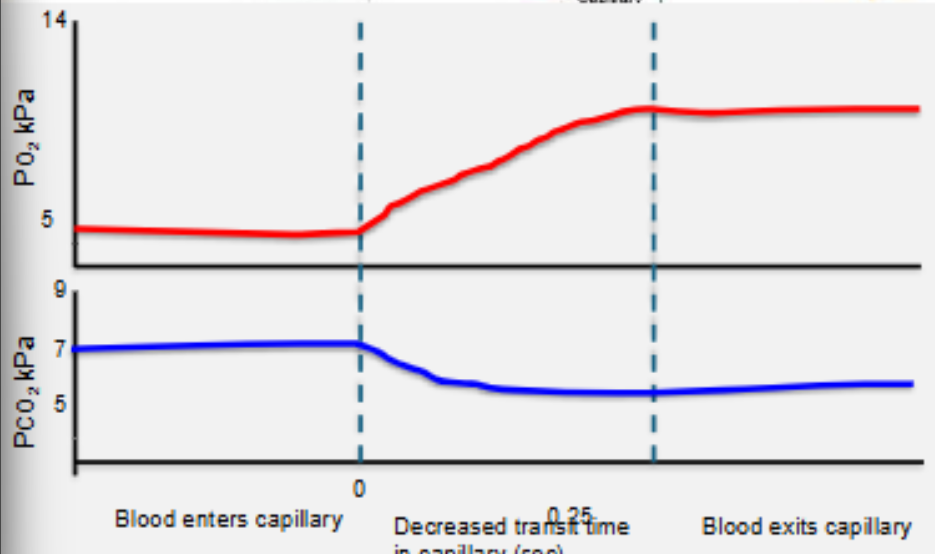
clinical measurement of diffusing capcity
mean pulmonary capillary PO2 is difficult to measure, so this is generally not used
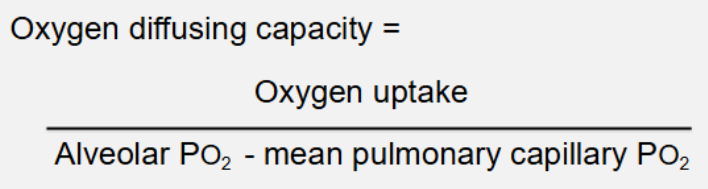
carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (transfer factor)
mean pulmonary capillary pCO effectively zero because of high affinity of CO for haemoglobin

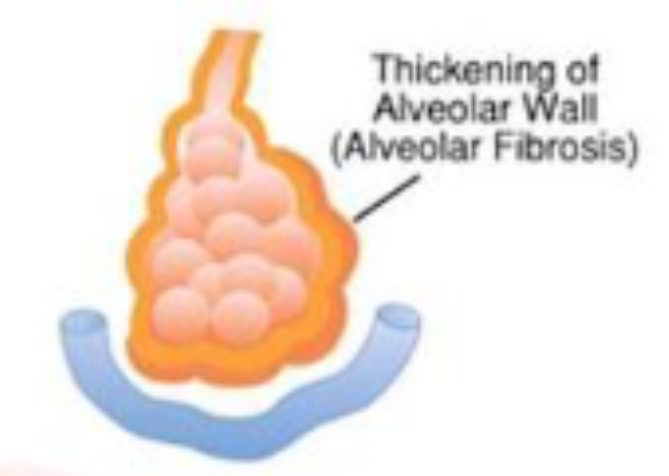
alveolar fibrosis
thickening of alveolar wall
higher diffusion distance→ less O2 in lungs
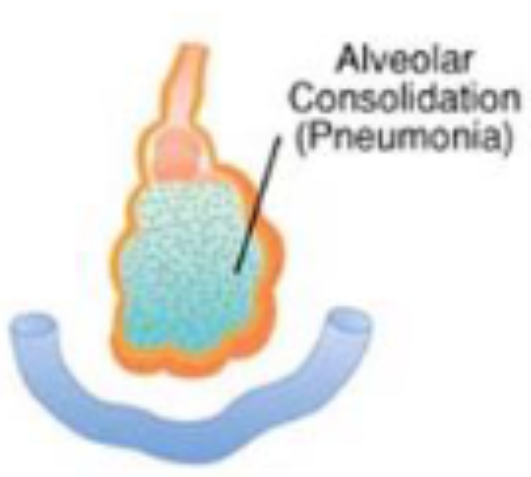
pneumonia
alveolar consolidation
gas cannot get into membranes
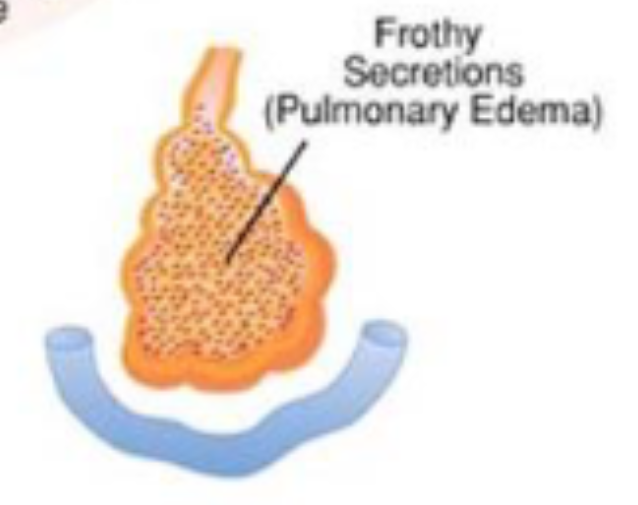
pulmonary edema
frothy secretions
often due to left-sided heart failure
pink frothy sputum
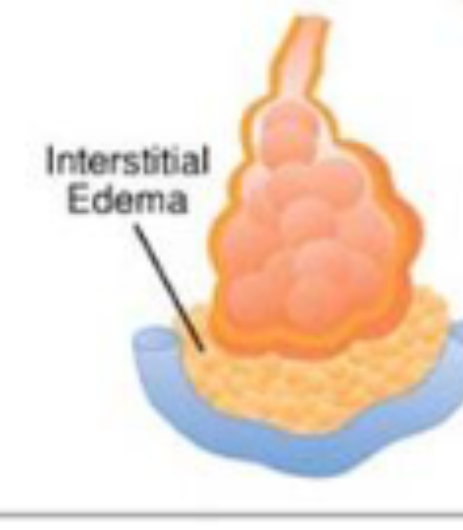
interstitial edema
froth in between alveolus and capillary
sepsis, surgery reaction, trauma
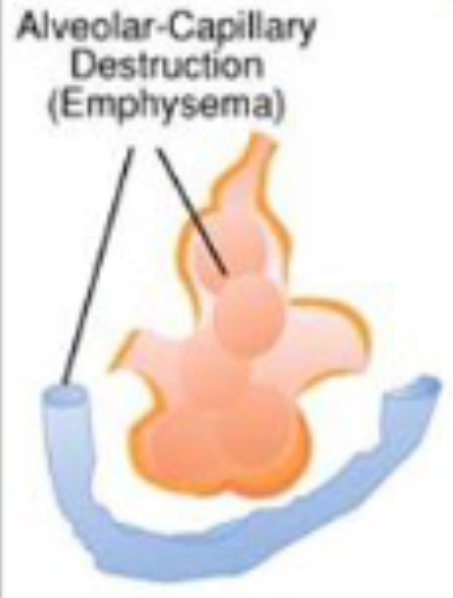
emphysema
alveolar-capillary destruction
caused by smoking
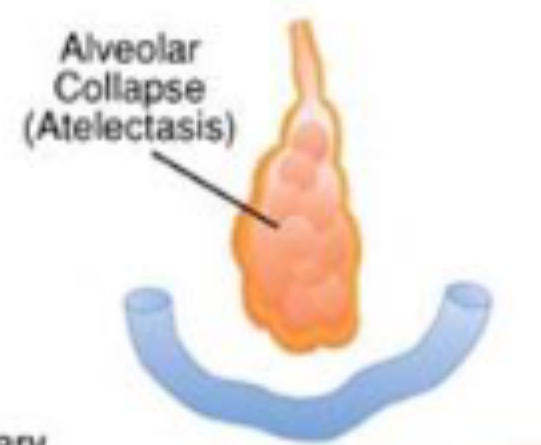
atelectasis
alveolar collapse
often caused by anaesthesia
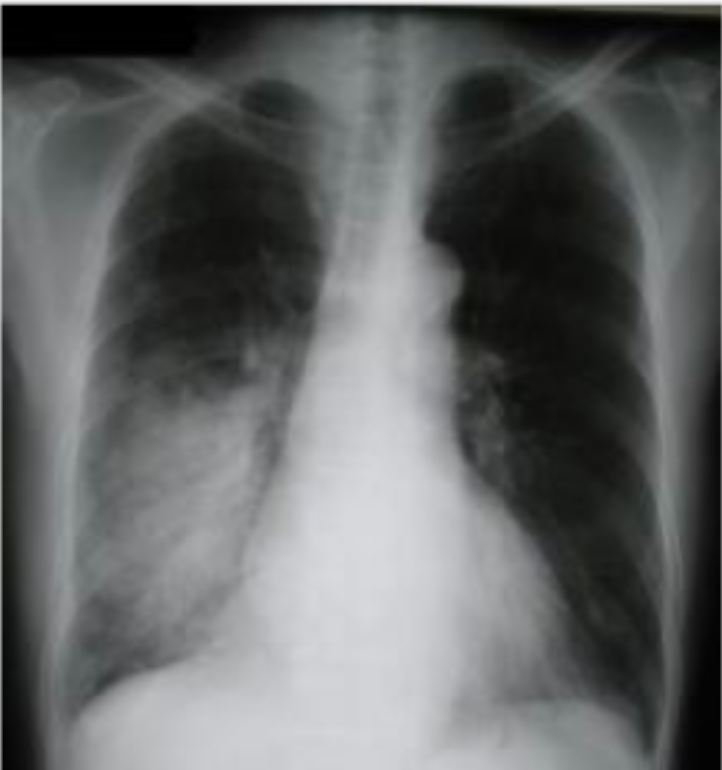
CRX of pneumonia
infection in lung
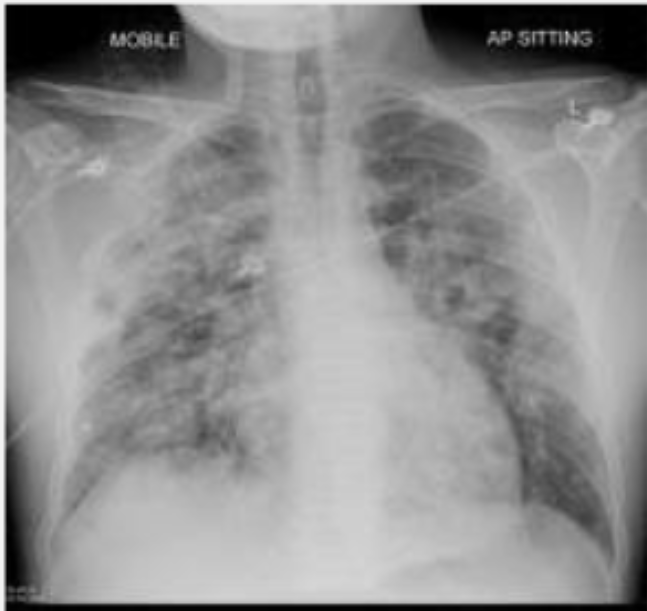
CRX of pulmonary oedema
adult respiratory distress syndrome
response to disease
lungs become stiff