pharmacology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
1
New cards
define ligand
any molecule that binds to a receptor
2
New cards
define endogenous ligand
ligand (naturally in body) normally produced by the body that binds a receptor (neurotransmitters)
3
New cards
define exogenous ligand
ligand introduced into the body (drugs)
4
New cards
Define agonist
ligand that activates receptors
5
New cards
Define antagonist
ligand that has no effect on its own but blocks binding of exogenous ligand (neurotransmitter receptor blocker)
\
\-competes w/ endogenous ligand
\
\-competes w/ endogenous ligand
6
New cards
Define non-competitive ligand
binds to site other than endogenous ligand binding site & modulates receptor activity (non-competitive inotropic neurotransmitter receptor blocker)
\
\-have agonist or antagonist properties
\
\-have agonist or antagonist properties
7
New cards
Define affinity
The strength of attraction between drug and receptor at any drug concentration concentration or firmness w/ which drug binds to receptor
8
New cards
Define efficacy
(intrinsic activity) is the ability of a drug to illicit a pharmacological response (physiological) when interaction occurs w/ a receptor (relationship between response & occupancy of receptor)
9
New cards
define binding affinity
"strength" of binding between ligand and receptor
10
New cards
A higher concentration for a low or high affinity drug/ligand?
LOW affinity drug/ligand
11
New cards
A lower concentration for a low or high affinity drug/ligand?
HIGH affinity drug/ligand
12
New cards
if high & low affinity are both at equal concentration...?
higher affinity drug binds to more receptors than low affinity
13
New cards
Kd (Affinity constant)
Dissociation constant. On graph it is the ligand concentration at which 1/2 receptors bound
14
New cards
low Kd = ___ affinity & why?
high affinity cuz need less concentration of ligand
15
New cards
high Kd = ______ affinity & why?
low affinity cuz need higher concentration to reach 100% binding
16
New cards
Define efficacy simpler def
max effect a drug can produce regardless of dose; ability of drug-bound receptor to produce a full response
17
New cards
EC50 stands for?
Concentration of the drug required to produces 50% of maximal effect; measures efficacy
18
New cards
a full agonist has a _____ efficacy & produces _____
response while occupying a relatively low proportion of receptors
response while occupying a relatively low proportion of receptors
a full agonist has a high efficacy & produces a full response while occupying a relatively low proportion of receptors
19
New cards
a ____ agonist has ___ efficacy then a ____ agonist
a partial agonist has lower efficacy than a full agonist
20
New cards
explain selectivity of a drug
\-common for some drugs to bind to many receptor types or bind to several members of same neurotransmitter receptor class
\-less common for drugs to selectivity bind to 1 or 2 receptors
\-less common for drugs to selectivity bind to 1 or 2 receptors
21
New cards
Why are relative affinities of a drug at diff receptors exploited?
to adjust the dose down so only highest affinity receptors are bound & activated ("targeted") minimize side effects
22
New cards
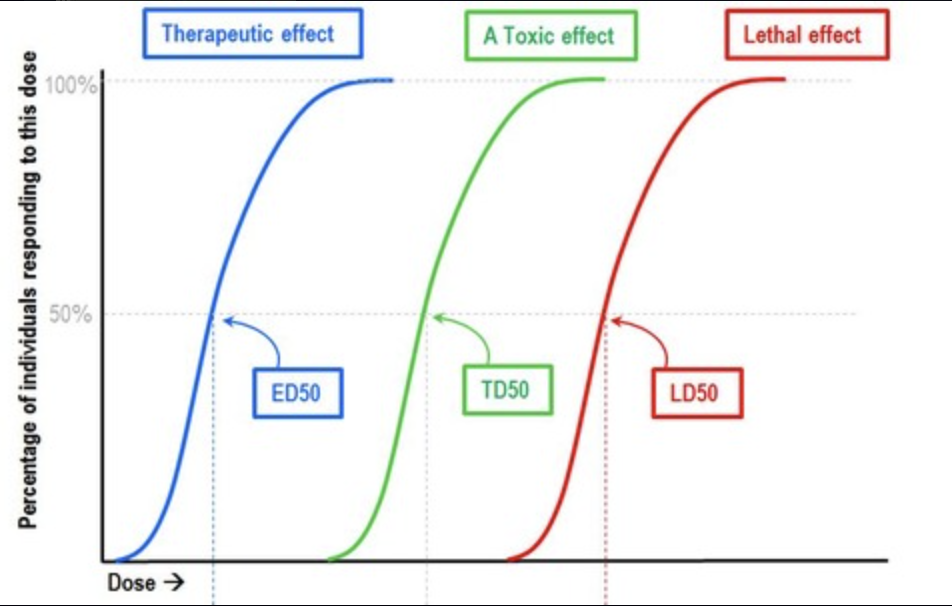
Evaluate dose response curves.
linear segment starts low, increases then levels off as it approaches max value (sigmoidal relationship) between dose & effect
\- w/in limits increasing dose=increase desired effect
\- w/in limits increasing dose=increase desired effect
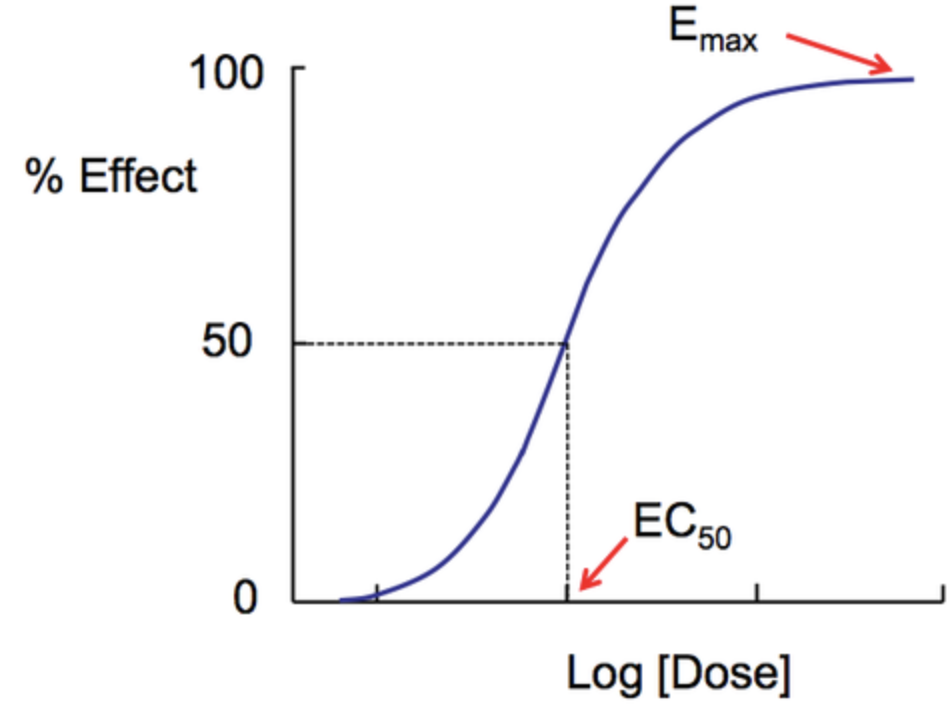
23
New cards
ED 50 (effective dose)
the dose where drug shows 50% of max effectiveness
24
New cards
therapeutic index
distance between LD50 & ED50 \n (lethal dose & effective dose)
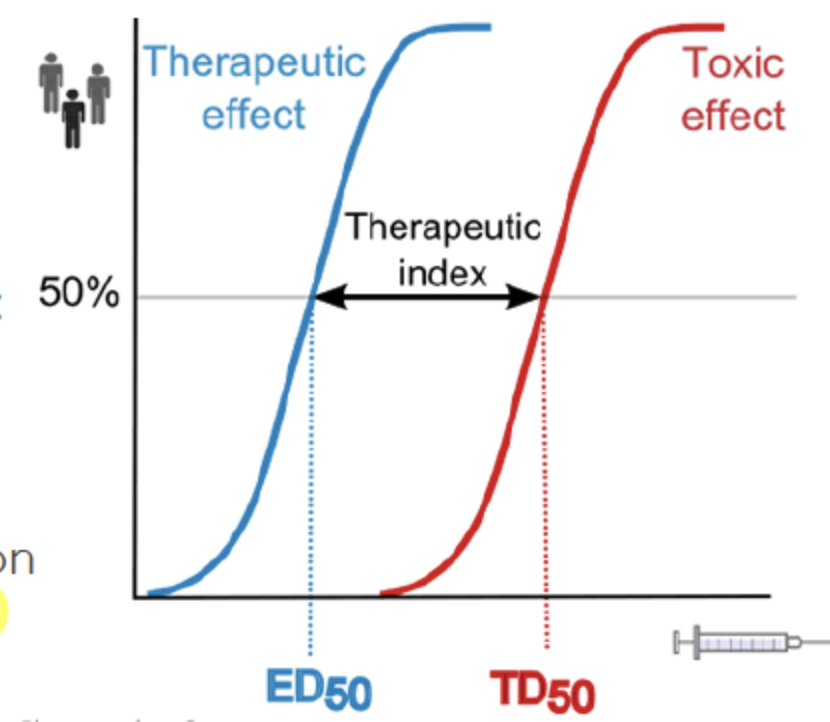
25
New cards
LD 50 (lethal dose)
dose of drug at which is lethal (death) in 50% of subjects
26
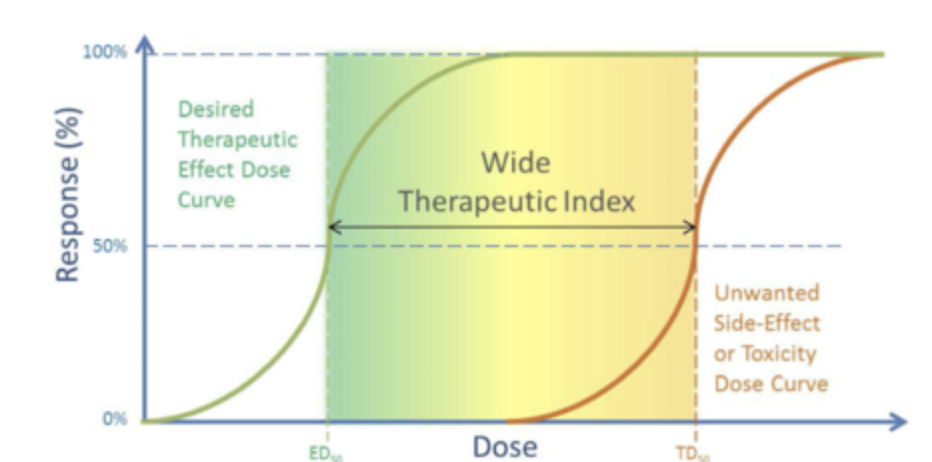
New cards
wide therapeutic index means?
the safer the drug (over the counter drugs)
27
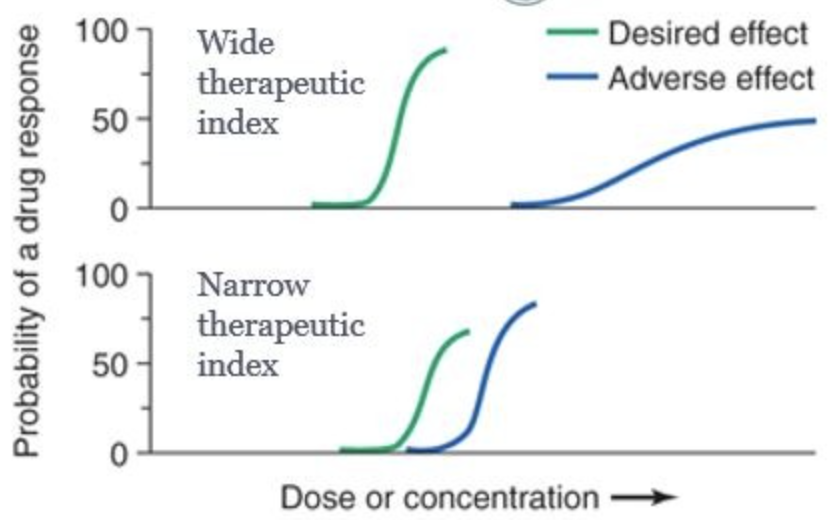
New cards
narrow therapeutic index means?
overdose is easier (needs higher regulation)
28
New cards
TD50 (toxic dose)
dose where drug causes some toxicity (harm) in 50% of subjects
29
New cards
Define psychoactive drugs
exogenous ligand that in small amounts alters experiences, emotion, mood, attention...
\-natural or synthetic
\-agonist, antagonist, or non-competitive ligand
\-natural or synthetic
\-agonist, antagonist, or non-competitive ligand
30
New cards
Define tolerance
decrease in effect of drug after repeated use; over time need higher dose to get same effect
31
New cards
define metabolic tolerance
body gets better at eliminating drug
32
New cards
define functional tolerance
targeted receptors adapt
33
New cards
functional tolerance: antagonist
neurons may express MORE receptors if drug is an antagonist
34
New cards
functional tolerance: agonist
neurons may express LESS receptors if drug is an agonist
35
New cards
define physical dependence
stop using drugs leads to physical withdrawal symptoms
36
New cards
define psychological dependence
stop using drugs leads to psychological withdrawal symptoms; anxiety, distress
37
New cards
Define withdrawal
actual symptoms after stop using drug; specific symptoms depend on drug
ex: fatigue after stop using caffeine
ex: fatigue after stop using caffeine
38
New cards
define addiction
chronic relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking behavior
-physical dependence, tolerance, & sensitization do not equal addiction
-physical dependence, tolerance, & sensitization do not equal addiction
39
New cards
rate of absorption for injections: highest to lowest
1. intravenous (IV); fastest
2. intraperitoneal (IP)
3. intramuscular (IM)
4. subcutaneous (SQ); slowest
40
New cards
rate of absorption for injections depends on?
density of capillaries/blood flow
41
New cards
1) intravenous (IV); fastest
inject into vein
42
New cards
2) intraperitoneal (IP)
inject into abdominal cavity
43
New cards
3) intramuscular (IM)
inject into muscle
44
New cards
4) subcutaneous (SQ); slowest
inject under skin
45
New cards
Routes of administration of drugs: inhalation
1. gases
2. smokes
3. solids
46
New cards
inhalation: gases
lungs - a lot of surface area exposed to air and capillaries
47
New cards
inhalation: smokes
different from gas because includes vapor and ash particles, but absorbed similarly
48
New cards
inhalation: solids
inhaled through nose; not as efficient as lungs
49
New cards
Routes of administration of drugs: slower routes
1. oral (ingested)
2. transdermal
50
New cards
slower routes: oral (ingested)
absorbed mostly through intestines, then through capillaries
51
New cards
slower routes: transdermal
not readily absorbed through epidermis (skin)
52
New cards
Typical Antipsychotics effectiveness
1st generation/typical in 1950s \n decrease positive effects of schizophrenia (hallucinations, delusions) \n -ex: chlorpromazine, haloperidol
53
New cards
Typical Antipsychotics side effects
\- dry mouth \n -hypotension \n -dystonia (involuntary muscle contraction) \n -tardive dyskinesia (repetitive movement) \n -Parkinsonism \n -weight gain
54
New cards
Typical Antipsychotics mechanism
antagonist. (block) D2 receptors (inhibitory dopamine)
55
New cards
atypical antipsychotics
2nd gen/1980s \n (ex: olanzapine & risperidone)
56
New cards
atypical antipsychotics effectiveness
decrease positive (hallucinations) & negative symptoms in schizophrenia (delusions, catatonia)
57
New cards
atypical antipsychotics side effects
hypotension, diabetes, weight gain
58
New cards
atypical antipsychotics mechanism
antagonist on 5-HT2 (serotonin), D1 (excitatory dopamine), D2, and α1 (norepinephrine) receptors
59
New cards
antidepressants
used to treat affective (mood) disorders
60
New cards
Antidepressants: SSRIs & SNRIs
\-selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors & serotonin & norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors \n \n block reuptake of 5-HT &/or NE (norepinephrine); antagonist at SERT & NET (transporters) \n increase serotonin activity
61
New cards
antidepressants: MAOIs
monoamine oxidase inhibitors \n -block monoamine (enzyme) from breaking down/degradation of DA, NE, & 5-HT
62
New cards
antidepressants: TCA's
Tricyclic Antidepressants \n -block reuptake of NE & 5-HT
63
New cards
Anxiolytics (Benzodiazepines) \n -depressants
ex: xanax, valium, Ativan
64
New cards
Anxiolytics: Benzodiazepines effectiveness \n -depressants
anxiety & panic
65
New cards
Anxiolytics: Benzodiazepines side effects
\-depressants
\-depressants
tolerance, cross tolerance, interaction w/ alcohol, high abuse potential
66
New cards
Anxiolytics: Benzodiazepines mechanism
\-depressants
\-depressants
bind to non-NT site on GABAa receptors, enhance Cl- currents triggered by GABA \n \n -non competitive agonist, increase GABA signaling
67
New cards
Alcohol side effect \n -depressants
\-addiction \n -tolerance \n -physical dependence
68
New cards
alcohol mechanism
agonist (activates) GABA receptors (also, DA, opioid, & NMDA receptors
69
New cards
Some structural effects of alcoholism are...
reversible since studies show improvements in MRI scans after one month of no alcohol
70
New cards
Opioid side effects
\n AKA opiate \n -euphoria \n -tolerance \n -physical dependence \n -cross tolerance \n -respiratory depression \n -constipation \n -high abuse potential
71
New cards
Opioid mainly acts on...
reward areas of the brain (nucleus accumbens)
72
New cards
endogenous opioids in brain?
endorphins, enkephalins, dynorphins
73
New cards
Heroin \n -opioids
\-structurally similar to morphine (convert to morphine in brain) \n -produces euphoria, highly addictive
74
New cards
Heroin mechanism \n -opioids
\-(agonist) acts on μ-opioid receptors in VTA (ventral tegmental area) & nucleus accumbens, parts of mesocorticolimbic DA pathway involved in reward/reinforcement \n \n -activates μ-opioid receptors hyperpolarizes (Cl- in) GABAergic neurons & inhibits GABA release onto DA neurons=increase DA in VTA (inhibits inhibition)
75
New cards
Nalaxone
opioid antagonist that rapidly reverses overdose
76
New cards
Cannabinoids: cannabis effectiveness
therapeutic uses: anxiety, pain (chronic>acute), chemotherapy side effects, glaucoma, epilepsy, MS (multiple sclerosis), spasticity
77
New cards
Cannabinoids: cannabis side effects
feelings of relaxation, hunger, sometimes paranoia
78
New cards
Cannabinoids: cannabis mechanism
agonist at CB1 & CB2 cannabinoid receptors (GPCRs)
79
New cards
stimulants: nicotine side effects
increase alertness, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion
80
New cards
stimulants: nicotine
mildly neuroprotective in Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, MCI (mild cognitive impairment)
81
New cards
stimulants: nicotine mechanism
agonist at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChRs) in CNS & autonomic ganglia (higher bind affinity AChR>ACh) \n \n -activates DA in VTA (reward)
82
New cards
stimulants: Caffeine side effects
increase blood pressure, tolerance, physical dependence
83
New cards
stimulants: caffeine mechanism
\n adenosine receptor (AR) antagonist on pre-synaptic terminals \n \n -adenosine=drowsy \n -activated AR inhibit monoamine & ACh (acetylcholine)
84
New cards
Stimulant: Amphetamines
increase alertness, motivation, endurance, euphoria \n -longterm lead to schizoid behavior
85
New cards
Stimulant: Amphetamines side effects
increased blood pressure, tolerance, physical dependence
86
New cards
Stimulant: Amphetamines mechanism
Increase DA & NE, levels at the synapse (by acting w/in axon terminals) and decreasing reuptake \n \n -DAT reverse transport send NT out instead of back
87
New cards
Stimulants: Cocaine
creates euphoric state, increases endurance
88
New cards
Stimulants: Cocaine side effects
long term use lead to psychosis, neurodegeneration, altered brain activity
89
New cards
Stimulants: cocaine mechanism
\-DAT (transporter) antagonist \n -blocks monoamine NT reuptake (especially DA)
90
New cards
Empathogen: MDMA
promising treatment for PTSD
91
New cards
Empathogen: MDMA side effects
\-social, empathic, visual, euphoric (pos) \n -neurotoxic to thermoregulatory systems (risk of hyperthermia; neg)
92
New cards
Empathogen: MDMA mechanism
\-agonist at 5-HT2a receptors, 5-HT1B & SERT (transporter) \n -inc release of DA, NE, 5-HT, oxytocin
93
New cards
psychedelics: LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) side effect
\-distorts visual perception, induces feeling of creativity \n -may cause long term changes in mood/personality
94
New cards
psychedelics: LSD mechanism
agonist at 5-HT2a receptor which is highly expressed in visual cortex
95
New cards
Dissociative: PCP and Ketamine
developed as anesthetics in 1960s \n -used in vet clinics & children in hospitals
96
New cards
Dissociative: PCP and ketamine side effects
produce dreamlike state, detachment from reality, separation between consciousness & sensory inputs
97
New cards
Dissociative: PCP (phencyclidine; aka angel dust)mechanism
antagonist of NMDA receptor-type glutamate receptors, inhibits DA reuptake \n \n -induces depersonalization, schizoid behaviors, hallucinations, aggressions
98
New cards
Dissociative: Ketamine (Special K) mechanism
competitive antagonist of NMDA receptor-type glutamate receptors, inhibits DA reuptake \n \n -medical use: anesthetic, pain killer, rapid long-lasting antidepressant (one dose lasts for weeks)
99
New cards
Reward circuitry:dopamine
\-DA=key NT affected by addictive drugs \n -DA released from VTA neurons into nucleus accumbens
100
New cards
Reward circuitry:
drugs like stimulants, opioids, etc directly or indirectly activate mesocorticolimbic neural circuit that mediates reward & pleasure