Nucleic Acids and Nucleotides
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are Nucleic acids?
Are large molecules found in the nucleus. There two types, DNA and RNA
What is a nucleotide ?
Acts as the basic building blocks for Nucleic acids
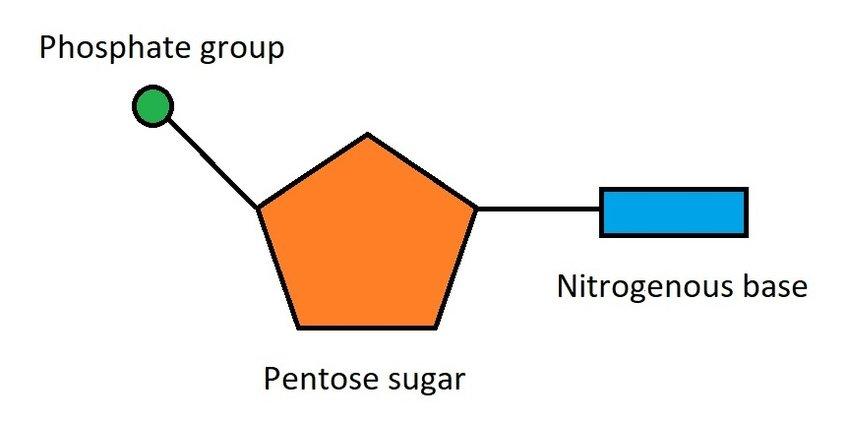
what are the three sections within a nucleotide ?
Phosphate group, Pentose/sugar, Base
what is the name of the bond that forms between
Polydiester bonds
what is the name of the polymer of a nucleic acid
polynucliatide
what does DNA stand for
Deoxyribose nucleic Acid
what is the difference between Deoxyribose and Ribose?
what does Pyrimidines mean ?
smaller carbon rings bases. Thymine and Cytosine
what does Purines mean ?
larger, carbon rings , Adenine and guanine
what are DNA ligase
they are enzmyes that catalyse the formation of phosphodiester bonds. It joins together shorter polynucloetide strands
what does complimentary base pairing mean? Give examples
hydrogen bonds will form between two bases. This will only happen if the bases are complimentary. For example A and T, G and C, and in RNA A and U
how many bonds form between each complimentary base?
A and T two bonds
g and c three bonds
a and u two bonds
what are the three types of RNA
mRNA: messenger rna
tRNA: transfer RNA
rRNA: ribosomal RNA
What is tRNA
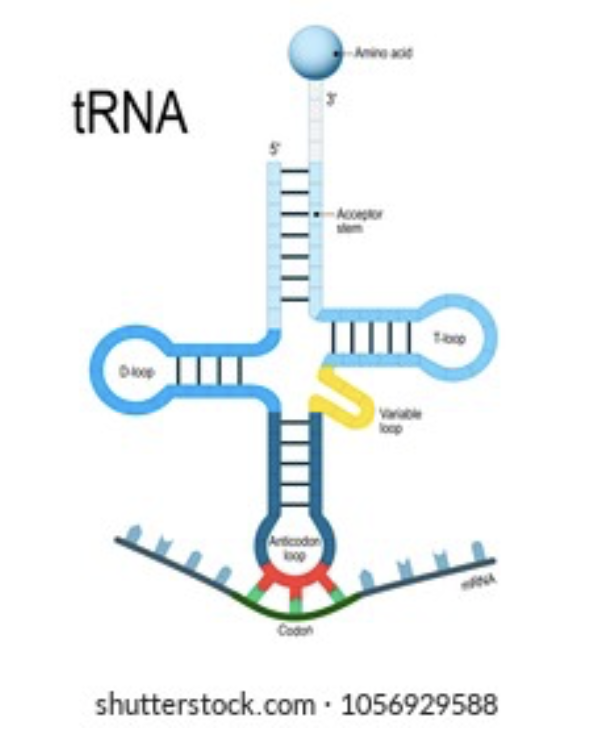
red = anti condonds, which bind to complimentary bases in mrna
circle = amino group
what does a nucleotide look like ?
what does nucliotides bonding look like ?

what is the difference between Deoxyribose and ribose

ribose as one more oxygen
Explain how DNA replication works
1- DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complimentary bases, unzipping the DNA, causing the two polynucleotides to move away from each other
2- then free DNA nucleotides line up with their complimentary bases, hydrogen bonds form but not phosophidester bonds
3- DNA polymerase then catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds, condensation reaction
semi conservative replication
Why is DNA replication described as semi conservative?
Strands from original DNA molecule act as templates. New DNA strands contain one old and one new strand
What is the role of DNA helicase in dna replication
Brakes the hydrogen bonds between bases
What is a mutation
An alteration to the DNA base sequence, usually that arise during DNA replication
Explain how transcription works?
1- DNA helicase catalyse the separation of the DNA strands, by braking the hydrogen bonds between the complimentary bases
2- free RNA nucleotides are attracted to their complimentary bases on the exposed DNA strand ( adenine bonds with uracil in RNA), temporary hydrogen bonds
3- RNA polymerase catalyse the formation of phosphodieseter bonds
4-the non coding strand then leaves through the nuclear pores
What is a codon ?
Three bases that will code for a specific amino acid
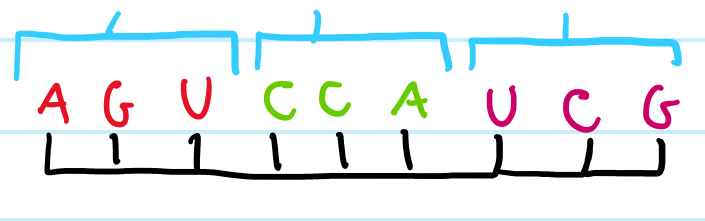
Explain what happens during translation
1- ribosomes moves along mRNA
2- tRNA anticodons attach to mRNA codons forming temporary hydrogen bonds
3- condensation reaction occurs between the amino acids on the tRNA forming peptide bonds
4- tRNA will then leave, leaving behind its amino group
5- this chain will increase, until it reaches the stop codon, the chain will then fold up on itself to make a protein
What catalyses the forming of phosphodiester bonds
DNA/RNA polymerase
what is ATP
adenosine triphosphate, nucleotide derivative, adenine as base and has 3 phosphate groups
what is ATP hydrolase
energy released when ATP is hydrolysed to from ADP and a phosphate group
how is the structure of guanine different from adenine
has a c=o
how to tell the difference between CUT
c has only one c=o
t has a methyl group