AP Bio - Cell Signaling
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Paracrine Signaling
A form of cell communication where a cell produces signals to its nearby cells at affect their behavior and functions. (Local Signaling)
Receptor
Chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and responds to signals from other cells or the environment.
Direct Contact in Plants
Plasmodesmata
Direct Contact in Animals
Gap Junctions
Endocrine Signaling
Long distance signaling (blood stream)
Direct Signaling
Cells communicate through physical contact, often via cell junctions such as gap junctions in plants or intercellular junctions in animals.
Autocrine Signaling
A form of cell communication where a cell releases chemical messengers that bind to receptors on its own surface
Ligands
molecule that binds to the receptor
Signal Transduction
when the ligand-proteins changes its shape and somehow starts to catalyze a reaction which leads to a response
Signal perception
when the ligands latches to the receptor
Quorum Signaling in bacteria
Bacterial quorum sensing is a system of chemical communication where bacteria release and detect signaling molecules to sense their population density, allowing them to coordinate group behaviors.
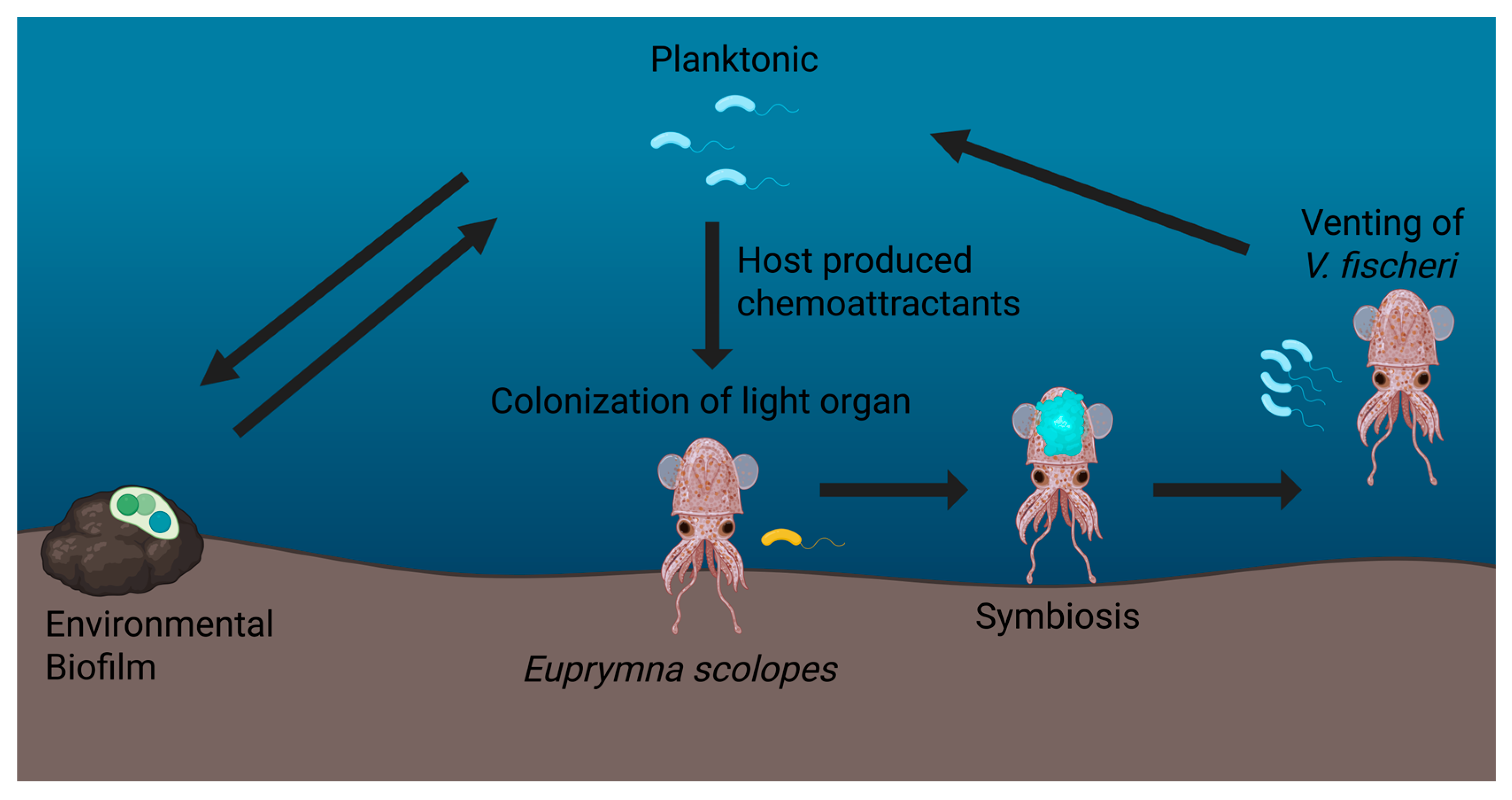
Quorum sensing in Alii vibrio fishery
Alii vibrio fishery uses quorum sensing to coordinate bioluminescence and host colonization.
Hormones
Hormones are chemical messengers that coordinate bodily functions by traveling through the bloodstream to tissues and organs, signaling cells what to do and when to do.
Hormone secreted by the Pituitary Gland
Thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH)
Hormone secreted by the Thyroid Gland
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)
Membrane Receptor
Integral proteins (receptors) which is embedded in the cell membrane
Induced fit
describes how an enzyme's active site isn't rigid but conformationally adapts upon binding with a substrate, creating a optimal fit to facilitate catalysis.
Intracellular receptors
receptor proteins found on the inside of the cell, typically in the cytoplasm or nucleus (hydrophobic in most cases)
Cell Surface receptor
they are proteins embedded in a cell's membrane that receive external signals and convert them into internal cellular responses
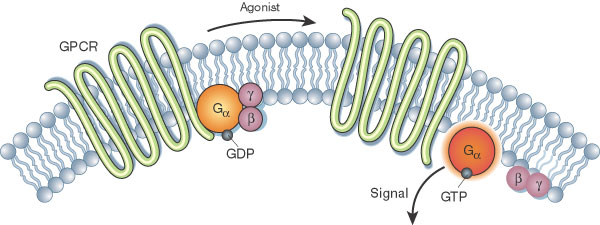
GPCR
G-Protein Coupled Receptors bind extracellular ligands and activate a G-protein by causing GDP to be replaced with GTP. The activated G protein then triggers intracellular signaling pathways, often using second messengers, to produce a cellular response.
Kinases
Adds phosphate group
Phosphatase
Removes phosphate group
cAMP
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate is a crucial second messenger molecule which acts as a temporary "on/off" switch in intracellular signal transduction.
GDP and GTP
Guanosine Diphosphate and Guanosine Triphosphate
MAP-K
Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase