Unit 1 : (1.3) Aquatic Biomes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
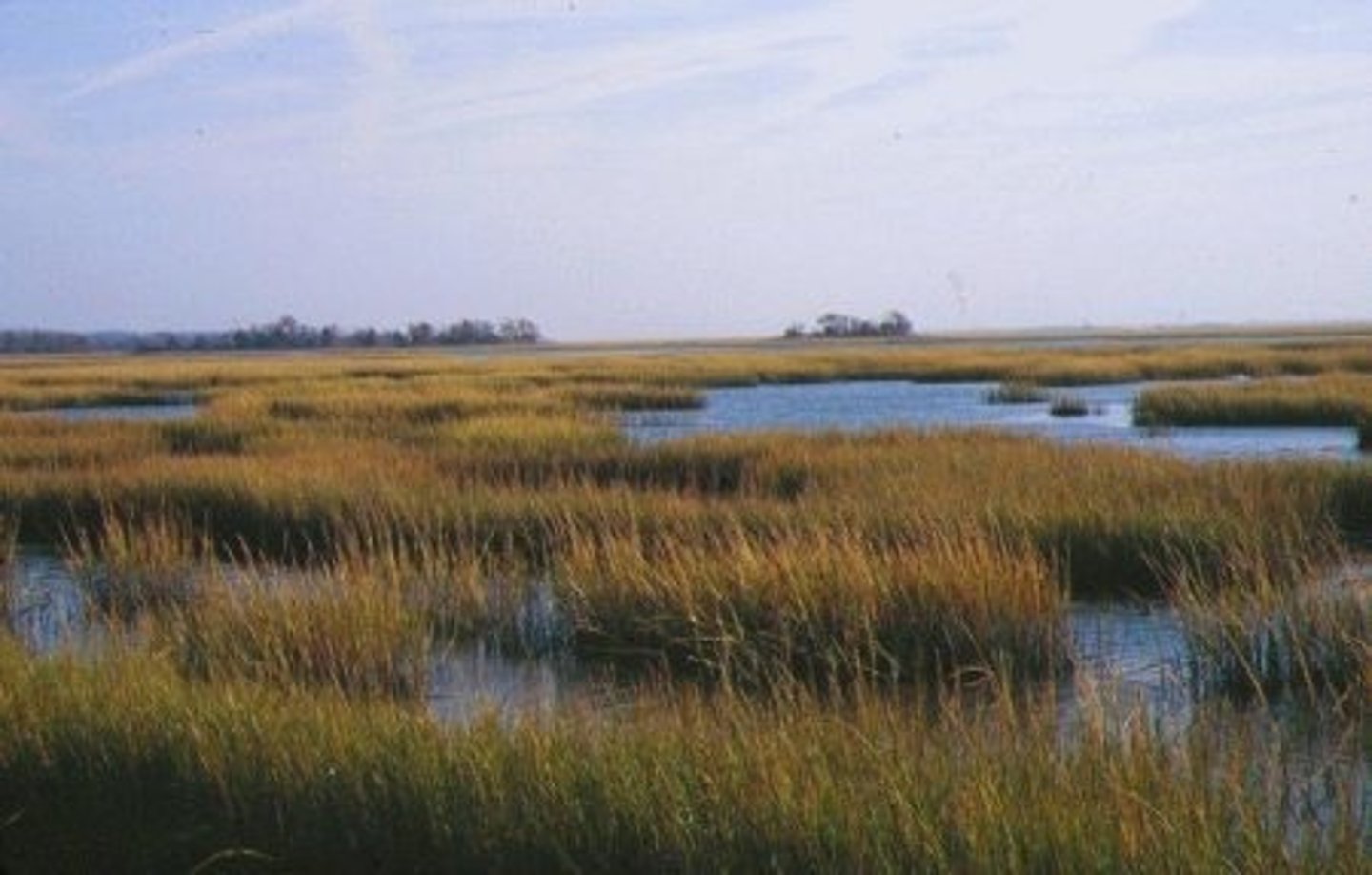
Salt Marsh
An estuary marsh, found along the coast in temperate climates. Mix of fresh and salt water. Highly productive breeding grounds for many fish and shellfish species.

Aquatic
relating to water
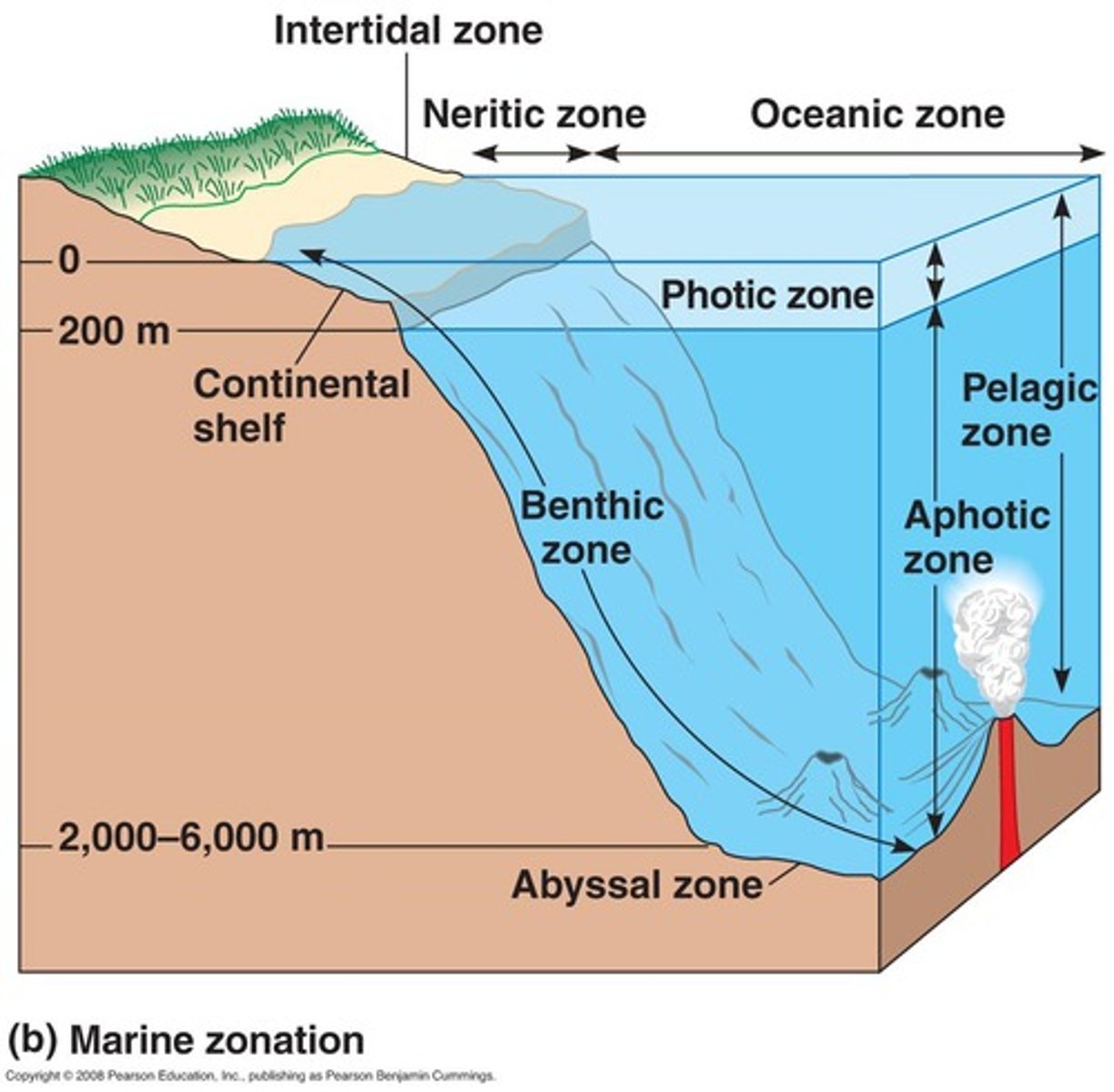
benthic zone
bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms
Open Ocean
Deep, salty aquatic biome. Largest boime on earth. Algae in this biome produce a significant portion of earth's oxygen via photosynthesis
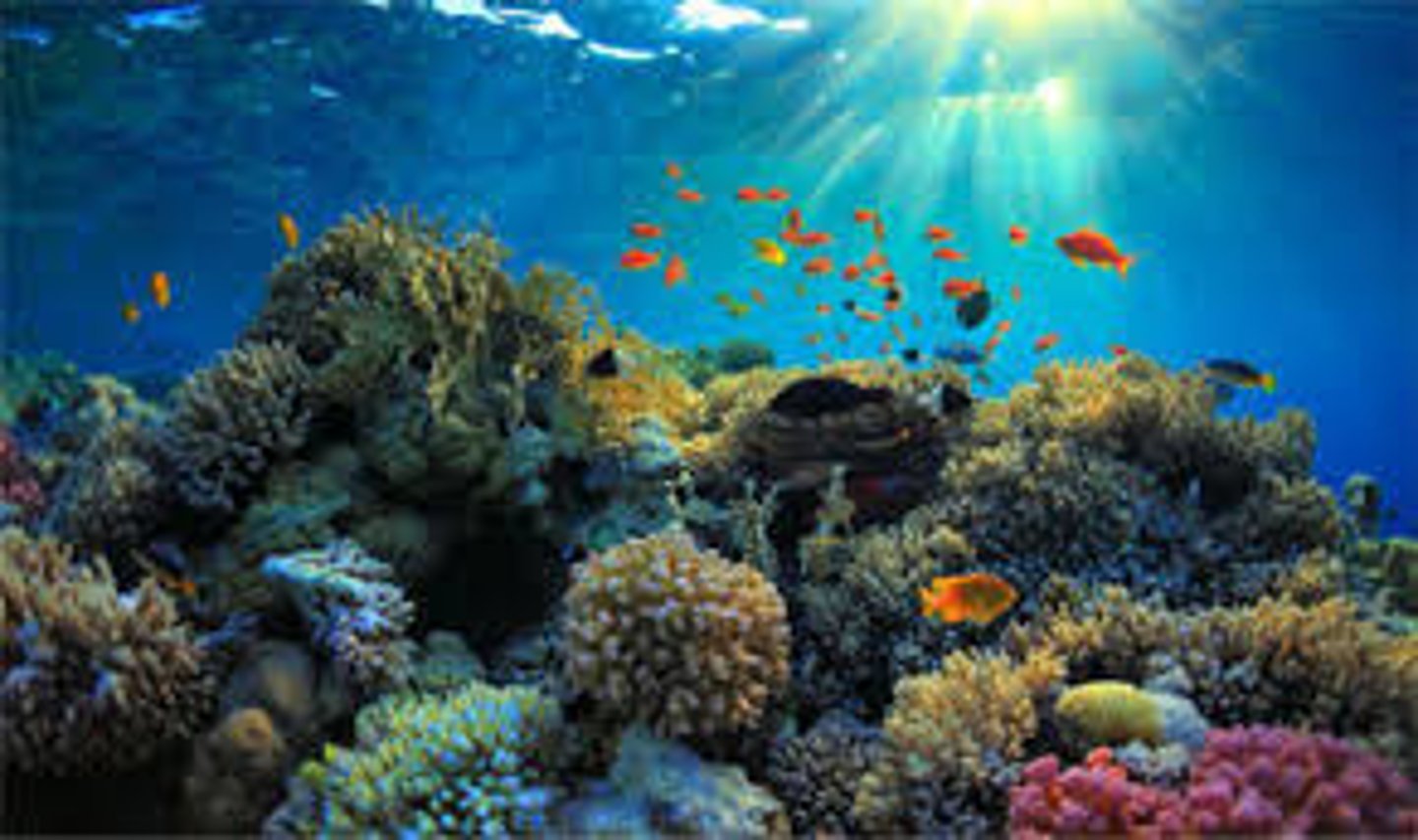
Coral reef
Shallow, warm, ocean biome featuring the symbiotic relationship between coral and algae. Coral supply the calcium-carbonate reef for algae to live in, as well as nutrients and CO2. The algae use nutrients and CO2 for photosynthesis and release sugar for the coral to use as energy.

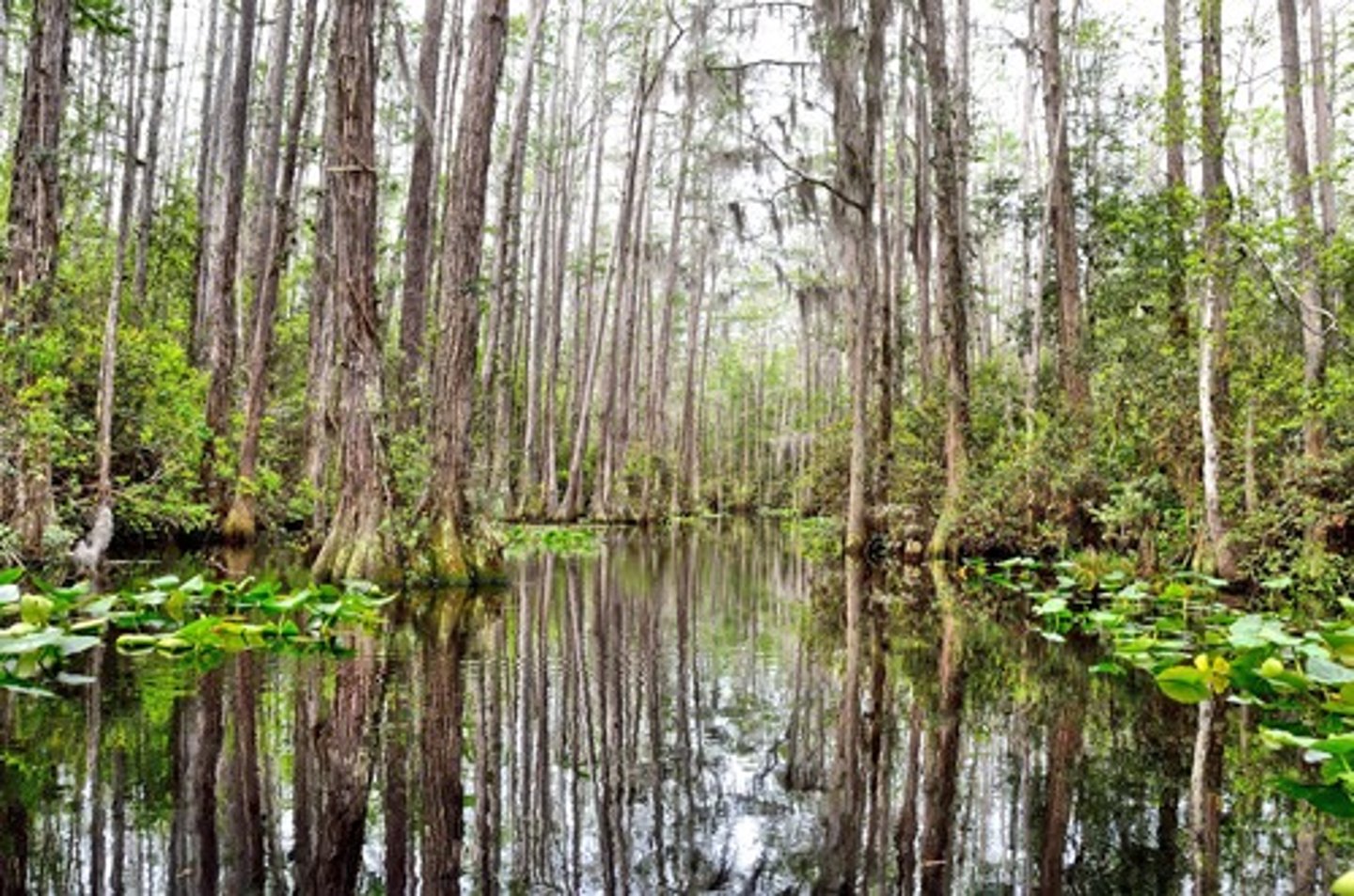
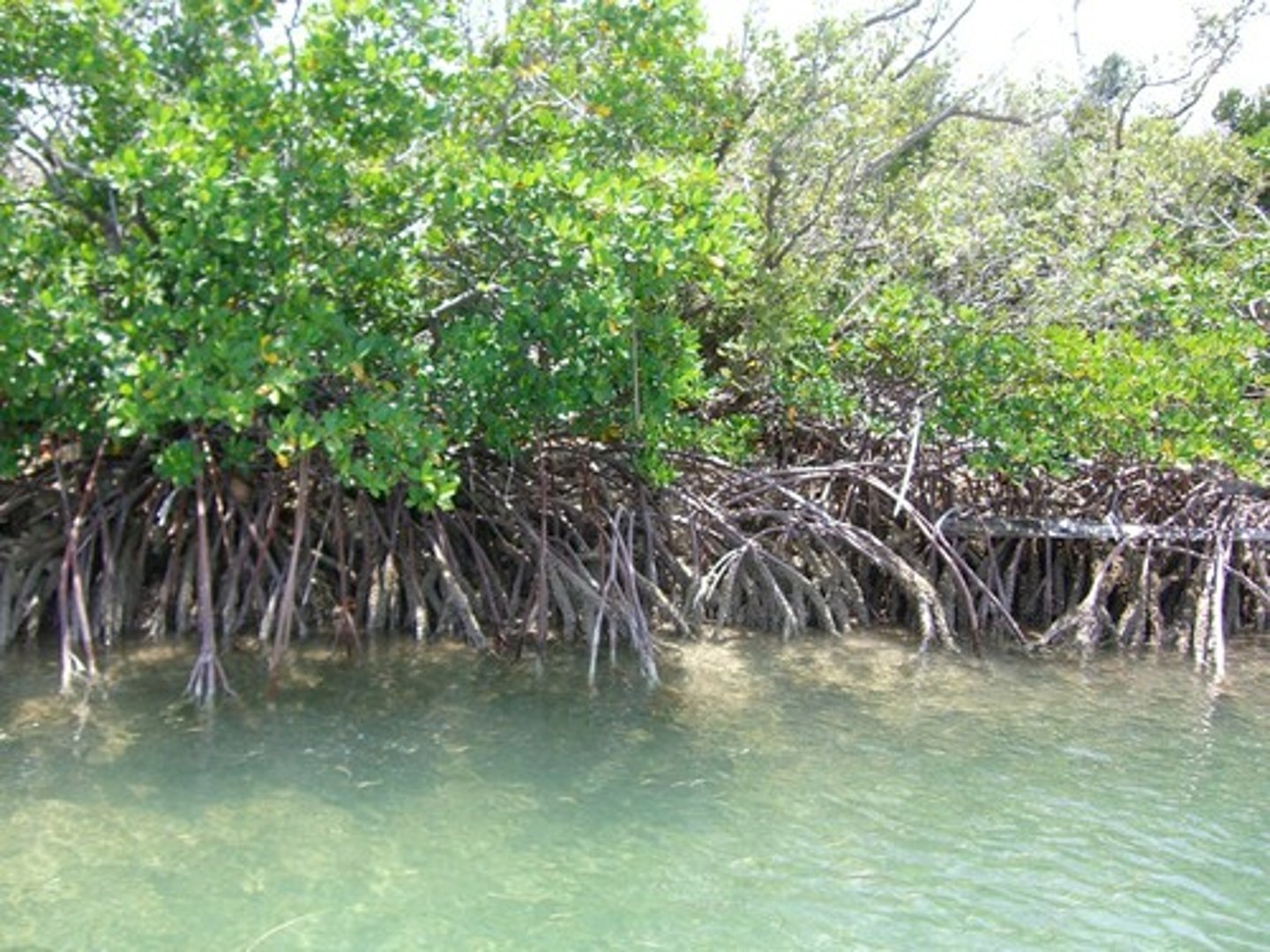
Mangrove swamps
A swamp biome that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts, and contains salt-tolerant trees with roots submerged in water. Roots provide organic matter and habitat for many fish & shellfish species as well as stabilizing the shoreline from erosion.

Estuary
A habitat in which the fresh water of a river meets the salt water of the ocean. High levels of organic matter term-50are deposited by the river, making them high nutrient, highly productive ecosystems.
Algae
a very simple plant without stems or leaves that grows in or near water.
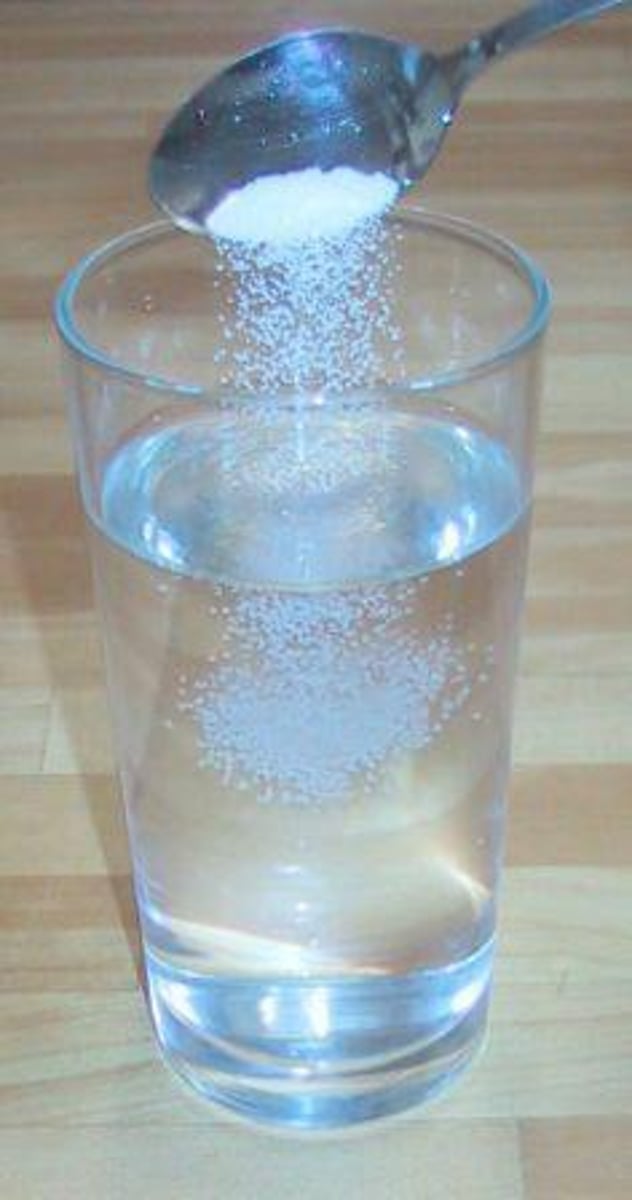
Salinity
A measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid.

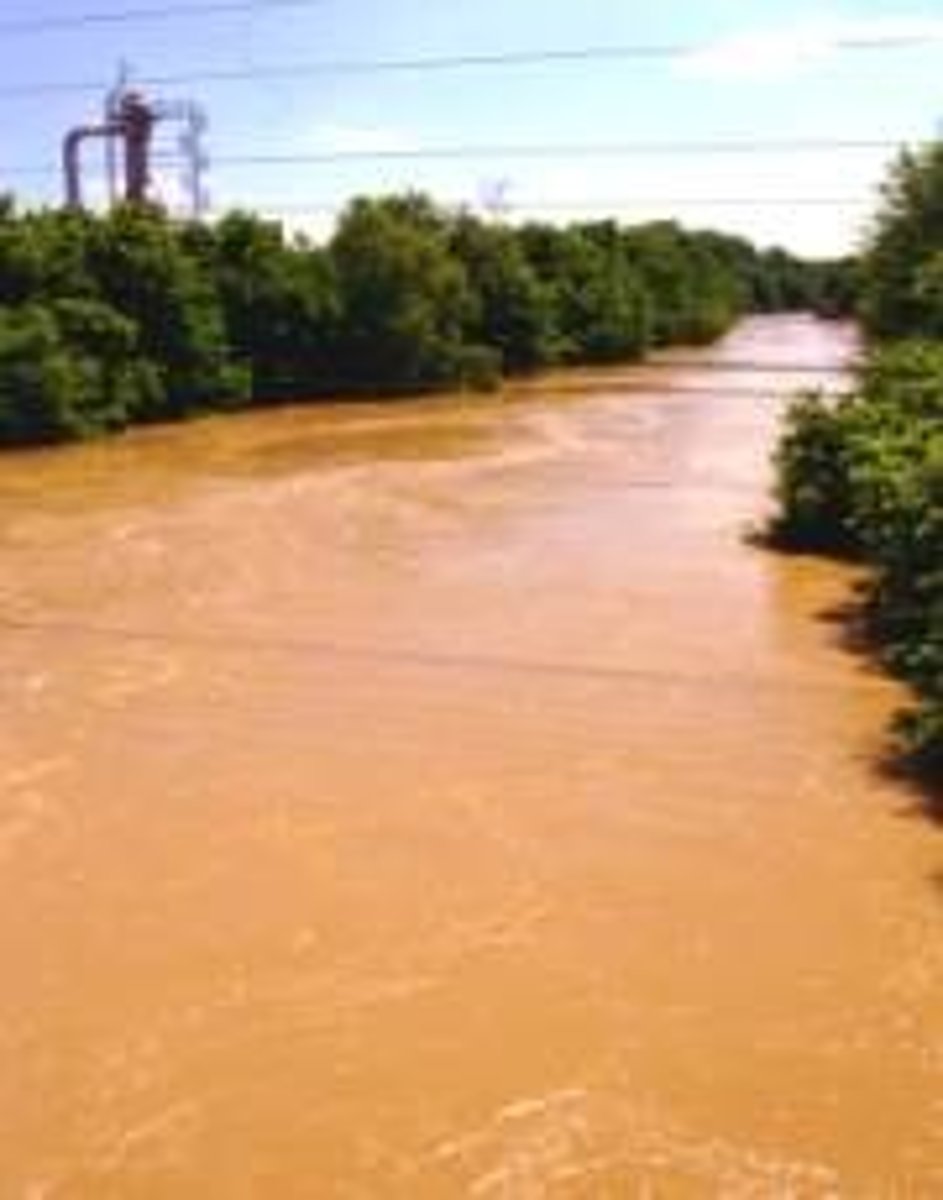
Turbidity
A measure of how cloudy water is (higher turbidity = more cloudy). Sediments like sand and leaf litter increase turbidity.

Freshwater Wetlands
An aquatic biome that is submerged or saturated by water for at least part of each year, but shallow enough to support emergent vegetation such as trees and cattails. Plants must have adaptations to allow them to survive water-logged soil.
