Physics Newton's Laws thru Atwood Machines
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Newton's 1st Law of Motion
An object at rest will stay at rest, amd an object in motion will stay in motion, at contant velocity and in a straight line, unless acted upon by a net force
Force
A push or pull on an object, measured in Newtons
Net force
The vector sum of all the forces acting on an object, if the forces are balanced there is no
Inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in velocity, is basically synonymous with mass
Free body diagram
Draw object as dot as origin of two axes, draw forces acting on object as vectors
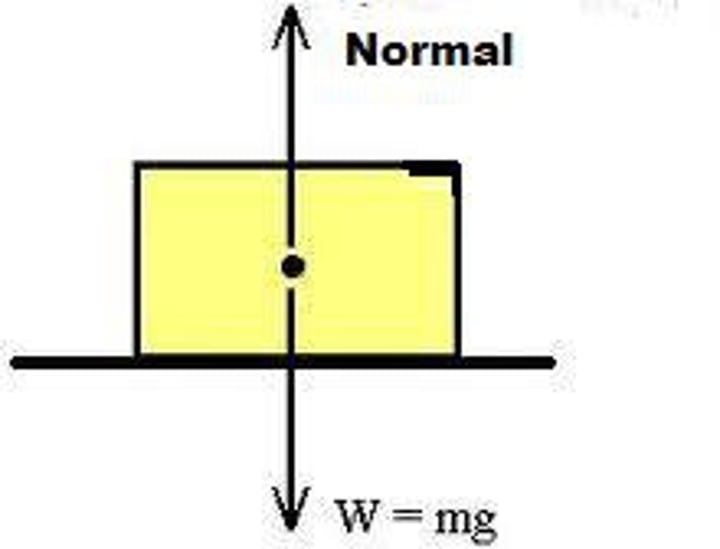
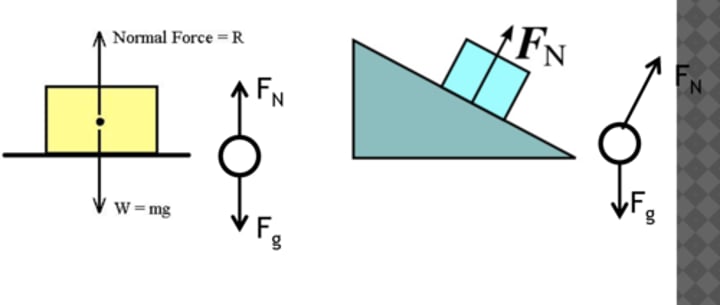
Normal Force
Force coming perpendicularly out of a surface upon which an object is pressed
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion
The acceleration of an object is in the direction of and directly proportional to the net force applied, and inversely proportional to the object's mass
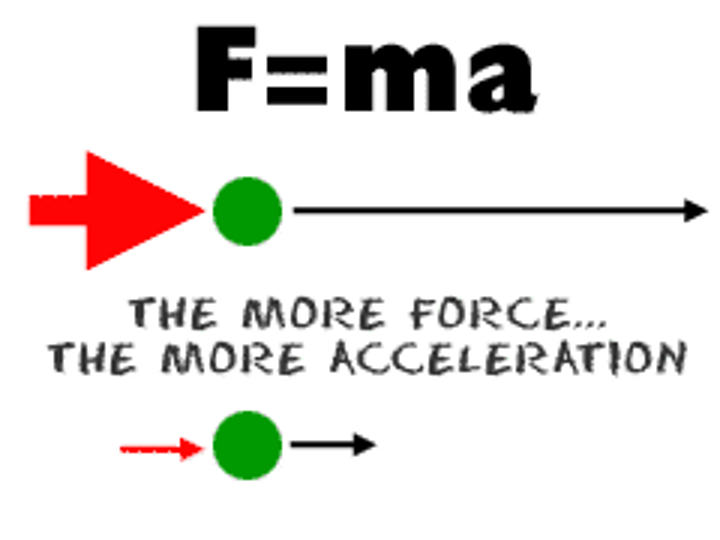
Fnet = ma
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion equation net force
mg =Fg
Equation for weight
Newtons
Unit for weight
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
All forces come in pairs. If Object 1 exerts a force on Object 2, then Object 2 must exert a force back on Object 1 that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
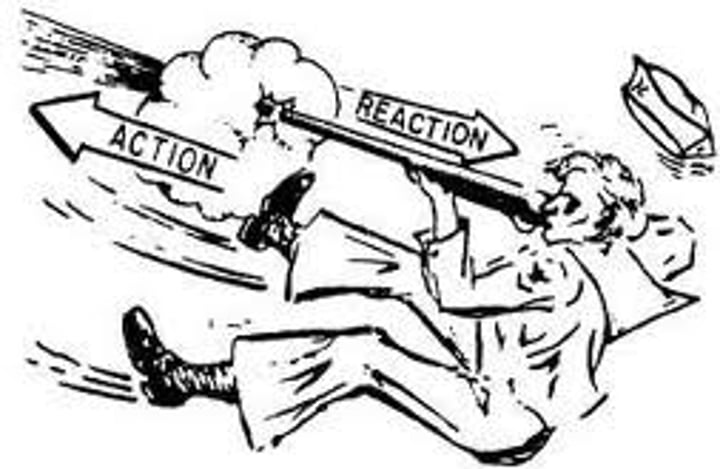
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
Friction
Force that opposes motion, its magnitude is determined by the nature of the surfaces and the normal force, kinetic is less than static
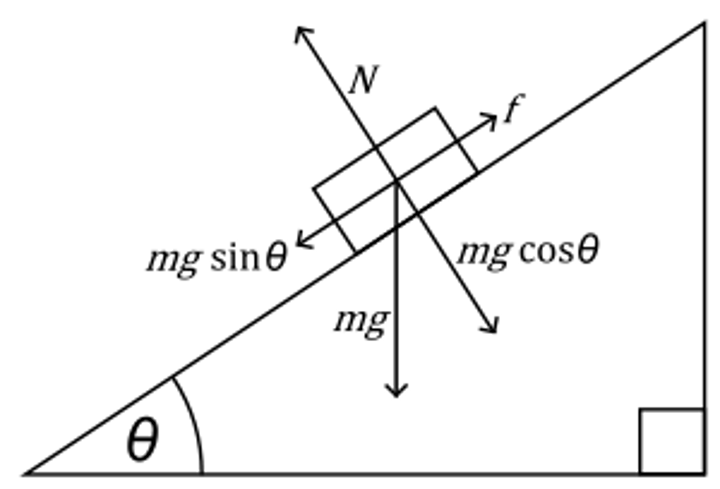
mgy = mgscosø
Y component of mg in incline problems
Atwood machine
Experimental device in which 2 object's of masses m1 and m2 are connected by a massless string over a massless pulley, pulley is frictionless, tension on string is constant
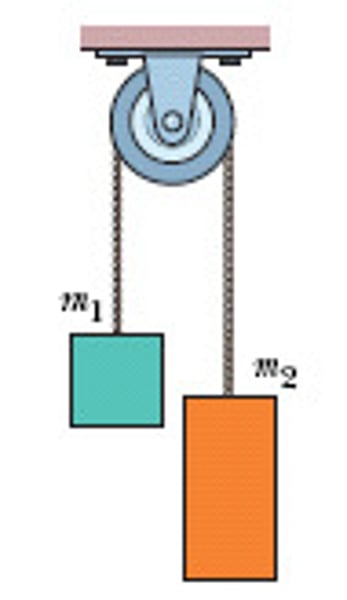
a = g (m1 - m2)/(m1 + m2)
Equation for acceleration in Atwood Machine problems
mgx = mg sinø
x component of mg in ramp problem down the ramp
3.26 m/s2
An Ideal pulley has a 4kg block resting on a frictionless table attached to a 2 kg block. What will the acceleration of the two block be when released?
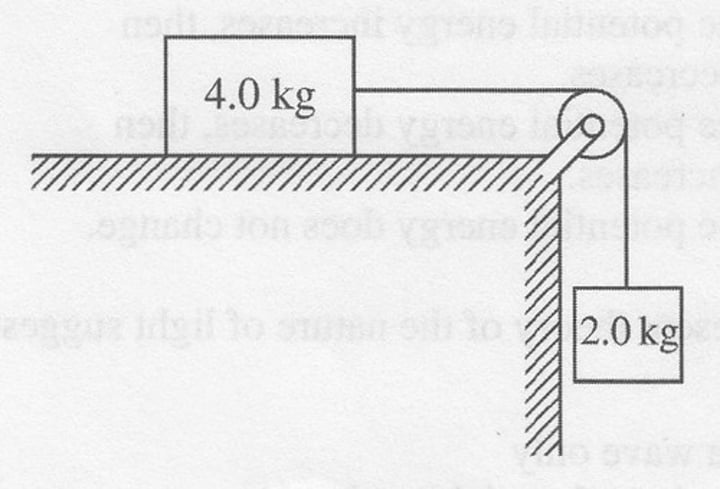
3.26 m/s2
If the larger mass of 10 kg is released what will the acceleration of the masses be if the lighter mass is 5kg?
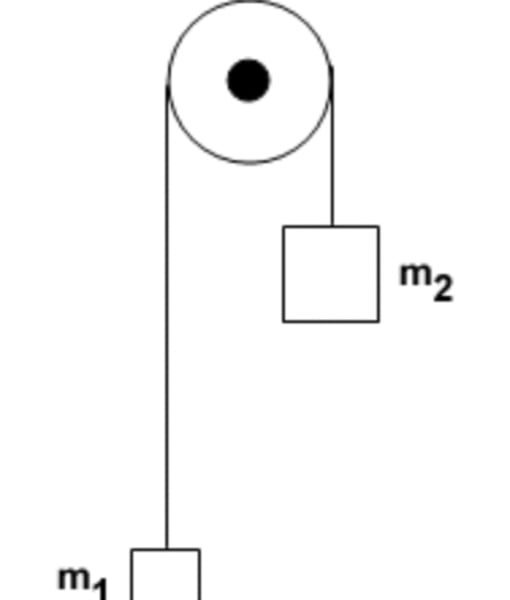
ideal string
String that has no mass can only pull and does not streatch
ideal pulley
Frictionless pulley
mgsinθ
The Fnet down the incline
m1gm-m2gsinθ / m1 +m2
Equationn acceleration for an incline atwood machine
Normal force times coeffieient of kinetic friciton
Equation for kinetic friction
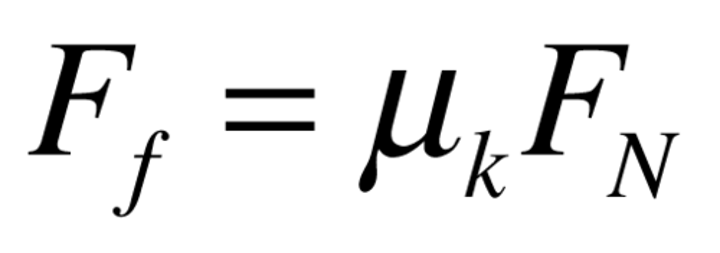
normal force
force opposite of the weight and perpendicular. to the surface
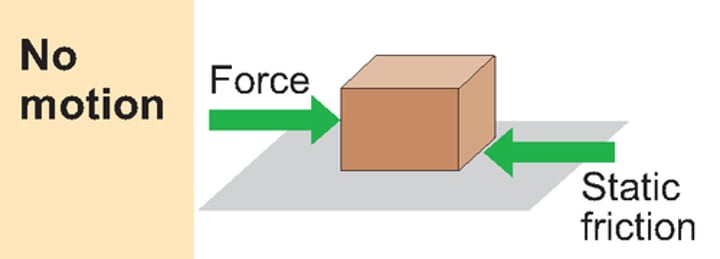
static friction
the force that resists the initiation of sliding motion between two surfaces that are in contact and at rest
kinetic friction
Friction between moving surfaces