Lecture 4: The Eye and the Retina
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
finished 9/8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is the role of the retina in visual perception?
it is the neural portion of the eye, part of the central nervous system
What are the different cells in the retina and what are their roles?
photoreceptors (rods/cones) - detect light, send signal
bipolar cells - transmit signals from the photoreceptors to the ganglion cells
ganglion cells - receive and process visual info from photoreceptors
horizontal cells - modulate the output of photoreceptors, generate surround antagonism
amacrine cells - interneurons
What is the difference between rods and cones in the retina?
rods detect light (more sensitive), cones detect color
Explain the role of glutamate and GABA for horizontal cells and cone cells
glutamate depolarizes horizontal cells (results in the release of GABA to hyperpolarize photoreceptors).
Describe each of the three tissue layers of the eye
Retina - neural portion of the eye that is part of the CNS
Uveal layer - contains the choroid, ciliary body, and iris
Sclera - tough white fibrous tissue
What is the choroid?
contains capillaries and melanin
What are the ciliary bodies?
muscles to adjust the lens
what is the iris?
colored portion with muscles that regulate size of the pupil
What are the two distinct fluid environments of the eye?
Aqueous humor and vitreous humor
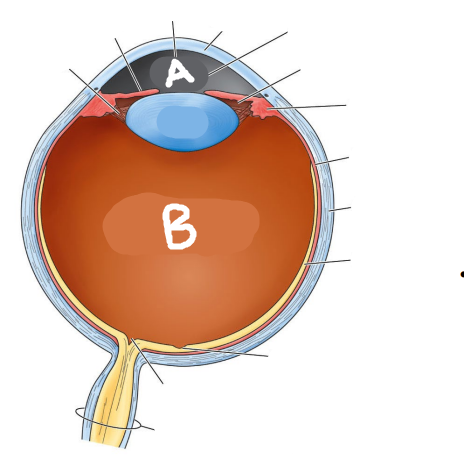
Which is the aqueous humor?
A
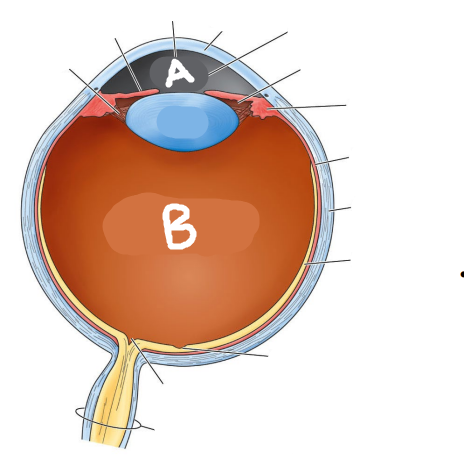
Which is the vitreous humor?
B
The image seen on the retina is
upside down and curved
the lens of the eye is flat to view ___ and round to view ___
distant objects, near objects
dynamic changes in the shape of the lens are called
accommodation
myopia
nearsightedness. images come to focus before the retina
hyperopia
farsightedness. image doesnt come to focus by the time it hits the retina.
emmetropia
normal vision. image comes to focus at the retina.
What are the two visual structures of the retina? describe them.
The macula lutea - dark spot towards center of the retina. region with highest visual acuity, fovea in center.
optic disk - light spot towards the side of the retina. no photoreceptors, where blood vessels enter and retinal axons leave. forms a blind spot
what is macular degeneration?
progressive loss of vision in the center of the visual field (the macula)
What are the five basic classes of neurons in retinal circuitry?
photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, amacrine cells.
Describe the general order of light processing in the eye
light goes to the back of the retina, then works forward. photoreceptors, bipolar/horizontal cells, amacrine cells, ganglion cells.
photoreceptor disk life span
limited, about 12 days
light stimulation ___ photoreceptors
hyperpolarizes
what is the dark current?
in the dark, photoreceptors are in a depolarized state. in the outer segment, there are high cGMP levels. cGMP binds to sodium permeable channels in the membrane allowing sodium/other cations to enter. the inward depolarization current through cGMP-gated channels is “the dark current”
how does light affect cGMP?
light reduces cGMP in the outer segment of photoreceptors. this reduces sodium and calcium flow inward and causes hyperpolarization from inner segment to dominate.
how do rods and cones differ in terms of bipolar cell access?
Cones are connected 1:1 to bipolar cells (increases spatial resolution). 15-30 rods connected to 1 bipolar cell (increases light sensitivity)
(cones/rods) have a high density throughout the retina, except for at the fovea
rods
(cones/rods) have low density throughout the retina with a sharp peak in the center of the fovea
cones
describe the three kinds of cones humans have
L - long wavelengths (red)
M - medium wavelength (green)
S - short wavelengths (blue) (least abundant)
protanopia
loss of long wavelength → red-green color blindness
deuteranopia
loss of medium wavelength perception → red-green color blindness
tritanopia
loss of short wavelength perception → blue-yellow color blindness (rare)
on-center ganglion cells increase firing when
light increases in their receptive field center
off-center ganglion cells increase firing when
light decreases in their receptive field center
why do on and off center bipolar cells have selective responses?
different glutamate receptors. on center cells have mGluR6 receptors that close sodium channels (results in hyperpolarization of cell). off center cells have ionotropic AMPA and kainate receptors that cause cell to depolarize.
Describe surround antagonism
Horizontal cell inputs oppose changes in the photoreceptor that are induced by light events in the surround area