General Chemistry
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Rutherford’s Model of an Atom
The [... Model] states that an atom is mostly empty space, with electrons orbiting a fixed, positively charged nucleus.
Atomic weight is
the weighted average of the masses of an element's isotopes.
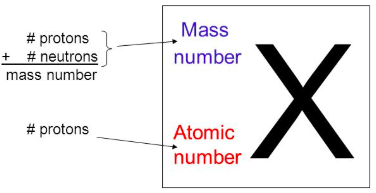
In element notation, Z is the [...]
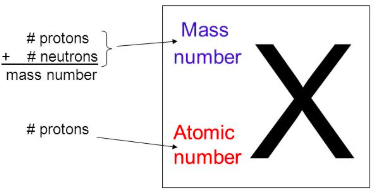
In element notation, A is the [...]
According to the Bohr Model
electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that have a set size and energy.
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that
it is impossible to know the momentum and position of an electron simultaneously.
Hunds rule
states that all orbitals must first have one electron before any orbital can obtain a second electron.
Grandma Hund was like, "don't be greedy now kids!"
Pauli Exclusion Principle
states that no two electrons can share the same four identical quantum numbers.
That means, for paired electrons, one must be +1/2 spin and the other -1/2 spin
Avogadro’s Number = [...]
6.022 × 1023 = 1 mol
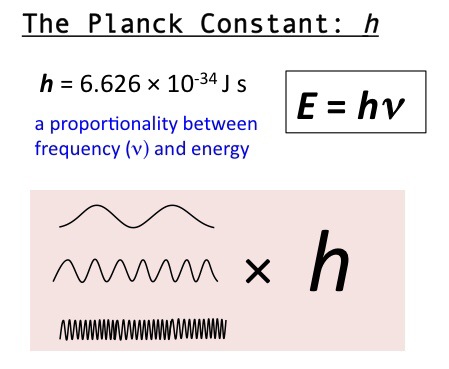
Planck’s Constant (h)
h=6.626 × 10^-34
E=hv
proportionality between frequency (v) and energy
Speed of Light (c)
3.0 × 10 ^8 m/s

Paramagnetic materials
are pulled into external magnetic field.pulled into
Contain one or more unpaired electrons with spin ↑
He atom is paramagnetic or diamagnetic
diamagnetic
Li is paramagnetic or diamagnetic
paramagnetic
azimuthal, 3D shape
Quantum number l is the___quantum number and gives the ——- (subshell)of an orbital
m1 , orbital sub type
Quantum number ___ is the magnetic quantum number and gives the ____
ms , electronic spin
Quantum number is the ____quantum number and gives the ___ of the electron
n , principal , energy level , shell number
Quantum number __ is the ____ quantum number and gives the electron ___ or ____
energy level , principal , 2n²
The maximum number of electrons in a single ___ in terms of ___ quantum number = [...]
What is the maximum number of electrons that can be in the second energy level?
2n2 = 2(22) = 8 electrons
subshell, azithum
The maximum number of electrons in a single___in terms of the___quantum number = 4l+2
s 2
p 6
d 10
p 14
free radical, unpaired electron
A/an ____ is an atom or molecule with an
Aufbau principle
.
The______states that electrons will fill the lower energy levels before moving to higher energy orbitals.
Give the Arrhenius equation:
K=A x e -Ea/RT
You can use the Arrhenius equation to show the effect of a change of temperature on the rate constant and therefore on the rate of the reaction
k = rate constant
A = frequency factor
Ea = activation energy
R = gas constant
T = temperature in K
K number of molecular collisons per second
A number of molecular collisions per second with proper orientation
e-Ea /RT probability of succesful collisons
absorbed
If an electron moves to a farther orbital a photon is absorbed
f an electron moves to a farther orbital
different masses
Protons and electrons have different masses.
Protons and neutrons same mass
Electrons have smaller mass
Give the equation for the cell potential (electromotive force) of an electrochemical cell
E cell =Eredcathode - Ered anode
Zeff
is the attractive positive charge of nuclear protons acting on valence electrons.
Give the approximate electronegativity values of H,C,N,O and F
H - 2.0 C-2.5 N-3.0 O-3.5 F-4.0
Ionic bonds
are formed by the complete transfer of valence electron(s) between atoms.
Bond order
refers to the number of bonds between two atoms (single, double, or triple bond).
Higher the bond strenth the shorter the bond H-H 436 C--C 602 C- - -C 835
Coordinate Covalents
bonds are when a single atom provides both bonding electrons.
Covalent bond
is the sharing electrons between two elements
Cations
are ions with a positive charge.
more protons than electrons
Anions
are ions with a negative charge
more electrons than protons
Crystalline lattices
are large, organized arrays of ions.
solid carbon
the greater the number of bonds (bond order)
the higher the bond strength and the shorter the bond.
Hydrogen bonds are most often formed between hydrogen and the following elements
O, N and F.
Non-polar bonds have a △EN that is
less than 0.5.
Polar bonds have a △EN that is between
0.5 and 1.7.
Van der Waals Forces is a general term that includes ——— forces and ——- forces
dipole-dipole and london dispersion forces
Dipole-dipole
forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.
Place in order of strength: Highest frist —-then small last
hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole forces, and London dispersion forces
Strength Hydrogen Dipole-Dipole London Dispersion
Sigma
bonds are formed by head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals.
Pi
bonds are formed by lateral (side-by-side) overlap of atomic orbitals.
Give the formula for formal charge
Formal Charge
valence electrons − dots − sticks. dots - nonbonding sticks pairs of bonding electrons
The bond angle of an sp hybridized atom is
180
The bond angle of an sp2 hybridized atom is
120°
The bond angle of an sp3 hybridized atom is
109.5°
Bond angles of an sp3d hybridized atom are
90 and 120
The bond angle of an sp3d2 hybridized atom is
90°
An H2O molecule is a bent because
the lone pair of electrons repulse each other and push the H atoms away
Formal Charge
is the charge given to an individual element within a molecule.
Reaction order
is a number that relates the rate of a chemical reaction to the concentrations of the reacting substances
London dispersion
forces are temporary attractive forces created when a temporary dipole induces a dipole in a neighboring molecule.
The units for the rate constant of a first order reaction are
1/s
The units for the rate constant of a zeroth order reaction are
M/s
or a first order reaction:
Rate Law: [...]
Integrated Rate Law: [...]
R=k[A]
[A]=[A]0xe^-kt
For a zeroth order reaction:
Rate Law:
Integrated Rate Law:
R=K
[A]=[A]0 -kt
or a second order reaction:
Rate Law: [...]
Integrated Rate Law: [...]
R=k[A]2
1/[A] =1/[A]0+kt
Electronegativity
measure of how strongly atoms attract electrons.
s
The units for the rate constant of a second order reaction are
1/Ms
In decomposition reactions,
a single reactant breaks down.
A/an hydrolysis
uses water to break the bonds in a molecule.
A/an neutralization reaction
is when an acid and base react to form water and salt
Combustion reactions
are exothermic reactions in which something reacts with oxygen.
the reaction quotient (Qc)
is a measure of the relative amounts of products and reactants present in a reaction at a given time.
The units for the rate constant of a first order reaction are
1/s
You exclude pure solids and liquids in the reaction quotient and equilibrium constant because
heir effective concentrations stay constant throughout the reaction.
If Q < Keq, then the reaction will move to the
right
The reaction quotient (Qc)
is a measure of the relative amounts of products and reactants present in a reaction at a given time.
Exclude pure solids and liquids
If ∆G = O, the reaction will b
equilibrium
If ∆G < O, the reaction will be [...].
spontaneous.
Give the formula for the standard entropy of reaction
Srxn = Sf products-Sfreactants
If ∆G > O, the reaction will be
non-spontaneous
Le Châtelier’s Principle
states that if a stress is applied to a system, then system shifts to relieve that applied stress.
Ionic bonds have a △EN that is
greater than 1.7
The orbital hybridization of an atom with 3 electron groups is
sp2
The orbital hybridization of an atom with 2 electron groups is
sp
Room temperature is approximately
25°C aka 75°F
Deposition
is the phase change from gas to solid.
Give the formula for ∆H when using heat of formations
Hrxn=Hproducts - Hreactants
Body temperature is approximately
37°C aka 98.6°F
Phase changes from solid → liquid → gas are
endothermic.
Give the formula for ∆H when using bond dissociation energies
Hrxn=Hreactants-Hproducts
Enthalpy (H)
is a measure of the potential energy of a system found in intermolecular attractions and chemical bonds.
Gibbs Free Energy
combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value and is used to determine the spontaneity of a reaction
Sublimation
is the phase change from solid to gas.
If a reaction has a negative ∆H and negative ∆S,
then it will be spontaneous at low temperatures
G =H-TS
Give the Gibbs Free Energy equation that uses the equilibrium constant Keq
Grxn=-RT In(Keq)
Give the Gibbs Free Energy equations that use the reaction quotient Q
Grxn=RTIn (q/Keq)
Grxn=Grxn+RT In (Q)
phase changes from gas → liquid → solid are
exothermic
solution
is a special type of homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances.
Equilibrium Constant (Keq)
is the value of the reaction quotient at chemical equilibrium.
solvent
/an [...] is a liquid that dissolves a solid, liquid or gaseous solute