Chapter 2: Cognition
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Is it possible to create cognition?
Cognition is the study os us: how we think
Cognition uses measurement and observation to test hypothesis… claim, prediction
Cognition studies how animals work, not how they should work
WHY do we need Cognition?
Intuition overestimation
Hindsight bias
Overconfidence
Tendency to perceive patterns in random events
We cannot rely solely on intuition and common sense
leads us to overestimate our intuition
and make errors because we are error prone
Why is it a science?
Way of evaluating explanations
A way of making observations about the word
A way of interpreting observations about the world
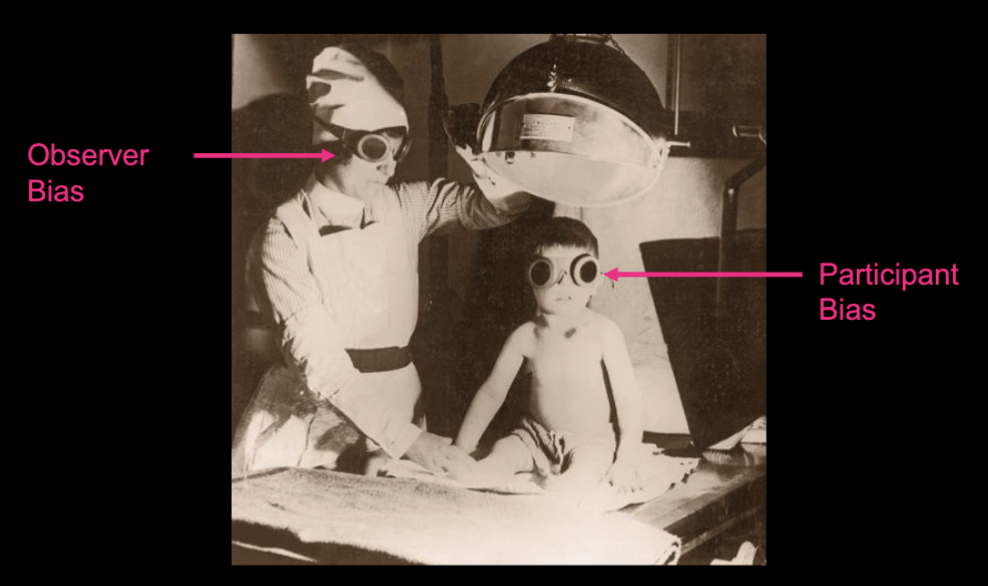
Clever Hans - Expectancy Effect
Mr. von Osten (math teacher)
Intellectual ability of his horse
Arithmetic
Add fractions, give values of german coins
Method: lifted foot once, twice
About Clever Hans and his Expectancy Effect
Horse “could do math”, he learned to read people’s body langauge (leaning in to look at his hoof and slight change in facial expression when the right answer was announced) and he would then lift his hoof
The art of looking
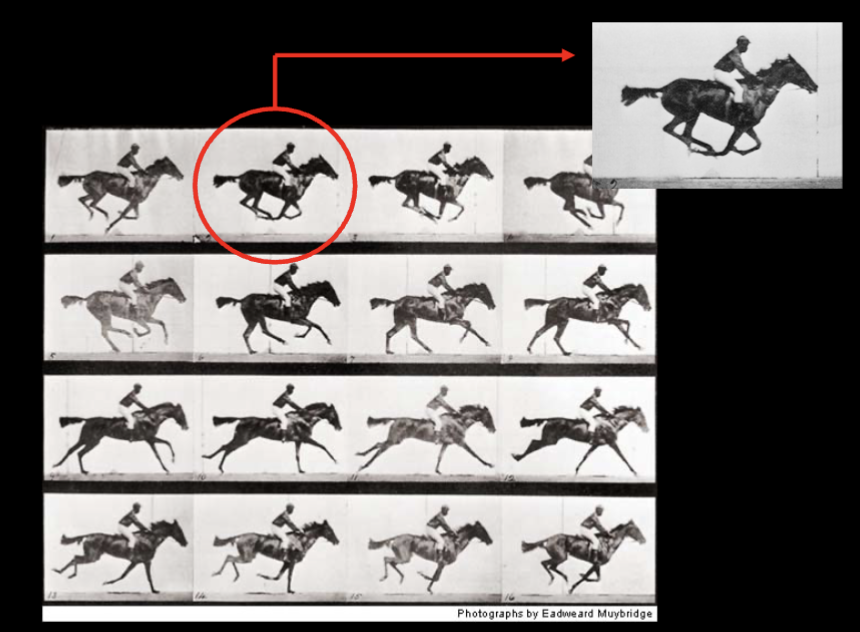
Horse race question
All 4 of a horse’s hooves are off the ground at the same time during a gallop
Painting showed the front and rear legs extended and backwards
To prove scientifically…
Cali governor Stanford hired Muybridge to photograph a horse in fast motion (1878)
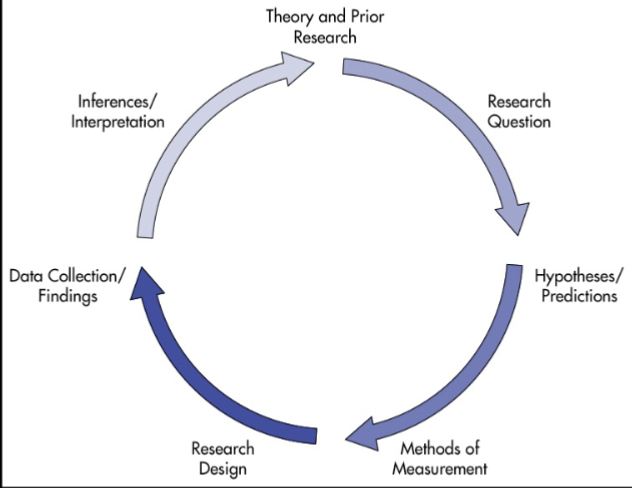
The Scientific Method
The process of testing ideas about the world
Setting up situations that test our ideas
if the data don’t fit our ideas, then our ideas are modified and tested again
Making careful, organized observations
Analyzing whether the data fit our ideas
How do we support claims scientifically?
Seek evidence to support or disprove a claim
Scientific word for a claim is..
HYPOTHESIS!
any falsifiable prediction about new facts from a theory
testable prediction
What is Scientific Attitude?
Empirical approach
data
Curios skepticism
how and why
Humility
aware of error-proneness
Good Scientific Theory
FALSIFIABILITY
precise predictions
evidence to confirm or contradict the theory
THE LAW OF PARSIMONY
the principle that all else being equal, the simplest theory is the best
reliance on the fewest and simplest possible assumptions
Why does a claim need to be falsifiable?
Vagueness cannot be falsifiable, meaning it cannot be TESTED, meaning it cannot be considered in the realm of science
General Principles of Research
Measurement problem
to measure phenomena accurately, we develop observable definition
Operational definitions: give a numerical value to variables; its operation
Specifics the procedures used to measure something
Gives a numerical value
How do we conduct research?
Research design!!!
many methods
REPLICABLE, following the same procedures
what happens and under what circumstances does it seem to occur?
we try to choose the best procedure
each method has advantages and disadvantages
Importance of Replicable Results
Testing of hypotheses must be repeated
Report their methods
could repeat the study to confirm or contradict the validity of the findings
Replicable results can be obtained
following the same procedures
Which of the 3 research designs?
Description
case study
survey
naturalistic observation
Correlation
Experimentation
Research Strategies: Description
Descriptive research is systematic, objective observation of people
Goal is to provide a clear, accurate picture of people’s behavioris, thoughts, and attributes
Descriptive Research
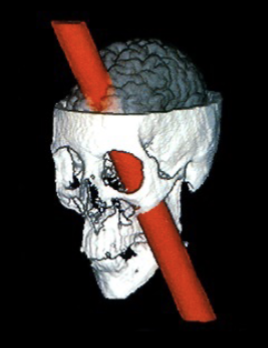
Case History (Study): A thorough observation and description of an individual usually in an unusual condition or circumstance
Ex: The case of Phineas Gage
The case of Phineas Gage (1848)
Tragic and bizarre accident
13lbs steel rod impaled
landed 80 feet away
Personality change
taught about the prefrontal cortex of the brain
Second type of Descriptive Research
SURVEY!!!
Study of the prevalence of certain beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors
based on people’s responses to specific questions
Third type of Descriptive Research
NATURALISTIC OBSERVATION!!!
careful monitoring and examination under natural circumstances
example: Dr. Jane Goodall’s long-term observation of chimpanzees in the forest
recording their social organization and biological functioning

What are limitations of Observations/Case studies?
May not help us really predict behavior in the future
doesn’t help us undercover the underlying mechanisms behind the behavior most likely
unable to control behavior to test specific questions
Correlation: The Measure
Correlations range from -1.00 to 1.00
the CLOSER to -1.00 or 1.00, the stronger the relation between two variables
Remember: Correlation does not equal causation
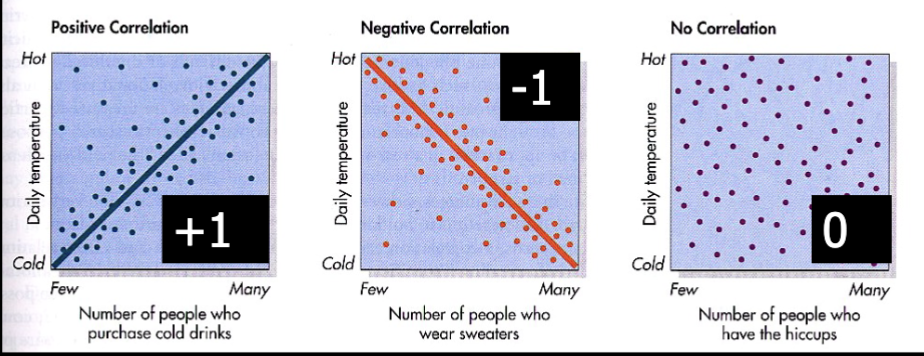
A study of married couples showed that the longer they had been married, the more similar their opinions on social and political issues were.
CORRELATION… POSITIVE OR NEGATIVE?
POSITIVE because when X increases, Y increases too
X: Time married
Y: Opinion similarity
An intelligence test was given to all the children in an orphanage, The results showed that the longer the children had lived in the orphanage, the lower their IQ scores
CORRELATION: POSITIVE OR NEGATIVE?
NEGATIVE because when X increases, Y decreases
X: time living in orphanage
Y: IQ level
Science is a way of making…
Observations
What is an experiment?
A technique for establishing the causal relationships between variables
Key ingredients: Manipulation and Control
Tools of experimental control
Holding constant
ensuring that the two groups are treated identically expect for the manipulation
Random assignement
ensuring that each subject has an equal chance of being assigned to each group