Center of Mass and Equilibrium
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Center of Mass
defintion
How it applies to linear and angular motion
Conceptual point where all mass of body considered consentrated
Point mass
For linear motion to occur = Force through CoM
For Angular motion to occur = Force not through CoM (rotation)
Difference between Center of Mass and Center of Gravity
COM = point where distribution of MASS equal
COG = point where distribution of WEIGHT equal (depending on gravity, Newtons)
Gravitational Forces
Definition
force of attraction between 2 masses
Depends on masses involved and their separation
Finding COG from the COM
method
knifes edge method to find equilibrium of unequal shape
Balance it on its COM = indirectly used to estimate COG
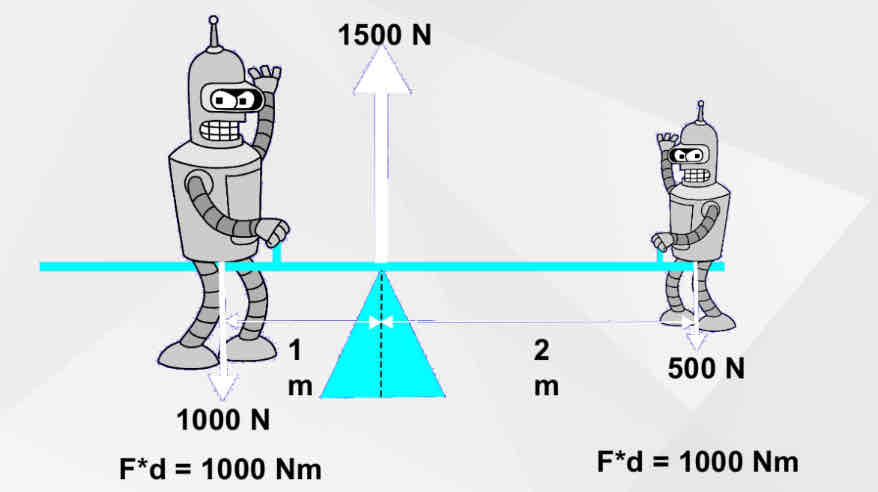
Equilibrium of System
what creates equilibrium (2 things)
Explain moments
Equation for moments
∑ forces on body = 0
∑ moments about a point = 0
The moment of force (torque) about an axis depends on the applied force, and the distance of the force from the pivot point
Moment (Nm) = Force (N) x Perpendicular distance (m)
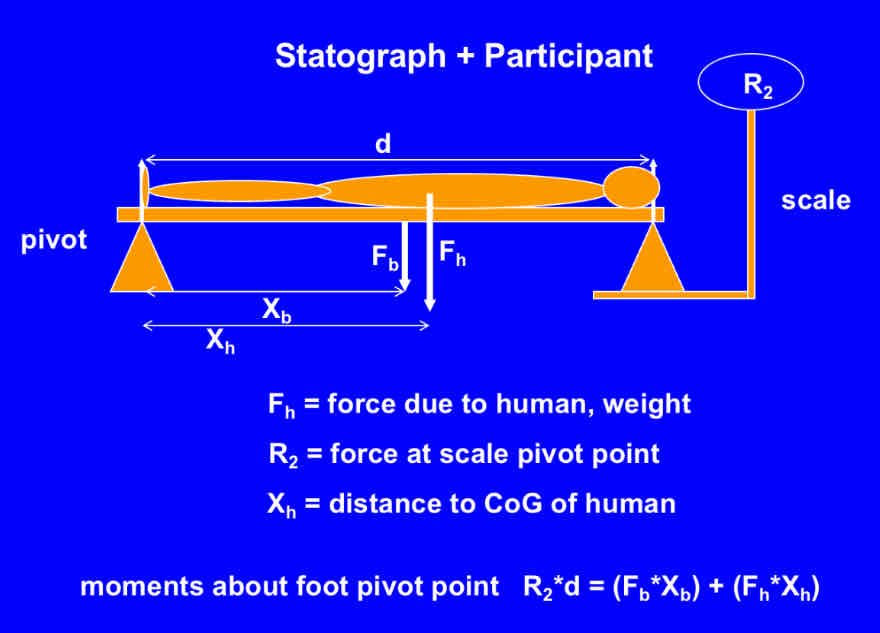
Determining COG of whole body
2 methods and defintion
Statograph - device that sums the moments about an axis
Reaction Board - device that sums 2 axis
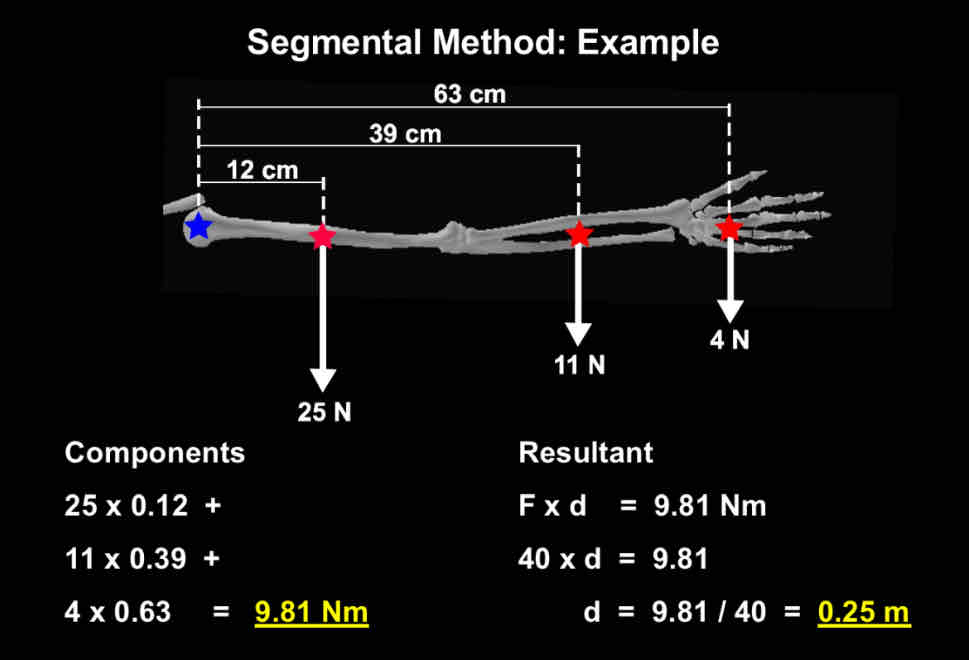
Determining COG for parts of a body
method
Limitation
Why we have to use it nonetheless
Segmental Method
Not accurate = assumptions and standard data
Arm connected to body so can’t use reaction board or statograph