Skeletal system
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
what are the main components of the skeletal system
bones cartilage and ligaments
what is in each bone
connective tissue blood vessels nerve lymph vessels cartilage connective tissue coverings
hyaline cartilage
found in articular costal respiratory and nasal
elastic cartilage
external ear and epiglottis
fibrocartilage
meniscus between vertebrae
axial skeleton
creates the longitudinal axis of the body houses vital organs
axial skeleton pic
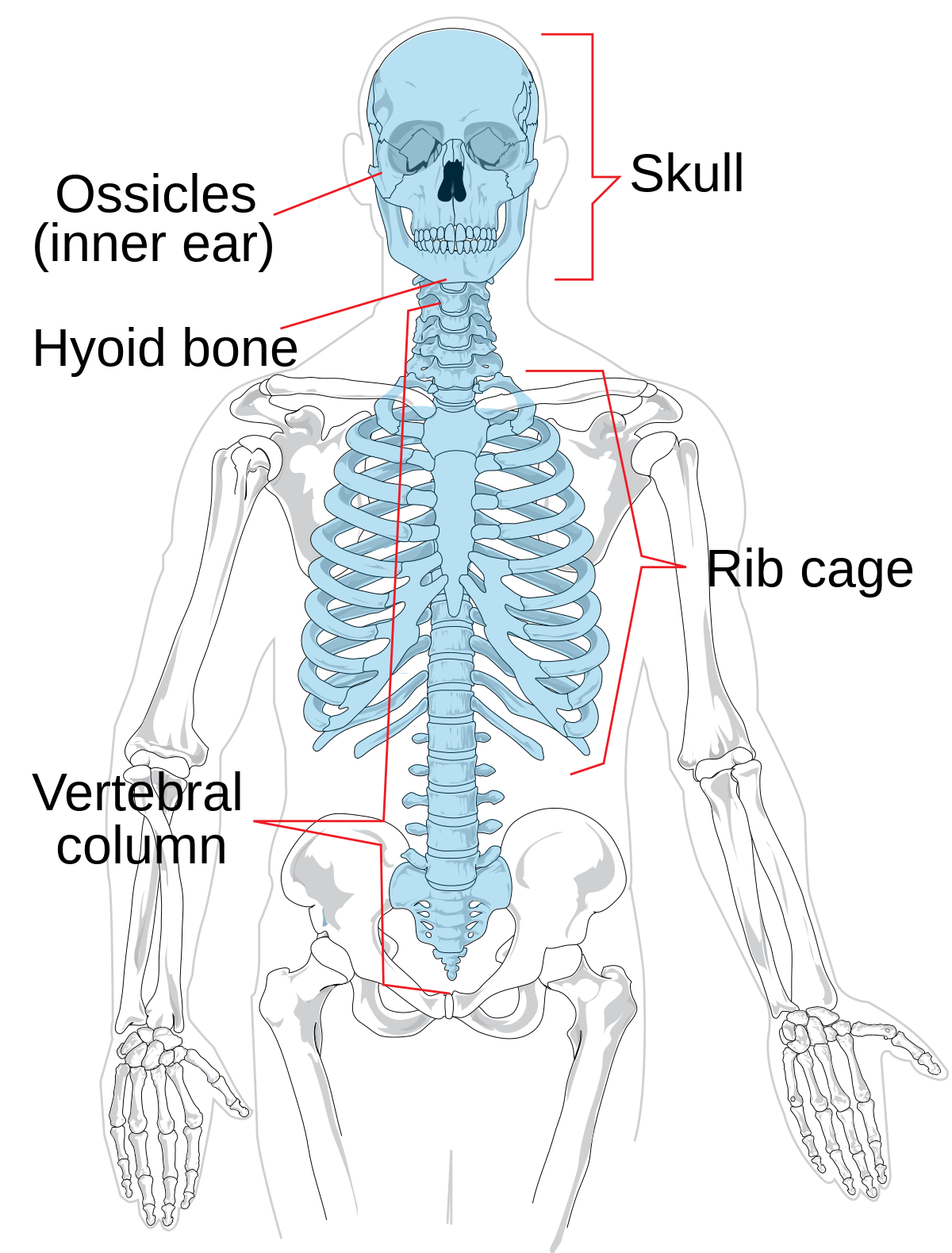
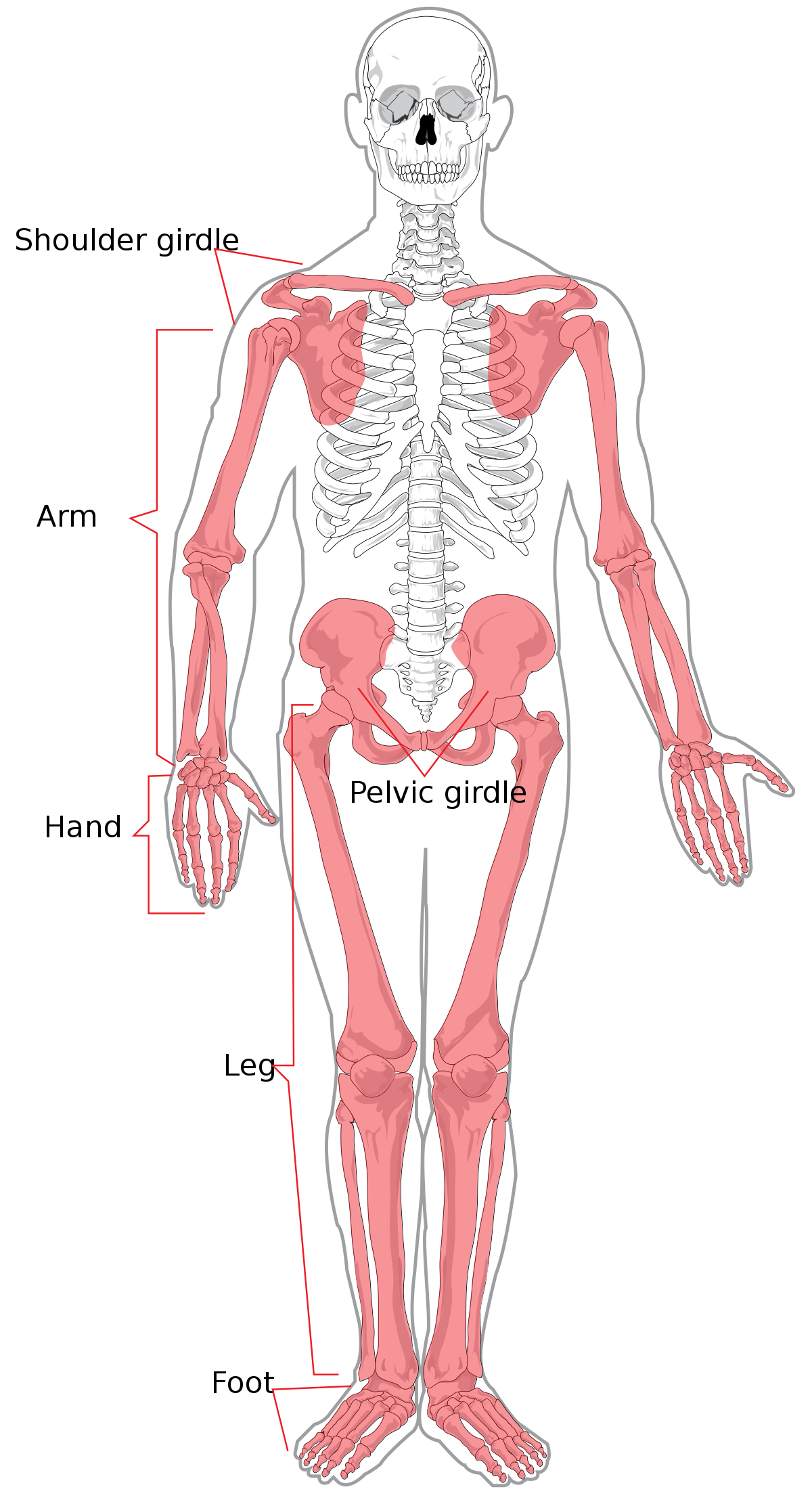
appendicular skeleton
appendages girdles connects to axial much greater mobility
appendicular skeleton pic
long bone
longer than wide humerus femur
short
roughly cube-shaped ex wrist and ankle bone
flat
thin flattened curved ribs sternum cranial bones
irregular
complex shape vertebrae
sesamoid
shaped like a sesame seed at points of high friction patella
sutural
forms between cranial bones vary between individuals
compact bone
forms outer layer of most bones
spongy bone
surround inner cavity
compact bone pic
spongy bone pic
whats the deepest one
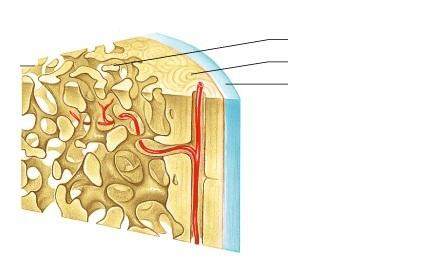
diploe
layer of spongy bone in cranial bones
short irregular and flat bone anatomy
sandwich of compact bone - spongy bone - compact bone
epiphysis
end
diaphysis
middle
metaphysis
connects epiphyses to diaphysis
layers of long bones
periosteum
compact
spongy
endosteum
medulllary cavity ( marrow
connective tissue- periosteum loc
covers the outer surface of living bone
periosteum func
isolates and protects bone
supports blood vessels and nerves
connects to other tissues
growth and repair
fibrous layer
interwoven collagen fibers with either deep fascia or bone
osteogenic layer
contains osteogenic cells (bone stem cells)
endosteum location
lines medullary cavity and covers spongy bone surface
endosteum function
reticular connective tissue
contains osteogenic cells that are important for bone growth
skeletal blood supply
extensive network of blood vessels
skeletal innervation
sensory neurons throughout the periosteum
osseous tissue
support connective tissue
contain specialized cells -protein fibers-ground substance
osteogenic cells
stem cells
formed from mesenchyme and give rise to osteoblasts
osteogenic cells processes
osteogenic cells - mitosis - daughter osteogenic cells - differentiation - osteoblasts
osteoblasts
builders and secrete organic components of extracellular matrix
initiate calcification
osteogenic cells
stem cells
osteoblats are
builders
osteocytes are
maintenance crew
osteocytes
mature bone cells
maintain existing matrix in response to bone density needs
act as strain sensors - regulate remolding in response to mech areas
send signals to osteoblasts and osteoclasts via dendritic process
osteoclasts are
destroyers
osteoclats
derived from blood cells
contain resorption bays where they secrete acid and proteolytic enzymes to dissolve matrix (bone respiration)
special about osteoclasts
resorption bay
ruffled border
resorption bay
pit in the compact bone where remodeling is active
ruffled border
exaggerated portion of the osteoclasts membrane where enzymes and acid are released and broken-down minerals are brought into the cells
osseous matrix organic
1/3 of matrix
produce and secretes by osteoblasts
glycosaminoglycans
proteoglycans
collagen fibers
glycosaminoglycans
trap water due to negative charge
glycoproteins
collagen fibers
fibrous protein arranged in helical form
very resistant to pulling forces
provides flexibility and a framework for the deposition of calcium crystals
type 1 collagen fibers
must abundant collagen and also the most abundant protein in the human body
found in the bone as well as fibrous tissue like tendons ligaments and skin
glycine combo with another amino acid to make a collagen polypeptide three collagen polypeptides coil around each other to make tropocollagen
inorganic matrix
other 2/3
crystallizes around collagen fibers
osseous matrix
composite material
combined very strong slightly flexible matrix
composite material
combo of a ceramic + polymer
inorganic on its on strong and inflexible
organic- tough but too flexible
what does bone need for strength
collagen and minerals
osseous matrix special property
the sacrificial bond between collagen molecules
break under mech stress which dissipates the force and reduces the likelihood of fracture
can reform once the stress is removed
rickets
calcium deficiency due to lack of vitamin D
leads to bowed legs
scurvy
problem with collagen synthesis due to vitamin c deficiency
leads to brittle bones that can fracture
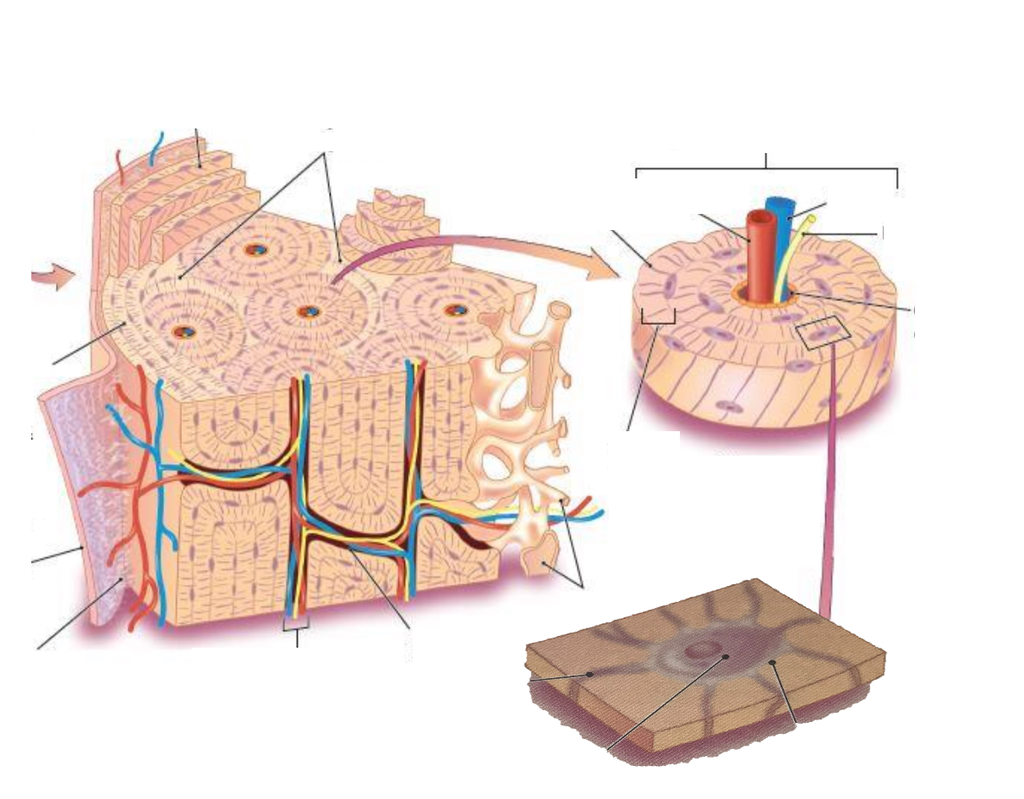
compact bone
functional unit bone
concentric lamellae around central canal
made up of osteons
perforating canals connect osteons to each other and medullary cavity
interstitial lamellae
circumferential lamellae
surround entire bone at internal and external surfaces
interstitial lamellae
fill in gaps between osteons
usually remnants of olds osteons
spongy bone made of
spicules and trabeculae
spicules and trabeculae
thin silvers or branching plates
interconnected spaces throughout
same cells as compact
strong but light
compact bone vs spongy bone
compact
-dense
covers bone surface
thick where stress is high
handles stress well in one direction
spongy bone
-lightweight
resists stress from multiple directions
provides support for bone marrow
diaphysis loc
shaft of long bone
diaphysis func
leverage
epiphysis loc
head of long bone
epiphysis func
strengthen joint and surface area for the attachment of ligaments and tendons
articular cartiledge
a thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the articular surface of the bone as at a synovial joint, serving to reduce friction and ease joint movement
periosteun
a layer of fibrous connective tissue covering surface of a bone
lacuna
A small cavity or depression in a tissue such as bone or cartilage
ossification
the formation of bone
step one of intramembranous ossification
mesenchymal cells line blood cells
osteogenic cells become osteoblasts
osteoblasts start secreting osteoid
second step of IO
calcium salts crystallize on osteoid calcification to spicules
osteoblasts turn into osteocytes when surrounded by matrix
third step of IO
mesenchyme differentiates to periosteum
ossification centers meet and make branching plate called trabeculae
fourth step of IO
osteoblasts in the periosteum crate outside layer of compact bone called diploe structure
continued remodeling of spongy bone by osteoblasts and osteoclasts
calcification
deposition of ca
ossification
replacement of connective tissue by bone tissue
diploe
layer of spongy bone in cranial bones
spongy bone
made of spicules and trabeculae
strong but light
compact bone
mostly osteons and circumferential lamellae
composite material
combo of ceramic and polymer
inorganic on its own
strong but inflexible and would easily shatter
organic on its own
tough but too flexible and wouldn’t resist direct pressure well
what is the special property of the osseous matrix
sacrificial bonds between collagen molecules
rickets
inorganic component deficiency which leads to bowed legs
scurvy
organic component deficiency leads to brittle bones and problems with collagen synthesis
osseous matrix
produced and secreted by osteoblasts
contain glycosaminoglycans
perichondrium
fibrous connective tissue that envelops the surface of hyaline or elastic cartilage
periosteum
layer of connective tissue that covers the surface of a bone
chondrocytes
cartilage cell that was chondroblast enclosed in lacunae in cartilage matrix
endochondral ossification precursor and bones it creates
use hyaline cartilage precursor - most bones below the skull
step one of endochondral ossifciation
mesenchyme turns into hyaline cartilage surrounded by perichondrium
step 2 of endochondral ossifciation
bone growth begins in middle of future diaphysis creating primary ossification center
step 3A of EO
periosteal but invades shaft making primary marrow cavity
step 3B of EO
secondary ossification centers form
step 4 of EO
secondary marrow cavities form in epiphyses
step 5 of eo
further growth due to inc in cartilage first followed by ossification
epiphyseal plate
thin wall or cartilage separating diaphysis and epiphysis
primary ossification
marrow cavity formed
replaces all cartilage with bone
located in diaphysis
occurs before birth
secondary ossification
no marrow cavity
some cartilage is left for the epiphyseal plate and articular cartilage
found in epiphyses
occurs around the time of birth