Percussion Midterm
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Chimes RAnge
Treble Clef C one ledger line below to F 5th line

Marimba Range
bass clef first space A to Treble clef C above the staff 8VA

Vibes Range
Treble Clef F below the staff to F above the staff

Glock Range
Treble Clef G below the staff to C above the staff
Sounds 2 octaves higher than written

Xylo Range
F below treble staff to C above treble Staff 8va

Name three characteristics common to all Percussion Instruments.
Strike them, fixed resonance, all have resonating chamber
Other than striking, name some other ways percussion instruments are played
Shaking, air, rub, bow,
Describe the Piston Stroke
Speed of the stroke on the way down is equal to the speed of the stroke on the way up.
Down stroke and up stroke
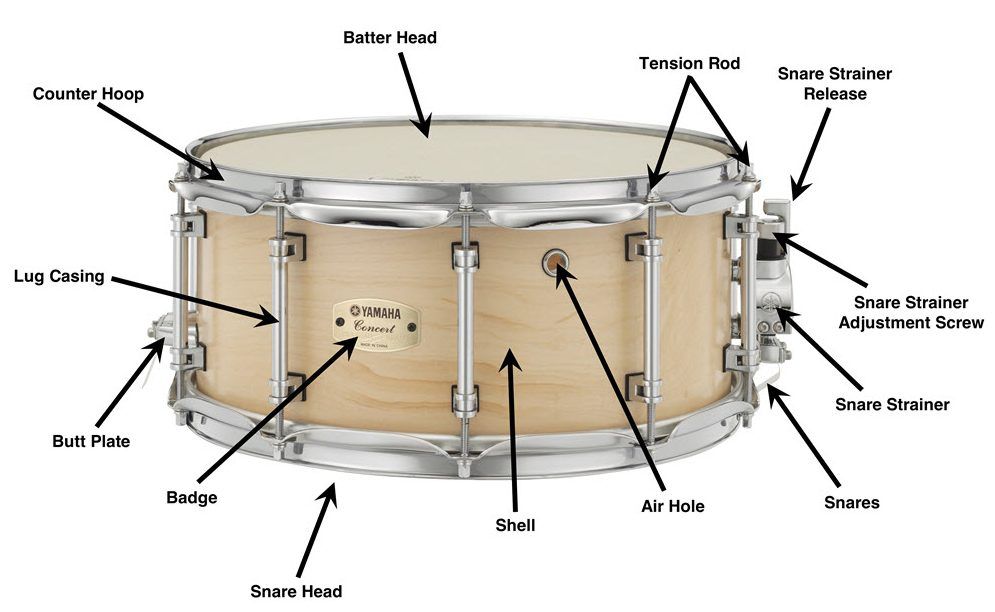
Name the parts of the Snare drum.
Batter head – head you hit
Snare or resonant head – bottom head
Snare throw, snare switch –
Tension road
Counter hoop or rim
Shell
Butt assembly
Name three companies that produce snare drums.
Pearl, Yamaha, grover, black swamp,
What are the three basic depths of snare drums?
4 or 5 inch, 6 and a half, 8 inch,
2. Name the parts of the Snare Stick.
Butt, shaft, shoulder, taper, tip or bead

Name three companies that produce sticks.
Vic virth, pro mark, cooperman
Describe how these factors influence the sound the stick produces?
How long, how thick, bead shape, wood type,
2. Describe how sound is produced on the snare drum (how the parts move)
Strike the batter head, air moves on the inside of the shell, air vibrates shell, vibrates resonant head, vibrates snares
Warmer sound on wood shell, more snare response metal shell
Describe the process for starting a young student on snare drum.
!-include drum height, grip, stroke, playing surface, and beginning exercises/method books.
Describe the parts of a mallet instrument (common to all instruments)
String, resonators, bars, frame, posts
Describe the parts of a mallet
Shaft- ratan, birch, and fiberglass
Ball- rubber, plastic, poly material, brass, aluminum
Wrap for marimba and vibraphone mallets, chord and yarn,
Name the differences between the marimba and the xylophone.
Type of mallet used on them. Xylophone sounds an octave higher than its written, marimbas have wider range and read grand staff, marimbas have thinner bars than xylophones
Describe the best playing areas on a keyboard bar.
Slight below or above center, or right on the edge of the bar
Where is it NOT advisable to play?
over the string
Name three companies that make keyboard percussion instruments.
Yamaha, musser, marimba one, mallet tech, majestic
Name three companies that make mallets.
Vic virth, mallet tech, innovative percussion,
Name the three different four-mallet grips
Traditional, berton, musser stevens
common errors
Fingers off stick, using arm and not wrist, bad stick height, one hand being stronger than the other
describe process for beginning a student on snare drum
Opening stand, putting it on the stand, teach the grip, stick goes across palm, thumb on flag, wrap index finger around,
How do variances in mallet parts affect the sound?
Hard mallets: sharper, brighter sound, creating more percussive tone
Soft mallets: emphasize fundamental pitch rather than overtone, create more sustained sound
rubber or plastic: defined articulation, more piercing
yarn or felt: warmer, rounder sound,
brass or aluminum: louder, cut more, very bright, strong
Different types of materials used to create mallets
Ratan (bendy)
Birch, firm (used for marimba)
fiberglass (very bendy)
core: rubber, plastic, aluminum or brass,
wrap: yarn or cord (marimba or vibraphone)