psych unit 4 aos 2 - mental wellbeing
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
3 characteristics of a mentally-well person
high levels functioning
high levels resilience to life stressors
high levels social + emotional wellbeing
characteristics of a mentally-well person — high levels functioning
ability carry out wide range daily activities, self-care, maintain relationships, resilient to everyday challenges
higher overall ind level functioning = higher level functioning when face everyday challenges → ind is adaptive/resilient as these chals don’t sig impact their functioning
how can levels of functioning be assessed
WHODAS (WHO disability assessment schedule) questionnaire
— assesses 6 life domains:
cognition (understanding + communicating)
mobility (moving + getting around)
self-care (hygiene, dressing, eating, staying alone)
getting along (interacting with ppl)
life activities (domestic responsibilities, leisure, work, school)
participation (joining comm activities)
characteristics of a mentally-well person — high levels resilience
resilience = ability to adapt + cope when stressors arise to return to high functioning state (bounce back better than before)
inds mentally healthy learn from stressful exp → next time face smth similar they can use coping strats to adjust
characteristics of a mentally-well person — high levels social + emotional health
social wellbeing = based on ability to have satisfying relationships + interactions with others
— develop +ve bonds with fam and friends
— respect ppl from diff ethnic + cultural backgrounds
— work part of team
— contribute to comm some way (e.g. volunteering)
emotional wellbeing = based on ability control emotions + express them appropriately
— express range emotions relevant to context
— control diff emotions + respond to them +vely
— act +vely and have +ve affect
— identify emotions others and respond appropriately
— respond with appropriate emotions to setbacks
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework (SEWB)
— holistic ATSI understanding of social + emotional wellbeing that varies between diff groups
framework model seven domains (bmfs ccc) :
body
mind + emotions
fam and kinship
spirituality + ancestors
community
culture
country
framework model 3 determinants:
social determinants
historical determinants
political determinants
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework domains — body
physical aspect of person h+w & how ind perceives and connects with their bodies
risk factors e.g. = chronic disease, poor diet
protective factors e.g. = healthy diet, exercise
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework domains — mind and emotions
managing thoughts and feelings
risk factors e.g. = racism, mental illness
protective factors e.g. = education, assertiveness and confidence
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework domains — fam and kinship
goes beyond fam, includes cultural roles and shared responsibilities, identity, and support systems
risk factors e.g. = fam members absence, fam violence, child abuse/removal
protective factors e.g. = supportive fam, adequate income
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework domains — community
gives opportunities for inds connect + support each other
risk factors e.g. = isolation, fam fueding
protective factors e.g. = support networks, comm services
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework domains — culture
gives sense of continuity with past + builds strong identity — includes cultural expression
risk factors e.g. = elders premature passing, languages under threat
protective factors e.g. = cultural institutions, attention local cultural events
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework domains — Country (land)
deep experience of belonging to Country + trad and spiritual associations to kin and culture
risk factors e.g. = restricted access to country
protective factors e.g. = time spent on country to heal body + mind + spirit, cultural renewal
lands, waters, skies which First Nations peoples are connected thru ancestral ties?
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework domains — spirituality + ancestors
knowledge and belief systems + the Dreaming + cultural healing practices + value of wisdom and hope
risk factors e.g. = mission life and assimilation (stolen gens?)
protective factors e.g. = attending cultural events and ceremonies
ATSI social and emotional wellbeing framework determinants
social determinants = how ppl grow, live, work and systems to deal with illness
— e.g. SES, poverty impact, racism
political determinants = ongoing influence of events, policies → can cause trauma on grps
— e.g. past gov policies for colonisation → stolen gens → loss of culture
historical determinants = policies shape resource distribution
cultural?
FAQ summary for ATSI SEWB
ATSI have holistic view h+w for thousands yrs
framework is unique to ATSI
defs of framework vary across diff cultural grps
changes thru life span
places ind (self) within network of relationships (domains) → quality of ind’s connections to these domains is what influences their s + e wellbeing (experiences and expressions)
self is inseparable from each domain
mental wellbeing def
state of SEWB which inds can cope with normal life stressors, work productively and contribute to community
mental wellbeing continuum def + explanation
tool used to track mental w progression which constantly changes over time (progresses from mentally well to mental wellbeing problems to mental health disorders)
mw viewed in varying degrees on continuum
mw not fixed in one position on continuum → mw fluctuates over time bc diff life exps → always constantly changing at point in time too (NEVER STATIC)
the mental wellbeing continuum
MENTAL WELLNESS
person has high levels functioning, high levels social and emotional wellbeing, high level resilience to stressors (can adapt when facing challenges)
MENTAL WELLBEING PROBLEMS
involves temp disturbance to mental wellbeing (rough patch in lives)
temp decrease functioning, temp decrease social and emotional wellbeing, temp decrease resilience but person can still bounce back
MENTALLY ILL / MENTAL HEALTH DISORDER
involves severe disturbance to mental wellbeing that ongoing for weeks/months
low levels functioning (struggle functioning independently, effectively), low levels emotional and social wellbeing, low levels resilience to challenges

high mental wellbeing def (mental wellness)
beneficial emotional state where ind realises their abilities
copes with normal life stressors
works productively
contributes to comm
mental wellbeing problems def
psychological state temporarily hindered by a disturbance to normal functioning → has -ve but not severe impact on everyday functioning
mental health disorder def (mentally ill)
psychological state where there’s a severe disturbance and sense of distress → sig decrease ind’s ability to function independently
characteristics of mental health
mental wellness = form +ve relationships with others, cope with normal stressors of everyday life, think logically, manage emotions, experience enjoyment, use abilities to reach potential
mental wellbeing problems = feel tense + low + irritable, unusual sleep or appetite, loss of energy and motivation, difficulty concentration, become withdrawn
mental illness (disorder) = e.g. anxiety disorder (phobia), mood disorder (depression), psychotic disorder (schizophrenia), impulse control disorder (pathological gambling)
factors that affect mental wellbeing (and where we are on continuum)
internal factors = influences originate within ind
external factors = influences originate outside ind from envo
— note: can interact with each other to influence ind’s mental wellbeing
factors that affect mental wellbeing — internal factors
PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS:
self esteem
personality traits
emotions
thought processes
BIOLOGICAL FACTORS:
genetics (g predisposition)
hormones
neurotransmitter balances
diet
factors that affect mental wellbeing — external factors
healthcare access
fam and friends support
education
abusive experiences
loss of sig relationships
stressor exposure
cultural background influences (e.g. trads)
social stigma exposure
what accounts for ind differences in mental wellbeing
complex interaction of multiple factors
external factors influencing ind’s internal envo (e.g. drug exposure → impact internal hormone levels)
stress def
psychobiological experience occurs when ind. encounters smth that demands their attention + efforts to cope
anxiety def
physiological arousal when ind think they cannot cope with stressor they may face in future
phobia def
excessive/unreasonable fear to particular object, situation→ cause sig distress + interfere with everyday functioning
phobic stimulus def
specific object or situation prod fear associated with phobia
physiological symptoms when experiencing stress, anxiety, phobia
same as flight-fight-freeze response (sympathetic ns activates)
compare and contrast — stress and anxiety
SIMILARITY = sympathetic NS becomes dominant, potential risk factor to mental health disorder
DIFF = stress response to known stimulus, anxiety response can be to unknown or generalised stimulus AND stress can be eustress or distress, anxiety is distress only
compare and contrast — stress and specific phobia
SIMILARITY = response to known stimulus, sympathetic ns becomes dominant
DIFF = stress can sometimes be adaptive, phobia is maladaptive AND stress is potential risk factor to mental health disorder but phobia is diagnosable mental health disorder
— specific phobia is a diagnosed mental health disorder but stress can only attribute to development of one?
compare and contrast — anxiety and specific phobia
SIMILARITY = sympathetic ns becomes dominant, distress only, influenced by biological psychological social factors
DIFF = anxiety response can be to unknown or generalised stimulus, but specific phobia response is to known stimulus AND anxiety can decrease person functioning if not managed but phobia sig decrease person functioning
— specific phobia is a diagnosed mental health disorder but anxiety can only attribute to development of one?
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development
biological = GABA dysfunction, LTP
psychological = behavioural models (precipitation by CC, perpetuation by OC), cognitive bias like memory bias and catastrophic thinking
social = specific envo triggers, stigma for seeking treatment
— memory hack = LG OCES (ltp, gaba, operant c, classical c, envo triggers, stigma)
for diagnosis of a specific phobia…
symptoms must be present 6 or more months + disrupt ind’s life (esp social or work relationships) or cause them serious distress
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — BIOLOGICAL
involves internal and physiologically based factors
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — BIOLOGICAL = GABA DYSFUNCTION
GABA is primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in CNS
GABA reduces likelihood of post-synaptic neurons firing → reduces brain activity so neural transmission not excessive
GABA dysfunction = sig low levels GABA → neural activity sig increase throughout brain → cause overthinking → easily triggered FFF response → can lead to development specific phobias
low levels GABA = high levels anxiety (FFF activation)
strategies to raise GABA levels
improve sleep
improve microbiome
regular exercise
deep breathing
GABA levels in brain can be negatively influenced by
genetic inheritance
NS damage
exposure prolonged stress
nutritional deficencies e.g. B6
high caffeine intake
— they can:
inhibit GABA release
inhibit GABA ability bind to post-s neurons
stimulate over-prod of glutamate
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — BIOLOGICAL = LONG-TERM POTENTIATION
LTP = long-lasting strengthening synaptic connections that regularly coactivated, increasing efficiency neural transmission
repeated pairing phobic stimulus with fear response (FFF) → cause stronger connections for neural pathways associated with this → ind more likely react fearful way to specific stimulus
EXTRA KNOWLEDGE = LTP 2 neural pathways of fear response
phobic stimulus → thalamus send info from sensory neurons to sensory cortex → to amygdala (implicit memory to be scared of stimulus) and hippocampus (explicit memory that stimulus is smth to fear)→ amygdala signal hypothalamus initiate FFF response
phobic stimulus → send info from sensory neurons to amygdala directly → FFF initiated before sc and hippoc works out why response occurring
the more these pathways used to specific phobic stimulus → more these neural connections strengthen
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — PSYCHOLOGICAL def
thoughts and mental processes that lead to development of specific phobia
— has behavioural and cognitive models
psychological factors : behavioural vs cognitive models
behavioural = only external observable actions — OC and CC
cognitive = internal mental processes — inaccurate mental processes can develop phobias (cognitive bias) — memory bias, catastrophic thinking
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — PSYCHOLOGICAL = CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
behavioural model
repeated pairing of NS (phobic stimulus) with UCS (unpleasant stimulus) can cause phobic reaction (CR) to the NS
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — PSYCHOLOGICAL = OPERANT CONDITIONING
behavioural model
after acquiring phobia via CC → phobia maintained with avoidance to phobic stimulus → avoidance = negative reinforcement (removal of undesired fear feelings → ind more likely repeat behaviour)
— ind don’t confront phobic stimulus → perpetuates phobia (prevents recovery)
precipitation and perpetuation def
precipitation = development (of phobia via CC)
perpetuation = maintenance (of phobia via OC) — prevents recovery
two-factor theory of conditioning a phobia
phobia develops thru CC (precipitated) and maintained by OC (perpetuated)
CC = UCS (fear causing stimulus) paired with NS (to become the phobic stimulus as CS) leads to CR (phobia, fear, anxiety)
OC = antecedent (envo cue to expose to phobic stimulus, the CS) → behaviour (avoid this CS) → consequence (fearful feelings removed) → behaviour maintained due to negative reinforcement
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — PSYCHOLOGICAL = cognitive bias
inaccurate mental processes developing and maintaining phobia → pairing faulty reasoning with fearful stimulus so faulty cognition formed
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — PSYCHOLOGICAL = COGNITIVE BIAS - memory bias
error in thinking that can impair memory recall / alter memory’s contents
can recall -ve info more readily than +ve info about specific stimulus from memory → contribute to phobia development
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — PSYCHOLOGICAL = COGNITIVE BIAS - catastrophic thinking
occurs after memory bias formed when ind repeatedly overestimates potential dangers of stimulus and assumes worst
— predict irrational future outcomes
— ind exp increased distress and anxiety levels + underestimate their ability to cope with situation
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — SOCIAL = (specific?) ENVO TRIGGERS
exposure to traumatic event that increase risk developing phobias
the more severe the trauma associated with an experience → more likely phobia develop
biopsychosocial factors that contribute to phobia development — SOCIAL = STIGMA FOR SEEKING TREATMENT
stigma about getting help for mental disorders (including phobias) prevents ppl seeking treatment → prolong phobia + can worsen over time
— ind may fear ridicule bc others think they overreacting (esp if phobic stimulus harmless)
— ppl around sufferer perceive behaviour to be irrational → hard to understanding and empathise with sufferer
biopsychosocial interventions for phobias
BIOLOGICAL = short-acting anti-anxiety benzodiazepine agents (GABA antagonists) in management of phobic anxiety and breathing retraining
PSYCHOLOGICAL = cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) + systematic desensitisation as psychotherapeutic phobia treatments
SOCIAL = psychoeducation for fams/supporters with reference to challenging unrealistic or anxious thoughts + not encouraging avoidance behaviours
BBC SP (benzodiazepines, breathing retraining, CBT, systematic desensitisation, psychoeducation)
— note all these interventions can be used as protective factors for inhibiting phobia development
biopsychosocial interventions for phobias — BIOLOGICAL
targeting of bod processes to assist in management phobic anxiety and associated symptoms
biopsychosocial interventions for phobias — BIOLOGICAL = benzodiazepines
GABA agonist → imitate/assist GABA’s inhibitory effects on post-s neurons thru brain
anti-anxiety drugs used in short term to calm body (initiate parasympathetic ns)
depressant and induce symptoms like sleepiness
if used long term can lead to tolerance and addiction
reduce physiological symptoms but doesn’t cure phobias or anxiety
dangerous to use in high dosages → if dose increased can lead to coma or death
agonist drugs def
stimulate post-s neuron to fire by binding to matching shaped receptors and enhancing activity
imitate GABA inhibitory effect on post-s neurons (make less likely to fire)
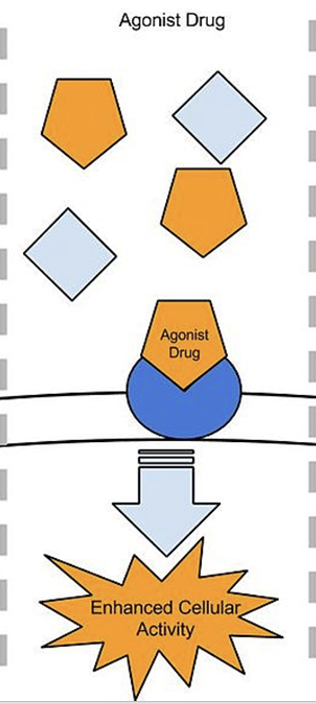
biopsychosocial interventions for phobias — BIOLOGICAL = BREATHING RETRAINING
breathing retraining → teach person to consciously slow their breath when experiencing phobic anxiety
exp phobia → symptom of excessive breathing → can upset balance of O and CO2 → cause dizziness, blurred vision, panic attack, heightened feelings fear and anxiety
reduces physiological arousal for phobic response by restoring balance O and CO2 + activates parasympathetic ns
biopsychosocial interventions for phobias — PSYCHOLOGICAL = CBT
target thoughts and behaviours that perpetuate phobia → if ppl change thoughts about smth then can change behaviour to it
cognitive = using knowledge to overcome irrational thinking → replace with reasonable, realistic thinking
behavioural = mod unhelpful behaviours that developed bc of faulty cognitions
technique = identify anxiety related thoughts and cognitive biases → check evidence that rejects these biases → replace irrational thoughts to evidence based rational thoughts → use systematic desensitisation to reduce fear (so gives inds technique to actually cope in fearful situations)
biopsychosocial interventions for phobias — PSYCHOLOGICAL = SYSTEMATIC DESENSITISATION
unlearning connection between fear and phobic stimulus + reassociating feelings of relaxation and safety with that stimulus
teach ind relaxation technique with psychologist → break down phobic stimulus into sequence arranged from least to most fear-producing (fear hierarchy) → pair items in hierarchy with relaxation by working thru items (one by one) until feel calm → at final stage ind should able to expose directly to phobic stimulus and stay calm
biopsychosocial interventions for phobias — SOCIAL = PSYCHOEDUCATION FOR FAMS/SUPPORTERS
educate fams/friends + sufferers of phobia with info about disorder, how triggered, how can assist in management
encouraged to help by:
— challenging unrealistic thoughts
— not encouraging avoidant behaviours
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing
biological factors = originate internally and relate to physiological functioning
psychological factors = originate internally and relate to non-physical functioning
social factors = originiate externally from envo around person
protective factors for mental wellbeing
+ve influences that enable ind to promote and maintain high levels mental wellbeing
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing — biological protective factors
adequate nutrition intake
adequate hydration
adequate sleep
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing — BIOLOGICAL = ADEQUATE NUTRITIONAL INTAKE AND HYDRATION
consuming enough nutrients ad vitamins that body needs to function well → gives enough energy to function effectively in daily life → improves physical and mental wellbeing
reduces risk physical health issues, aids sleep + energy levels + mood + mental health
hydration with water imp for keeping body functioning
strategies for ind to achieve adequate nutrition and hydration:
— eat balanced diet of fresh fruits, veges, protein, carbs
— drinking at least 2-3 L water per day
— limiting fast food, alcohol, caffeine consumption
— not skipping meals, eat regularly thru day
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing — BIOLOGICAL = ADEQUATE SLEEP
regularly getting rec hours sleep for your age → refreshes and repairs body + resources to cope with daily needs
uninterrupted REM sleep imp for mental health as assists brain to process emotional content
helps us think, feel, perform better of life + enhance enjoyment
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing — psychological protective factors
mindfulness meditation
cognitive behavioural strategies
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing — PSYCHOLOGICAL = MINDFULNESS MEDITATION
mindfulness = being focused on present moment + not being judgemental of thoughts
meditation = calming the mind and focus on smth specific
takes practice, used few mins each day to benefit wellbeing
reduces rumination + stress, boosts working memory, allows greater focus
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing — PSYCHOLOGICAL = COGNITIVE BEHAVIOURAL STRATEGIES
undergo cognitive behavioural therapy
— (targeting thoughts and behaviours that can perpetuate phobia/mental disorders → if ppl can change the way they think abt something can change their behaviour to it)
focus on changing ways ppl think to influence behaviour
replacing unhealthy thinking patterns with helpful ways of thinking → can influence behaviour and mood
increase ind resilience level by equipping them with strategies to manage challenging situations
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing — social protective factors
support from fam, friends, comm that authentic and energising
biopsychosocial model to influence mental wellbeing — SOCIAL = SUPPORT FROM FAM, FRIENDS, COMM THAT AUTHENTIC AND ENERGISING
support = genuine and effective assistance from fam, friends, comm
can give comfort + reassurance and encourage inds to develop diff strategies to promote mental wellbeing
must be authentic and energising:
— gen aims to promote mental wellbeing
— focused on creating envo likely to improve mental wellbeing
— legitimate and effective advice
e.g. unconditional love when ind makes mistake
e.g. support in difficult times like providing distractions from difficult emotions
e.g. sense of belonging and connection to wider circle
culture def
characteristics and knowledge of particular grp
can involve lang, music, religion, food etc
often also includes shared patterns of behaviours, interactions, understandings learned via socialisation
way of life for ppl that shared and learned
provides sense of belonging, influences ppl nature → hence imp to ppl → hence ppl want their culture passed onto members of comm
to promote ATSI wellbeing must consider
health holistically — not only physical health but cultural determinants of wellbeing too
cultural factors that support good h+w
cultural continuity
self-determination
cultural factors that support good h+w — cultural continuity
passing down and actively practicing cultural knowledge, traditions and values from gen to gen
ability to preserve historical trads of culture and carry them forward into future
ability for ATSI to practice culture not always been present bc of European colonisers denial → impacted their ability to maintain cultural continuity
enables comms to heal and form strong identities → vital cultural determinant for re-establishment and maintenance of wellbeing
how? — lang programs so young FN can learn mother tongues so they can build identity and cultural expression
cultural factors that support good h+w — self determination
right for ATSI make decisions on matters affecting their lives and comms
colonisation meant this was lost → contributed to sig low levels wellbeing
requires FN be involved in every layer of decision making
can include endeavours like: aboriginal comm-controlled orgs, land resources and management, partnerships with gov orgs
HOW SELF-DETERMINATION IMPROVES SWEB FOR FN PEOPLE
empowerment = FN have control over their affairs like health and education → gain sense of autonomy → increased self-esteem and greater sense purpose
cultural safety in services = when FN face cultural barriers when accessing mainstream services like healthcare and education → self-d can create culturally safe services → meets unique social and emotional needs of comm