Special Senses
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
palpebrae
upper and lower eyelids
palpebral fissure
opening between eyelids
lacrimal caruncle
fleshy elevation at the medial commissure; produces a whitish oily secretion
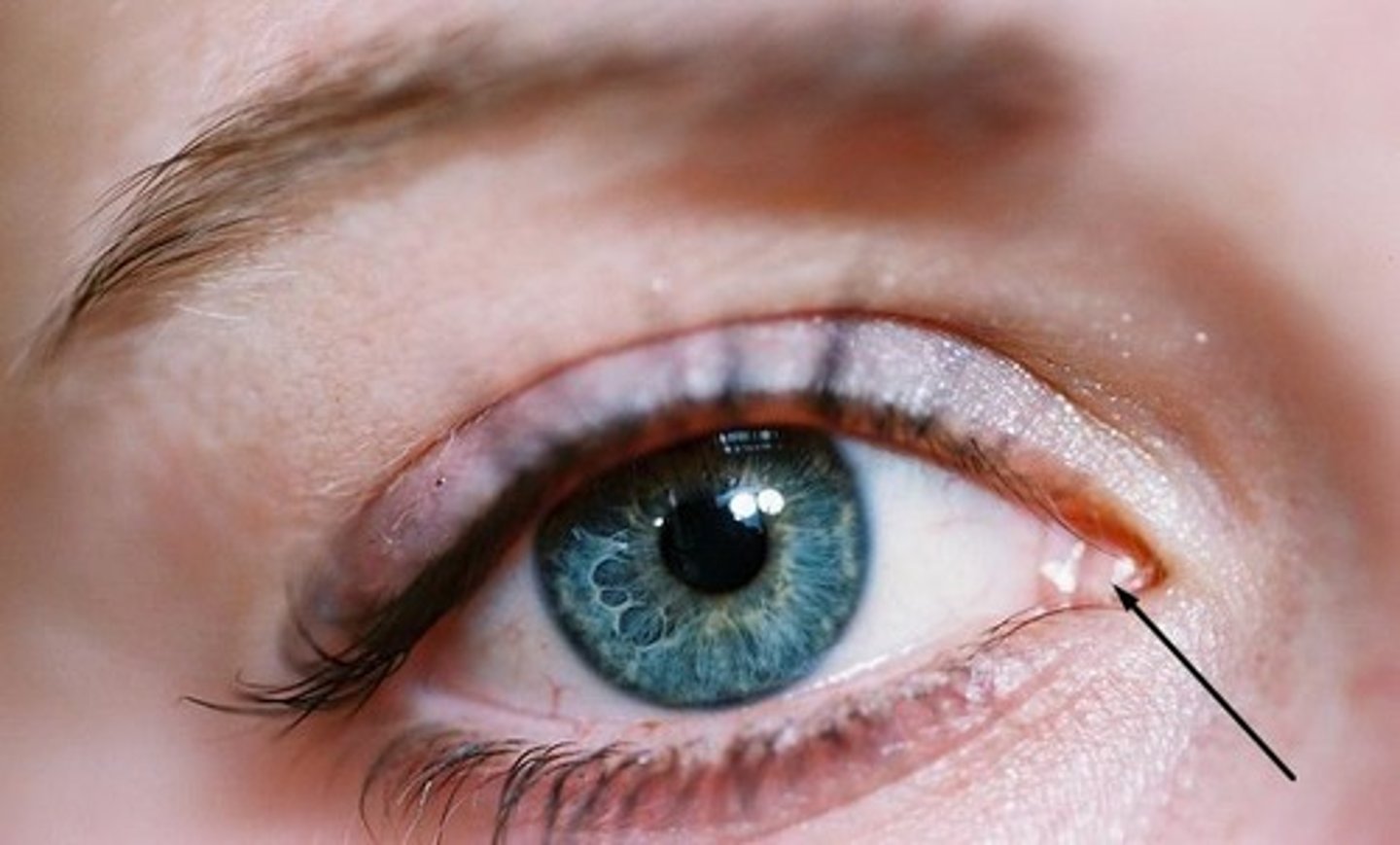
conjunctiva
Delicate membrane lining the eyelids and covering the eyeball
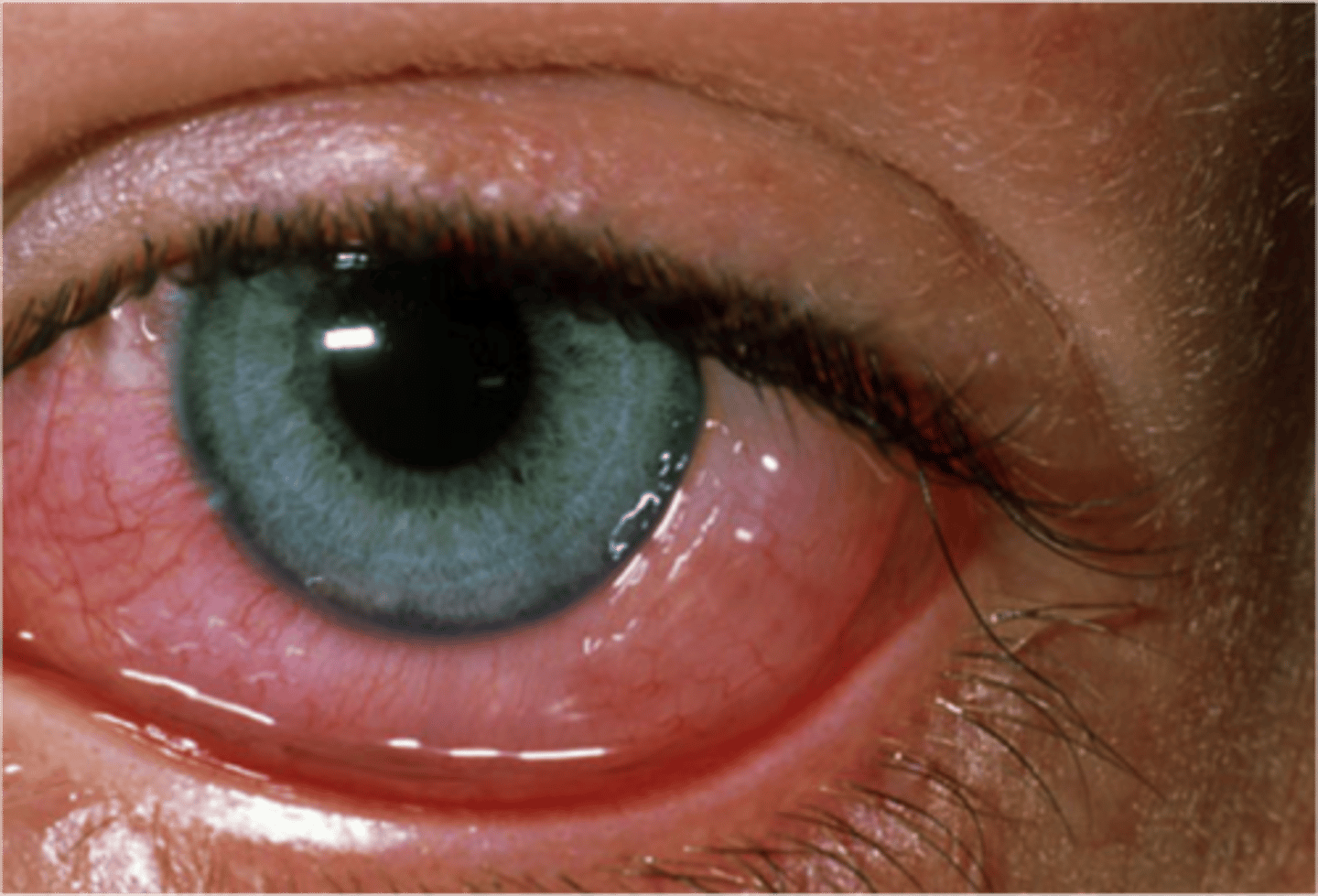
conjunctivitis
inflammation of the conjunctiva
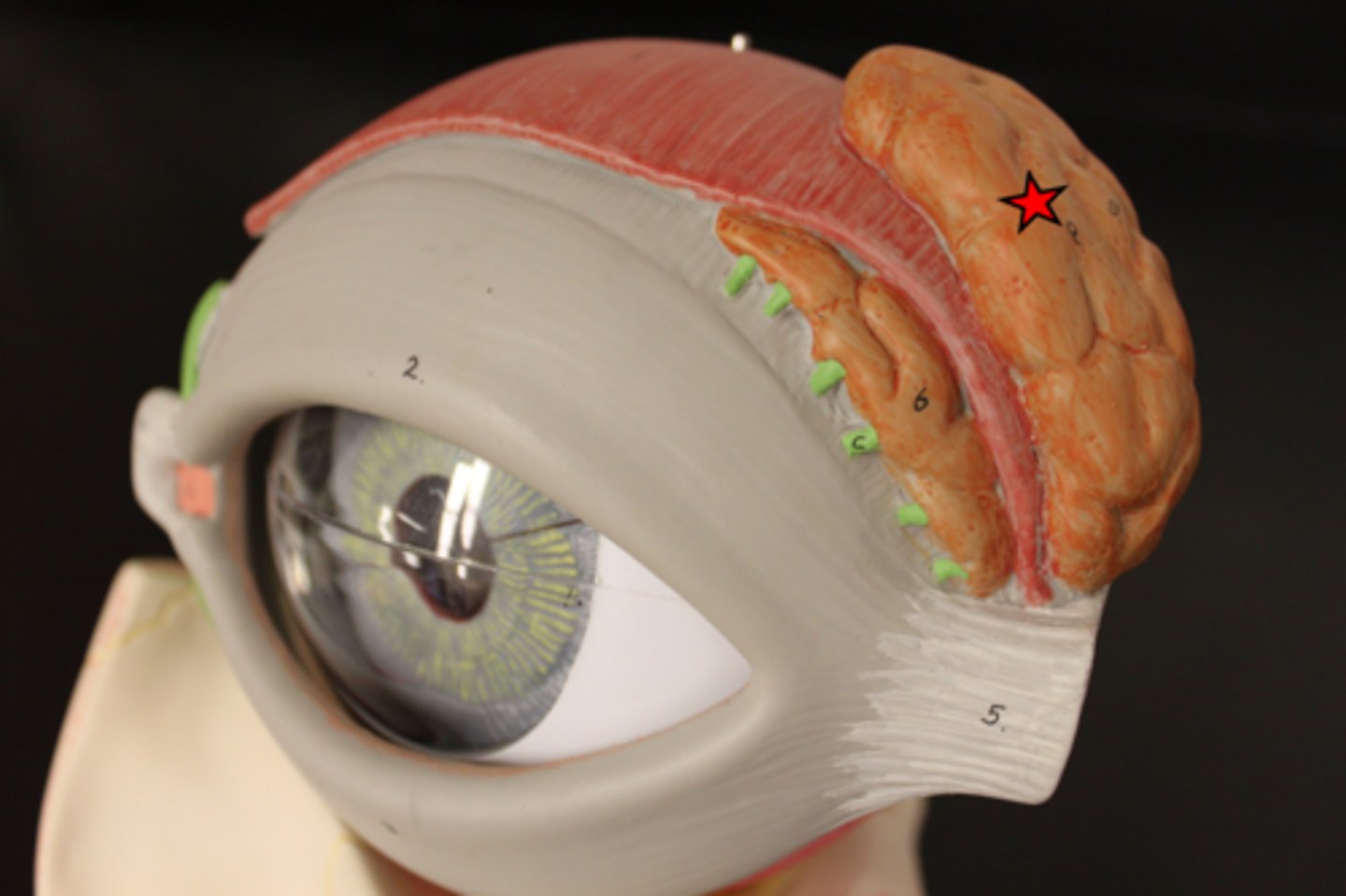
lacrimal apparatus
the structures that produce, store, and remove tears
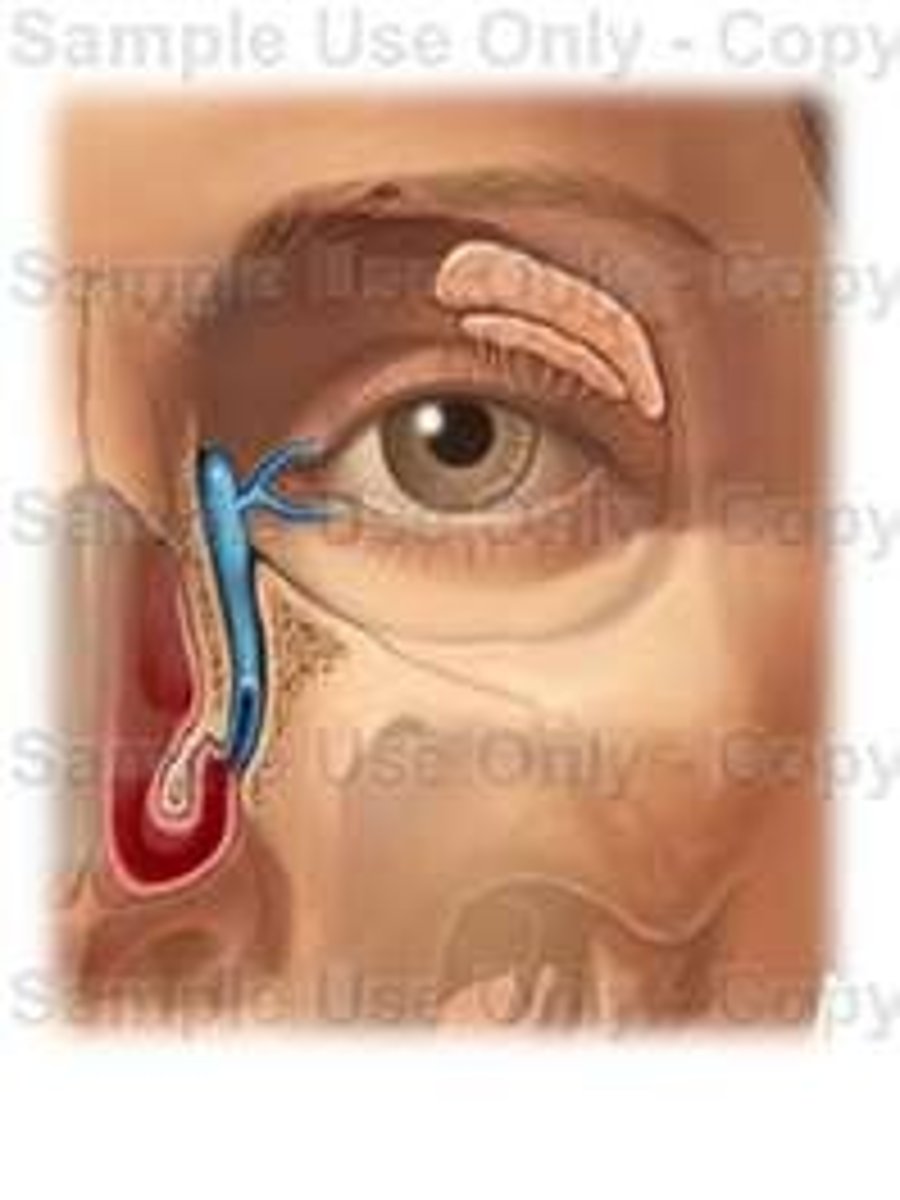
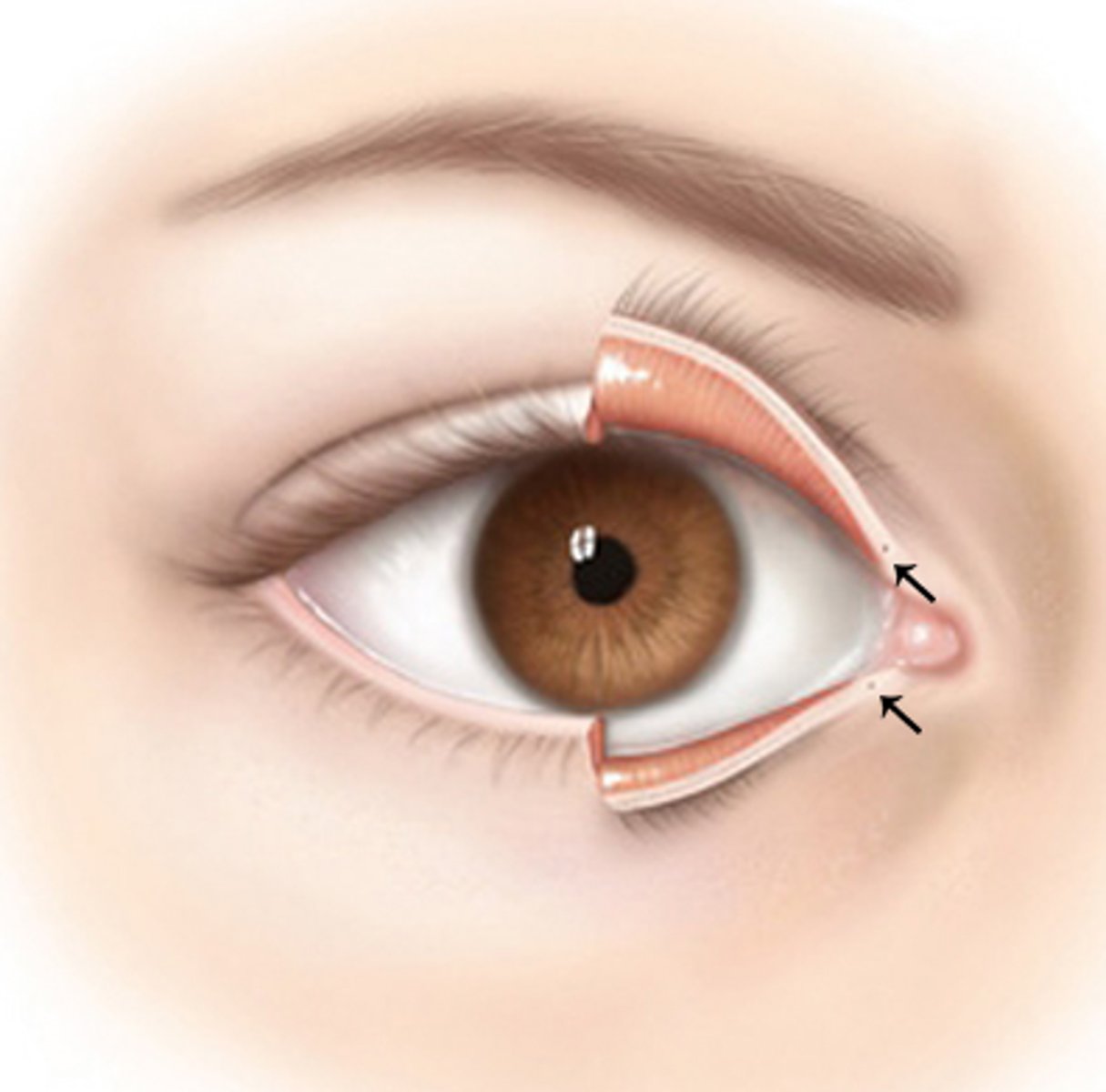
lacrimal puncta
pores that drain the tears
lacrimal canaliculi
drain lacrimal fluid from eyes medially
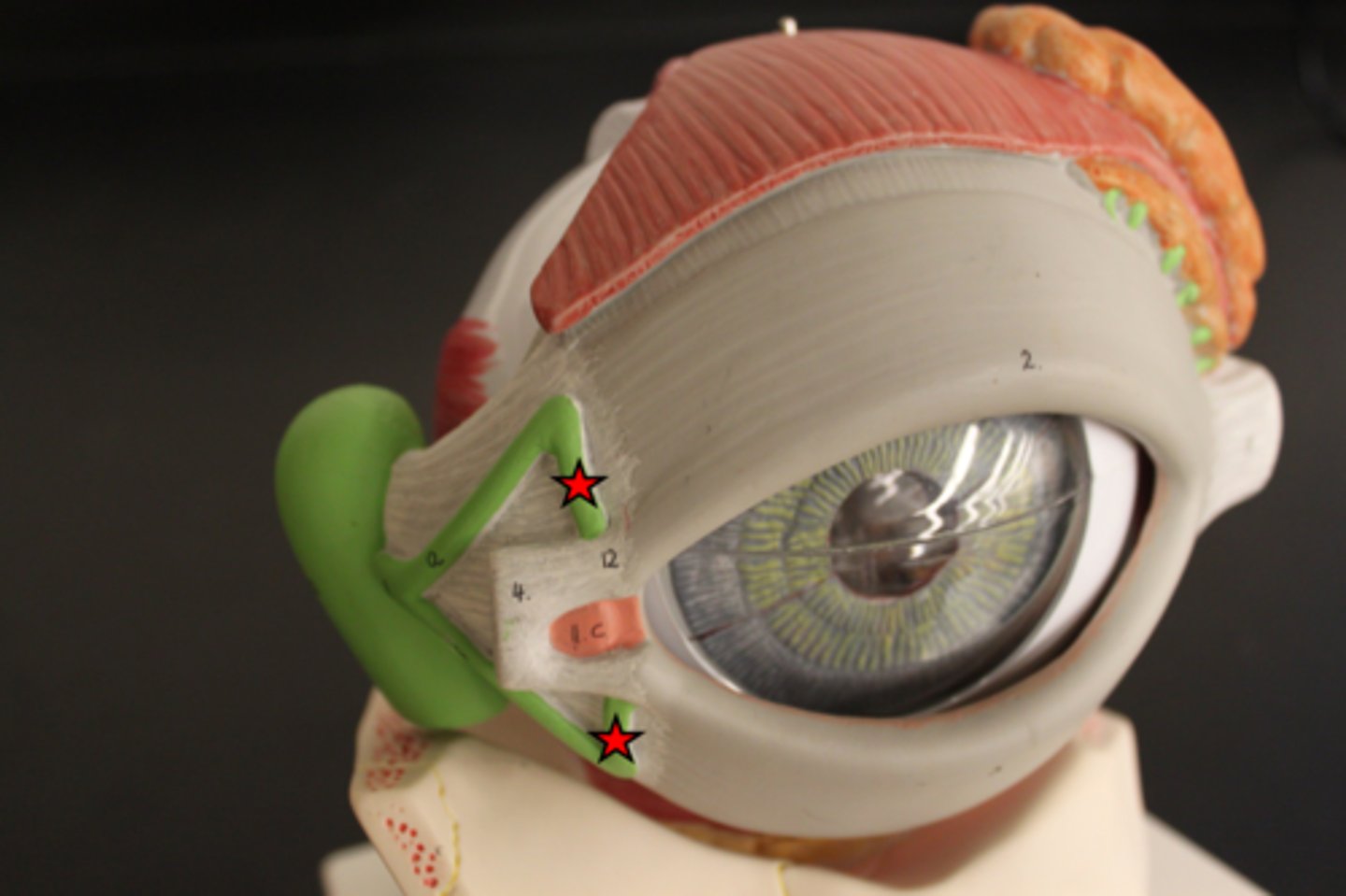
lacrimal gland
produces tears
nasolacrimal duct
drains tears into the nasal cavity
lysosyme
Antibacterial enzyme, attacks the cell wall of some bacterial
fibrous layer of eye
Sclera and Cornea; outermost layer
vascular layer of eye
middle layer
retina
Contains sensory receptors that process visual information and sends it to the brain
sclera
white of the eye
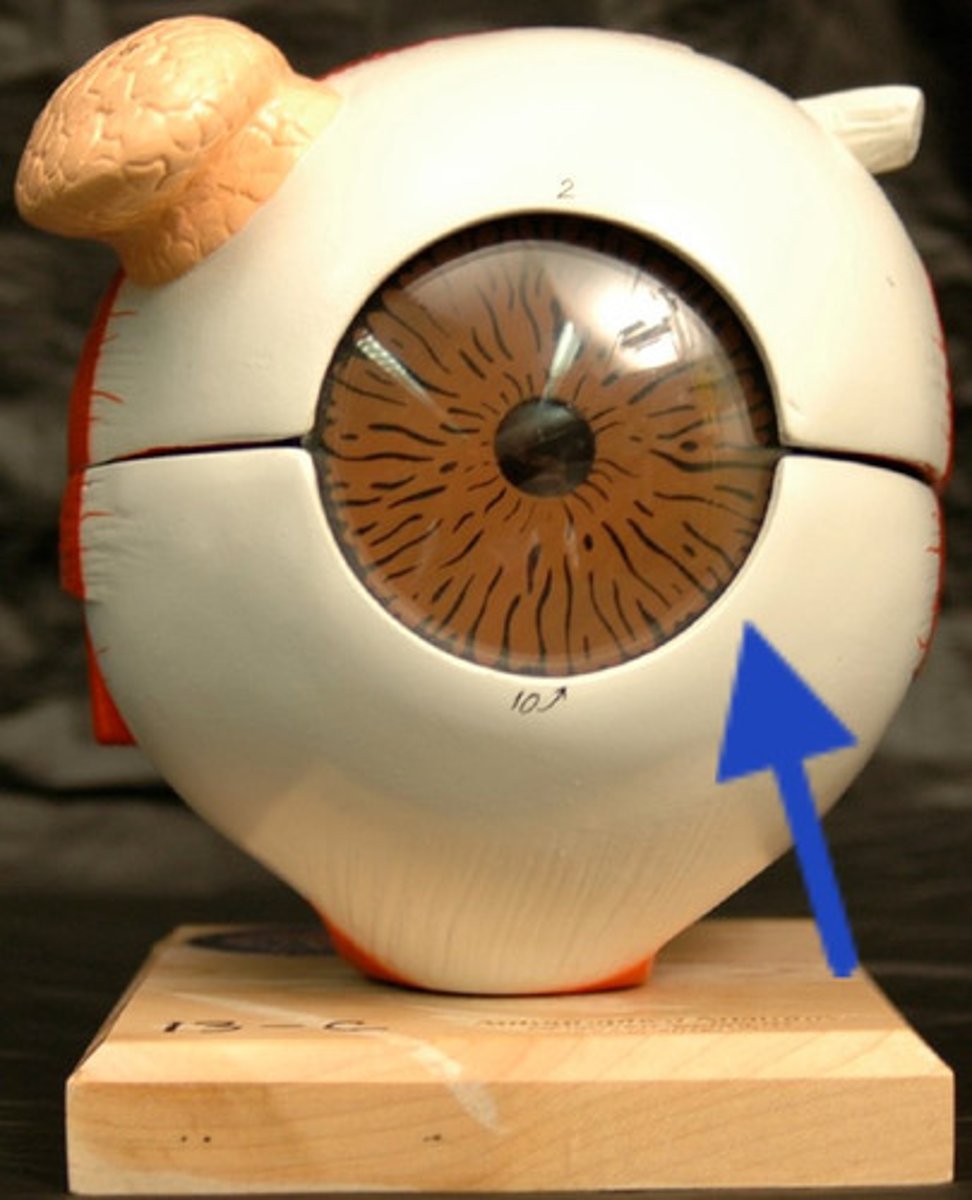
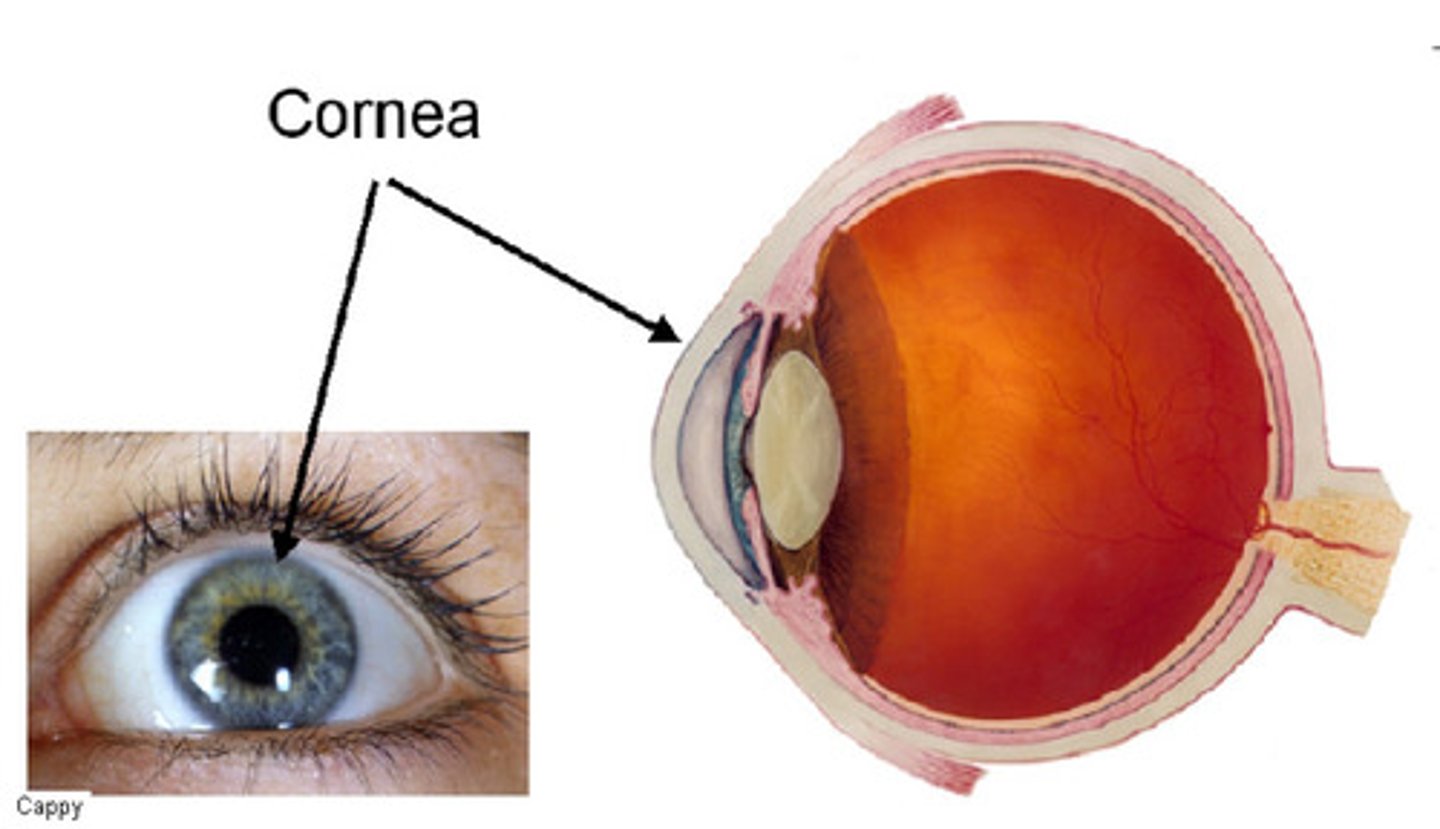
cornea
The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye
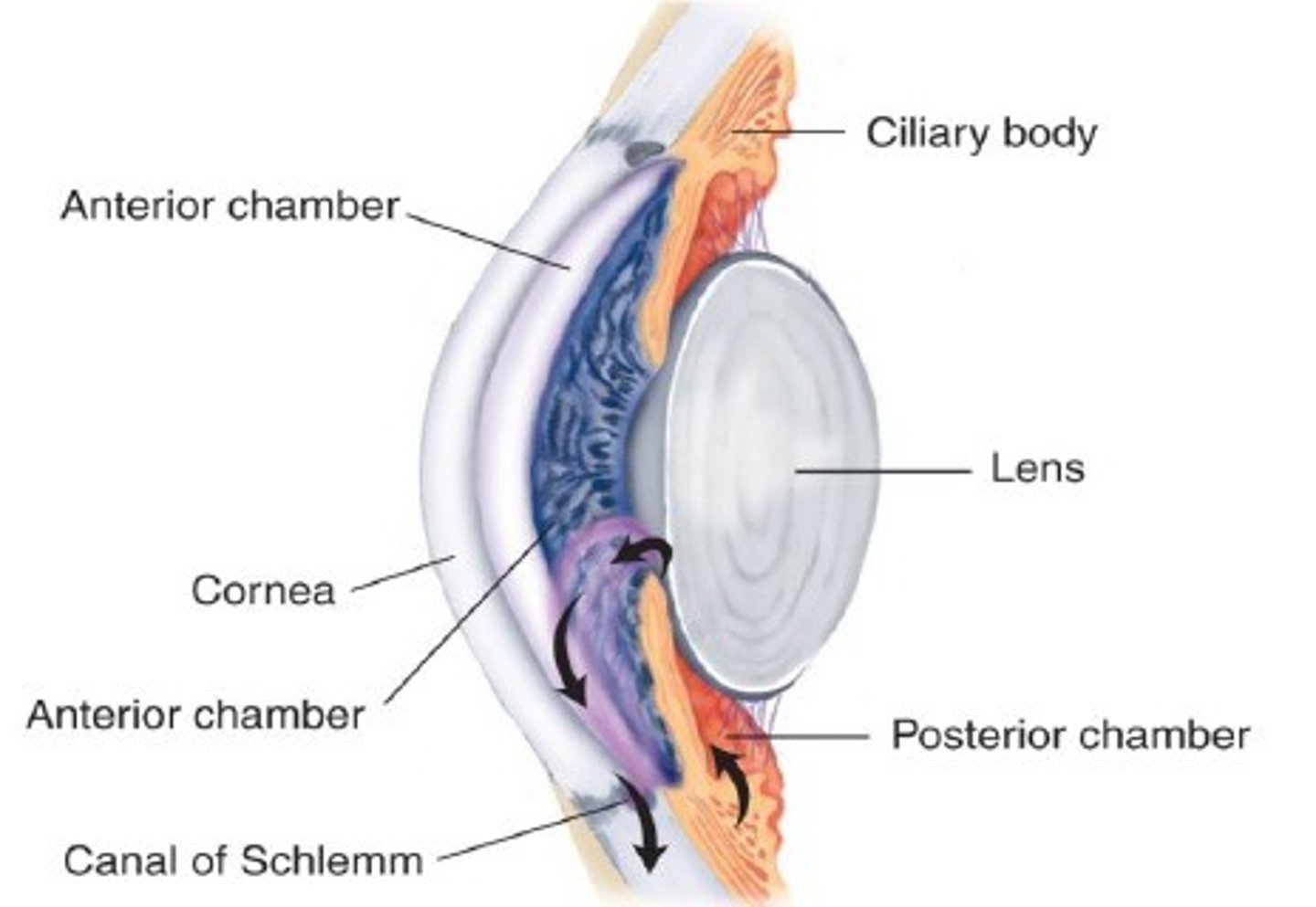
Canal of Schlemm (scleral venous sinus)
drains aqueous humor
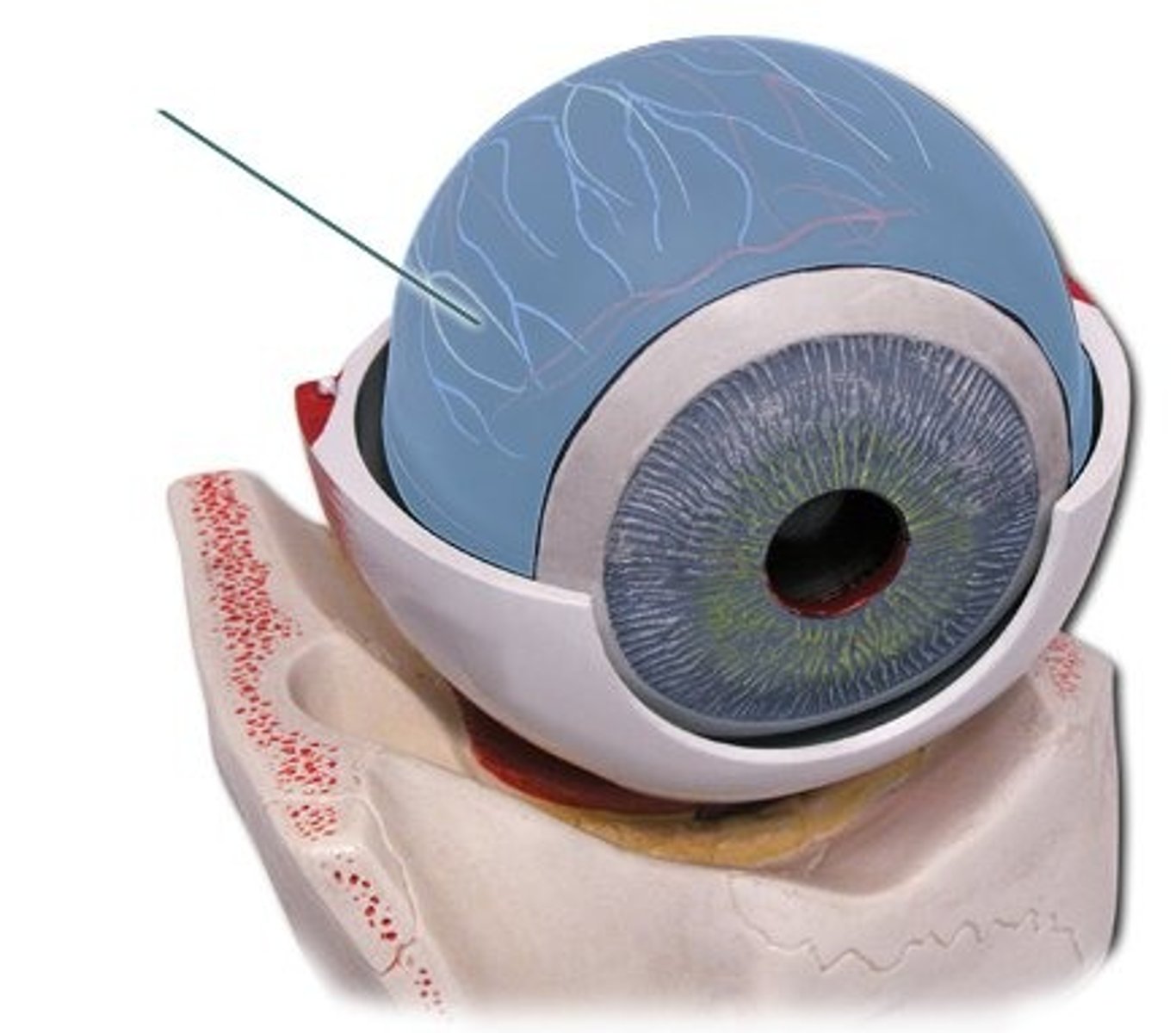
choroid
contains blood vessels and melanin
ciliary body
changes the shape of the eye and makes aqueous humor
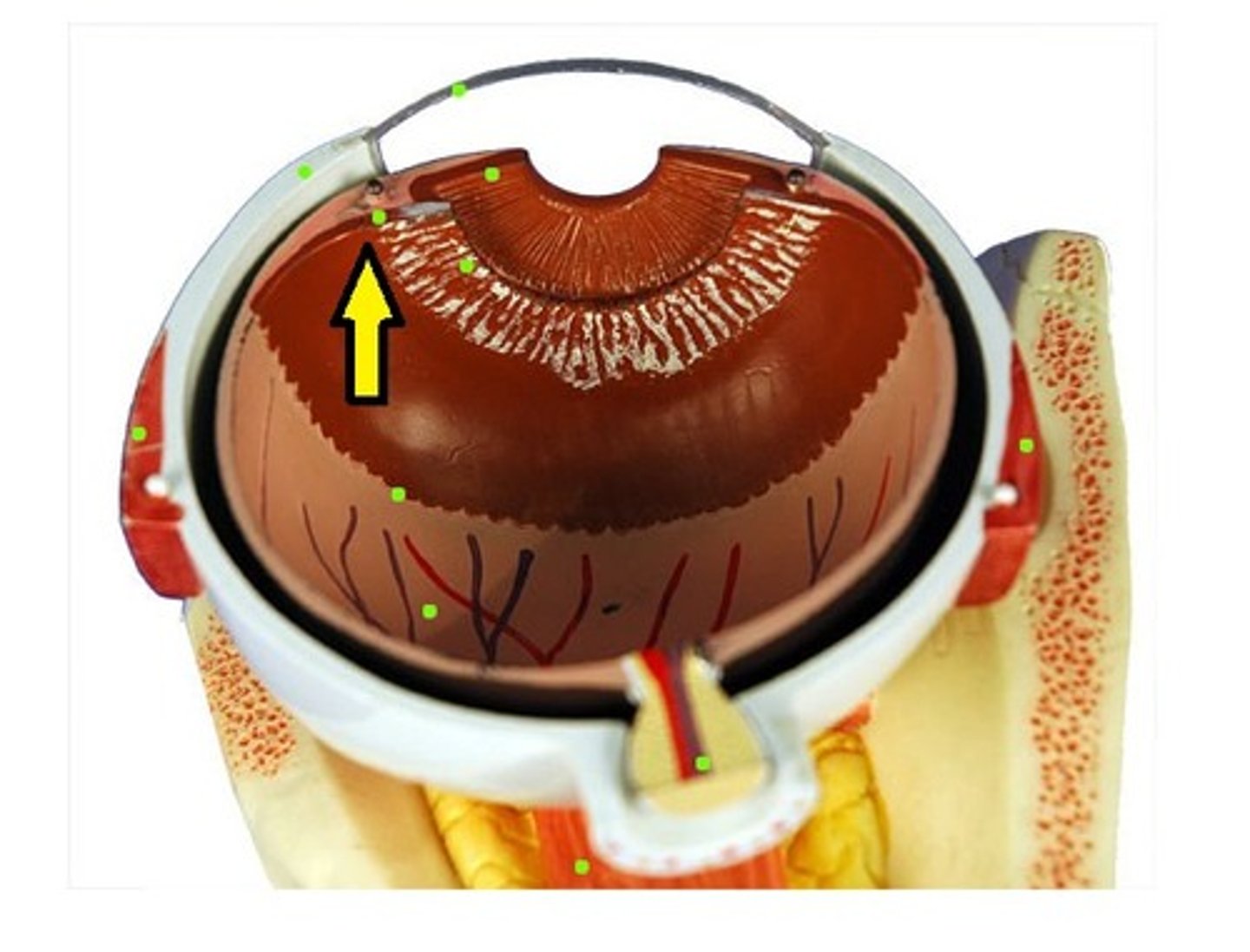
ora serrata
the serrated boundary between the ciliary muscle and the retina
ciliary processes
folds of ciliary body that secrete aqueous humor
suspensory ligaments
hold the lens in place
ciliary muscle
smooth muscle portion of the ciliary body, which contracts to assist in near vision
lens
Focuses light onto retina
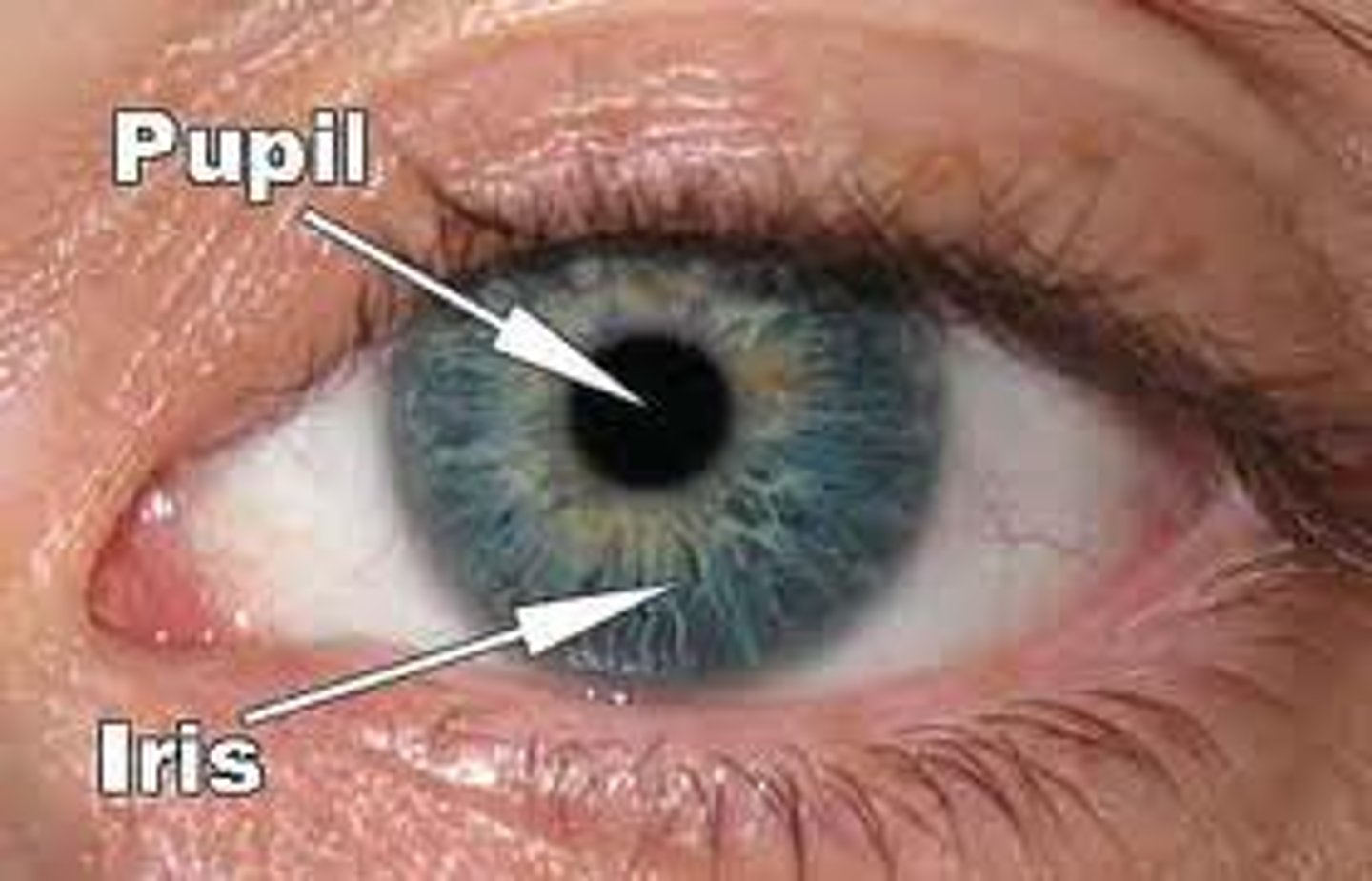
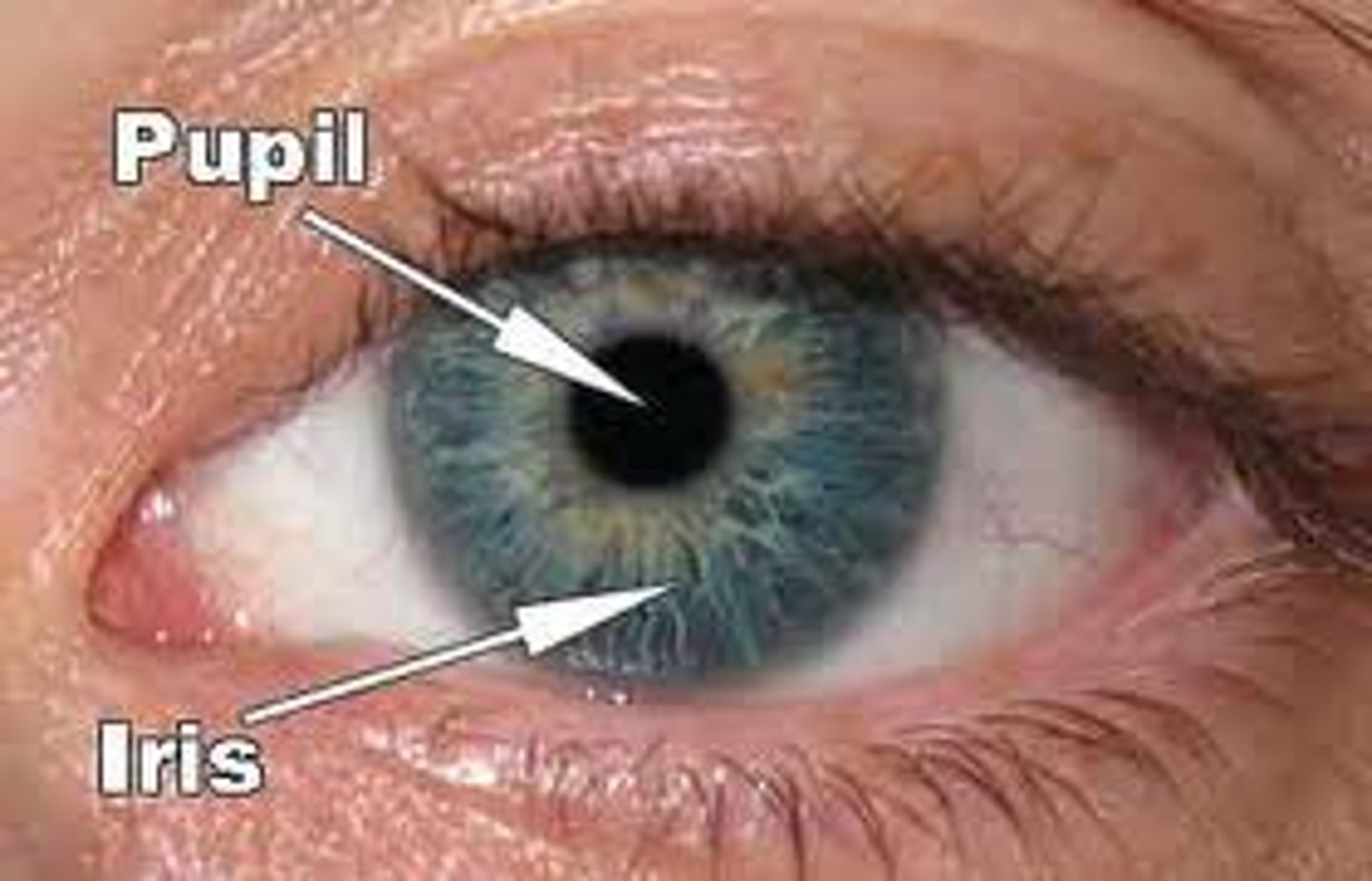
iris
Colored part of the eye
radial muscles of iris
contracts to dilate pupil
circular muscles of the iris
Smooth muscle that contracts to constrict pupil
anterior segment/cavity
between lens and cornea; filled with aqueous humor
Anterior chamber
between cornea and iris
Posterior chamber
between iris and lens
posterior segment/cavity
between lens and retina; contains gel-like vitreous humor
pupil
opening in the center of the iris
aqueous humor
fluid found anterior to the lens; nourishes the eye
viterous humor
jellylike substance posterior to the lens; holds the retina in place
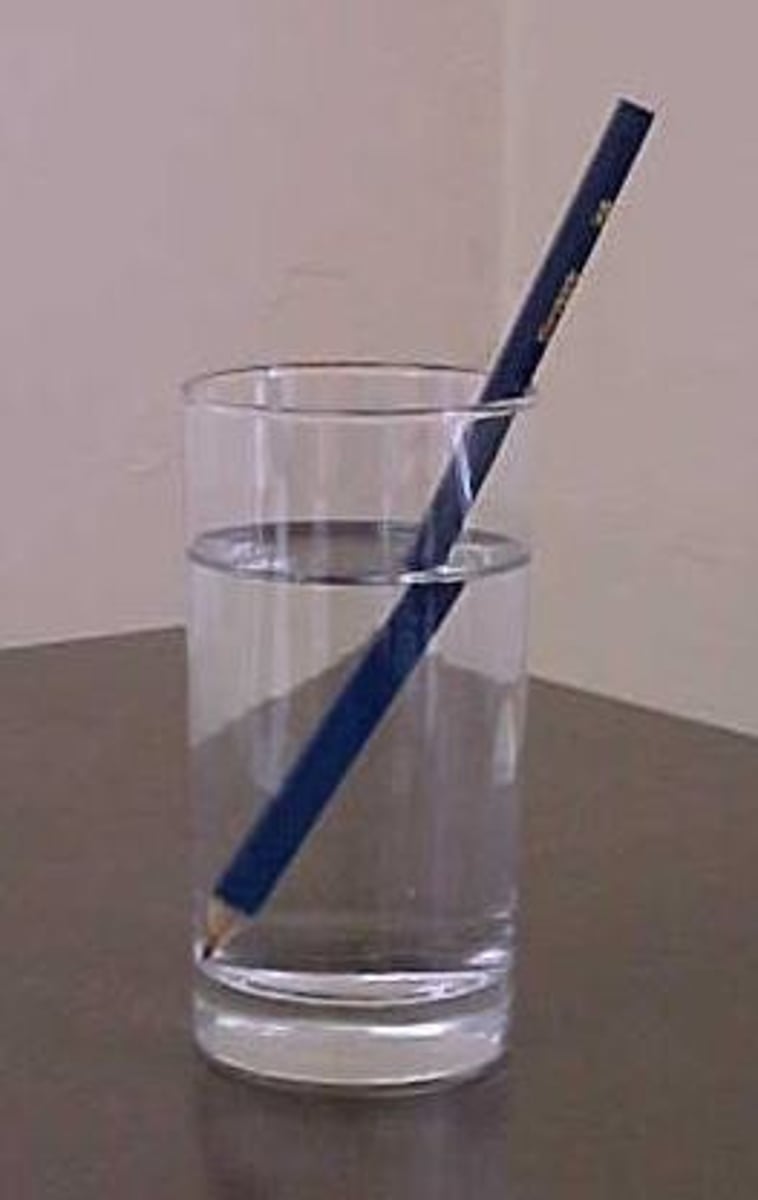
refraction
The bending of a wave as it passes from one medium to another

macula lutea
a yellowish central area of the retina that is rich in cones and that mediates clear detailed vision
fovea centralis
pinpoint depression in the center of the macula lutea that is the site of sharpest vision
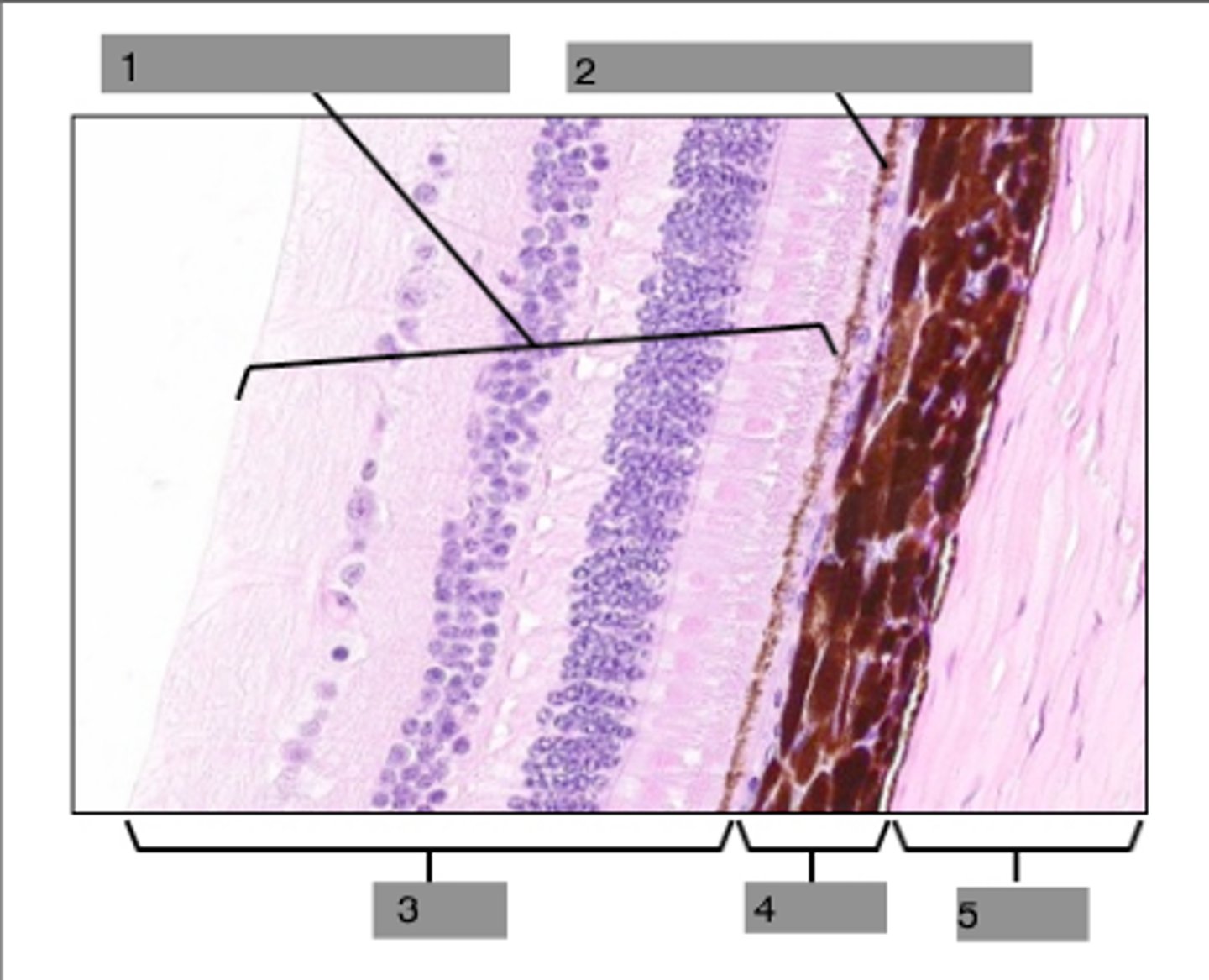
neural layer of retina
houses photoreceptors and other associated neurons
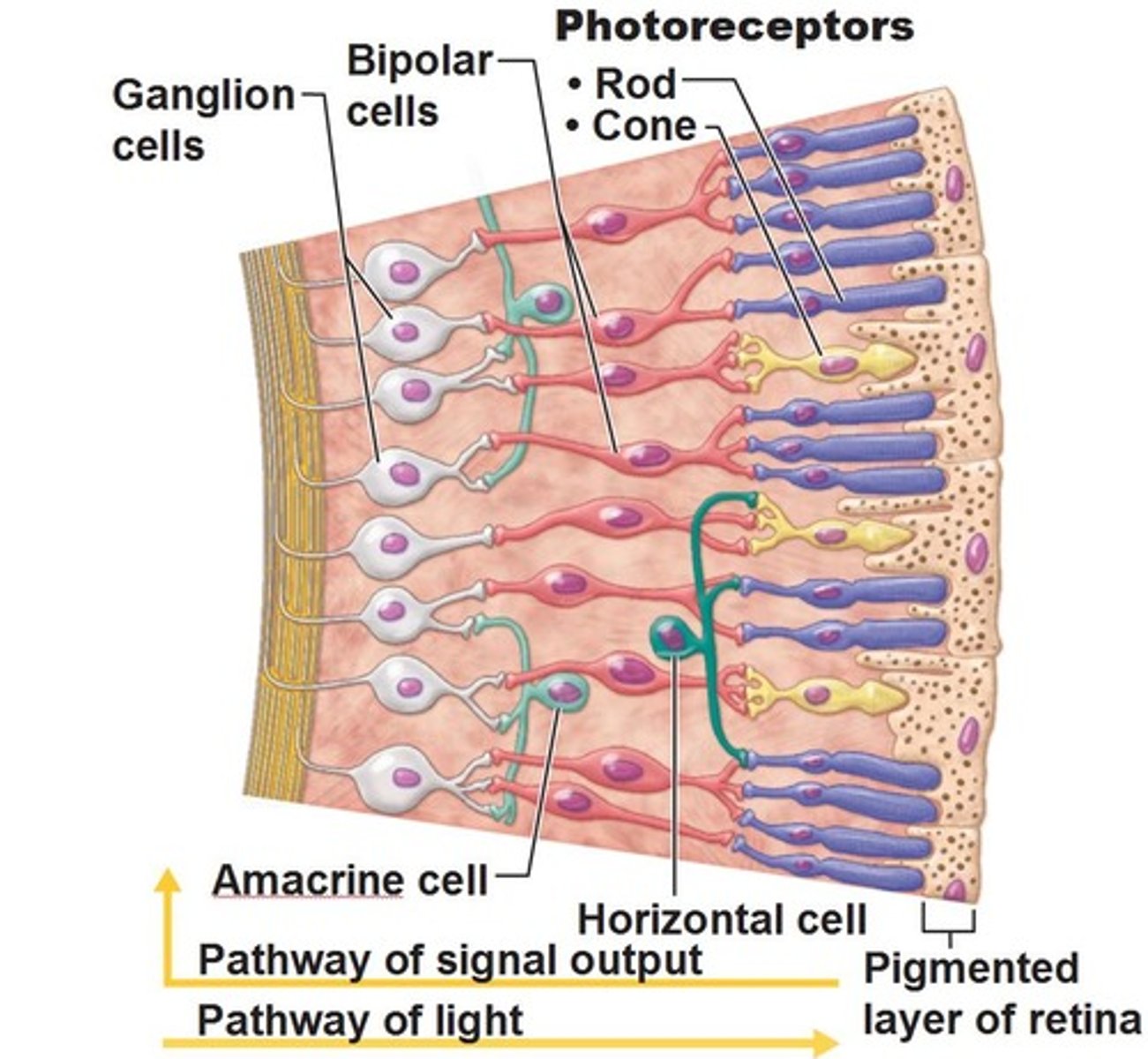
pigmented layer of retina
absorbs light and prevents it from scattering in the eye
rods
receptors that detect black, white, and gray
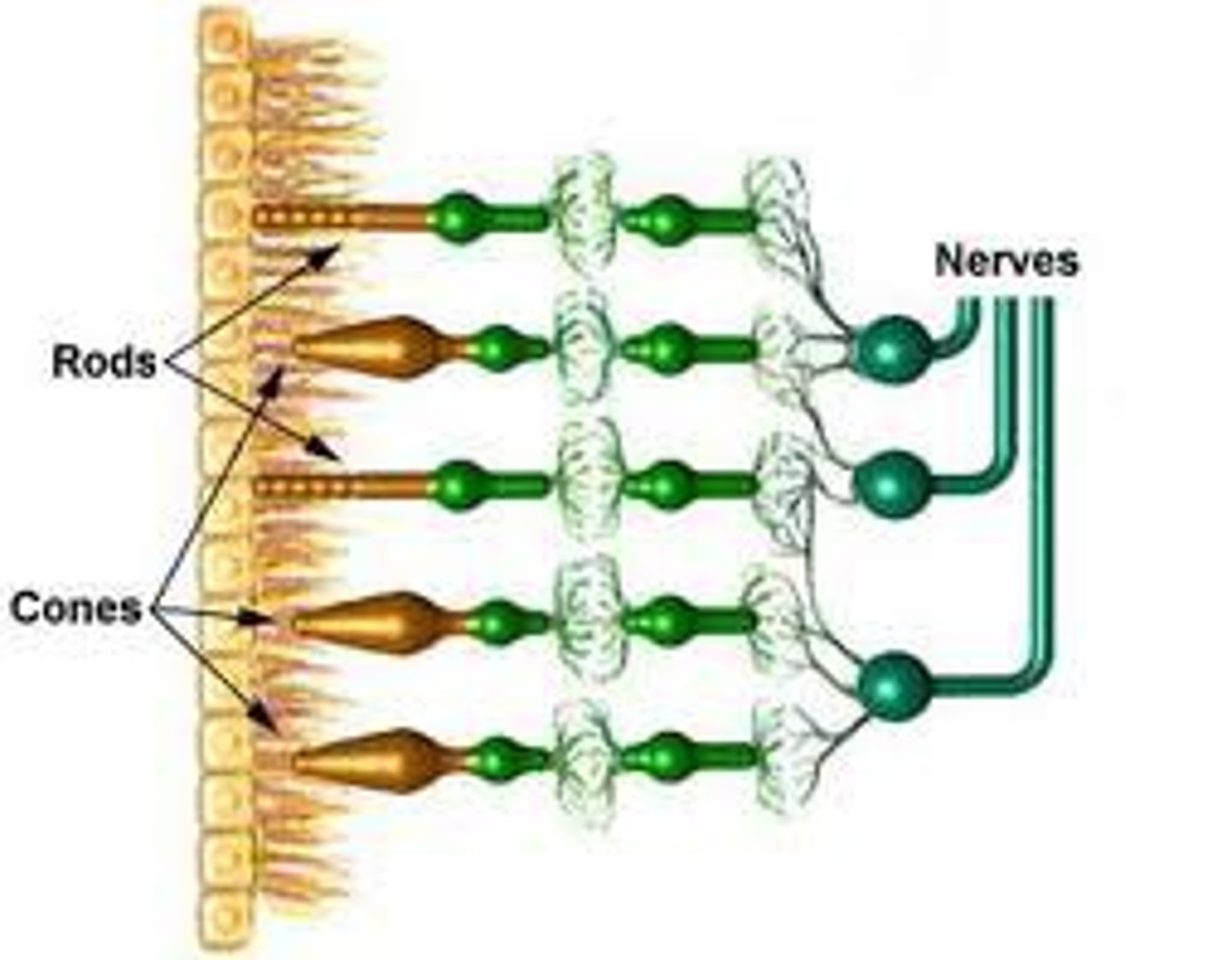
cones
color vision
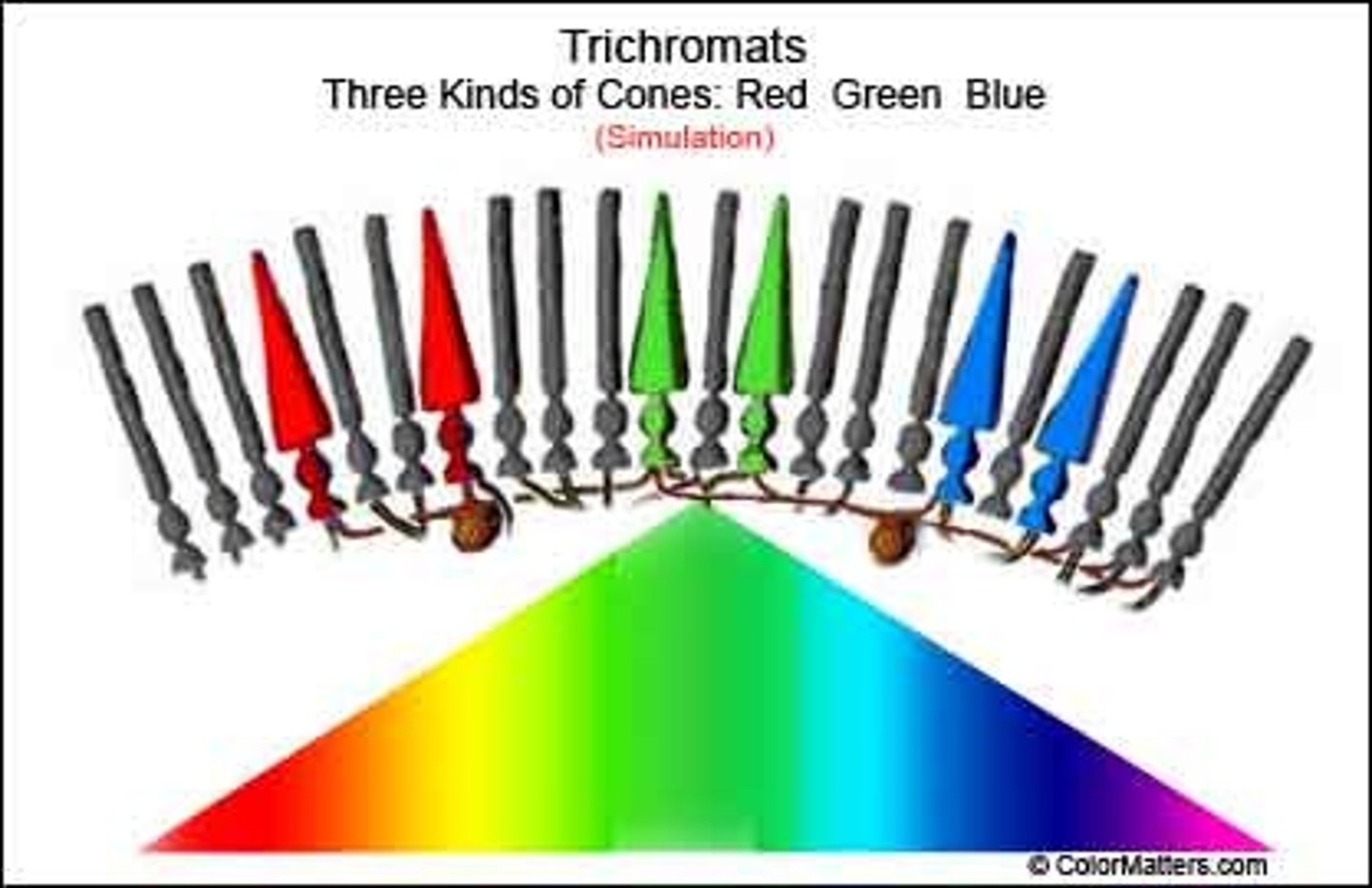
photoreceptor layer
contains rods and cones
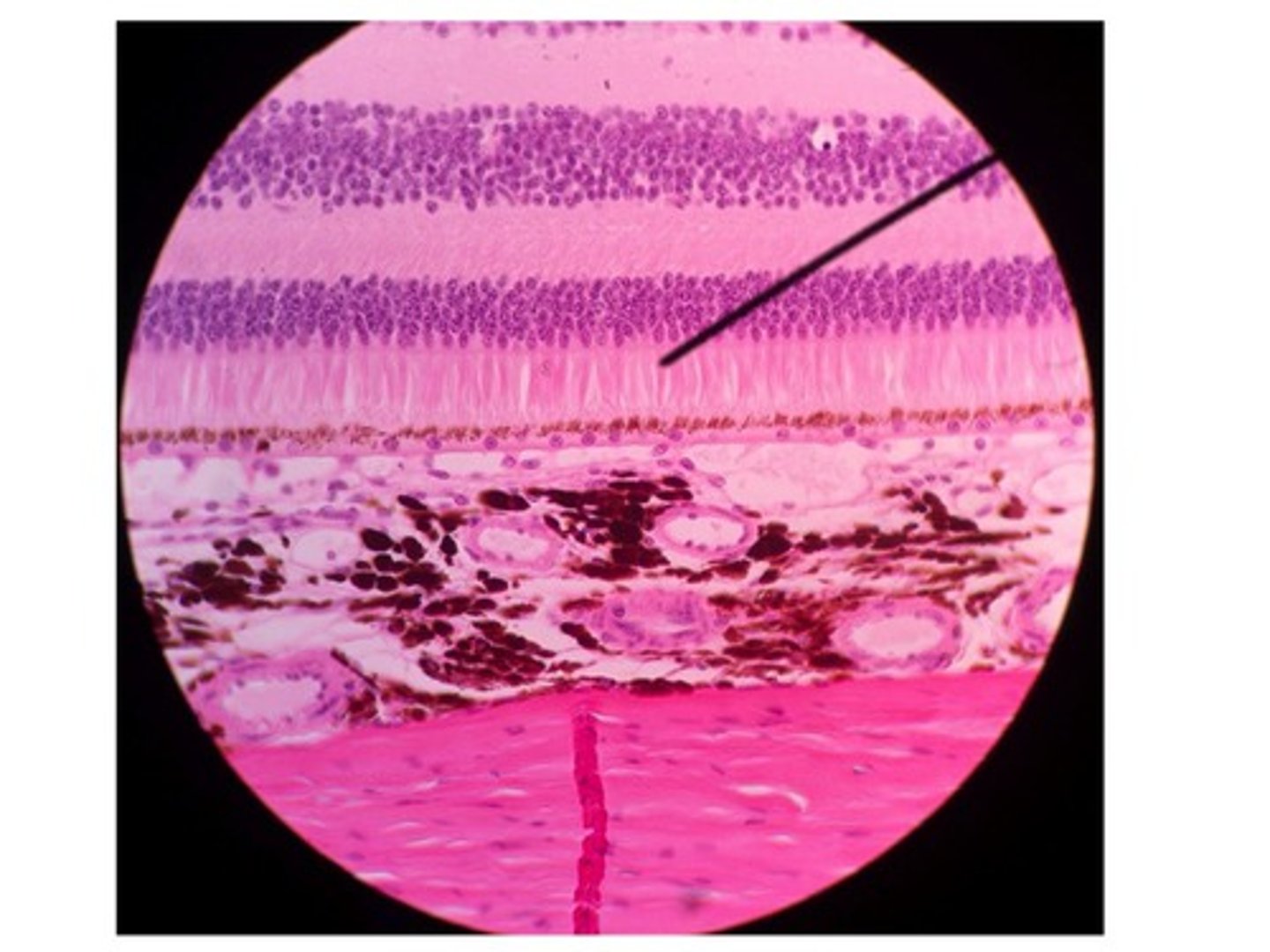
bipolar cell layer
rods and cones synapse on these cells
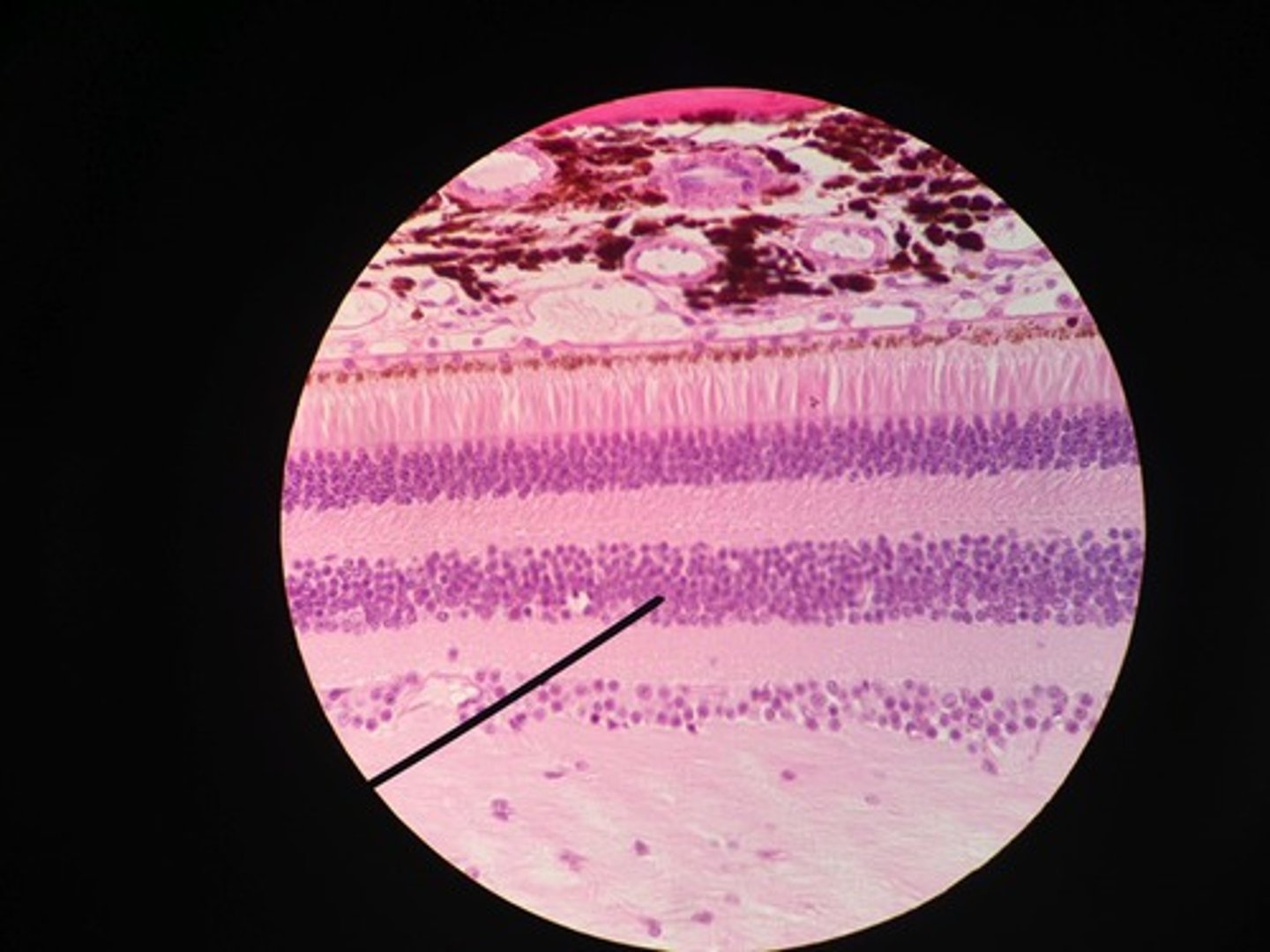
ganglion cell layer
A layer of the retina closest to the center of the eye, containing ganglion cells
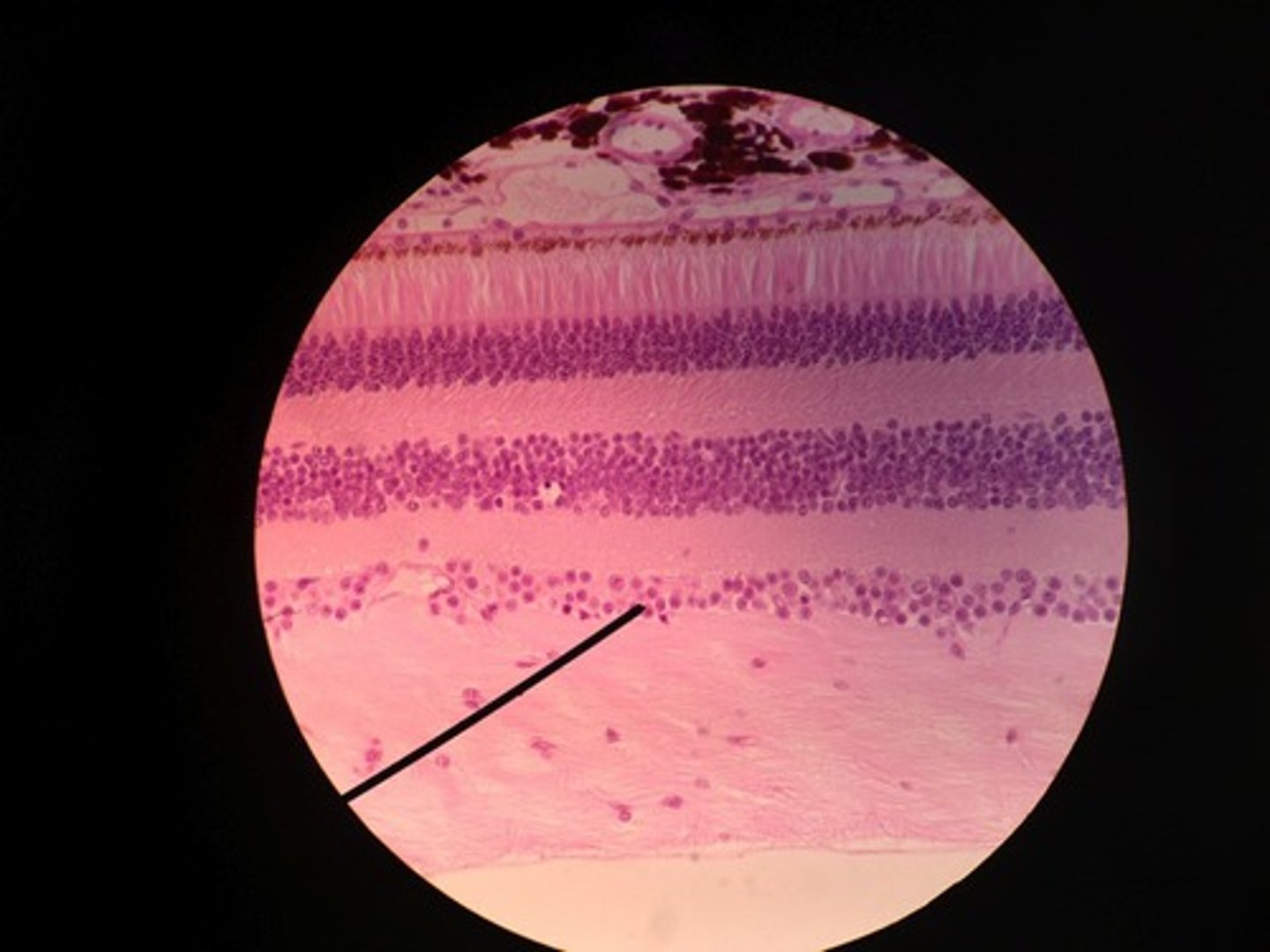
optic disc (blind spot)
Region at the back of the eye where the optic nerve meets the retina. No photoreceptors are here
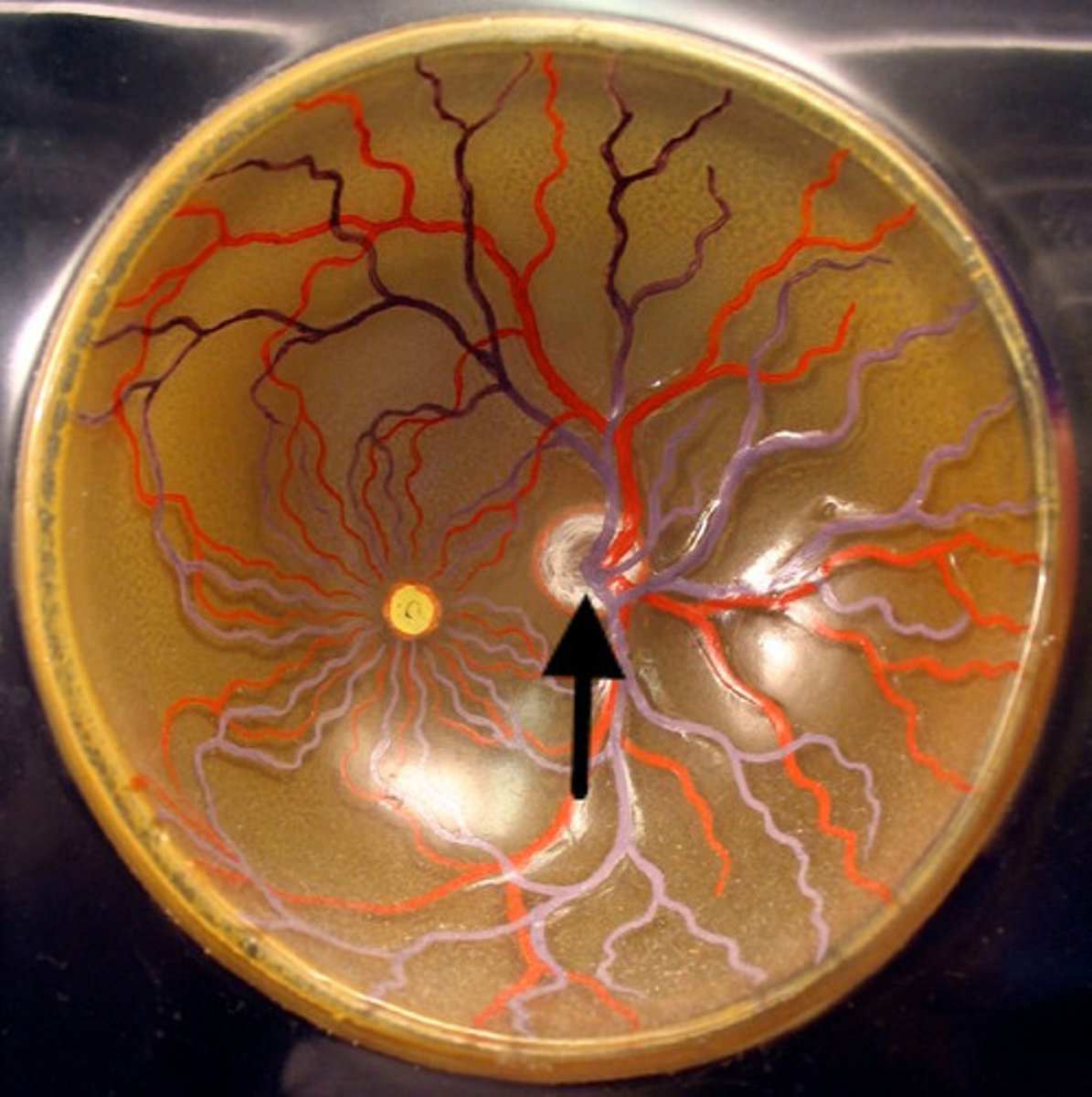
optic chiasm
point at which optic nerve fibers cross in the brain
optic tract
leads from optic chiasma to terminate in lateral geniculate body
optic radiations
the diffuse neural pathways from each lateral geniculate nucleus to the primary visual cortex of the same hemisphere
fixation
looking at a motionless object
saccades
moving the eyes rapidly from one location to another
smooth pursuit
tracking objects
pretectal nuclei
involved with pupillary reflexes
external ear
outer structures of the ear that collect sound
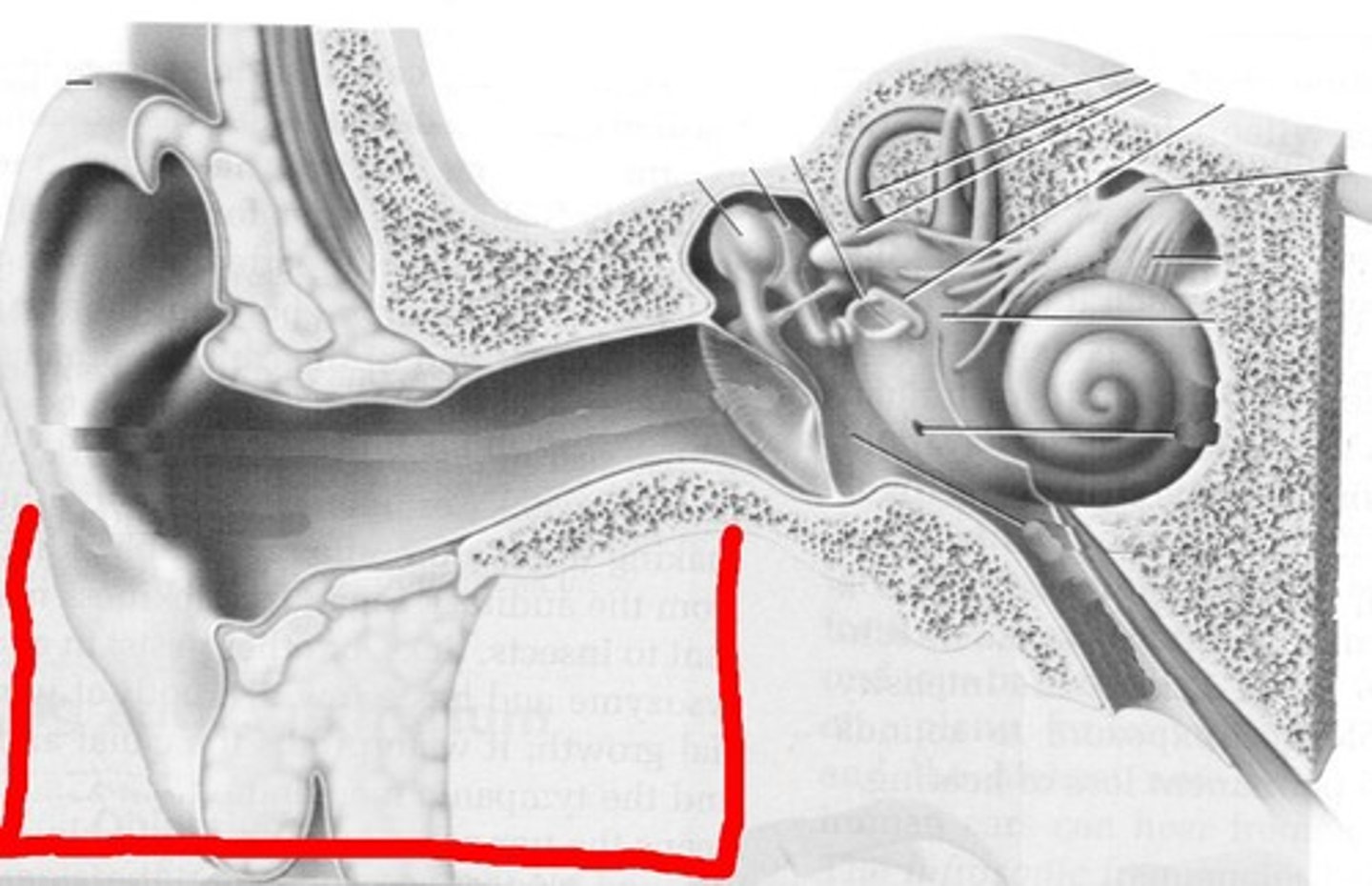
middle ear
conveys sound vibrations to the oval window
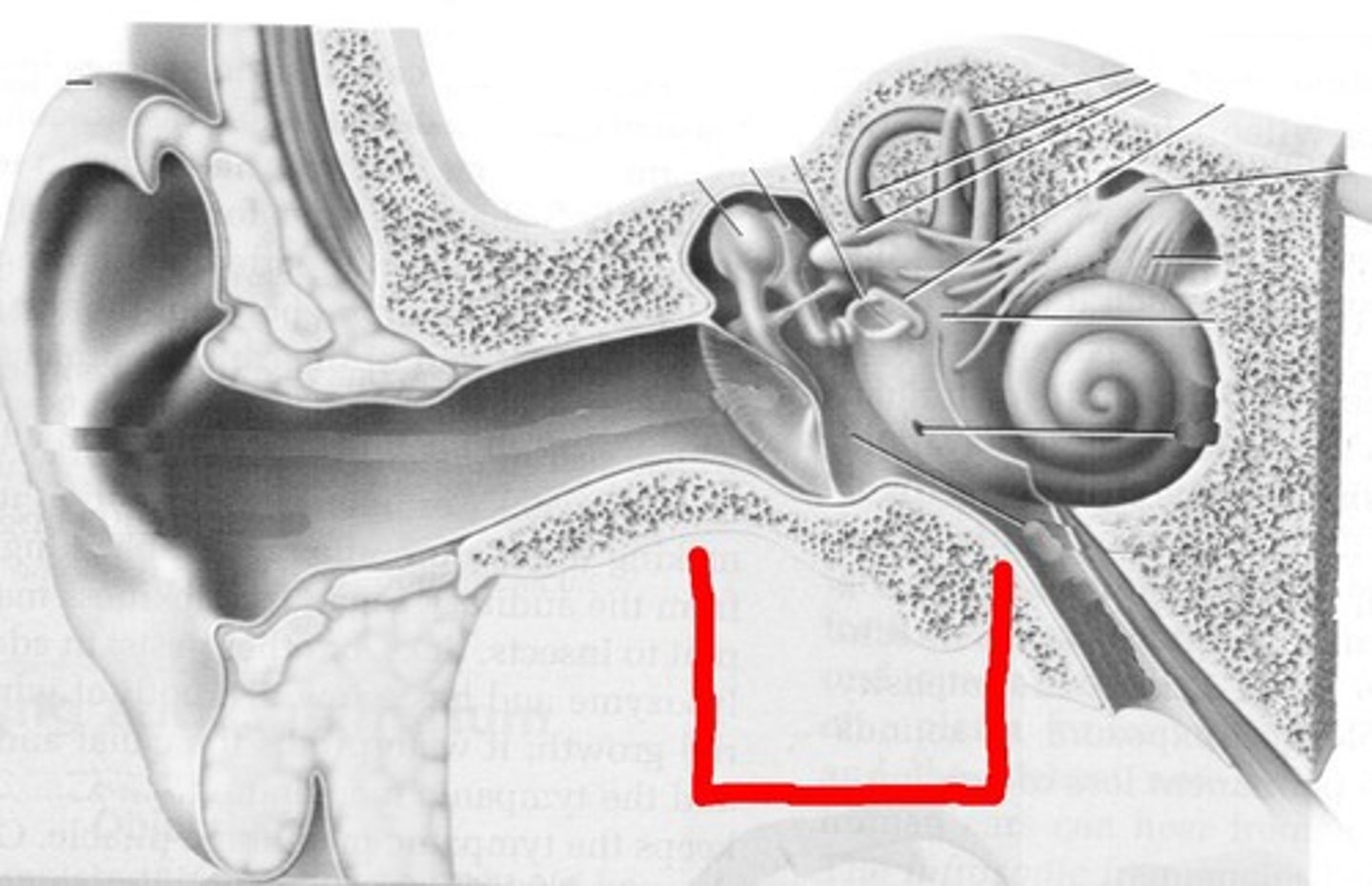
inner ear
contains cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibule
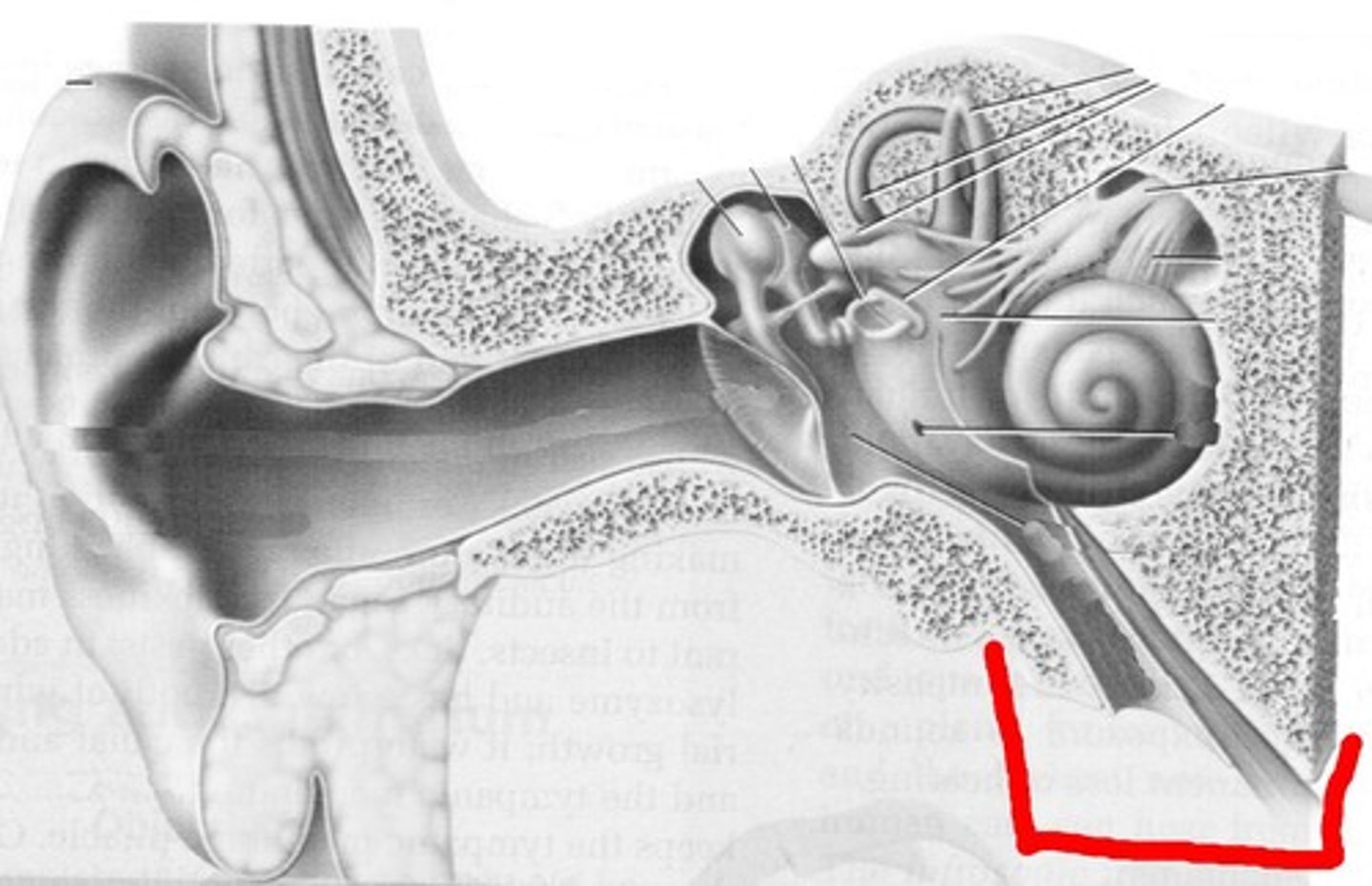
auricle
external portion of the ear
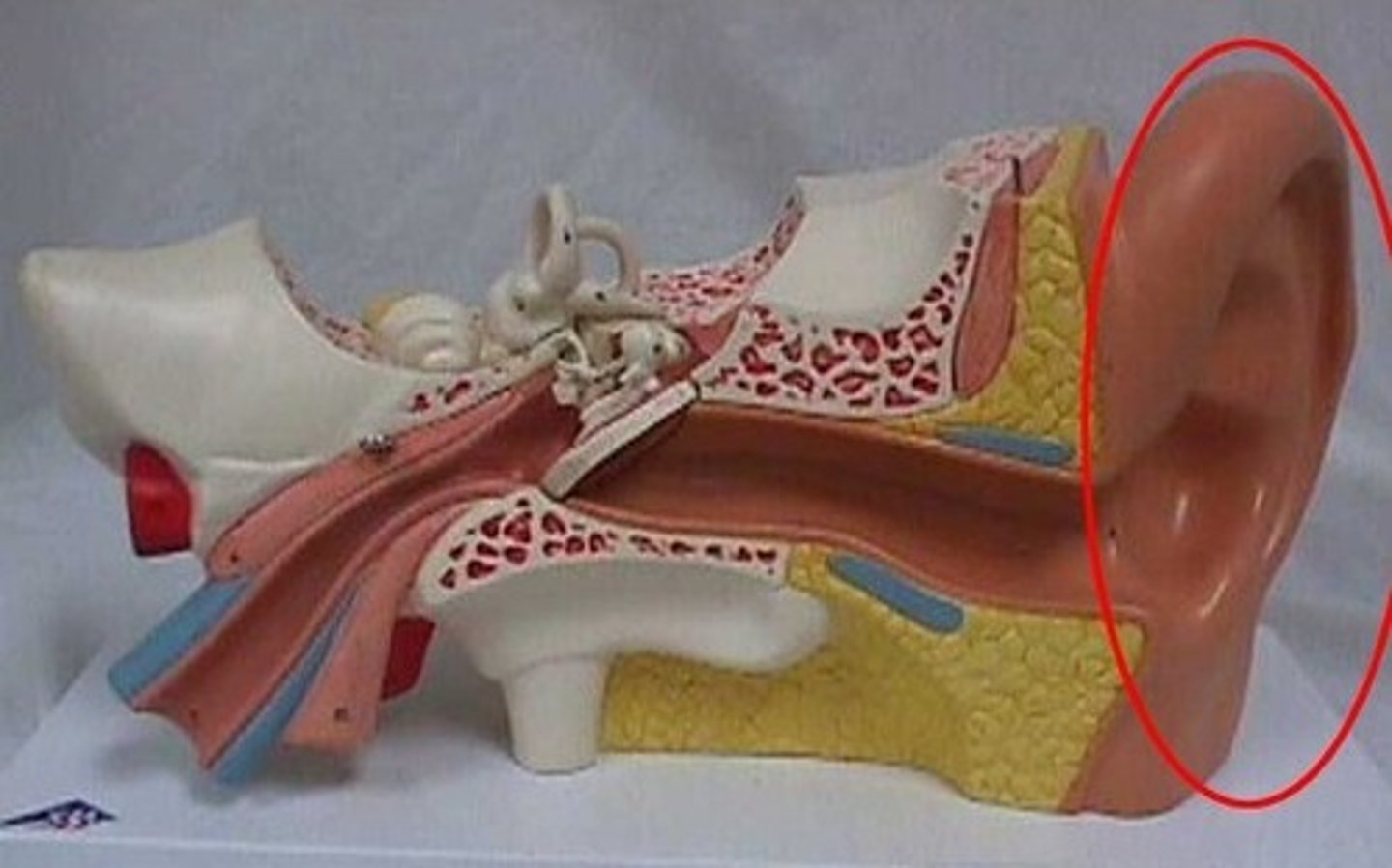
helix
rim of ear
lobule
earlobe
External acoustic (auditory) meatus
transmits sound waves from the auricle to the tympanic membrane of the middle ear
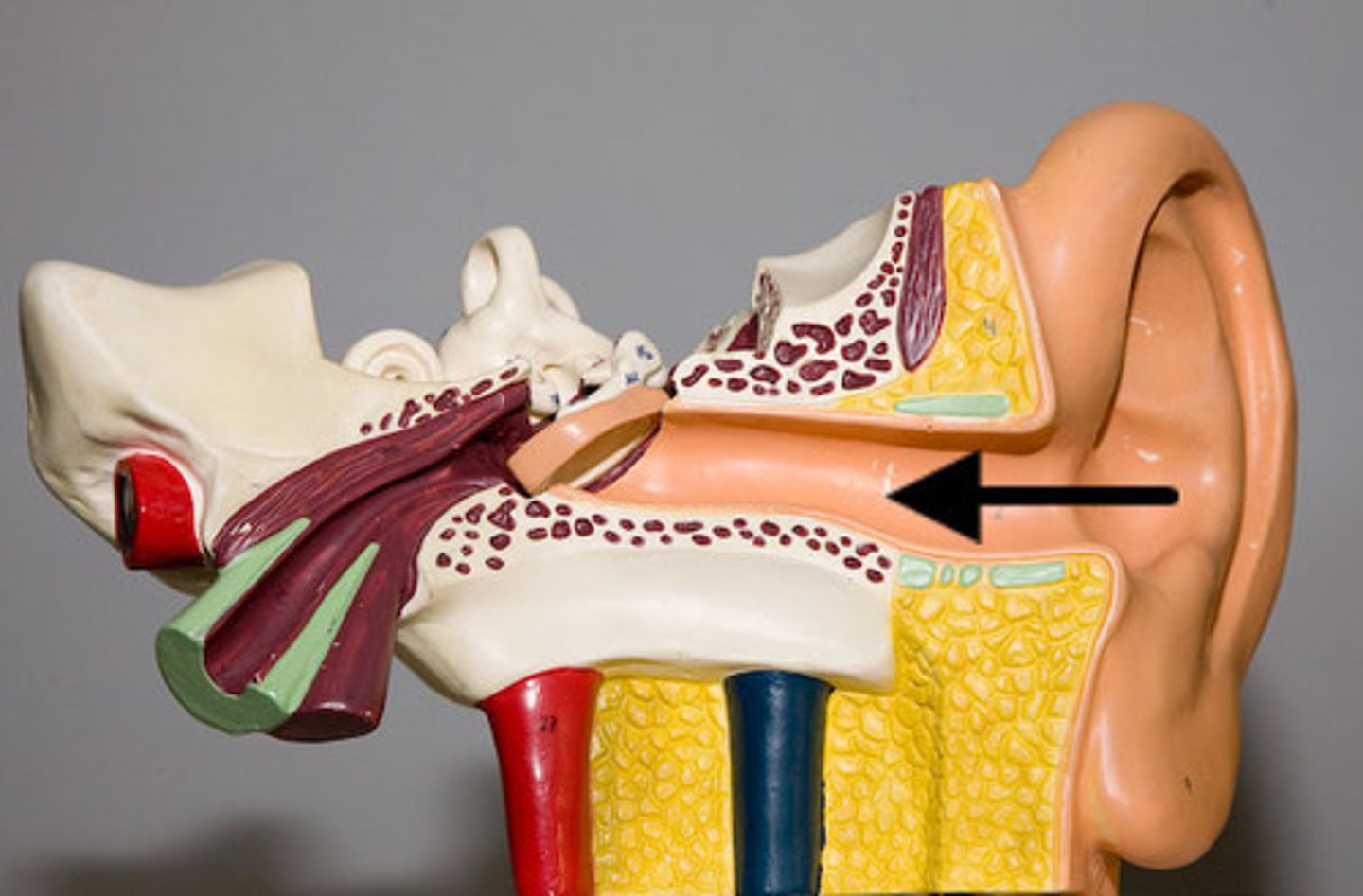
tympanic membrane
eardrum; turns sound waves into vibrations
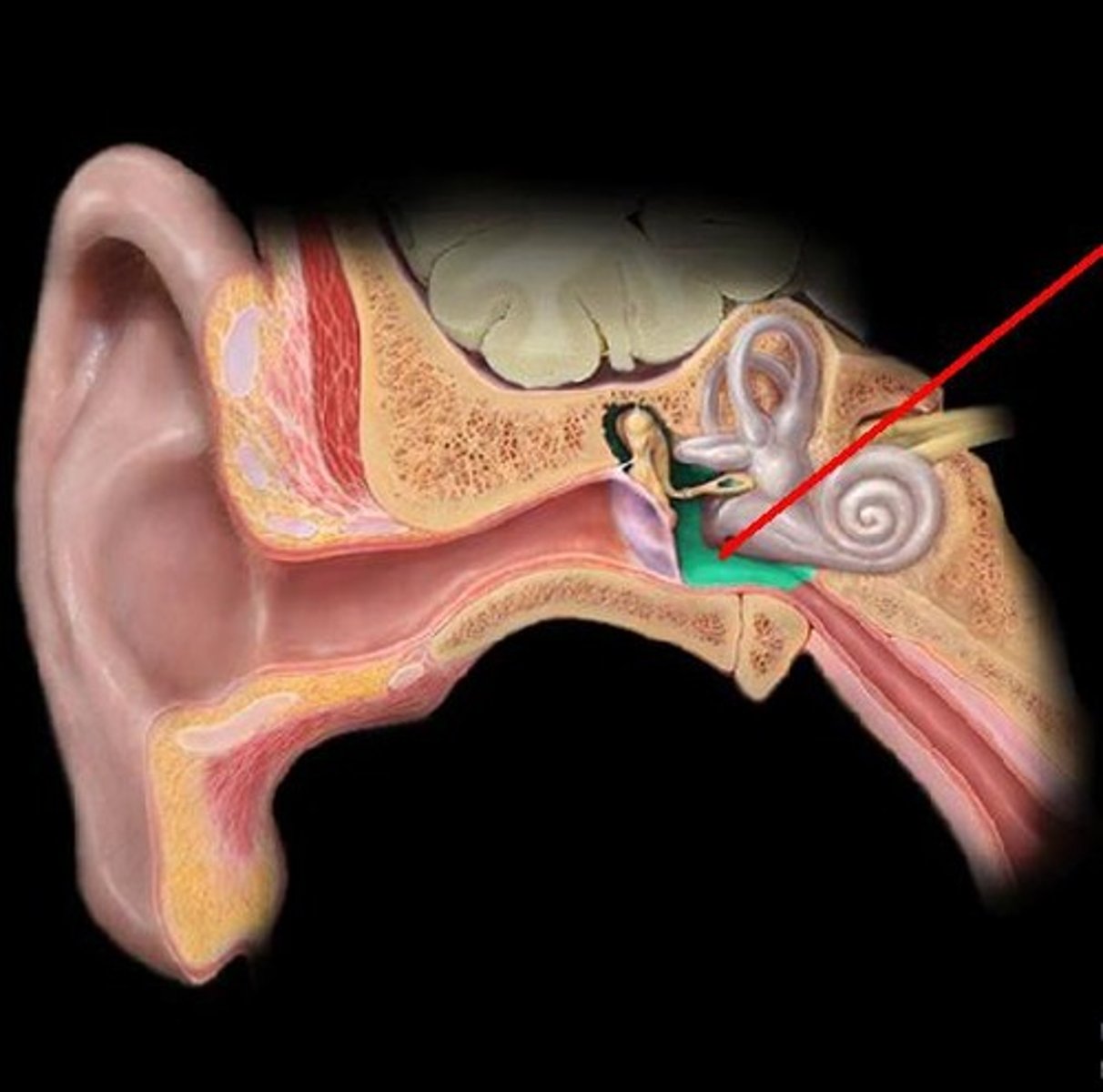
pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube
channel between the middle ear and throat
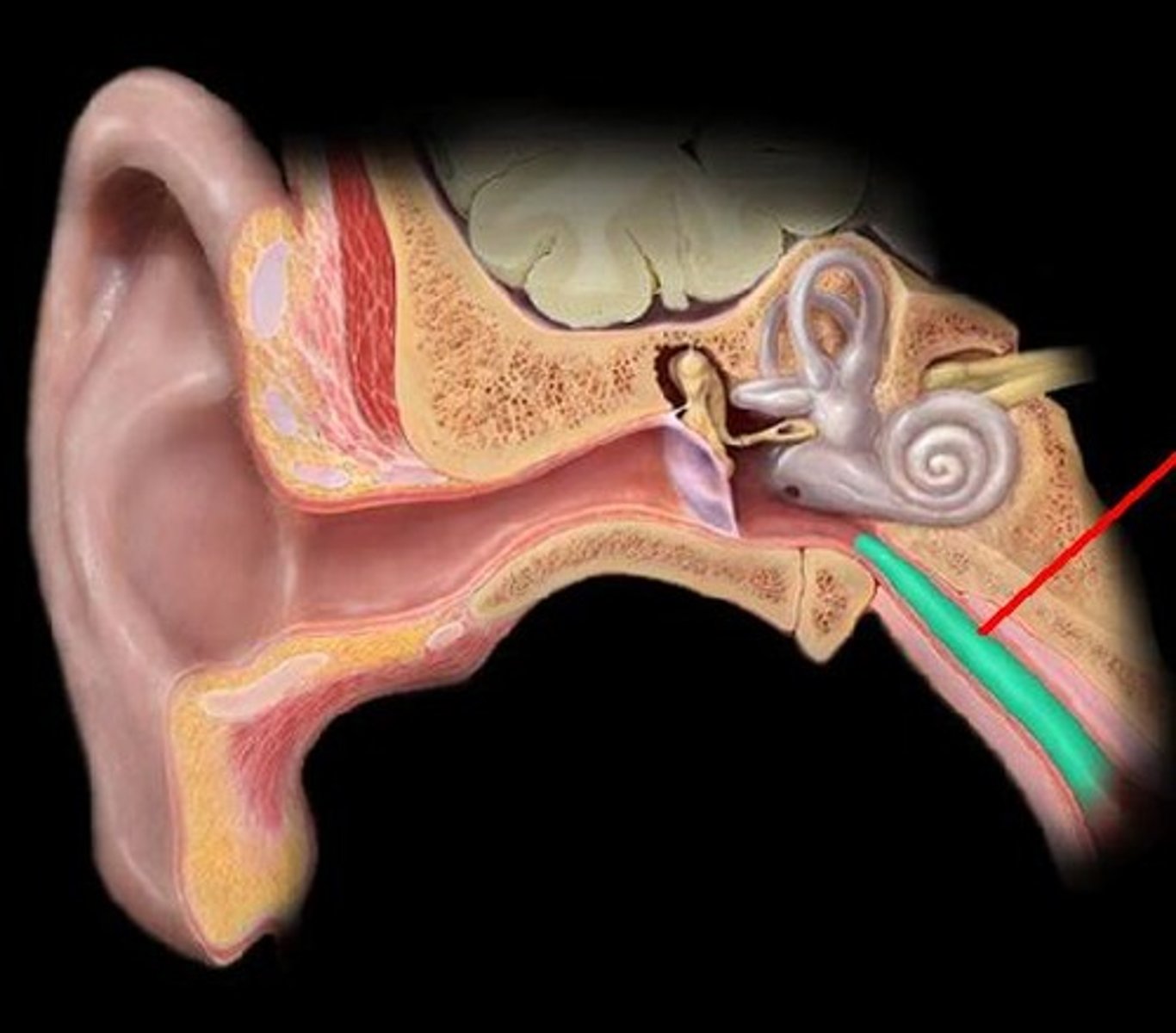
ossicles
three tiny bones in the middle ear; transmits vibrations to the inner ear
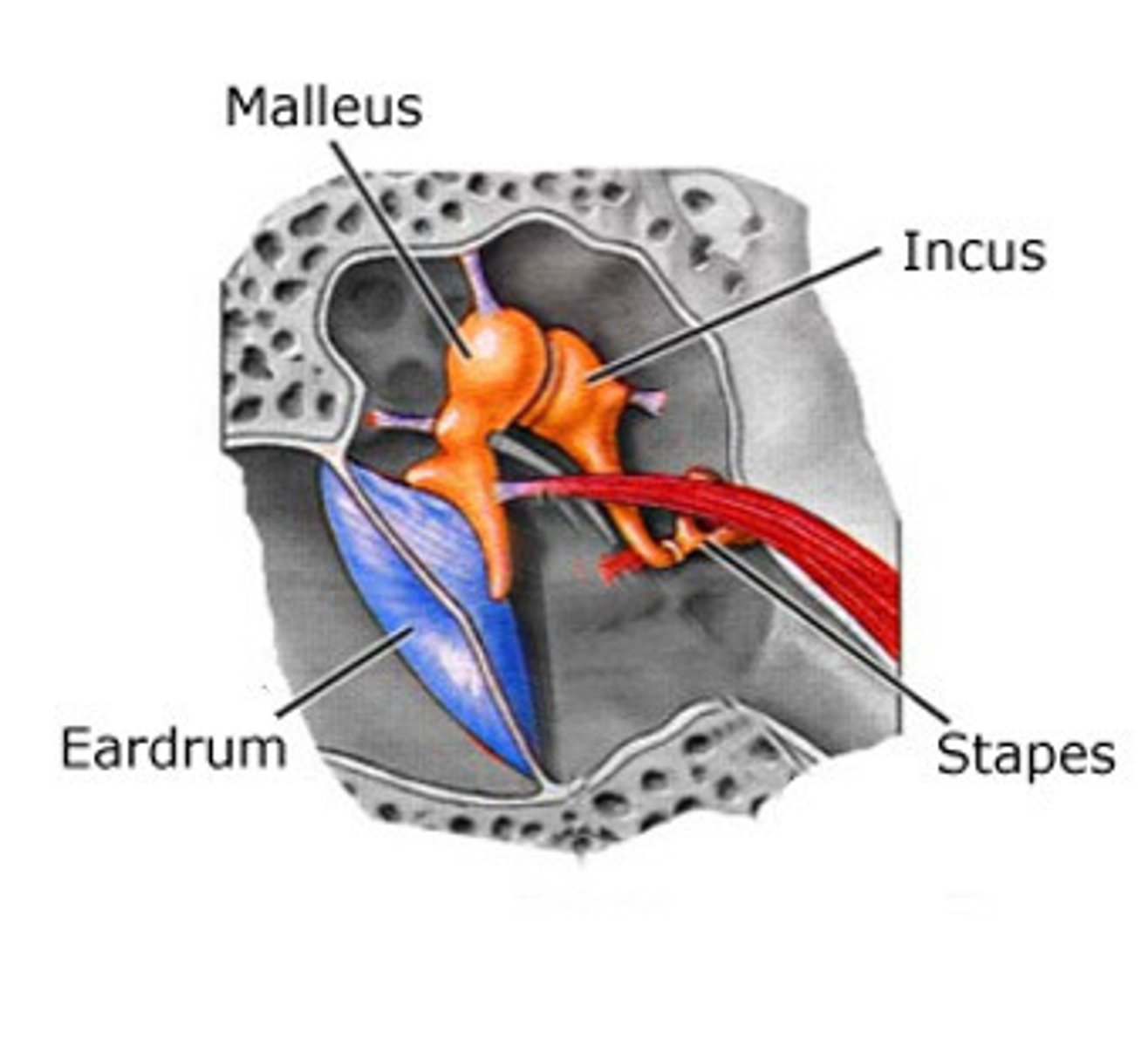
malleus
hammer; first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
incus
anvil; middle of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
stapes
stirrup; last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
round window
A membrane-covered opening in the inner wall of the middle ear that compensates for changes in cochlear pressure.
middle ear infections
Usually result when infections of the nose and throat move through the auditory tubes
More common in children because their auditory tubes are horizontal, allowing easier access to bacteria
bony labyrinth
winding tunnels located in the inner ear
membranous labyrinth
membrane-covered tubes inside the bony labyrinth
perilymph
fluid contained in the bony labyrinth of the inner ear
endolymph
fluid within the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear
vestibule
the area between cochlea & semicircular canals. detects linear acceleration and head position
otolith organs
the mechanical structures in the vestibular system that sense both linear acceleration and gravity
utricle
horizontal sac; detects side to side and forward backward motions
saccule
vertical sac; detects up/down and forward/backward motions
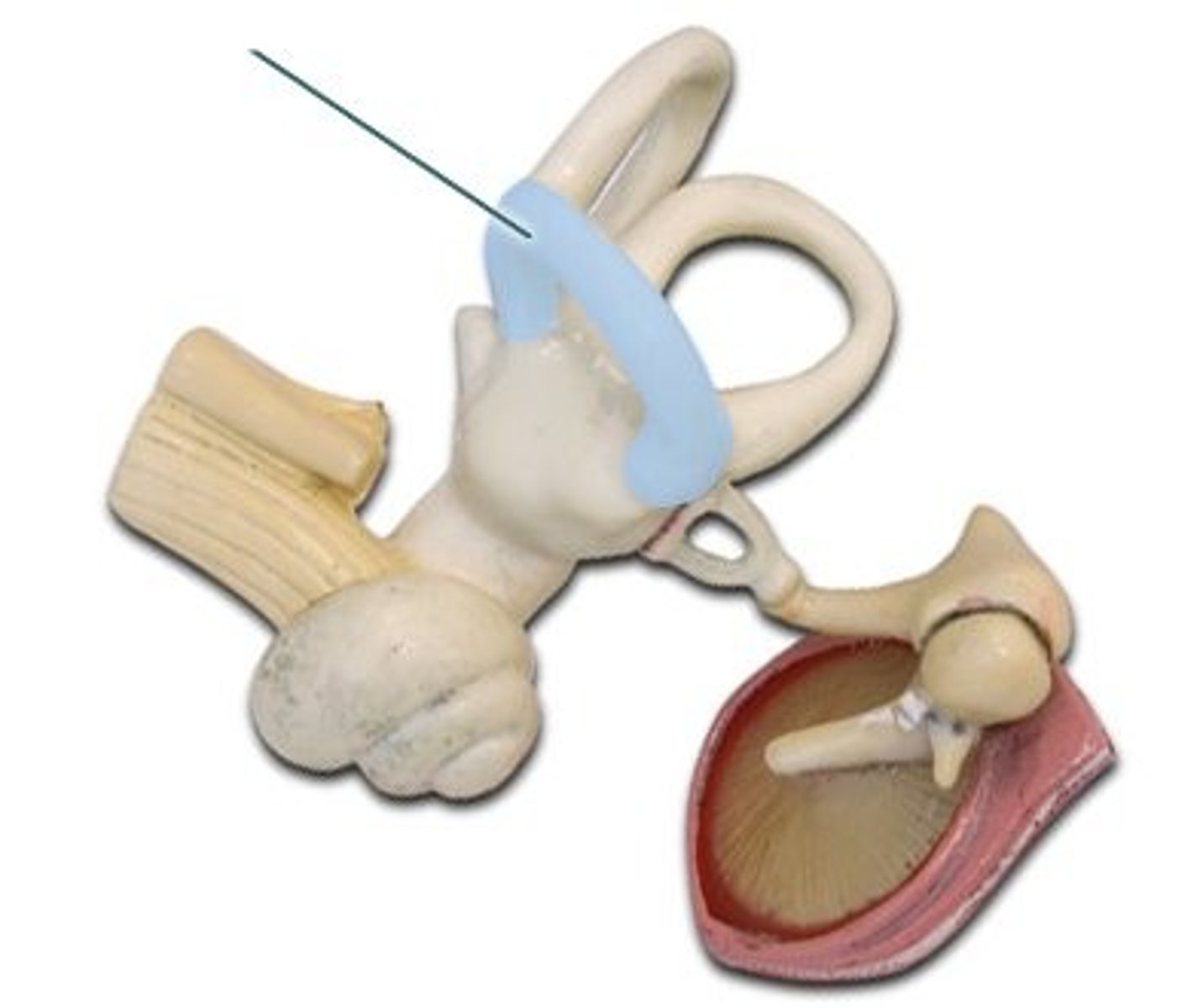
semicircular canals
three canals within the inner ear that contain specialized receptor cells that generate nerve impulses with rotational acceleration
anterior semicircular canal
nodding yes
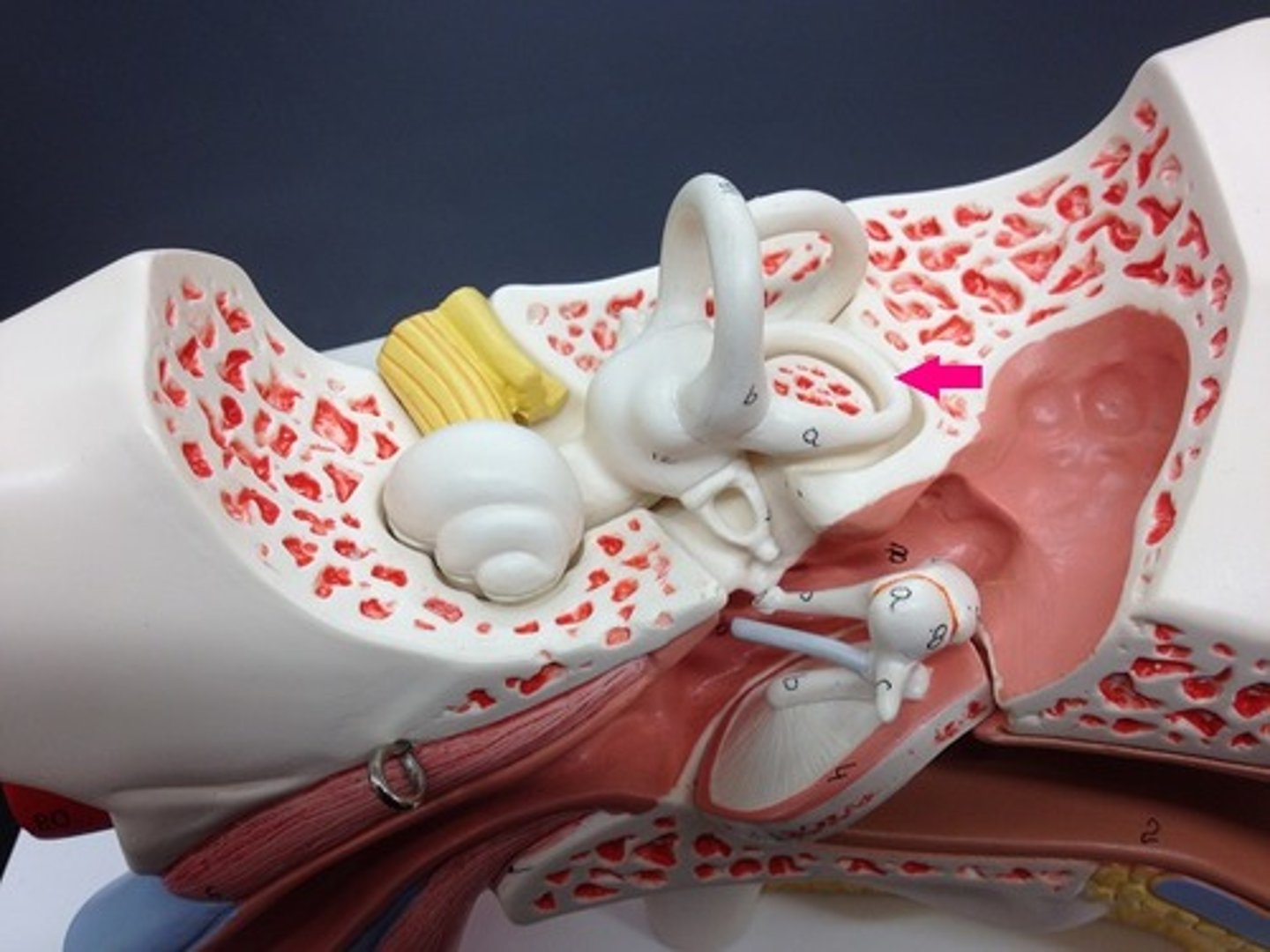
lateral semicircular canal
saying no
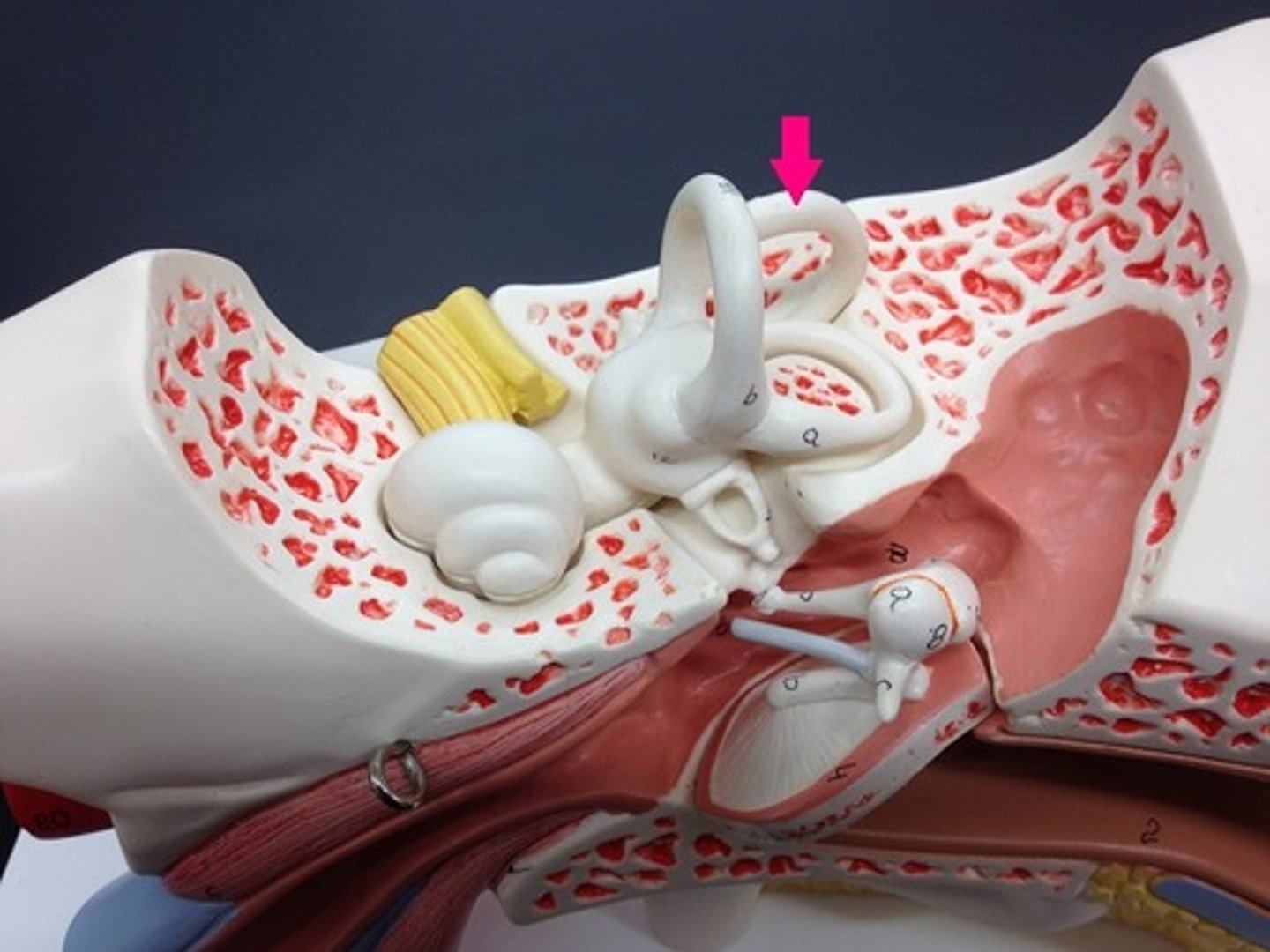
posterior semicircular canal
ear to shoulder
equilibrium pathway
CN8 to the vestibular nuclei; integration occurs and info sent out thru CN3, 4, 6, 11 and the vestibulospinal tract. Impulses to VPN for conscious awareness of balance
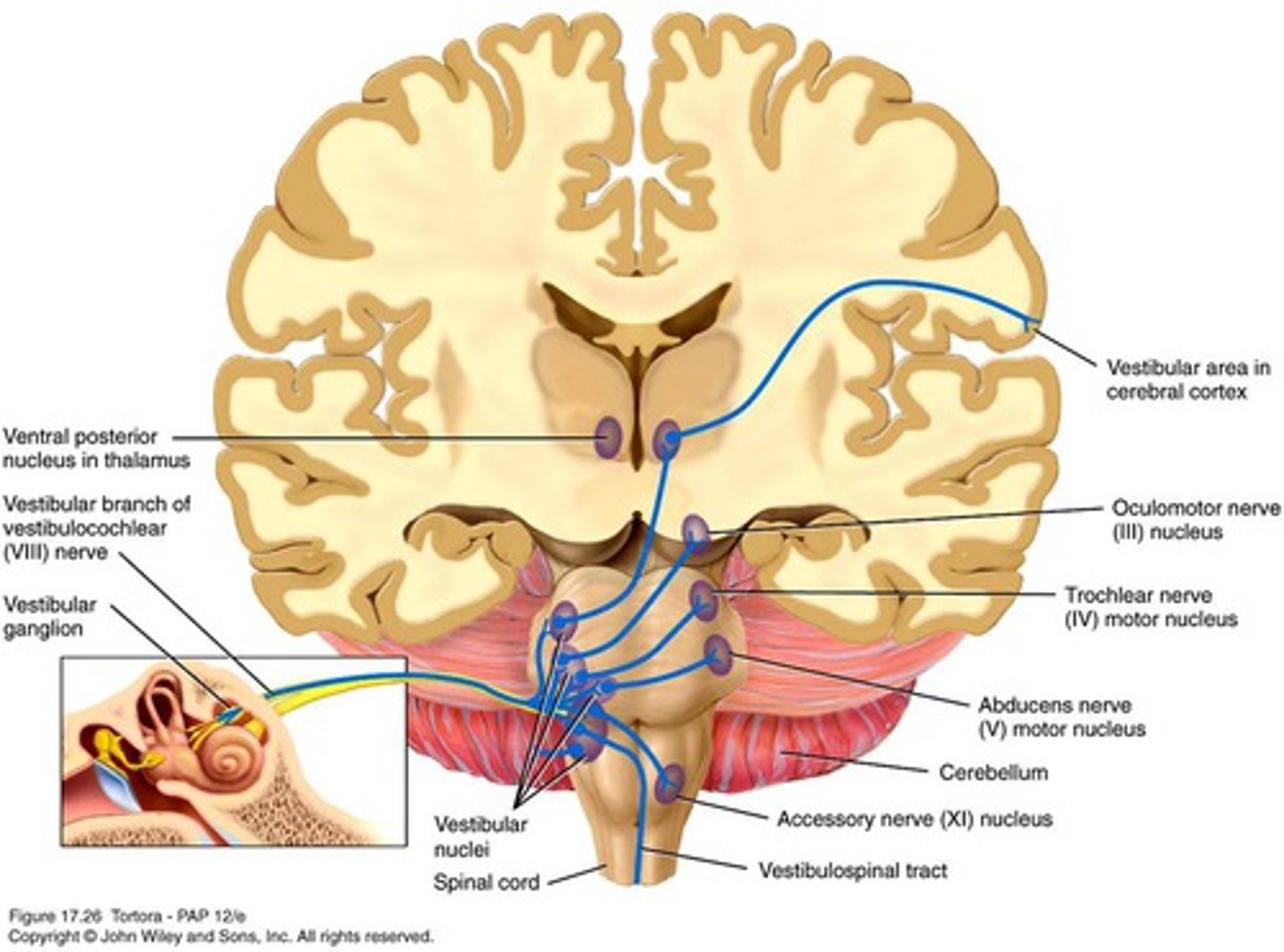
motion sickness
Effect when visual and/or motor feedback is inconsistent with vestibular info
inferior cerebellar peduncles
part of equilibrium pathway; aid in balance and coordinating postural adjustments
cochlea
site of hearing receptors
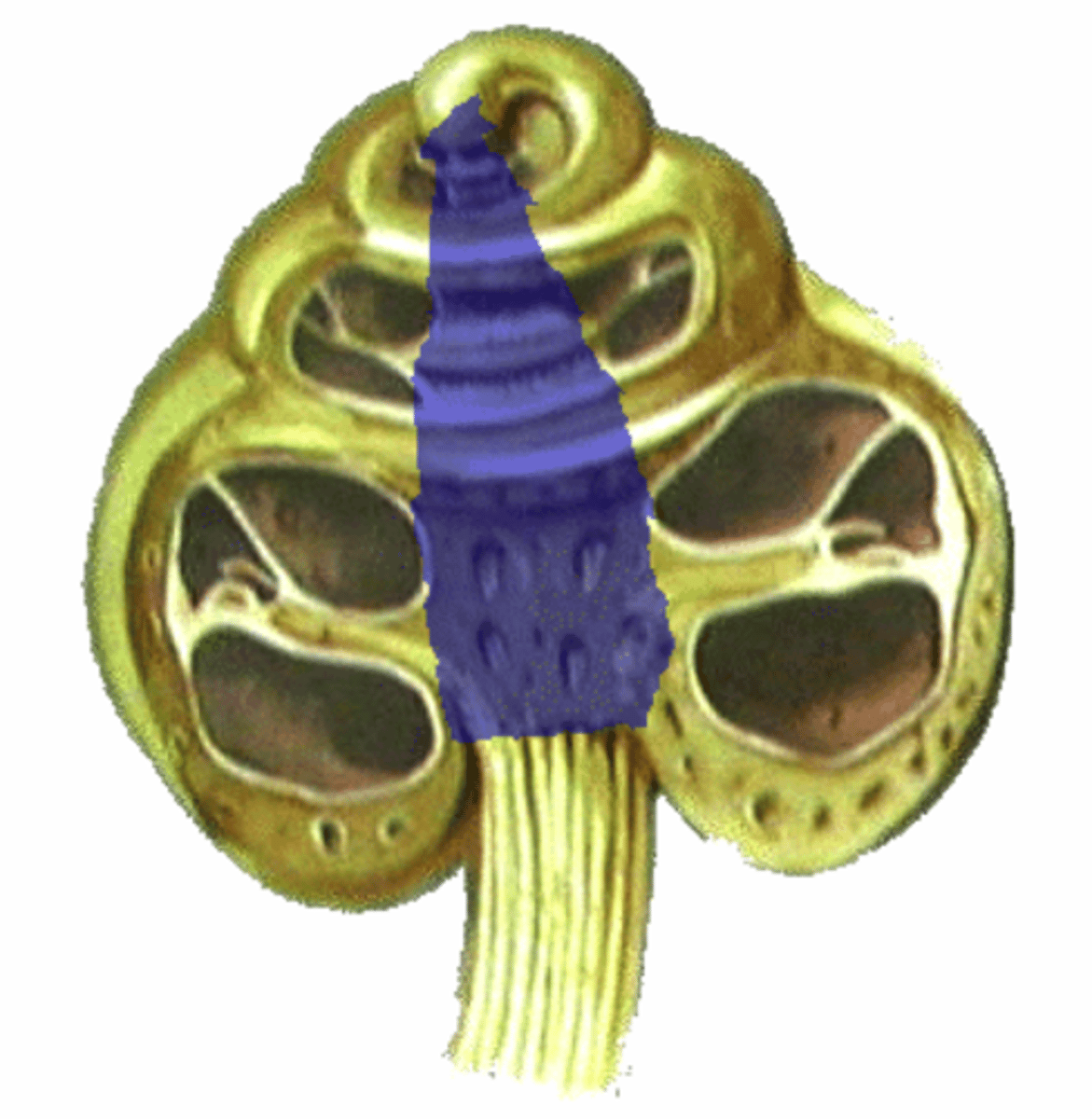
modiolus
bony core of cochlea
helicotrema
the opening that connects the tympanic and vestibular canals at the apex of the cochlea
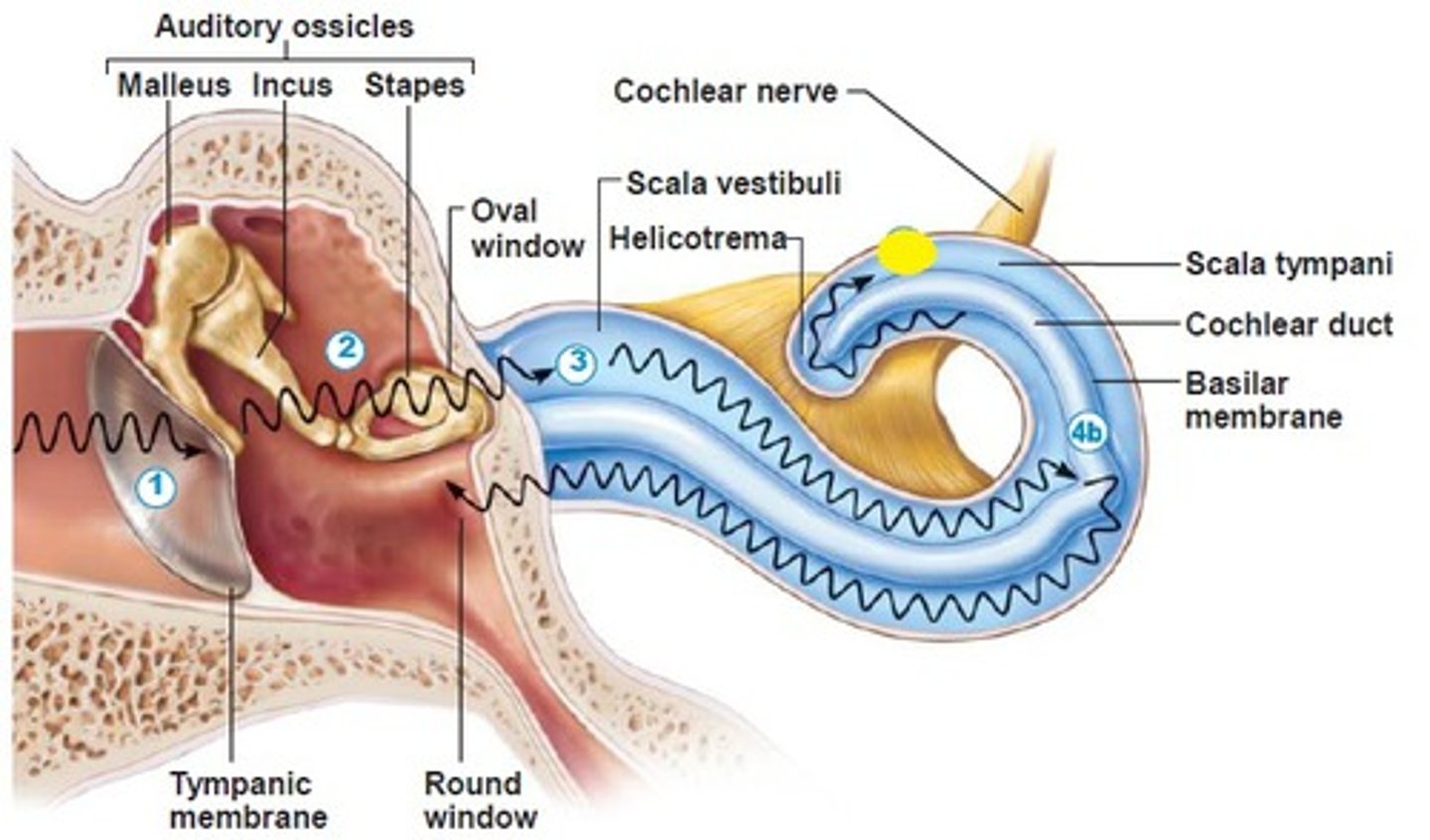
oval window
entrance to the inner ear
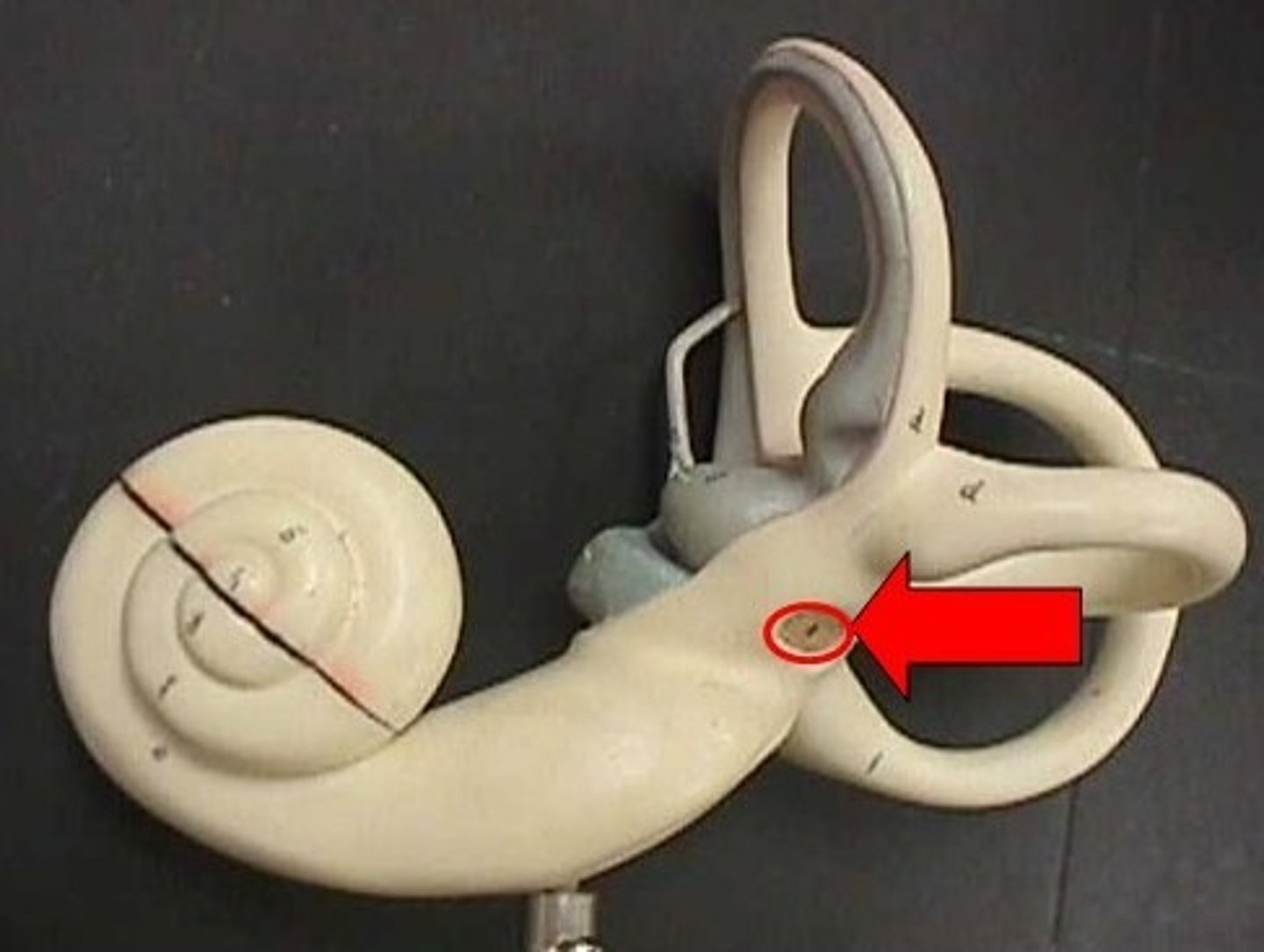
scala tympani
inferior chamber of cochlea
scala vestibuli
superior chamber of cochlea
cochlear duct
middle chamber of cochlea that houses the organ of Corti
vestibular membrane
separates the cochlear duct from the scala vestibuli
tectorial membrane
A rigid membrane in the cochlear duct, against which the stereocilia in the organ of Corti bend when stimulated by vibration, setting off an action potential.
basilar membrane
separates the cochlear duct from the scala tympani
Rotational acceleration/deceleration
sensation sensed in the semicircular canals
linear acceleration/deceleration
sensation sensed in the vestibule
stereocilia
hair-like extensions on the tips of hair cells in the cochlea
organ of corti
sensory organ of hearing
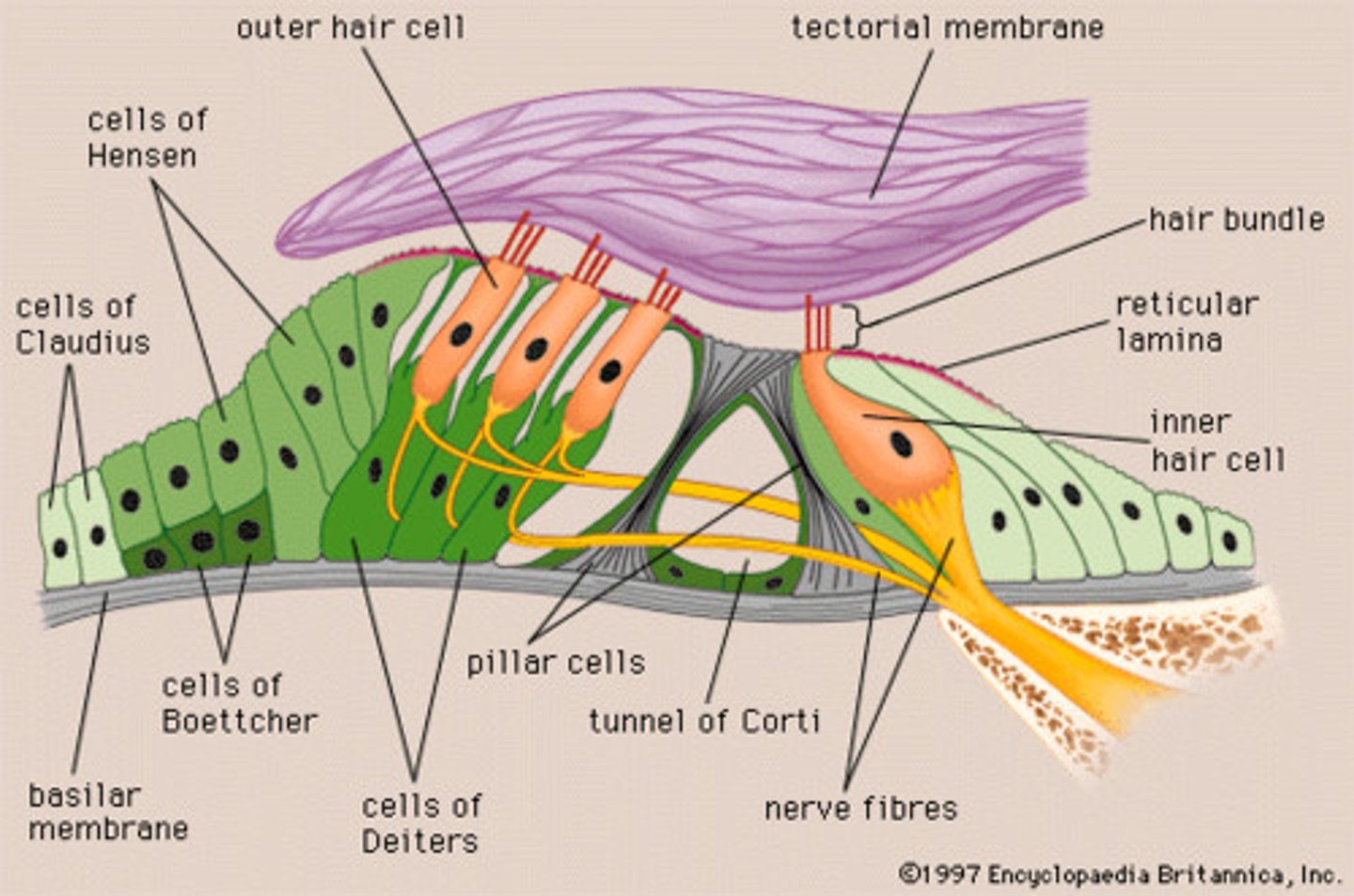
organ of corti receptor type
mechanoreceptor
Fast auditory pathway
CN8 to the cochlear nuclei; decussation and movement toward lateral lemniscus and inf. colliculus, synapse in med. geniculate nuclei to auditory cortex
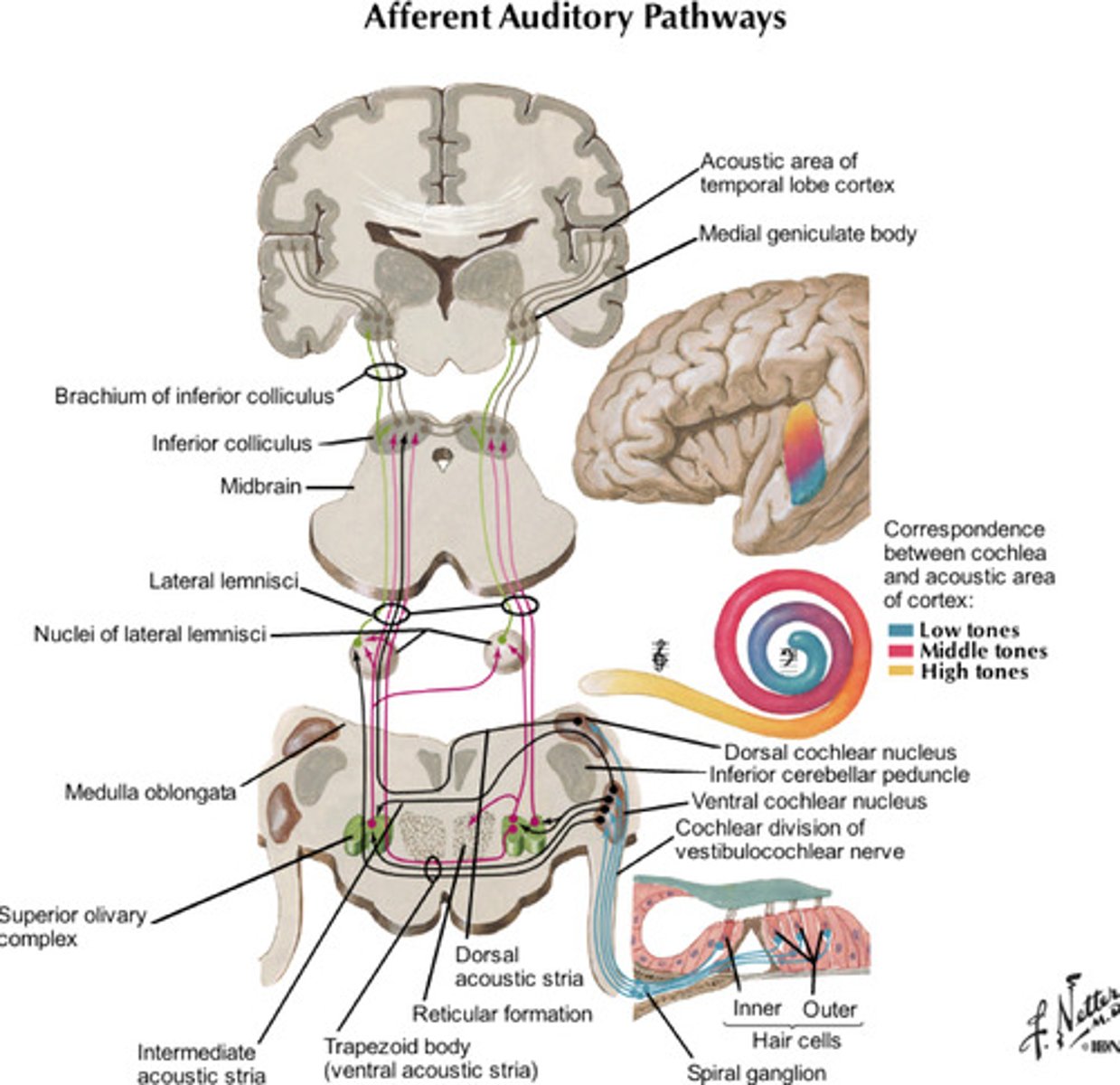
fast auditory pathway example
jumping from a loud noise
slow auditory pathway
CN 8 to cochlear nuclei to superior olivary nucleus, lateral lemniscus to inferior colliculus, synapse in med. geniculate nuclei to auditory cortex