4.5 Forces
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are scalar and vector quantities?
Scalar: Quantities that only have magnitude
Vector: Quantities that have magnitude and direction
Describe how a vector quantity can be represented
It can be represented as an arrow
The length represents the magnitude
The direction of the arrow represents the direction of the vector quantity
What is a force and what are the two types and give examples of each?
A push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object
Contact:
Normal contact force, friction, air resistance (drag), tension (pulling or stretching force)
Non contact
Gravitational force, electrostatic force, magnetic
What type of quantity is force?
Vector
What is weight, what does it depend on and recall the equation
The force acting on an object due to gravity
It depends on the gravitational field strength at the point where the object is
weight = mass x gravitational field strength
N = kg x N/kg
What is the force of gravity around Earth due to?
The gravitational field around Earth
Where does the weight of an object act?
The centre of mass is the single point where the weight of an object will act.
What is the relationship between mass and weight?
They are directly proportional
How to measure weight?
Using a calibrated spring balance (a newtonmeter)
What is meant by resultant force?
A single force that has the same effect as all of the forces acting on an object
How to resolve forces?
(HT only) A single force can be resolved (broken down) into two components acting at right angles to each other. The two component forces together have the same effect as the single force. | 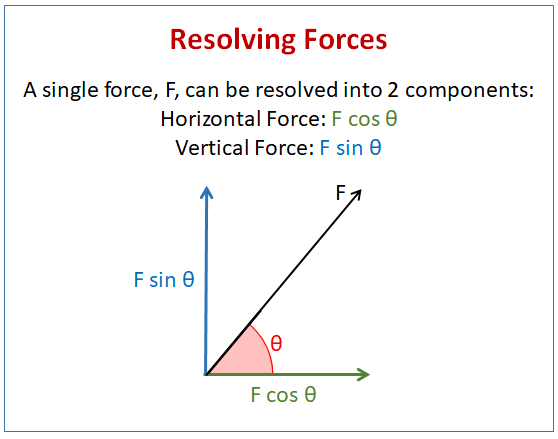 |
How to use free body diagrams to describe qualitatively examples where several forces lead to a resultant force on an object
Free body diagram: isolates an object and illustrates all of the external forces acting on it as vectors, showing their magnitude and direction to work out the resultant force (a single force that has the same effect as all of the forces acting on an object)
When is work done on an object and give the equation
When a force has caused an object to move through a distance
A force does work on an object when the force causes a displacement of an object.
work done = force x displacement (moved along the line of action of the force)
J (or newton-metres) = N x m
One joule of work is done when a force of one newton has caused a displacement of one metre
What does work against the frictional forces on an object cause?
A rise in temperature of the object
Give examples of the forces involved on:
stretching an object
bending an object
compressing an object
Stretching:
two tension forces pulling at each end in opposite directions
Bending:
forces that act in different directions at different points
Compressing:
forces that act towards eachother
Why must more than one force be applied to change the shape of a stationary object?
If you apply only one force, the object would accelerate and move rather than change shape
According to Newton’s First Law, a single unbalanced force would cause acceleration, not deformation
What is the difference between elastic deformation and inelastic deformation caused by stretching forces?
Elastic:
The object returns to its original shape after the forces are removed; the deformation is temporary
Occurs when the object has not been stretched or compressed past its elastic limit
Inelastic:
The object does not return to its original shape after the forces are removed; the deformation is permanent
Occurs when the object has been stretched or compressed past its elastic limit
What is the relationship between the force applied to an object and the extension of the object
The extension of an object is directly proportional to the force applied to it, provided that the limit of proportionality is not exceeded
Give the formula for extension of an object
force = spring constant x extension
f = k * e
N = N/m x m
The relationship also applies to the compression of an object where e would be compression
When a force has stretched or compressed an object, what happens to the energy transferred?
A force that stretched or compresses an object does work on that object.
The energy is transferred and stored as elastic potential energy within the object; provided that the limit of proportionality has not been reached (the object is not inelastically deformed) the work done on the spring and the elastic potential energy stored is equal.
What is the moment and give the equation
Moment is the turning effect of the force
moment = force x perpendicular distance from pivot to the line of action from the force
Nm = N x m
If an object is balanced, what is the moment?
The total clockwise moment about a pivot is equal to the total anticlockwise moment of the pivot
What does a moment cause?
An object to rotate
What is a linear and non-linear relationship between force and extension?
Linear: force is directly proportional to extension
Non linear: force is not proportion to extension
Explain how levers transmit the rotational effects of forces
A lever is a rigid bar that rotates about a pivot (or fulcrum).
Levers increase the distance of the force from the pivot, increasing the moment.
When a force is applied to a lever, it creates a moment around the pivot. The moment can be transmitted to another point on the lever to lift or move a load.
This means that a small force applied at a large distance from the pivot can produce a large moment, allowing you to lift a heavier load.
Explain how gears transmit the rotational effects of forces
Gear systems transmit the turning effect of the force from the engine to the wheels.
The turning effect depends on the distance between the edge of the gear and the centre; the larger the radius of the gear, the greater the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied
What is a fluid?
Liquids and gases