Atomic Structure & Time Of Flight Spectrometry
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what condition must the whole mass spectrometer apparatus be kept under, and why?
under a high vacuum
to prevent the ions that are produced from colliding with molecules present in the air
Definition of relative atomic mass
The average mass of an atom of an element, compared to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Definition of relative molecular mass
The average mass of a molecule compared to the 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Stages of TOF
Ionisation
Acceleration
Ion drift
Detection
Electrospray ionisation
typically used with large, organic molecules (so that fragmentation does not occur)
the sample is dissolved in a volatile and polar solvent
the sample is injected at high pressure through a fine, hollow needle connected to the positive terminal of a high voltage supply
this causes the sample molecule to gain a proton from the solvent
X(g) + H+ ———> XH+ (g)
electron impact ionisation
Electron gun fires high energy electrons
Vapourised atoms are bombarded by high energy electrons, which knocks out an electron
X(g) ——→ X+ (g) + e-
why must the sample be ionised?
so that it can accelerate towards the detector
so that it can be detected
acceleration
the positive ions formed from either of the ionisation methods are then accelerated to a constant kinetic energy by an electric field, towards a negatively charged plate
all ions have the same kinetic energy, but the lighter ions travel faster
Ion drift and detection
the ions travel along the flight tube, where they reach a detector
the positive ions hit the detector, causing the electrons to flow, producing a current
the amount of current produced is proportional to the abundance of the species
the greater the current, the greater the abundance
Identify which one of the isotopes will be deflected the most
the one with the lowest m/z value
suggest what might causes the RAM of a sample to be different from the RAM given in the periodic table
Other isotopes are present

Similarity: the peaks would be at the same m/z values
Reason: because the same element is being detected
Difference: there would be an additional peak at ½ m/z valye
Reason: because 2 electrons are knocked out
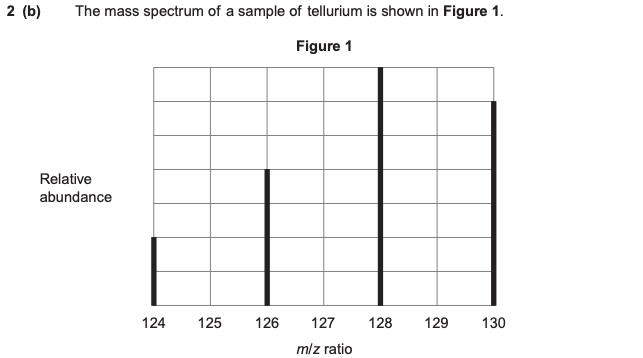
The mass spectrum of tellurium also has a small peak at m/z = 64. Explain the existence of this small peak.
2 electrons are removed from tellurium, forming 128Te2+