Chemistry Ch. 6 - Electronic Structure of Atoms
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Quantum Theory
Describes an atom’s arrangement/electronic structure and behavior
Number of electrons
Distribution about the nucleus
Energy of electrons
Quantum Mechanics
Describes atoms correctly
Electronic Structure
Number of electrons, distribution, and charge in the nucleus
What causes atoms to glow/emit light
Because of energy changes
Electromagnetic Radiation aka Radiant Energy
Light energy that is in waves
Electric field
Magnetic field
and travels at the speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Wavelength (λ)
Is the length between each peak/dip, measured in meters or nanometers
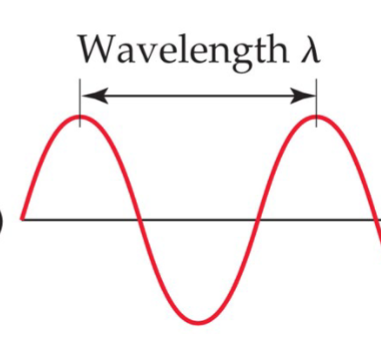
Frequency (v)
The number of complete waves per second, measure in 1/s or s-1 or Hertz (Hz)
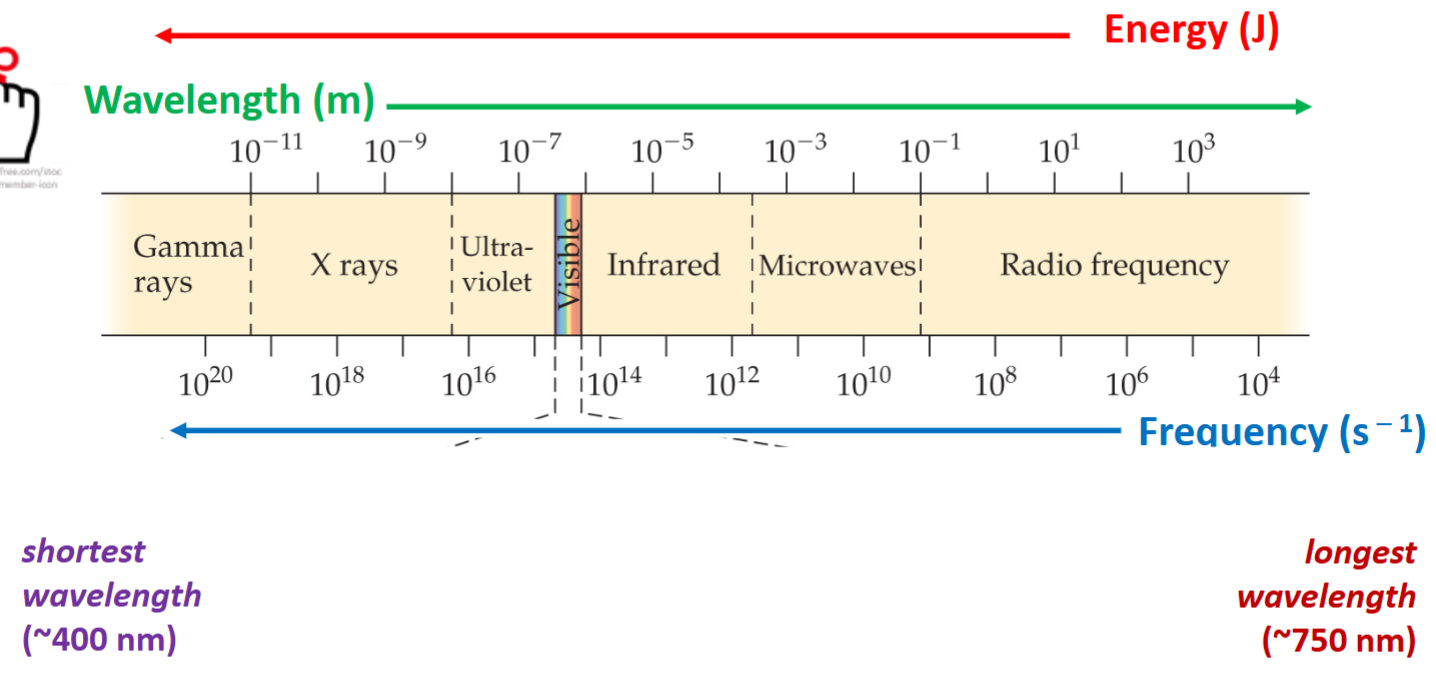
What is the Electromagnetic Radiation Spectrum Order
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportionate. Just know the order and relationships, but not the numbers.
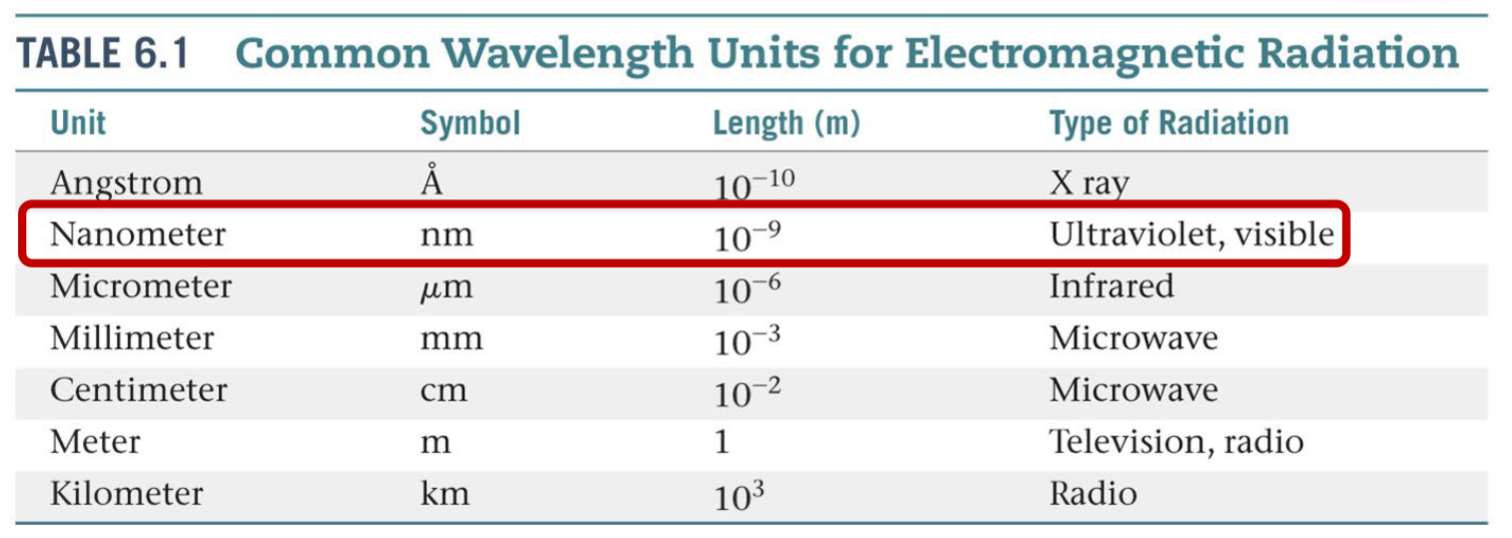
Common Wavelength Units in Electromagnetic Radiation
Speed of Light
c = 3 × 108 or c = λv (frequency x wavelength), frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional
Behavior of Light
Blackbody radiation - Emits a light when heated (a stove coil turning red)
Photoelectric Effect - Emits electrons from metal surfaces when light shines
Emission Spectra - Emits electrons
Blackbody radiation
Light is emitted when heated, wavelength depends on the temperature, not the surface or composition
Ex) A stove glowing red
Max Planck (1900)
Energy can be released/absorbed only in packets of quantum and E=hv
Energy exists at small levels
A single quantum energy is, E= constant(h) x frequency(v), h = 6.626 × 10-34
Ex) For each temperature, there is a maximum intensity for the radiation
Threshold Frequency
The minimum energy required to emit electrons from metal, 1.602 × 10-19
A lower threshold ejects no electrons
A higher threshold ejects electrons with radiation and kinetic energy
Binding Energy
Energy needed to remove an electron
Photon
A stream of tiny energy packets
Rydberg equation
Used to calculate the wavelengths for hydrogen.
Use the smaller one for n1, and the larger number for n2
RH=1.097 × 107m-1
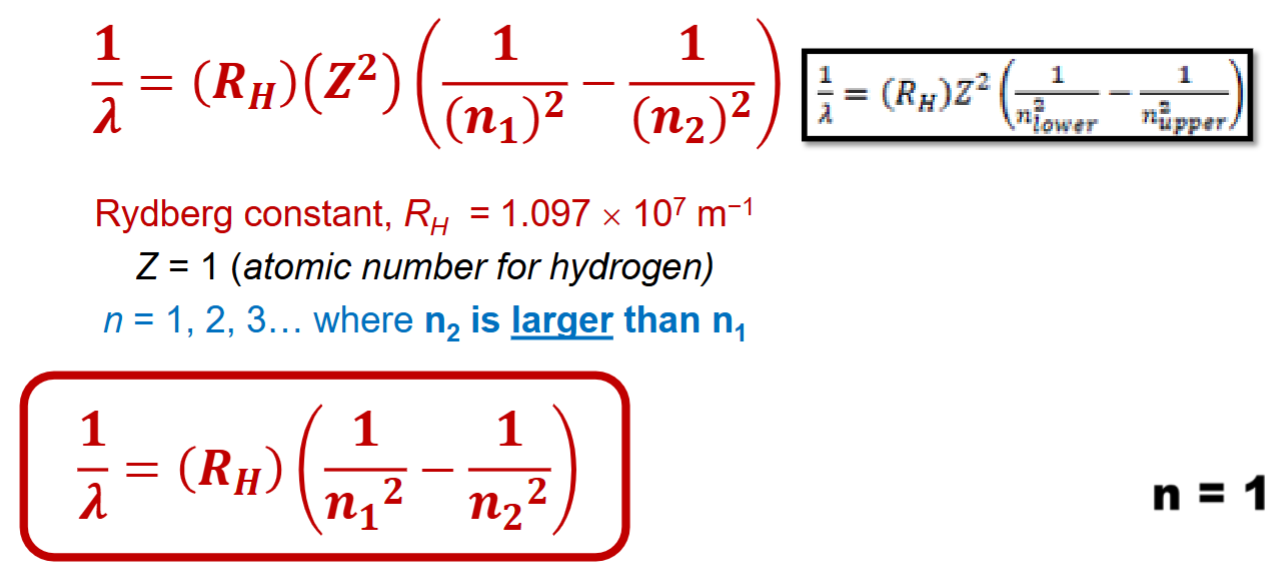
Limitations of the Bohr Model
It cannot predict the shape of multi-electron atoms
Electrons have wave properties and do not circle in perfect circles
We cannot know their exact location
Electrons exist in specific energy levels
Energy is involved when moving energy levels
Representation of Orbitals
S - spherical shape, holds 2 electrons, 1 orientation (ml=0), l=0
P - dumbbell shape, holds 6 electrons, 3 orientations (ml= -1, 0, 1), l=1
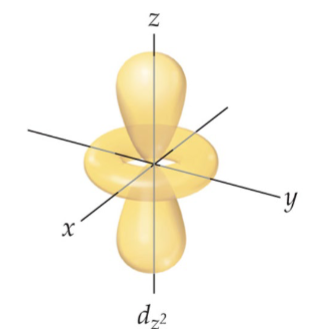
D - four leave clover shape, holds holds 10 electrons, 5 orientations (ml= -2, -1, 0, 1, 2), l=2
F - ring shape, holds 14 electrons, 7 orientations (ml= -3,-2,-1, 0,+1,+2,+3), l=3