4.2 Alcohols, haloalkanes and analysis
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
What is the general formula for alcohols? (1)
CₙH₂ₙ₊₁OH
What functional group do alcohols have? (1)
Hydroxyl (-OH) group
How do you name an alcohol? (2)
- Use the carbon atom number to indicate the position of the hydroxyl group.
- Use the suffix "-ol".
What is a primary alcohol? (1)
The carbon attached to the -OH group is bonded to one other carbon.
What is a secondary alcohol? (1)
The carbon attached to the -OH group is bonded to two other carbons.
What is a tertiary alcohol? (1)
The carbon attached to the -OH group is bonded to three other carbons.
Why are alcohols polar molecules? (1)
Due to the electronegative hydroxyl (-OH) group.
What type of intermolecular forces do alcohols form? (1)
Hydrogen bonds
How does chain length affect the boiling point of alcohols? (3)
- As chain length increases, boiling point increases.
- More surface interaction leads to stronger London forces,
- requiring more energy to overcome.
How does branching affect the boiling point of alcohols? (3)
- As branching increases, boiling point decreases.
- Less surface interaction leads to weaker London forces,
- requiring less energy to overcome.
Why do alcohols have higher boiling points than alkanes? (2)
- They form hydrogen bonds,
- which require more energy to overcome.
What is volatility? (2)
- How easily a substance evaporates
- at room temperature and pressure.
How is boiling point related to volatility? (1)
The higher the boiling point, the lower the volatility.
Why do alcohols have lower volatility than alkanes? (2)
- Alcohols have higher boiling points than alkanes
- due to hydrogen bonding
- Therefore alcohols are less volatile
What makes alcohols soluble in water? (2)
- Hydrogen bonds are formed
- between the alcohol and water.
How does chain length affect the solubility of alcohols? (3)
- As chain length increases, solubility decreases
- because the size of the non-polar carbon chain increases
- cannot form hydrogen bonds as well.
What is a general formula for the combustion of alcohols? (1)
Alcohol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
What is the oxidising agent used for alcohol oxidation? (1)
Potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇) with sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
What is the general symbol for an oxidising agent? (1)
[O]
What colour change is seen during the oxidation of alcohols? (1)
Orange to green.
What product is formed when a primary alcohol is oxidised under distillation? (1)
An aldehyde
What product is formed when a primary alcohol is oxidised under reflux? (1)
A carboxylic acid
How can an aldehyde be further oxidised? (2)
- By refluxing
- with acidified potassium dichromate (H₂SO₄/K₂Cr₂O₇).
What product is formed when an aldehyde is oxidised? (1)
A carboxylic acid.
What product is formed when a secondary alcohol is oxidised? (1)
A ketone
What reaction conditions are needed to oxidise a secondary alcohol? (2)
- Reflux
- with acidified potassium dichromate (H₂SO₄/K₂Cr₂O₇).
What is the colour change when a secondary alcohol is oxidised? (1)
Orange to green.
What product is formed when a tertiary alcohol is oxidised? (1)
No reaction
Why can't tertiary alcohols be oxidised? (1)
- There is no hydrogen atom attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group
What type of reaction is the dehydration of an alcohol? (1)
An elimination reaction.
What are the products when an alcohol undergoes dehydration? (1)
- A water molecule
- An alkene
What are the conditions needed for the dehydration of an alcohol? (2)
- A strong acid catalyst (e.g. H₂SO₄)
- heat.
From which atoms is the water molecule formed during alcohol dehydration? (2)
- The hydroxyl (-OH) group
- a hydrogen atom from the carbon adjacent to the hydroxyl carbon.
What type of reaction is used to form haloalkanes from alcohols? (1)
Nucleophilic substitution.
What reagents are needed to convert an alcohol to a haloalkane? (2)
- A halide salt
- a strong acid
What happens in a nucleophilic substitution reaction of an alcohol? (2)
- The hydroxyl (-OH) group is replaced by a halide ion (X⁻),
- forming a haloalkane.
What is the role of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) in the nucleophilic substitution reaction? (1)
It reacts with the halide salt to produce the hydrogen halide in situ.
What is the general equation for the reaction between an alcohol and a hydrogen halide? (1)
Alcohol + HX → Haloalkane + H₂O
What type of reaction occurs when a haloalkane reacts with OH⁻? (1)
Nucleophilic substitution (hydrolysis reaction).
What is the product when a haloalkane reacts with aqueous hydroxide? (1)
An alcohol.
What is the reagent and condition needed to convert a haloalkane to an alcohol? (2)
- Reagent: KOH or NaOH.
- Condition: Reflux in aqueous solution.
How can the rate of hydrolysis of different haloalkanes be experimentally determined? (3)
- By reacting with water
- in the presence of AgNO3 and ethanol
- Measure the rate of precipitate formed
What colour precipitate is formed from the reaction of AgNO3 and a chloroalkane? (1)
White
What colour precipitate is formed from the reaction of AgNO3 and a bromoalkane? (1)
Cream
What colour precipitate is formed from the reaction of AgNO3 and a iodoalkane? (1)
Yellow
What is a nucleophile? (2)
- An electron pair donor
- which attacks electron-deficient centres.
Why are haloalkanes susceptible to nucleophilic attack? (2)
- The carbon-halogen bond is polar,
- making the carbon δ⁺ and electron deficient.
Draw the mechanism for the substitution reaction between chloromethane and hydroxide ions. (5)
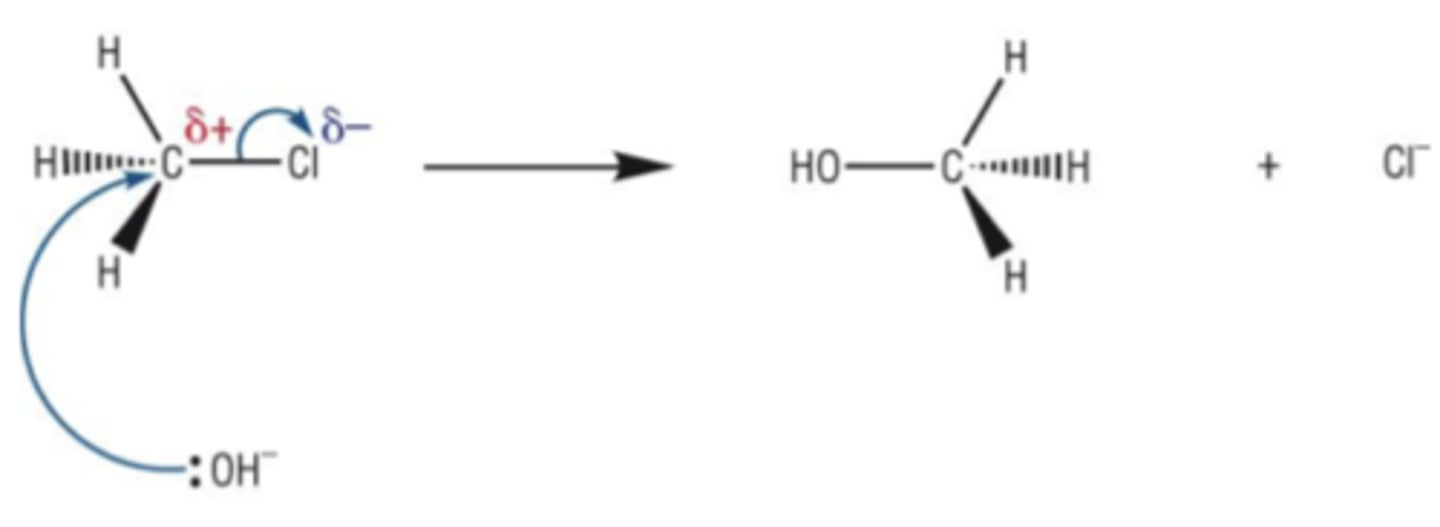
What are the conditions required for nucleophilic substitution? (2)
- Heat under reflux
- Aqueous solvent
Why is ethanol not a suitable solvent for the nucleophilic substitution reaction? (2)
- Elimination would occur
- Forming an alkene
How does the rate of hydrolysis relate to bond enthalpy? (1)
The lower the bond enthalpy, the faster the rate of hydrolysis.
Which carbon-halogen bond has the highest bond enthalpy? (1)
C-F
Which carbon-halogen bond has the lowest bond enthalpy? (1)
C-I
Why does bond enthalpy decrease down Group 7? (3)
- Increased atomic radius and shielding
- reduce nuclear attraction,
- weakening the bond.
How does electronegativity affect bond enthalpy? (2)
- More electronegative halogens form more polar bonds,
- increasing bond enthalpy.
What are chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and their uses? (2)
- CFCs are haloalkanes containing chlorine, fluorine, and carbon.
- They are stable, volatile, non-flammable, and non-toxic.
What are the uses of CFCs? (3)
- Used in fridges,
- aerosol cans
- firefighting equipment
What is the role of the ozone layer? (3)
- The ozone layer consists of O₃ molecules in the upper atmosphere.
- It absorbs harmful UV radiation, preventing sunburn and cancer.
- Helps stabilize Earth's temperature.
How is the ozone layer maintained? (2)
- O₂ is broken into two free radicals by UV radiation: O₂ → O + O
- Free radicals react with oxygen to reform ozone: O₂ + O → O₃
Why do CFCs damage the ozone layer? (3)
- UV radiation breaks C-Cl bonds in CFCs, forming chlorine radicals.
- Chlorine radicals catalyze ozone breakdown,
- allowing more UV radiation to reach Earth.
What is the mechanism of CFCs in ozone breakdown? (4)
1. CF₂Cl₂ → •CF₂Cl + •Cl (via UV radiation)
2. •Cl + O₃ → O₂ + •ClO
3. •ClO + O → O₂ + •Cl
- Overall: O₃ + O → 2O₂
Why are chlorine radicals dangerous to the ozone layer? (2)
- Cl radicals are regenerated in the reaction
- Therefore one radical can destroy many ozone molecules.
What other radicals contribute to ozone depletion? (2)
- Nitrogen oxides (NO) from car engines and lightning.
- NO reacts with ozone in the same way as chlorine radicals.
What is the mechanism of NO radicals in ozone breakdown? (3)
1. NO + O₃ → O₂ + NO₂
2. NO₂ + O → O₂ + NO
- Overall: O₃ + O → 2O₂
What is distillation used for? (1)
Separating substances with different boiling points.
Draw a diagram of an experimental setup for distillation. (5)
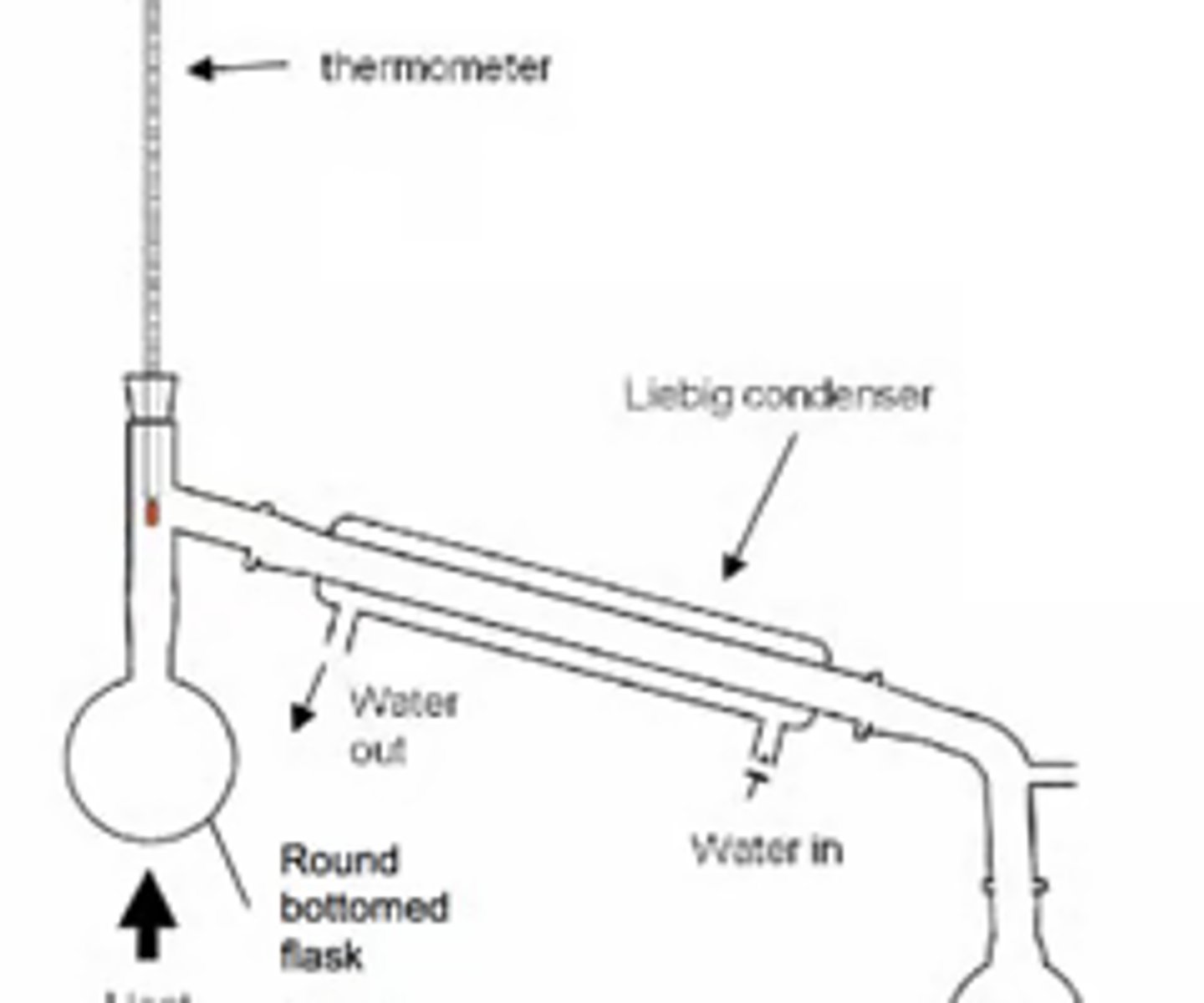
Why should cool water enter the condenser at the bottom in a distillation? (2)
- To prevent air bubbles
- and allow even cooling
Why should the condenser be tilted slightly downward in a distillation? (1)
To allow liquid to run into the collection flask efficiently.
What is the purpose of anti-bumping granules in distillation? (3)
- To prevent large bubbles from forming.
- To stop the mixture from boiling too vigorously,
- preventing impurities from contaminating the product.
Where should the thermometer bulb be placed in a distillation setup? (1)
- At the T junction connecting to the condenser
- In order to accurately measure the boiling point.
What is the purpose of reflux? (1)
Ensures volatile substances aren't lost during a reaction.
Draw a diagram of an experimental setup for a reflux. (5)
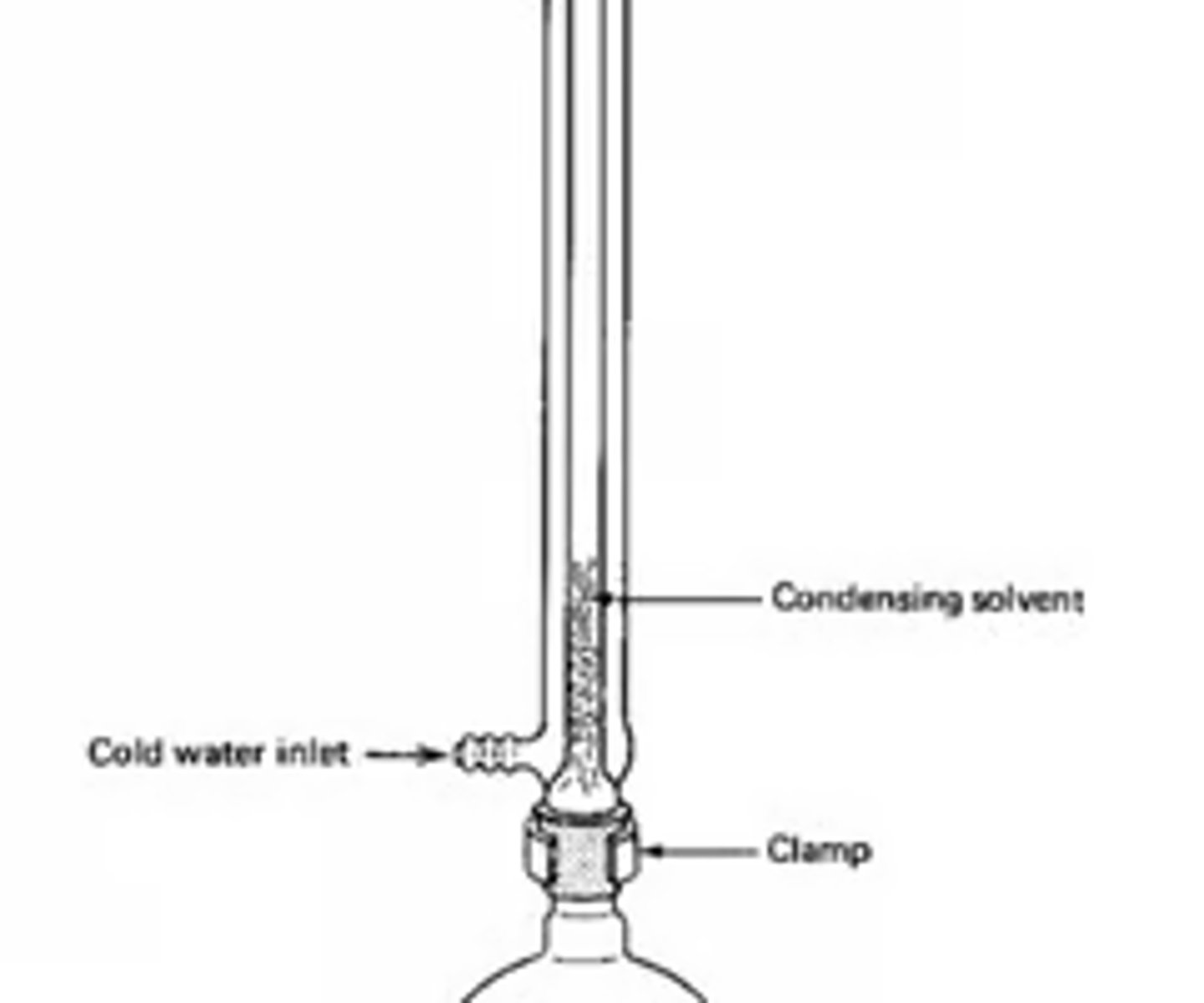
Why should the top of the condenser in a reflux setup be left open (2)
- To prevent pressure build up
- Preventing an explosion
Why should a water bath or electric heater be used to heat the mixture? (1)
To avoid open flames if there are flammable substances present.
Why should round-bottom flasks be used to heat mixtures in? (4)
- Round bottom flasks provide more surface area
- Therefore provides more uniform heating or cooling.
- Round glassware is more resistant to cracking
- So can be used at high temperatures and at vacuums
NOTE: This applies to both reflux and distillation procedures
What is the purpose of purification of an organic liquid? (2)
- To separate and purify an organic product from impurities
- and any unwanted byproducts.
What are the steps in purifying an organic liquid? (6)
1. Pour the mixture into a separating funnel.
2. Add water and shake the funnel to wash the mixture, releasing pressure every few shakes.
3. Allow time for the mixture to settle into two layers.
4. Run off both layers into separate beakers.
5. Add a drying agent to remove excess water.
6. Filter the mixture to remove the drying agent from the organic mixture.
Which layer in the separating funnel will contain the organic product? (2)
- The top layer is the organic layer
- As most organic solvents are less dense than water
How can purity of an organic liquid be tested? (2)
- Redistill the organic mixture and collect the fractions
- Test the boiling point of the product
What are some drying agents which can be used to remove excess water? (2)
- Anhydrous MgSO₄
- Anhydrous CaCl2
What is the functional group of an alkane? (1)
C-C
What is the functional group of an alkene? (1)
C=C
What is the functional group of an haloalkane? (1)
C-X
NOTE: X = C, F, Br, I
What is the functional group of an alcohol? (1)
OH
What is the functional group of an aldehyde? (1)
C=O adjacent to H
What is the functional group of an ketone? (1)
C=O adjacent to C
What is the functional group of a carboxylic acid? (1)
COOH
What is the importance of two-stage organic synthetic routes? (1)
Allows the production of a large number of organic products from a few starting compounds.
What is the effect of infrared radiation on molecules? (2)
- All molecules absorb infrared radiation
- causing covalent bonds to absorb energy and vibrate.
What is an atmospheric greenhouse gas containing C=O bonds? (1)
CO2
What is an atmospheric greenhouse gas containing O-H bonds? (1)
H2O
What is an atmospheric greenhouse gas containing C-H bonds? (1)
CH4
What is the consequence of infrared radiation absorption by atmospheric gases? (1)
- It contributes to global warming.
What changes are needed to address global warming? (2)
- There is a need for changes to be made to renewable energy resources.
- In order to not produce greenhouse gases
How can IR spectroscopy be used to identify functional groups? (2)
- Different bonds absorb at specific wavelengths, producing characteristic peaks.
- Compare peaks to known data to determine the presence of functional groups
What is the fingerprint region in IR spectroscopy? (2)
- The region below 1500 cm⁻¹,
- unique to each molecule but difficult to use for identification.
What IR peak is found in most organic molecules? (2)
- The C-H peak
- At approximately 3000cm-1
What IR peak can be used to identify an alcohol? (2)
- O-H peak only
- Between 3200-3600cm-1
What IR peak can be used to identify an aldehyde or ketone? (2)
- C=O peak only
- Between 1630-1820cm-1
What two IR peaks can be used to identify a carboxylic acid? (4)
- O-H peak
- Broad between 2500-3300cm-1
- C=O peak
- between 1630-1820cm-1