Psyc 213 - Memory
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
4 functions memory performs
1. routines + habits
2. sense of self
3. social functions
4. solving problems
Memory is not one thing - what happened to Clive Wearing
episodic memory = impaired
other forms of memory remained intact
- knew his wife (semantic memory)
- could play piano (procedural memory)
what are the distinct memory systems supported by
different neural circuits
what are the three stages of memory
1. Encoding
2. Storage
3. Retrieval
encoding definition
learning new information; forming new "memory trace" as a neural code
storage
retaining encoded memory trace/neural code
retrieval
activating a memory trace via a cue (probe for that memory) for a purpose
the process of going from encoding to retrieval is called
memory consolidation
what is encoding formed as
memory trace formed as a hippocampal-cortical activity pattern
what is storage in the brain and another word for it
consolidation
when a memory is transformed into a stable cortical pattern
what is retrieval in the brain
when a cue (part of a memory trace) triggers pattern completion of the brain pattern
the multi-store model: memory as systems
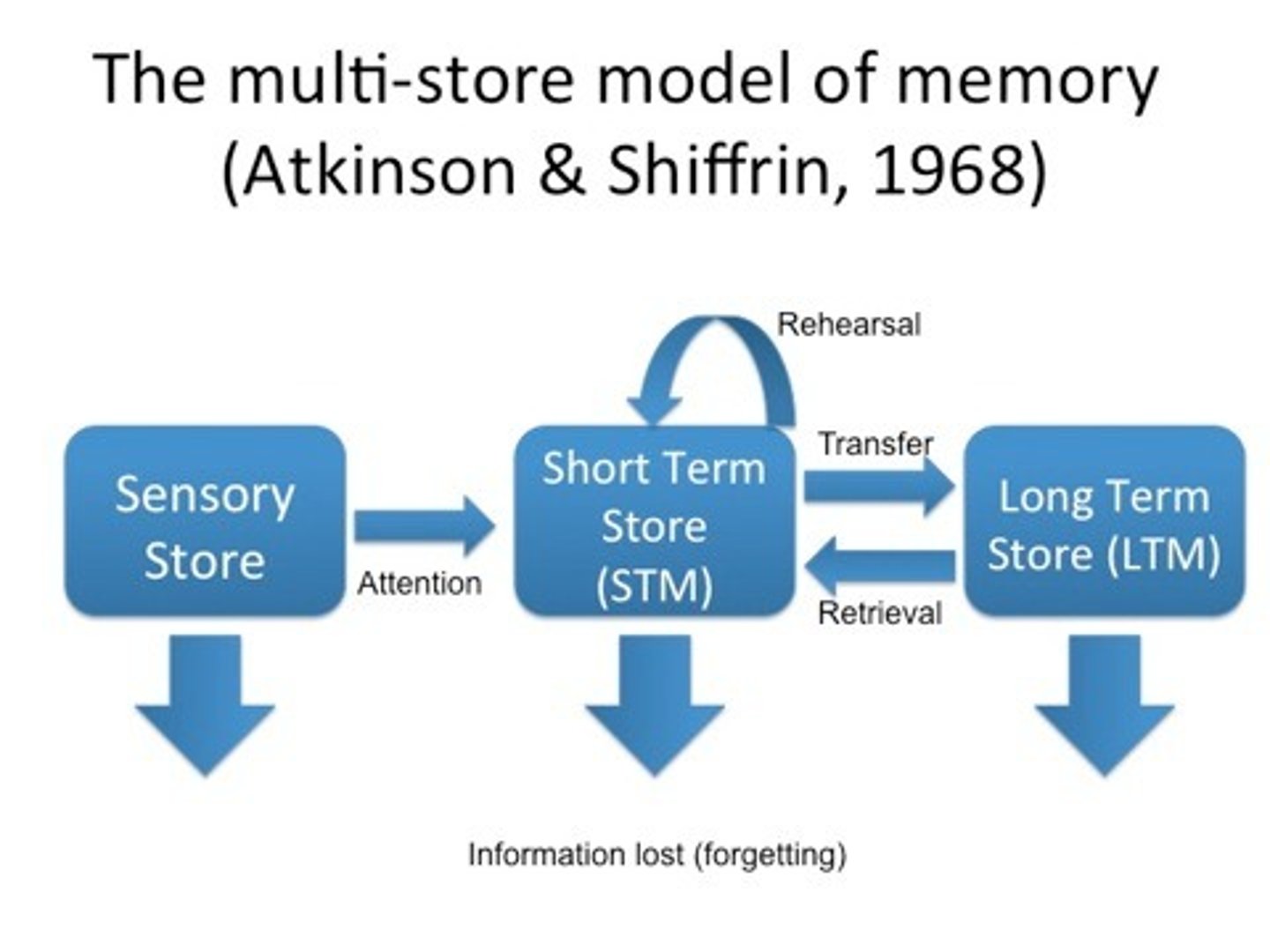
3 types of memory
sensory, short term, long term
3 aspects of sensory memory
iconic
echoic
haptic
what 2 things does the short term memory consist of
attentional control
working memory
what are the 2 major categories within long term memory
implicit
explicit
what are the 4 (ish) aspects of implicit memory
non-declarative; non-conscious memory
procedural
priming
what are the 4(ish) aspects of explicit memory
declarative; conscious memory
episodic
semantic
what is sensory memory
automatic reflections of a sense
what are the 5 subcategories of sensory memory - elaborate on the last 3
1. gustatory memory
2. olfactory memory
3. echoic memory
- sound-byte held for ~3s
4. haptic memory
- very brief memory of touch
5. iconic memory
- millisecond vision memory
- a 'persistence of vision'
iconic memory have what after
afterimages
what is a positive afterimage
visual memory that represents the perceived image in the same colours
why is it helpful and an example
helpful for seeing things smoothly
eg
- see 75 frames/second, movies are 24 frames/s, but view movies as a smooth event due to afterimage filling in holes
what is a negative afterimage + duration
visual memory is the (colour) inverse of the perceived image
slightly longer than positive afterimage (few seconds)
how long sensory memory lasts Sperling study
pps briefly (0.05s) viewed a visual display (3x4 letters)
recall the letters
1. whole report
- reported any letters from the whole display
2. partial report
- reported only one row of letters at a time over trials
where does short term memory come from
attended info moves from sensory to short term
where is short term memory in the brain
prefrontal cortex
STM time capacity
limited: ~20-30s
STM capacity
limited
7+/-2
what is the serial position effect
remember the first and last items in a list better than those in the middle.
primary effect
tendency to recall the first terms of list
rehearsal --> into long term
recency effect
tendency to remember words at the end of a list especially well
when is the recency effect eliminated
if the study-recall delay duration > 30s
how to overcome short term memory limits
chunking strategy
- grouping items together in a meaningful way so more information to be represented at one time
chunking increasing with knowledge example
expert chess players recall more pieces on chess board than new players
experts use knowledge of moves to 'chunk' pieces together
effect = not present if pieces on board randomly
what 3 aspects make the working memory important
1. retention + manipulation of info = not in our environment in conscious awareness
2. guides behaviour
3. essential for many cognitive functions
what 2 aspects are in the phonological loop
phonological store
articulatory control loop
what is the phonological store
passive store for verbal info
- the inner ear
what is the articulatory control loop
active rehearsal of verbal information
- the inner voice
used to convert written material into sounds (reading)
- specialised role in language
what 2 aspects are in the visuospatial sketchpad
the visual cache
the inner scribe
what is the visual cache
info about visual features
what is the inner scribe
info about spatial location, movement and sequences
what 2 types of evidence is there for separate short term memory stores
neuroimaging evidence
double dissociation in neuropsychological cases
neuroimaging evidence
difference areas of the brain are active for visual and verbal short term memory tasks
2 double dissociation in neuropsychological cases
1. Patient ELD
- problems recalling visual-spatial but not verbal material in short term
2. Patient PV
- problems recalling verbal but not visual material in short term
what is the episodic buffer
integrates information from short- and long-term memory
what is the central executive
Attentional process that monitors incoming data. Allocates data to certain slave systems. Has limited processing capacity.
what did Ebbinghaus do
learnt nonsense syllables, tested memory at various intervals, examined what was retained (forgotten)
Ebbinghaus study
2000 cards with nonsense syllables
learnt sets under strict testing conditions
- read without any inflection
- read consistently fast pace: 2.5 items/s
- do nothing else = remove confounds
what does it mean that the forgetting curve is exponential
memory loss is largest early on and slows down
what is the spacing effect
forgetting is reduced when learning is spread over time
spacing effect explanation
repeated info is more valuable = eg don't cram
active rehearsal: the testing effect study
pps studied a text passage
between group manipulation (studied more; practice test)
both groups took final test
retrieving memories after test leads to deeper encoding
what does the strength of a memory depend on
processes engaged at encoding
what are the 2 levels of processing theory
1. shallow
- focus on sensory info
2. deep
- integrate higher-level knowledge (things we know) with learned info
when is memory stronger
with deep processing
more elaborate memory traces
what is the self-reference effect
the tendency for people to better remember information when it has been encoded in reference to the self
what is the self-reference effect (link to identity) study
1. do these adjectives describe you? - happy, talkative
2. are these common words? - happy, talkative
first condition led to better memory
what is the generation effect (active rehearsal) study
1. read these pairs: king - crown; horse - saddle
2. generate the word: k___g - crown; H____e - saddle
second led to better memory
mnemonics use deep processing
organisational strategies to help encode info
involves linking new info to prior (semantic info) knowledge
- chunking
- acronyms for lists
imagery + method of Loci = use familiar image to link encoded info together
decay theory
memories are lost over time due to disuse
interference theory
interference is responsible for much of forgetting
- encoded memories are labile + need consolidating into stable long-term memories
- during pre-consolidation period = memories are susceptible to disruption + effects of interfering info
proactive interference
prior info interferes with encoding new memory
retroactive interference
newly learned info overwrites or interferes with prior encoded memory
similarity effects
the more alike something is to what already learnt = more they will mingle + interfere with memory