LEC Infectious Diseases (no tables)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Nucleic Acid-Based Tests (NATs)
Traditionally, the detection of pathogen has been based upon the phenotypic properties of the microorganisms grown in pure culture under different specific conditions.
Current molecular methods for detection of infectious pathogens includes the usage of ___________________
Target amplification
Signal amplification
NATs can detect pathogens using one of two amplification strategies:
PCR testing
One example of a test forTarget Amplification is _________
Target Amplification Methods
are enzyme-mediated processes (DNA polymerase) that use a single enzyme or multiple enzymes to increase the amount of target nucleic acid in an isothermal or thermal amplification reaction
Ex: Real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)
Signal Amplification Methods
involves the amplification of a signal produced when a target nucleic acid is detected, rather than directly amplifying the target sequence itself.
Largely been replaced by target amplification methods in routine setting
Detection of Bacteria
Most molecular diagnostic assays in medical bacteriology have been based around the amplification of DNA in a target gene rather than mRNA.
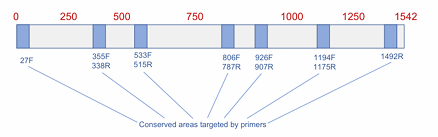
16s ribosomal RNA (rRNA genes)
This is the Amplification of DNA encoding ______________________?
Detection of Fungi
The internal transcribed spacer (ITS) elements are used for the identification and typing of yeast and molds.
ITS are usually found in regions separating the 18S and 28S rRNA genes of eukaryotes.
Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) elements
are used for the identification and typing of yeast and molds.
ITS are usually found in regions separating the 18S and 28S rRNA genes of eukaryotes
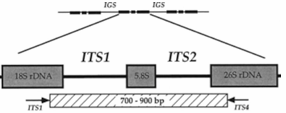
18S and 28S rRNA
ITS are usually found in regions separating the ________________ genes of eukaryotes
Detection of Virus
For the detection of viruses, scientists need to first determine the type of nucleic acid that serves as the virus’ genetic material.
The routine method used for the detection of virus is target amplification of the virus nucleic acid.
Target Amplification
The routine method used for the detection of virus is ____________ of the virus nucleic acid. (RT-PCR)
Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial agents are of two types, those that inhibit microbial growth, and those that kill organisms outright.
Molecular techniques are now used to determine resistance to antimicrobial agents, particularly target amplification, which targets genes conferring resistance to antimicrobial agents.
Antimicrobial agents
are of two types:
those that inhibit microbial growth
that kill organisms outright
genes conferring resistance to antimicrobial agents
Molecular techniques are now used to determine resistance to antimicrobial agents, particularly target amplification, which targets ________________________
Bartonellae species
Fastidious, facultative, intracellular zoonotic, and arthropod vector-borne bacteria
Vectors:
Sand flies
lice
fleas
biting flies
ticks
B. quintana causes Trench fever
Contains more than 30 species of bacteria include anthropogenic Bartonella (B. baciliformis, B. quintana) and the zoonotic species (B. henselae, B. grahamii)
qPCR is used to differentiate between Bartonella species and assay for primary testing
Sand flies
lice
fleas
biting flies
ticks
Bartonella species vectors are:
Trench Fever
B. quintana may cause?
qPCR
In Bartonella species, _____ is used to differentiate between Bartonella species and assay for primary testing
Borellia species
Transmitted by ticks in North America, Europe, and Asia
Lyme Borreliosis
Vector: Blood-sucking hard-bodies tick
Most often, there is an inflammation of the skin, typically in the form of erythema migrans, or seldom as borrelial lymphocytoma.
PCR provides a valuable diagnostic approach in acutely ill patients
Lyme Borreliosis
Disease associated with Borellia species
Blood-sucking hard-bodies tick
Borellia species vector is:
PCR
In Borellia species, _____ provides a valuable diagnostic approach in acutely ill patients
Chlamydia trachomatis
Most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the US
In contrast to Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection in which most patients develop symptoms and seek care promptly, most females and males with C. trachomatis infection were asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic upon clinical presentation
For molecular diagnosis, three main targets have been used for detection of C. trachomatis:
Cryptic plasmid
genomic sequence
rRNA (16s rRNA and 23s rRNA)
Cryptic plasmid
genomic sequence
rRNA (16s rRNA and 23s rRNA)
For molecular diagnosis, three main targets have been used for detection of C. trachomatis:
Clostridium difficile
______ is an anaerobic, Gram-positive, spore-forming bacillus that can be found in the environment and gastrointestinal tract of animals and humans
The pathogenicity of C. difficile is related closely to the production of toxins A and B
major causative agent of antibiotic-associated diarrhea, colitis, and pseudomembranous colitis and is the major recognized cause of nosocomial diarrhea.
Toxigenic C. difficile detection by:
Tissue culture cytotoxin assay
qPCR and multiplex PCR targeting the C. difficile toxin genes, including tcdA, tcdB and tcdC117
NAAT is the most sensitive analytically
gastrointestinal tract of animals and humans
Where is C. defficile commonly found?
Tissue culture cytotoxin assay
qPCR and multiplex PCR
NAAT
Toxigenic C. difficile detection by:
qPCR and Multiplex PCR
In C. difficile the _____ targeting the C. difficile toxin genes, including tcdA, tcdB and tcdC117
NAAT
In C. difficile the is the most sensitive analytically
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Common cause of upper and lower respiratory tract infections in children and adults
The organism spread easily through respiratory droplets and can cause a variety of clinical manifestations, including pharyngitis, tracheobronchitis, and pneumonia
M. pneumoniae is recognized as one of the most common pathogens causing community-acquired pneumonia
Primary atypical pneumonia
PCR is the most widely applied NAAT for detection of M. pneumoniae
LAMP assay also has been applied to detect M. pneumonia in clinical specimens using P1 sequences for primers in direct comparison to real-time PCR
Rickettsia species
Genus Rickettsia includes Gram-negative, small, obligate intracellular nonmotile, pleomorphic coccobacilli bacteria transmitted by arthropods
The main clinical manifestations of rickettsial syndrome in humans are fever, rash, and eschar with different combinations, but they are not pathognomonic
Regular PCR assays are used frequently for the characterization or detection of DNA of Rickettsia species from culture, arthropods, or eschar biopsies
The use of nested PCR technique for human specimens, such as blood, buffy coat, or plasma with low level of rickettsiemia
Staphylococcus aureus
Leading cause of bone and joint infections and one of the most common causative pathogens of bacterial pneumonia in children
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) causes increased risk of mortality from invasive staphylococcal infections
Compared to methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) strains
MecA and MecC are the main genes responsible for the resistance of MRSA to most of the Beta-lactam antibiotics
PCR is considered to be the best molecular diagnostic tool for MRSA detection
Streptococcus pneumoniae
It causes a variety of diseases like: simple respiratory infections, otitis media, pneumococcal pneumonia, meningitis, septicemia
Gram-positive coccus, surrounded by a polysaccharide capsule that allows the microorganism to avoid phagocytosis, representing a major virulence factor
Capsular variability also permits different subtypes to avoid immune detection by antibodies previously generated by infection or administration of vaccine
Ability to adhere to mucosal linings is another important virulence
Several PCRs have been employed with varying degrees of success, using primers specific to repetitive regions and genes encoding rRNA:
pneumococcal surface adhesion A molecule (psaA)
pneumolysin (ply)
penicillin binding protein and autolysin (lytA)
Streptococcus agalactiae
Beta-hemolytic group B streptococcus (GBS) is the leading cause of neonatal sepsis and meningitis
Responsible for high mortality and morbidity in neonates
Important pathogen in elderly patients and those with underlying diseases
Christie-Atkins-Munch-Peterson (CAMP) is a conventional test to differentiate GBS from other streptococci
Conventional and real-time PCR assays - rapid detection of GBS
Vaginal/rectal, amniotic fluid, neonatal screening swabs, blood/serum, breast milk, urine
LAMP for detecting GBS has been successfully by using probes targeting of cfb gene (genes codes for the CAMP factor)
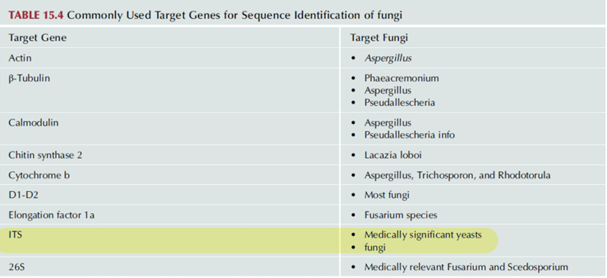
Fungal Pathogens
These are examples of ?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
_____ is classified as a member of the family Retroviridae and genus Lentivirus
Two types of HIV: HIV-1, HIV-2
HIV-1 is the most virulent and pathogenic
HIV-1
HIV-1 or HIV-2, which among the two is most virulent and pathogenic
HIV viral load
is used as a marker for disease prognosis as well as to track the efficacy of antiretroviral therapy.
Goal:
viral load < 50 copies/mL of blood
Viral load of <10,000 copies/mL in early stages
HIV viral load is performed in conjunction with determining CD4 counts.
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)
is indicated if there is no significant decrease in viral load 1 week after initiation of therapy.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
____________________ refers to a group of related papillomavirus strains that infect humans
Highly tissue tropic, and infection is limited to stratified epithelium at either cutaneous or mucosal surfaces, usually at specific body sites
HPV E6/E7 oncogene mRNA
detection in cervical cancer cells, alternative to detection of HPV DNA
DNA testing is more sensitive than cytology for identifying women with cervical precancer, cervical cytology serves as the primary screening test
RNA testing is used as a cotest or reflex test to triage patients with normal cytology
Hepatitis Virus
These are hepatotropic and noncytopathic in nature and cause liver damage by immune mediated cell lysis
The diagnosis of hepatitis viral infections is commonly through detection of serological markers in blood
Real time PCR - nucleic acid-based assay to detect the viral genome in serum for the diagnosis of viral hepatitis