11.3 Law of Independent Assortment
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:07 AM on 8/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
What are Pairs of Unit Factors (Genes)?
Mendel proposed the existence of paired unit factors (genes) responsible for heredity.
2
New cards
Explain Transmission of Genes
Mendel suggested that these unit factors are transmitted faithfully from generation to generation during gametogenesis and fertilization.
3
New cards
What are Discrete Units of Inheritance?
Mendel's experiments with pea plants and his observations of the F2 generation led him to deduce that hereditary factors are inherited as discrete units, not blended.
4
New cards
What is Independent Assortment?
Mendel's law of independent assortment states that genes do not influence each other's sorting of alleles into gametes, and every possible
5
New cards
How does Dihybrid Cross illustrate the Law of Independent Assortment?
The law of independent assortment can be illustrated through a dihybrid cross, where two true-breeding parents with different traits for two characteristics are crossed.
6
New cards
Explain Random Assortment of Alleles
The law of segregation requires that each gamete receives one allele from each gene, resulting in four equally likely gametes: RY, rY, Ry, and ry.
7
New cards
Explain the Physical Basis in Meiosis I for Law of Independent Assortment
The physical basis for the law of independent assortment lies in meiosis I, where homologous pairs align in random orientations, leading to the random assortment of alleles in gametes.
8
New cards
What are Complex Crosses?
When more than two genes are involved in a cross, the Punnett square method becomes cumbersome and impractical.
9
New cards
What is the preferred method for the Forked-Line Method?
The forked-line diagram is a preferred method for complex crosses involving multiple genes.
10
New cards
How do you Create a Forked-Line Diagram
To create a forked-line diagram, rows are made equal to the number of genes being considered, and alleles are segregated on forked lines based on probabilities for individual monohybrid crosses.
11
New cards
How do you Calculate Probabilities for the Forked-Line Method?
The values along each forked pathway are multiplied to obtain the probabilities of the F2 offspring genotypes, following the product rule.
12
New cards
What is the Probability Method for the Law of Independent Assortment?
The probability method provides proportions of offspring expected to exhibit each phenotype or genotype without the visual assistance of a diagram.
13
New cards
What is the Tetrahybrid Cross example for Probability Method?
In a tetrahybrid cross between heterozygotes for all four genes, and considering independent assortment in a dominant and recessive pattern, the proportion of offspring expected to be quadruply homozygous recessive is 1/256.
14
New cards
How do you Predict Genotypes and Phenotypes?
To predict genotypes and phenotypes in a multihybrid cross obeying independent assortment and a dominant and recessive pattern, determine the value of n, which represents the number of heterozygous gene pairs (genes segregating two alleles each).
15
New cards
What is Gene Linkage?
Gene linkage refers to genes located physically close to each other on the same chromosome, which are more likely to be inherited as a pair.
16
New cards
What is Recombination (Crossover)?
Recombination, or crossover, is the process during meiosis where segments of homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, resulting in a shuffling of alleles.
17
New cards
What are Linked Genes?
When two genes are closely located on the same chromosome, they are considered linked, and their alleles tend to be transmitted together during meiosis.
18
New cards
What can the Proportion of Recombinant Gametes be used to calculate?
The proportion of recombinant gametes can be used to measure the distance between genes on a chromosome.
19
New cards
Genes located on separate non-homologous chromosomes always sort ____ during inheritance.
Genes located on separate non-homologous chromosomes always sort independently during inheritance.
20
New cards
Mendel’s Study on Epistasis discovered what?
Mendel's studies implied that single genes control individual characteristics (phenotypes), but in reality, most characteristics are influenced by multiple genes acting together.
21
New cards
In what ways may Genes Interact?
Genes may interact in various ways, such as complementary, synergistic, or antagonistic (epistasis).
22
New cards
Define Epistasis
In epistasis, one gene masks or interferes with the expression of another gene, resulting in one gene being hypostatic to the epistatic gene.
23
New cards
Example of Epistasis
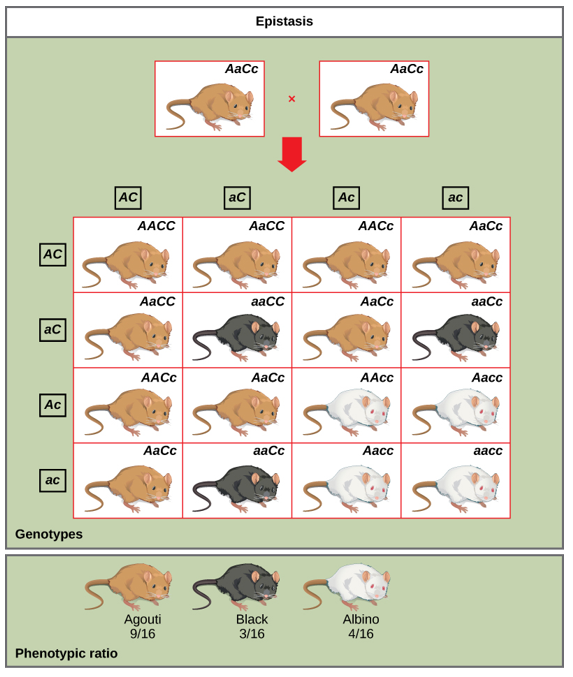
An example of epistasis is pigmentation in mice, where a gene controlling pigment production (C) is epistatic to the gene controlling coat color (A).
24
New cards
Explain Masking of Expression for Epistasis
Epistasis can also occur when a dominant allele masks the expression of another gene, as seen in fruit color in summer squash.
25
New cards
What is Reciprocal Epistasis?
In reciprocal epistasis, either gene, when present in the dominant form, produces the same phenotype. An example is seed shape in the shepherd's purse plant (Capsella bursa-pastoris).
26
New cards
What does a Phenotypic Ratio of 16 of indicate?
Characteristics resulting in a phenotypic ratio totaling 16 often indicate a two-gene interaction, assuming the interacting genes are not linked.
27
New cards
What is linkage?
The phenomenon in which alleles that are located in close proximity to each other on the same chromosome are more likely to be inherited together
28
New cards
Define Law of Dominance
In a heterozygote, one trait will conceal the presence of another trait for the same characteristic
29
New cards
Define the Law of independent assortment
Genes do not influence each other with regard to sorting of alleles into gametes; every possible combination of alleles is equally likely to occur
30
New cards
General Rules for Multihybrid Crosses

31
New cards
Mice example for Epistasis