Biotin (mine)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
biotin is found in what forms
free form and protein-bound form
Free form
biotin
Protein bound
Biocytin
protein bound is also known as what?
biotinylysine
Biotin is also synthesized by....
intestinal bacteria (only vit that does this (SI))
what do raw egg whites include
avidin
what does avidin do
irreversibly bind to biotin and prevent absorption
are egg whites always inhibiting biotin?
no, because avidin is heat-labile so when egg white is cooked it no longer affects absorption of biotin
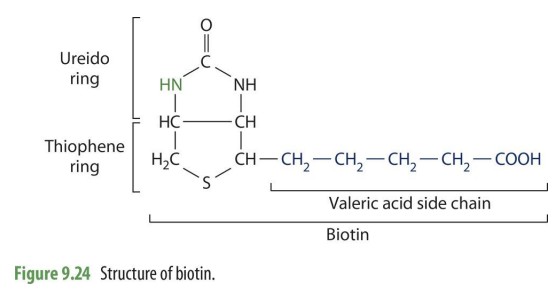
Biotin structure
Ureido ring, Thiophene ring, and valeric acid side chain
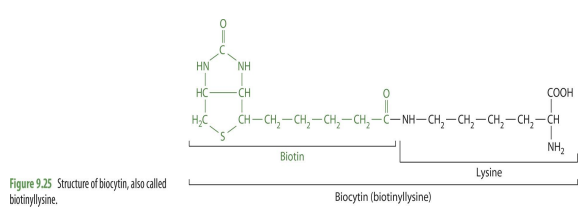
structure of biocytin
biotin + lysine
will usually include peptides but they vary; lysine tail is what is always present
absorption of biocytin (protein-bound) absorption
requires proteolytic digestion (breakdown)
after proteolytic digestion, what occurs in the small intestines
biocytin or biotinyl peptides are further hydrolyzed into free biotin
what enzyme is involved hydrozylation in small intestines
biotinidase (in small intestines)
will biocytin always be digested down to free biotin?
no, it may not be hydrolyzed…
what can occur to undigested biocytin
absorbed and acted on by biotinidase present in plasma or liver, kidney, and adrenal glands
where does biotin absorption mainly occur
upper half of Small intestines (a little in ileum)
how does absorption in upper part of SI occur
via SMVT (small amount by passive diffusion)
Transport across basolateral occurs how?
SMVT but NOT Na dependent
Bacterial synthesized biotin absorbed where...
proximal & mid-segment of colon
Alcohol affect on absorption
inhibits in SI & colon
Activity of biotinidase related to pH
Active over a wide range of pH:
acidic: it cleaves biocytin to produce biotin and lysine
alkaline: it is biotinylated and attaches to biotin (no breakdown but transport)
What type of genetic inheritance is associated with biotinidase deficiency?
Autosomal recessive error of metabolism.
What are some symptoms of biotinidase deficiency in infants?
Developmental delays, dermatitis, alopecia, seizures, acidosis, etc.
What percentage of biotin in plasma is free biotin?
80%
What proteins bind biotin to carry it to tissue sites?
Albumin, globulins, and biotinidase
Where and how much is biotin stored in the body?
In small quantities in muscle, liver, and brain
What is the main influence of the rate and uptake of biotin in cells?
localization of carboxylases
carboxylases require what (3)
biotin, presence of SMVT, and monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1)
MCT1
in cells—> because of relationship with carboxylase enzymes —> uniquely puts biotin directly to bind with those carboxylase enzymes (coenzyme role)
what enzymes is biotin associated with?
carboxylases
enzyme roles of Biotin (4- specific enzymes)
pyruvate carboxylase
acetyl-CoA carboxylase
propionyl CoA carboxylase
b-methylcronotyl-CoA carboxylase
non-coenzyme roles
•Cell proliferation, gene silencing, & DNA repair
•Gene expression & cell signaling
how does biotin attach to carboxylases? what does it result in?
Combines with carboxylase enzymes with the action of holocarboxylase synthetase to form halocarboxylases or biotinylated carboxylases.
in those carboxylases with the biocytin, gets biotinylated to assist in reactions
what enzyme is used to form halocarboxylases or biotinylated carboxylase
halocarboxylase synthetase
Biotin assist with the addition of what
It assists in the addition of CO2 to substances.
What is the role of biotin in fatty acid synthesis?
It carboxylates acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA for the elongation of a fatty acid chain.
carboxylation of acetyl CoA
acetyl CoA + CO2 —> malonyl CoA = fatty acid synthesis (elongation)
What reaction does biotin facilitate involving pyruvate?
It adds CO2 to pyruvate to yield oxaloacetate.
pyruvate becomes what due to biotin
pyruvate + Co2 —> OAA
What amino acid does biotin help break down?
Leucine
Which essential amino acids can be oxidized for energy with the help of biotin?
Isoleucine, threonine, and methionine.
Biotin dependent enzymes (4)
Pyruvate carboxylase
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
B-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase
Pyruvate decarboxylase role
Converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate
pyruvate decarboxylase function (why it does what it does)
Replenishes oxaloacetate for TCA cycle Necessary for gluconeogenesis
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase does what?
Forms malonyl-CoA from acetate
acetyl CoA + CO2—> Malonyl CoA
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase occurs why?
to commit acetate units to FA synthesis
propionyl-CoA carboxylase does what?
Converts propionyl-CoA to methylmalonyl-CoA
propionyl-CoA carboxylase does its job why?
Provides mechanism for metabolism of some AA and odd-chain FA
B-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase does what?
Converts B- methylcrotonyl-CoA to B-methylglutaconyl-CoA
B-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase does its job why?
Allows catabolism of leucine and certain isoprenoid compounds
remember biotin plays role in leucine catabolism
Biotin in relation to carboxylase in structure
Byoticyn attaches to carboxylase enzyme through the lysine chain
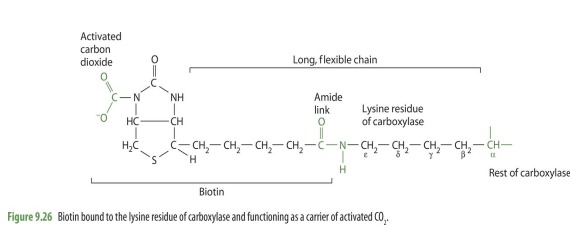
biotin bound to the lysine residue of carboxylase relation to CO2
will have CO2 attached to biotin portion making it a carrier of activated CO2
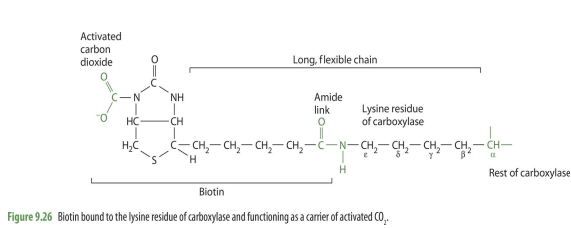
CO2 biotin enzyme complex
biotin gains CO2
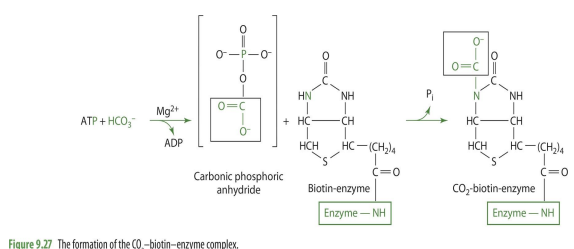
how is oxaloacetate made?
pyruvate —> OAA via pyruvate carboxylase
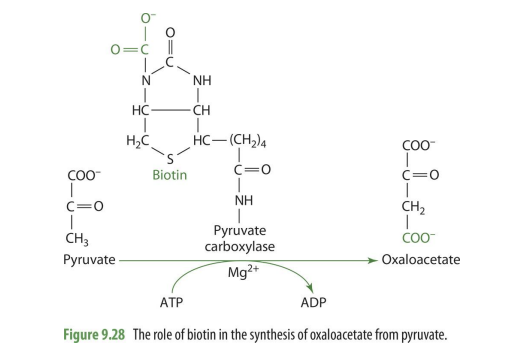
biotin role in synthesis of oxaloacetate (steps, enzyme, co-substrate, biotin’s role)
pyruvate —> OAA
enzyme: pyruvate carboxylase (biotin is coenzyme)
co-substrate: Mg2+ and ATP
role: biotin donates CO2
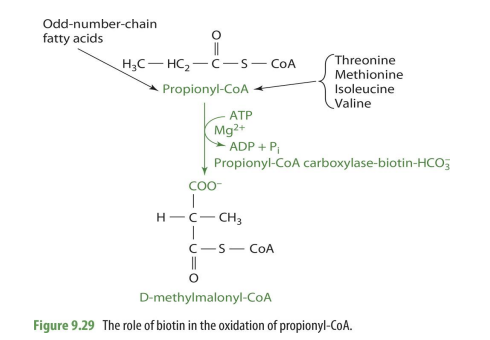
how is biotin involved with propionyl CoA
it aids in coverting it to D-methylmalonyl CoA
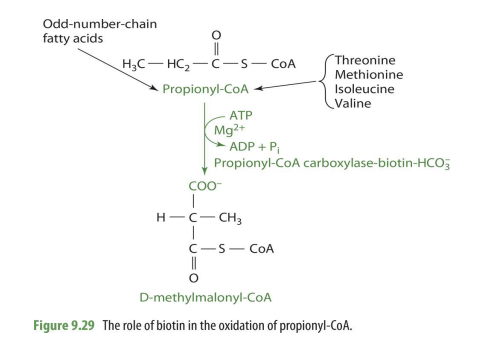
what substrates are used to make propionyl CoA
odd chain FA’s and essential amino acids (threonine, methionine, isoleucine, valine)
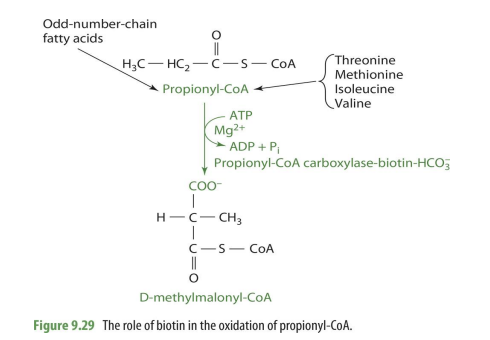
how is propionyl CoA converted into D-methylmalonyl-CoA
via propionyl CoA carboxylase
coenzyme: biotin
co-substrate: Mg, ATP
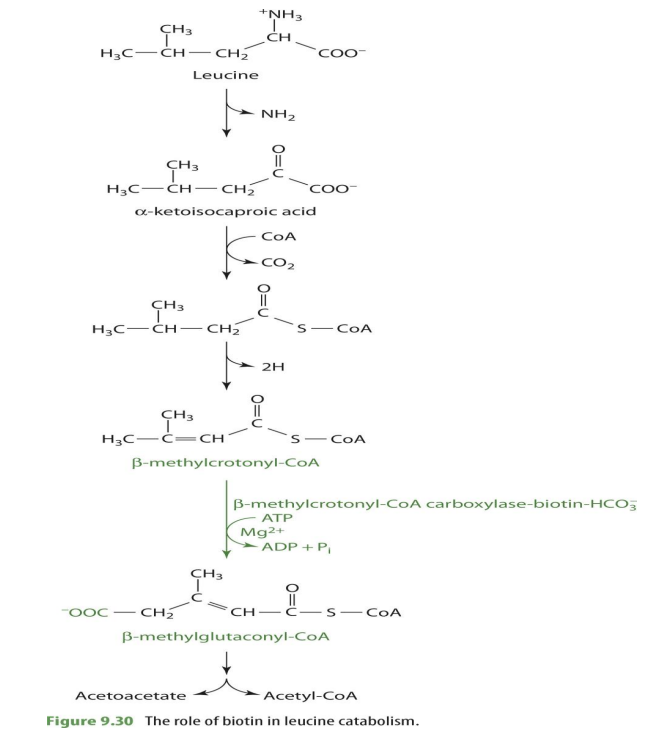
how is biotin involved with leucine
involved in leucine breakdown
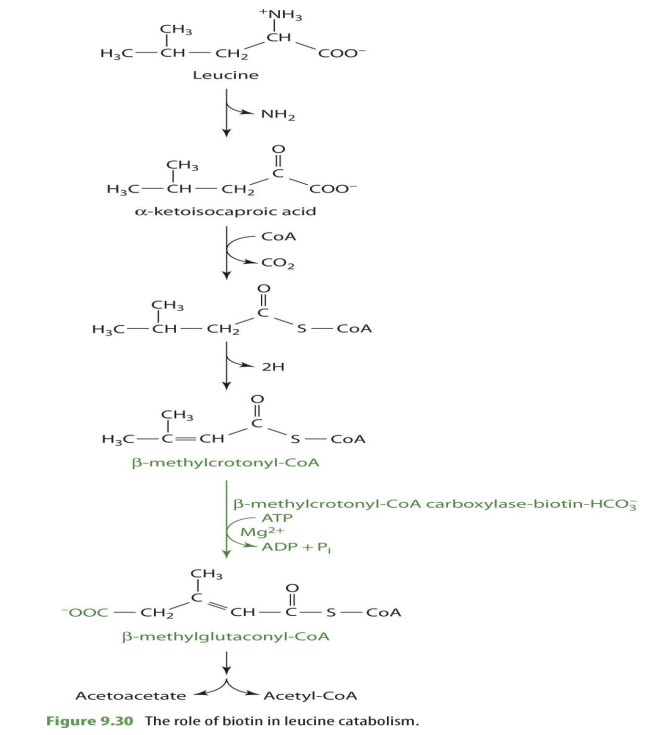
what part of leucine breakdown in biotin involved in?
b-methylcrotonyl CoA —> b-methylglutaconyl CoA
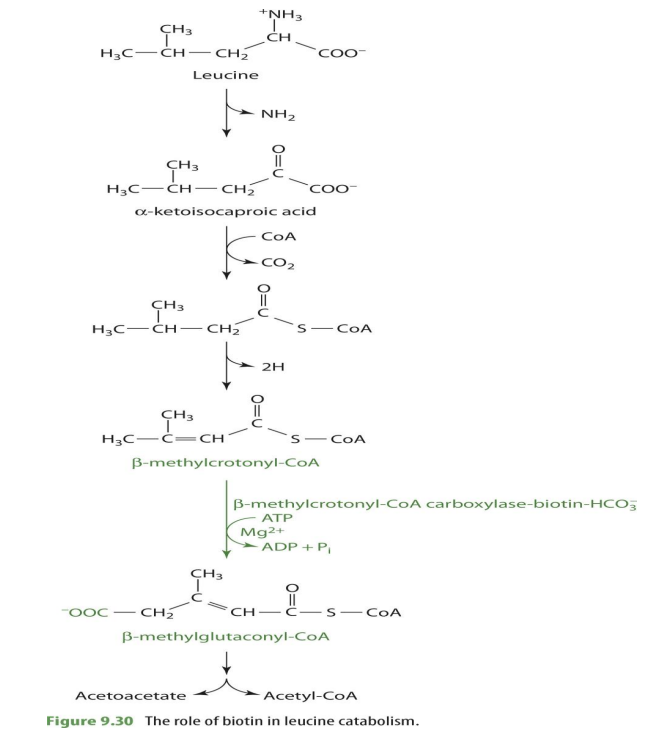
what is the enzyme that biotin is attached to for leucine breakdown?
b-methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase
what does biotin do in non-enzyme role?
Influence cellular function through biotinylation of proteins (non-histone & histone)
(similar to CoA and acetylation)
How does biotin affect histones?
It influences DNA and chromatin structure.
Name a biotin-dependent transcription factor (most important one)
cGMP, nuclear factor (NFKappaB), or tyrosine kinase.
How many genes in humans are dependent on biotin for transcription activity?
Over 2000 genes.
What critical role may biotin play in cellular processes?
It may play a critical role in the cell cycle.
What enzymes break down biotin holocarboxylases?
Proteases
because break at the lysine (amino acid)
What are biotin holocarboxylases catabolized to?
Biotin oligopeptides→ biocytin
remember that biocytin includes biotin and lysine. Lysine may be attached to peptides which is when we have the biotin oligopeptides.
one we have biocytin, what enzyme acts upon it
Biotinidase
what does biotinidase break biocytin Down to
biotin and lysine
what happens to the lysine and biotin after breakdown?
excreted via urine, reutilized, or excreted
What happens to biotin that is synthesized by intestinal bacteria that is not absorbed?
It is excreted in feces
What may the degradation of the vitamin ring structure yield?
Various metabolites
the ureido and thiophene ring
biotin degradation can result in what 2 metabolites
bisnorbiotin and biotin sulfoxide
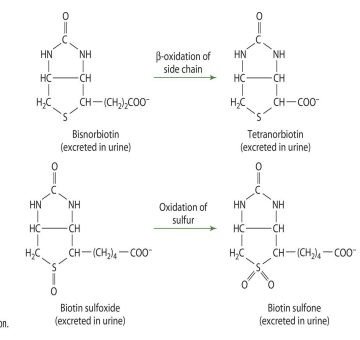
B-oxidation of side chain in bisnorbiotin produces what
tetranorbiotin
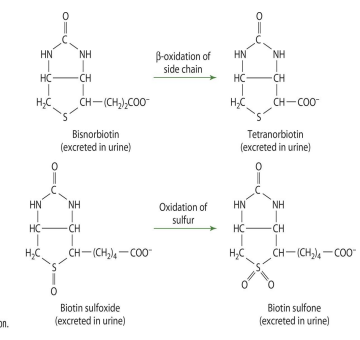
oxidation of sulfur in biotin sulfoxide produces what
Biotin sulfone
What are some food sources of biotin?
Cauliflower, egg yolk, liver, peanuts, cheese
What is a source of biotin synthesis in the body?
Intestinal synthesis of biotin
Is biotin content widely available in foods?
Biotin content is only available for a small number of foods
What is uncertain about synthesized biotin?
Unsure as to bioavailability of synthesized biotin
biotin excretion vs consumption amount
we excrete more than we consume
What substance inhibits the absorption of biotin?
Avidin inhibits absorption
AI
adult & preg: 30ug
lactation: 35ug
overestimate the amount needed
no UL
Who is at Risk For Deficiency?
rare
high raw egg white intake
biotinidase deficiency
anticonvulsant drug use
IBD
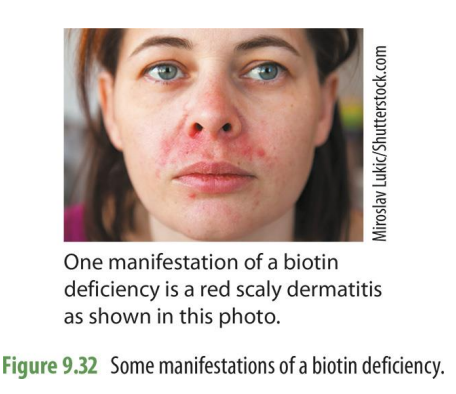
S/S of deficiency
skin rash
hair loss
convulsion
neurological dz
impaired growth in children
What are the most commonly assessed samples for nutritional assessment?
Blood and urine concentrations
what is not not representative of diet or storage
plasma levels
What indicates a deficiency in biotin?
Decreased urine concentration of biotin and increased excretion of 3-hydroxyisovaleric acid