chemistry exam 4
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
what type of radiation is light
electromagnetic
what are some different types of electromagnetic radiation
X-Rays, UV radiation, Infrared radiation
what are the different properties of electromagnetic radiation
waves and particles
what are the different descriptors that are used to describe waves
wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and velocity.
Wavelength
the distance between two peaks on a wave
Frequency
the number of wave peaks that occur in a given amount of time. Abbreviation is n Usual unit is Hertz (Hz), which means "per second".Sometimes also see s-1.
Amplitude
the height of a wave, measured from the baseline to the peak.
What is the speed of light in meters per second?
3.00 x 10^8 m/s
What is the abbreviation for the speed of light?
c
What is true about the velocity of all electromagnetic waves?
The velocity of all EM waves is constant.
For all EM radiation what is the constant speed ?
3.00 x 10^8 m/s
Blackbody radiation
As an object is heated, it gives of EM radiation/ the light given off by a hot object
The Photoelectric Effect
Electrons are given off when certainsubstances are struck by light
Emission spectra
when the electrons of a gas are excited, the gas gives off certain wavelengths of light
photon
a particle of light
quantum
The amount of energy contained in a photon
what prediction does blackbody radiation give us
that all objects should glow in the dark, even when cool
what is the incorrect prediction that states all objects should glow in the dark, even when cool known as
ultraviolet catastrophe
who proposed the particle nature
Max Planck
what did max planck state about blackbody radiation
that energy can only be released or absorbed in discrete chunks of some minimum size
what is the frequency of quantum light
E = hv
Planck's constant
6.626 x 10^-34
who was the first to explain the photoelectric effect
Albert Einstein
what did Einstein state about the Photoelectric effect
the light hitting the surface was behaving as a particle, which he called a photon
what was the equation used to determine the energy of the photon Einstein was describing
Planck equation: E=hv
what happen when a photon strikes a surface
its energy is transferred tothe material
binding energy
certain amount of energy needed to cause an electron to be ejected.
what happens if the amount of energy of the binding energy is greater than the energy of the photon
no electrons are ejected.
what happens if the energy of the photon is greater than the binding energy
an electron is ejected.
spectrum
the set of wavelengths given off (orabsorbed) by a material
what are the 2 types of spectrums
continuous or line
continuous spectrum
contains all the wavelengths overthe wavelength range being studied.
line spectrum
A spectrum consisting of only a few discrete wavelengths of light
The Bohr Model
1. Only orbits of certain radii, corresponding to certain energy, are allowed
2. An electron has a specific energy while in a specific orbit, and will not radiate energy while in that state.
3. Absorption or emission of energy only occurs when an electron moves from one energy state to another
what happens as the energy level goes up
The difference between the energy levels gets smaller.
Uncertainty Principle
states that we cannot know exactly the location and momentum of an electron at the same time
who developed equations which model electrons both as particles and as waves
Erwin Schrödinger
the uncertainty principle is based on what
the probability of the position a electron will be
What are the 4 quantum numbers?
n, l, ml, ms
what does n stand for
the principal quantum number, Describes the size of the orbital
what does l stand for
the angular momentum quantum number, Describes the shape of the orbita
what does ml stand for
The magnetic quantum number, Describes theorientation of the orbital.
what happen as n (l) increases
the orbital becomes bigger, and the electron is farther away from the nucleus, and the energy associated with the orbital becomes more positive
what is the shape of a s orbital
spherical
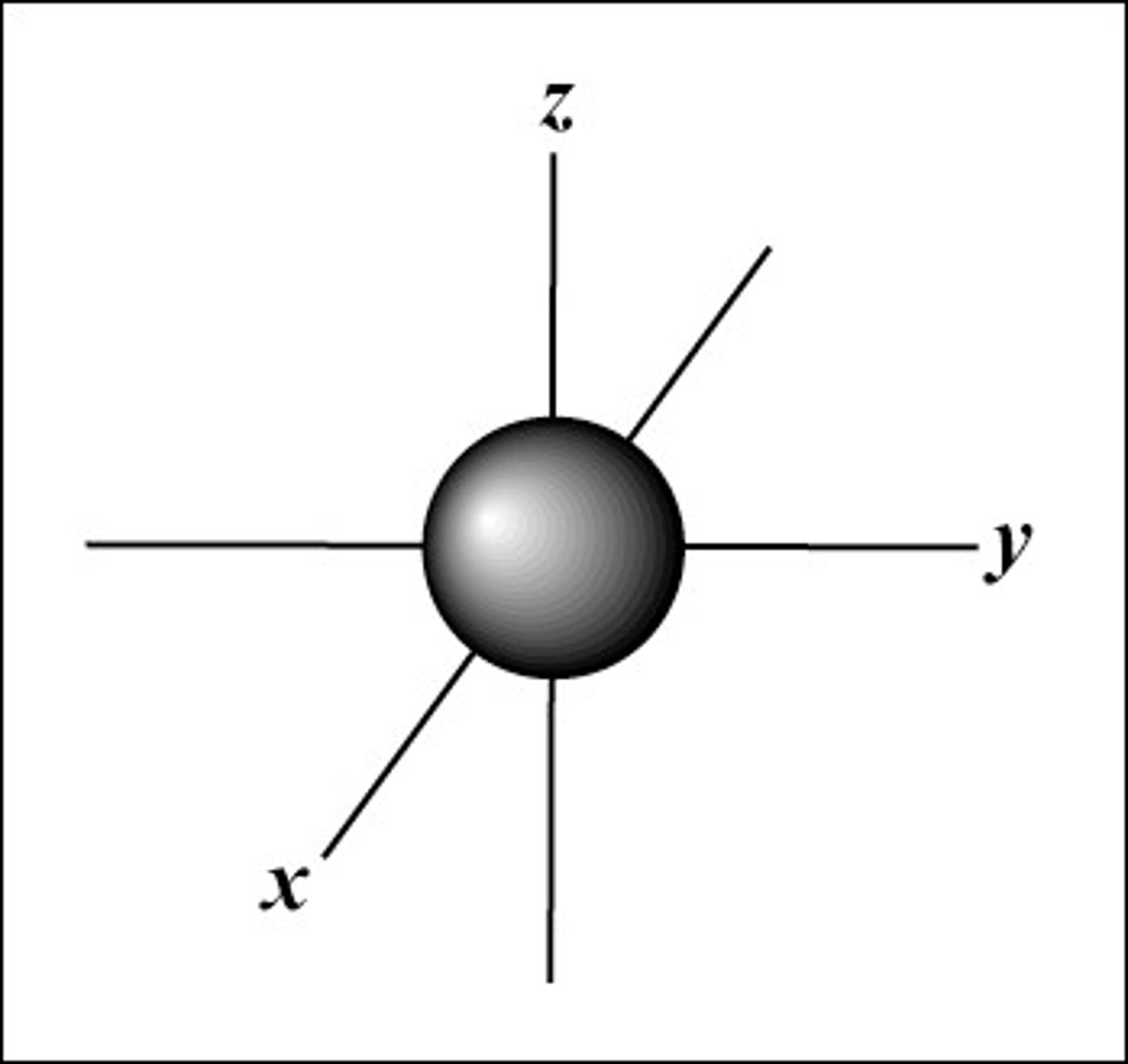
what is a node
A region where the probability of finding an electron goes to zero that is between two areas where an electron could be found
what shape is a p orbital
dumbbell/infinity sign
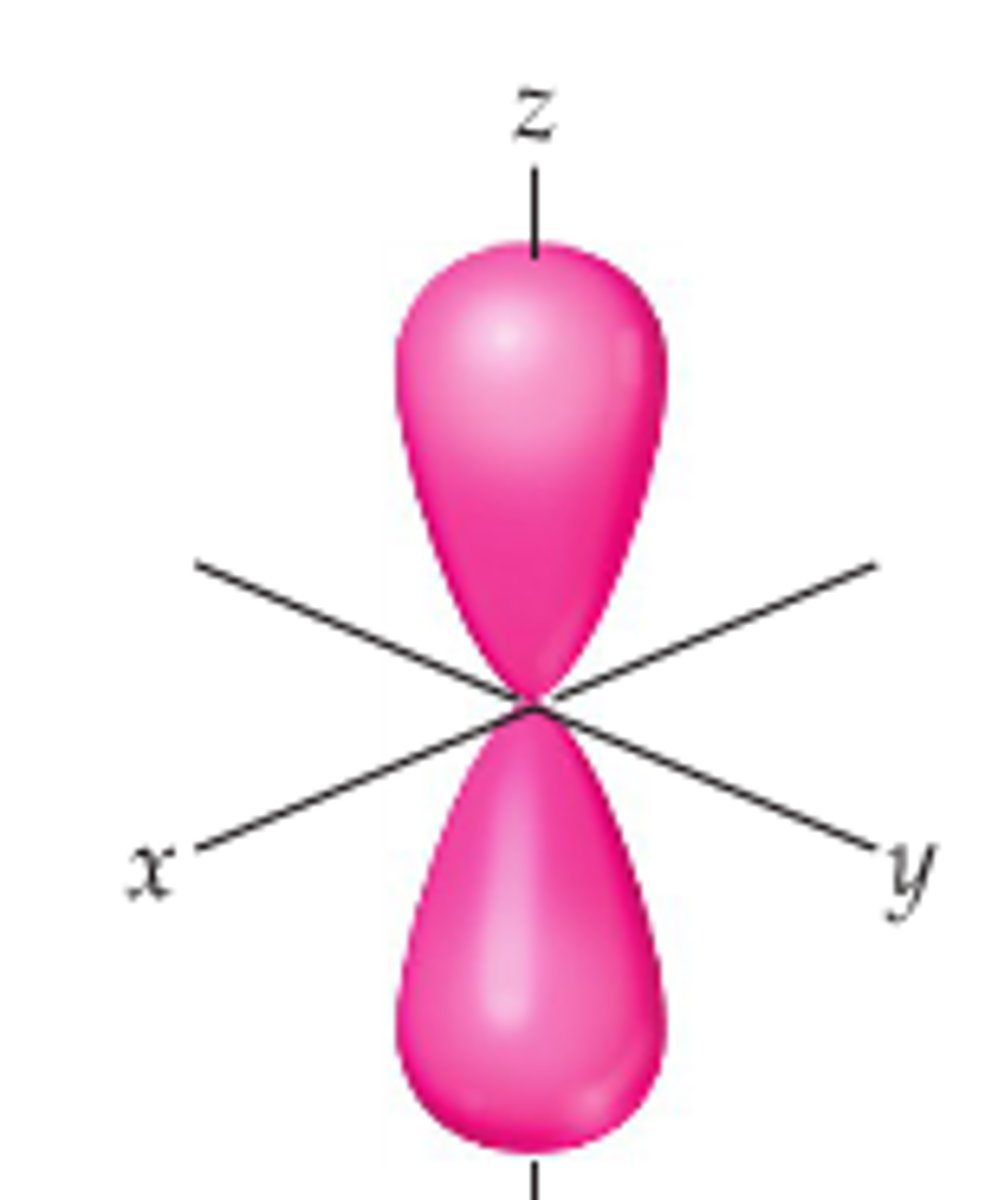
at what degree can a p orbital be centered at
90 degrees
what shape are d orbitals
clover
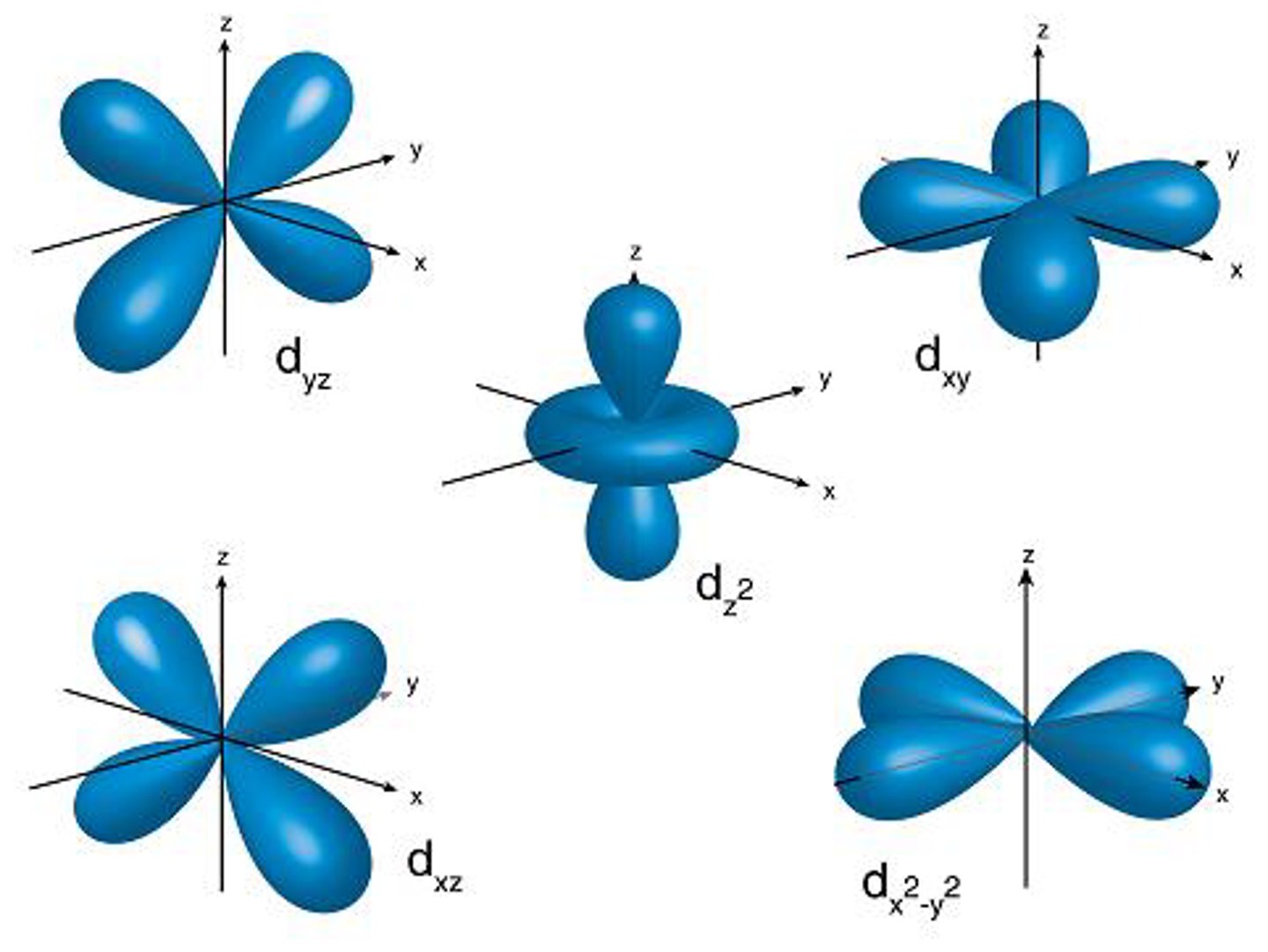
what does ms describe
the spin of electron/ the orientation of the electron
electron configuration
The way in which electrons are distributed in the orbitals of an atom
ground state
the most stable electron configuration
Hund's Rule
For degenerate orbitals, the lowest energy state (most stable) is obtained when the number of electrons with the same spin is maximized.
what is the primary driving force of Hund's rule
electrostatic repulsion between electrons
What type of charge do electrons have?
negative
valence electrons.
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
core electrons
The electrons that are not in the innermost shell of an atom.
in the earliest version of the periodic table, how were the elements classified
by atomic weight
who created the modern periodic table
Dmitri Mendeleev
atomic number
the number of protons in an atom
effective nuclear charge (Zeff)
average environment created by the nucleus and the other electrons in the atom
As we move across the periodic table from left to right, what happens to (Zeff)
it increases
As we go down a column, what happens to Zeff
it stays constant
as we go down the periodic table, what happens to the atomic radius
it increases
as we go across the periodic table, what happens to the atomic radius
it decreases
ionic radius
refer to the radius of the ion after electron(s) have been added or removed
ionization energy
the energy required toremove an electron from an atom
The higher the ionization energy......
the more difficult it is to remove an electron.
as we go across the periodic table from left to right, ionization energy
increases
as we go down the periodic table, ionization energy
decreases
electron affinity
is the change in energy when an electron is added to anatom or ion
chemical bond
the force that holds the atoms in position in a substance.
types of chemical bond
ionic, covalent, metallic
ionic bond
are formed by the electrostatic interaction between ions. Ions are formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another. Generally found between a metal and a nonmetal.
Covalent bonds
formed when atoms "share" electrons. Generally found between nonmetals.
Metallic bond
Each atom is bonded to its neighbors; electrons are shared throughout the lattice. Generally found between metals
what do chemical bonds depend on
he position ofelectrons in the atoms involved in bonding
Lewis dot symbol
used to illustrate the number of valence electrons
The octet rule
the tendency of atoms to form an octet of valence electrons
what are ionic bonds based on
the attraction between ions of opposite charge.
Ionic bonds are formed between....
metals and nonmetals
Lattice Energy
The energy released when the lattice is formed/the energy required to separate a mole of an ionic solid into its gaseous ions
what is lattice energy based on
The potential energy of two interacting charged particles
polyatomic ions
ions consisting of more than one atom bonded together
nonpolar covalent bond
Bonds where the electrons are shared equally
polar covalent bond
One atom exerts a greater "pull" on the electrons than the other
Electronegativity
defined as the ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a molecule.
what is the most electromagnetic element
Fluorine (F)
what is the least electromagnetic element
cesium (Cs)
What happens if the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is less than 0.5?
the bond is considered nonpolar covalent.
What happens if the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is between 0.5 and 2.0
The bond is considered polar covalent
what happens if the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is greater than 2.0
the bond is considered ionic
if there are 4 electron groups, what shape will they rearrange themselves in
tetrahedron
what is the degree of a linear electron domain
180
what is the degree of a trigonal planar electron domain
120
what is the degree of a tetrahedral electron domain
109.5
what is the degree of a trigonal bipyramidal electron domain
120 and 90
what is the degree of a octahedral electron domain
90
vector
a quantity that has both magnitude and direction
what is a example of a polar molecule
water
how do covalent bonds occur
when atoms share electrons