Unit 5 Thou Shalt Not Forget, AP Chemistry
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Increasing concentration leads to
faster rate of reaction
Increasing temperature
increases reaction rate
Catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction while remaining chemically unchanged
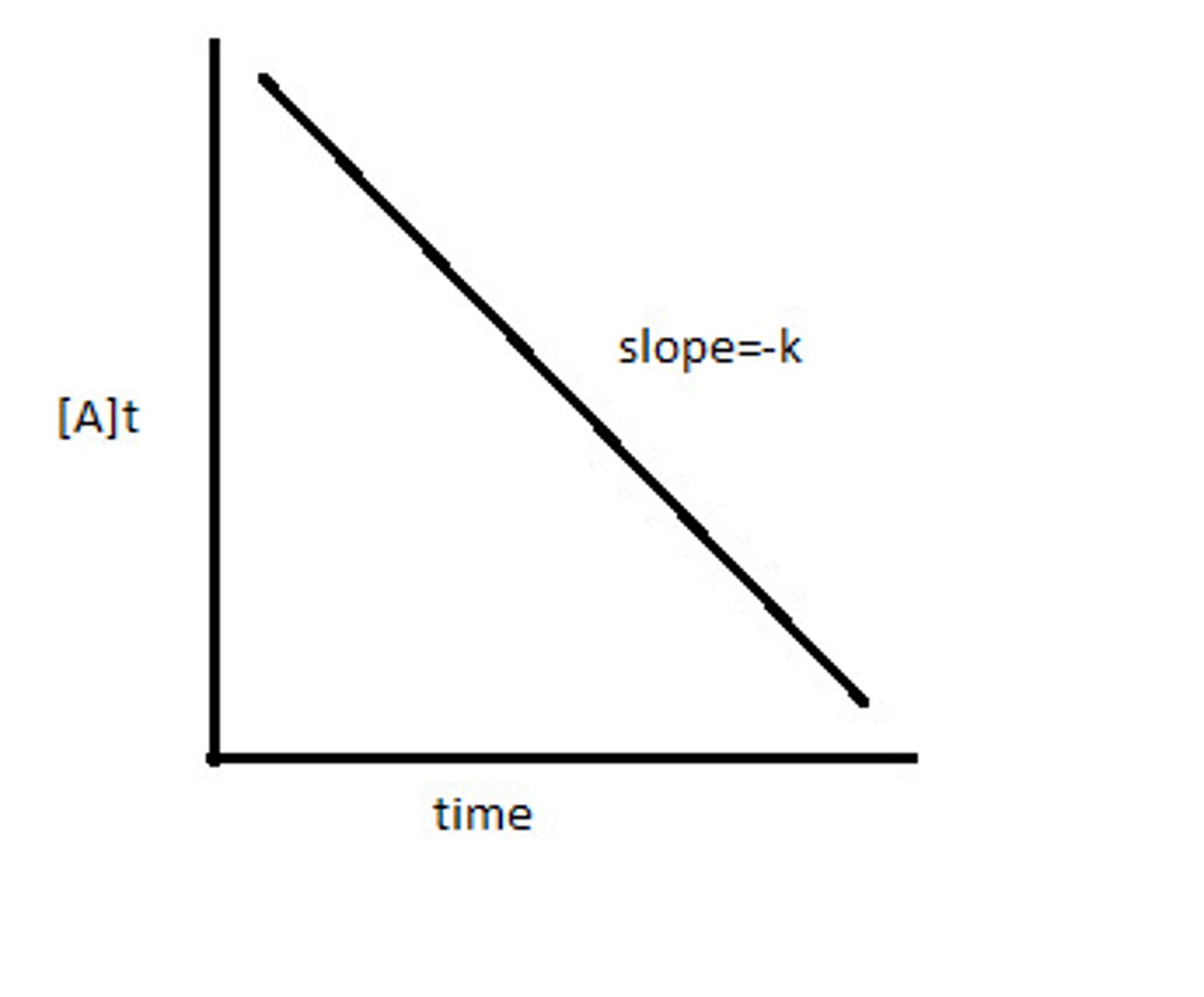
[Reactants] against time
straight line = shows zero order
[Reactants] against time First Order
Constant Half life
[Reactants] against time Second Order
Not constant Half life
Rate against [reactants] zero order
rate independent of concentration of reactants
First order
rate directly proportional
Second order
Rate varies to greater degree
The overall rate of a complex chemical reaction is only dependent upon
slowest stage
Collision theory says that a reaction will only take place if:
1. Reactants come into contact
2. The activation energy is met
3. The collision has the right orientation
Greater concentration means...
Faster rate of reaction
Increased temperature means...
Faster rate of reaction
If a solid is broken up into smaller pieces, the rate of reaction increases. Why?
The surface area increases
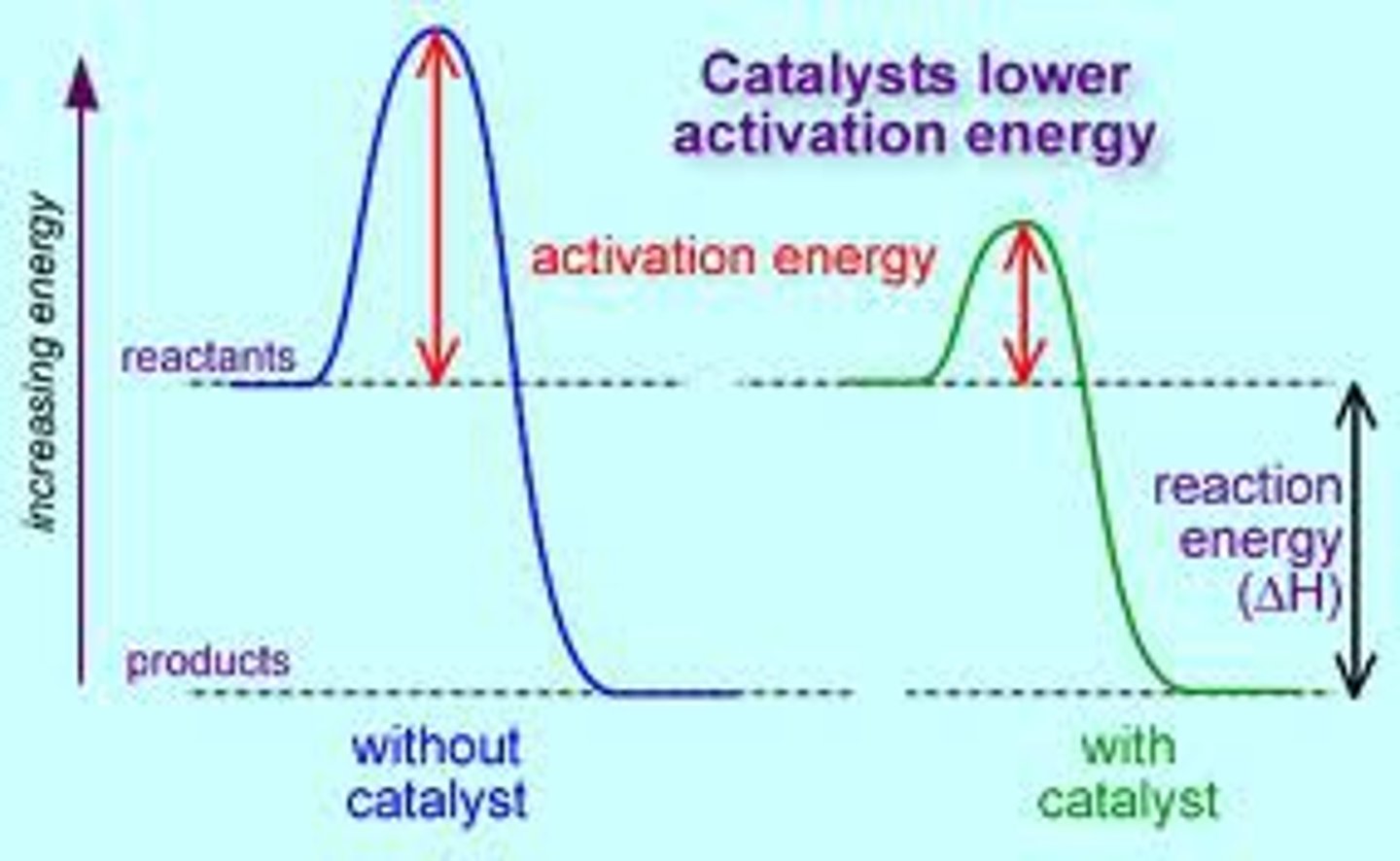
Addition of a catalyst does what?
Provides an alternate pathway (for the reaction to take place) that requires a lower activation energy
K
rate constant
In the rate law, x, y, and z are
the reaction orders
Only the reactants in the __________ step will be included in the rate law
slow, rate- determining
If a substance is present at the beginning of a reaction and present in the same form at the end of a reaction, it can be identified as a...
catalyst
To determine the order of a reaction from a graph, look for the graph with a
Straight line (constant slope)
rise in temperature
increase rate of reaction
increase concentration
increase collision frequency
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
enzyme
speeds up chemical reactions while lower activation energy
catalyst
provide a alternative pathway with a lower Eact.
K
equilibrium constant
Which step would included the reactants of the rate law?
slow, rate-determining
zero order
1st order
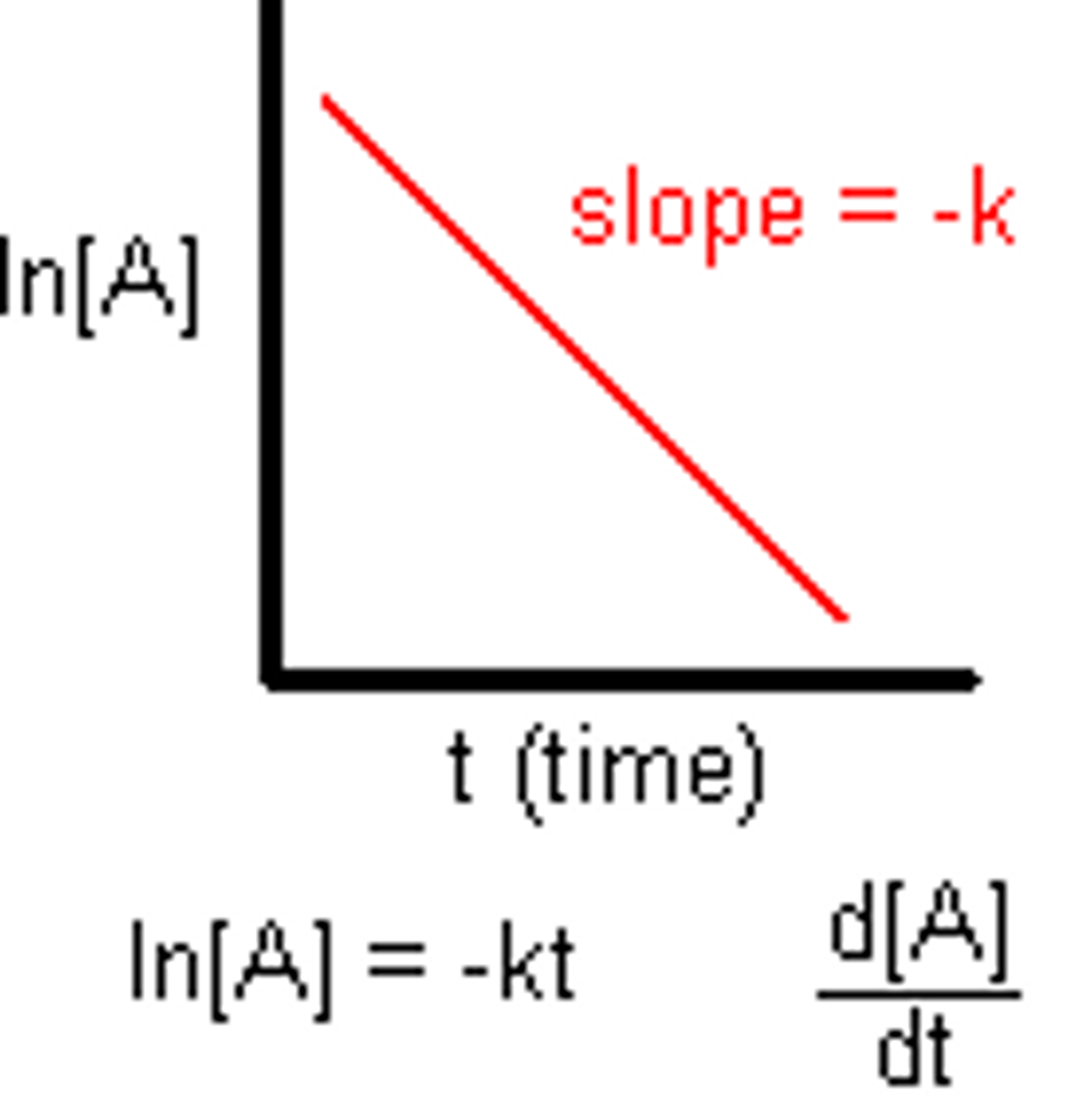
2nd order
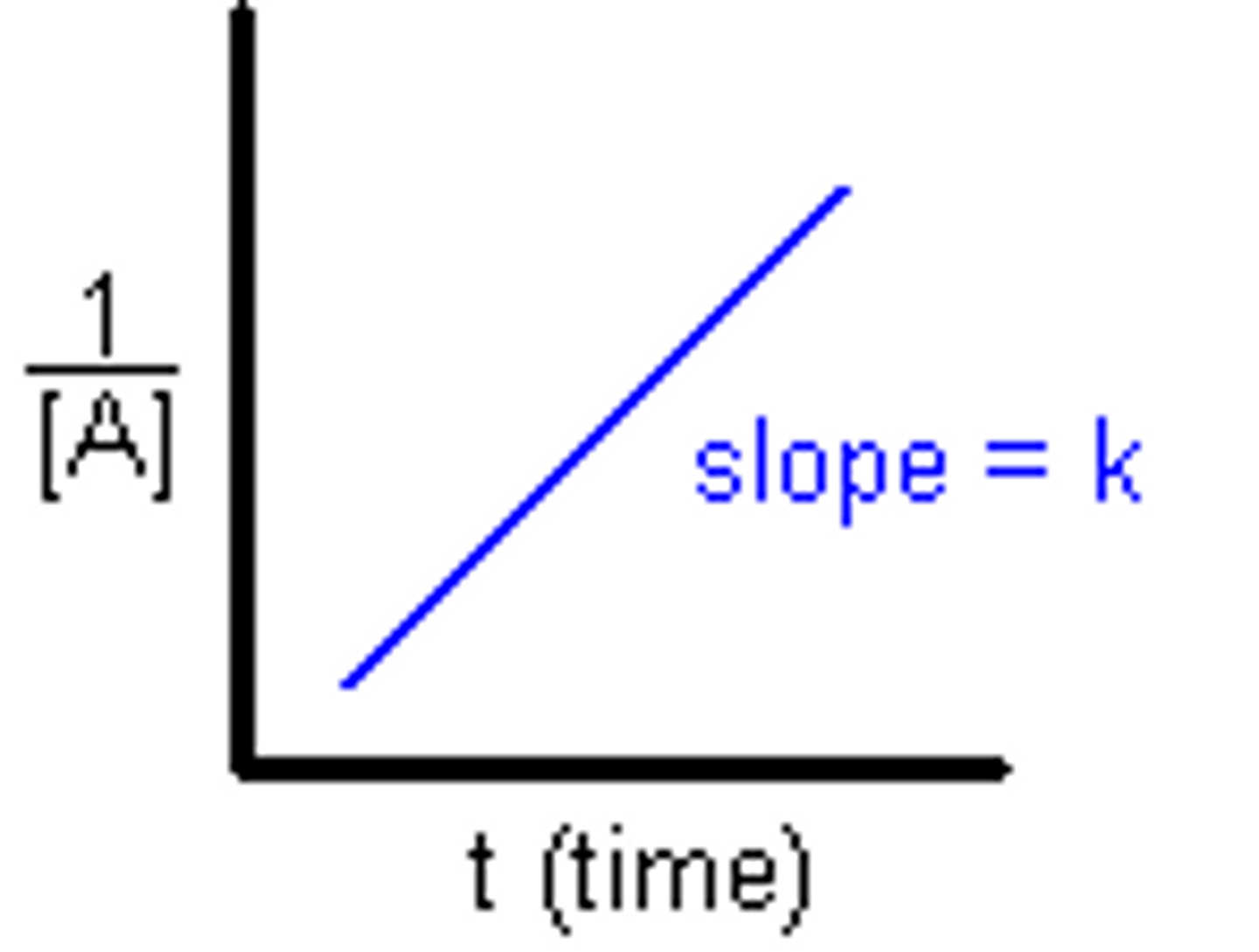
Activation Energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started
Unimolecular reactions
reactions in which a single chemical species decomposes or rearranges
Bimolecular reactions
chemical reactions that involve the collision of two chemical species
Trimolecular reactions
when three reactants collide to form new products: third order
First Order
rate=k[A]
In [A]t versus t
Second Order
Rate=k[A]^2
1/[A]t versus t
Catalysts
substances that speed up chemical reactions
Rise in temperature =
Increased rate of reaction (more particles have minimum energy needed)
Greater concentration =
Greater frequency of collisions and greater chance of success
Arrhenius equation
relates rate constants, activation energy, and temperature
Rate
Change in concentration of a substance/ change in time
Reaction Mechanisms
Series of steps by which a reaction occurs
Intermediate
a species that is neither a reactant nor a product but that is formed and consumed in the reaction sequence
molecularity
the number of species that must collide to produce the reaction indicated by that step
rate determining step
the slowest step in a reaction mechanism
A chemical eqaution
only tells us what reactants become products
What is K
rate constant
What is E
activation energy
What is R
universal gas constant
Remember to measure temperature
in kelvins
reactions must _______ in the correct _______ in order to occur
collide, orientation
________ must be met for reaction to occur
activation energy
Increasing reactant concentration
generally increases reaction rate
higher temperature has _______ arrows in a heat diagram
longer
higher temperatures cause molecules to move ________
faster
2 systems come together and energy moves from the _____ to the _____ one
hot to cold
exothermic
Releases heat
endothermic
Absorbs heat
negative delta H
exothermic
First electron affinity
The enthalpy change that takes place when one electron is added to each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1- ions
one
The rate of a reaction can be determined by the decreased concentration of the reactants and the increased concentration of the products
two
Collision theory tells that a reaction will only take place if the reactants collide with enough activation energy and at the right angle
three
elementary steps can have 1,2, or 3 species collide and react to form products. That being said, the fewer molecules involved in the elementary reaction, the more likely it is that one of the collisions will be in the correct orientation
four
Factors that can influence the rate of a chemical reaction are concentrations, temperature, solid particle size, and catalysts. Solid particle size matters because of surface area. The smaller the particles, the greater the surface area, and more particles can collide, increasing the rate of the reaction. Catalysts lower the activation energy, which allows more particles to meet that energy and collide more. This speeds up the rate of the reaction. With concentration, the more you have of something, the more particles you have, the more Collisions you will have. Temperature affects the rate by causing the kinetic energy of the particles to go up, making the particles move faster and make more collisions.
five
The overall rate of a chemical reaction is based on the slowest elementary step
six
Intermediates are created in one elementary step then used up in the following elementary step
seven
First order graphs show a constant half life. Second order graphs might look like they have a constant half life, but they don't.
eight
The order with respect to a given reactant is the power to which the concentration of that reactant is raised to the rate equation
nine
Catalyst are present at the beginning of the reaction and the end of the reaction in its same form
ten
A reaction that has no effect on the rate is said to have an order equal to zero
Minimum Energy
Activation Energy
Reactants
must collide at the correct orientation for the reaction to occur
Elementary Steps
form substances in a single step
The more molecules there are
the chances for correctly oriented collisions decreases
Increased Concentration
causes greater frequency of collisions and greater chances of successful collisions
Intermediates
are not apart of the product
Increase in temperature
results in increased rate of reaction
Catalysts
are present in the product
Zero Order
1st Order
2nd Order
Rate = k
Rate = ln[A]
Rate = 1/[A]
If the constant increases
the rate increases
the _______ determines the rate
slow step
What do catalysts affect?
Only the activation energy
bimolecular
two reactants form products
intermediate substance
formed in one step of reaction then used in subsequent reaction
Activation Energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started
First Order
rate=k[A]In [A]t versus t
Second Order
Rate=k[A]^2 1/[A]t versus t
Arrhenius equation
relates rate constants, activation energy, and temperature
Catalysts
substances that speed up chemical reactions
Greater concentration
Greater frequency of collisions and greater chance of success
collision theory
For a reaction to occur, the particles must collide, they must collide with the appropriate orientation, and they must collide with sufficient energy.
few molecules in the elementary reaction
the more likely it is that one of the collisions will be in the correct orientation
increase of molecularity
causes the chance of correct oriented collisions to decrease
an increase of reaction concentration
causes a greater frequency of collision
Increase in temperature
causes increase in the reaction rate
Addition of a catalyst
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering its activation energy. The catalyst may participate as a reactant but it is then regenerated as a product and is thus available to catalyze subsequent reactions. It also decreases the activation energy
Delta H (∆H)
remains the same in the presences and absence of a catalyst in a reaction
The overall rate of a complex chemical reaction is only dependent upon
the slowest elementary step
Rate= k[A]^x[B]^y[C]^z
k= rate constant
x,y,z= orders with respect to the concentrations
ABC= concentrations
Rate laws
it is possible to deduce anything about the order of a reaction from the stoichiometry of the balanced equation that describes the complete, complex, chemical reaction