Geography KS3 Year 9 End of Year Test
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Three types of rocks
igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
Uses of Rocks
Building houses/construction
Extracting metal
Building roads
Extracting precious stones
Extracting valuable minerals and salts
What does renewable energy mean?
The sources of the energy can never be used up, for example wind, waves and tides. Fossil fuels are non-renewable as they cannot be used again.
Barriers to using renewable energy
1. capital costs - upfront costs of the technology needed, like wind farms
2. Where to build them - some people find wind farms ugly and hdyro power needs to be built near fast flowing water.
3. not always consistent - not always enough sunshine for solar
4. investment in and reliance on fossil fuels
5. transmission infrastructure was built for fossil fuels - so might have to build new transmission for renewable energy
Primary Industry
The part of the economy that produces raw materials; examples include agriculture, fishing, mining, and forestry.
Secondary Industry
The part of economy that makes things from raw materials examples include carpenter, food factory worker, clothes factory
Tertiary Industry
A part of the economic system involved in the production of services and information
Quaternary Industry
Jobs that deal with the handling and processing of knowledge and information like IT, research scientist
Primary industry in the UK fell by what % between 1800 and 2000?
Primary industry in the UK fell by what 60% between 1800 and 2000?
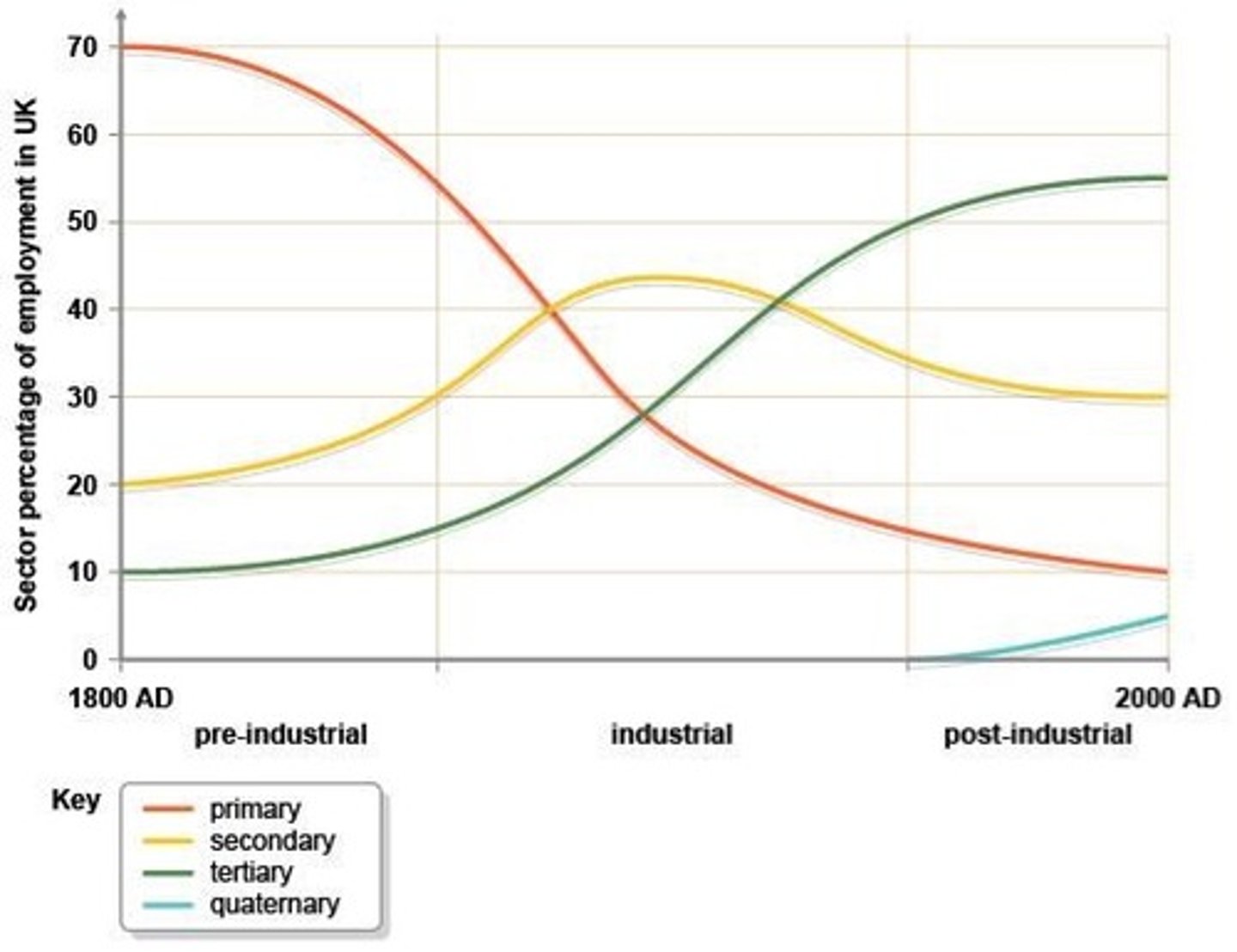
During the late 20th Century, tertiary industry levelled of at around what % of our employment?
During the late 20th Century, tertiary industry levelled of at around what 55% of our employment?
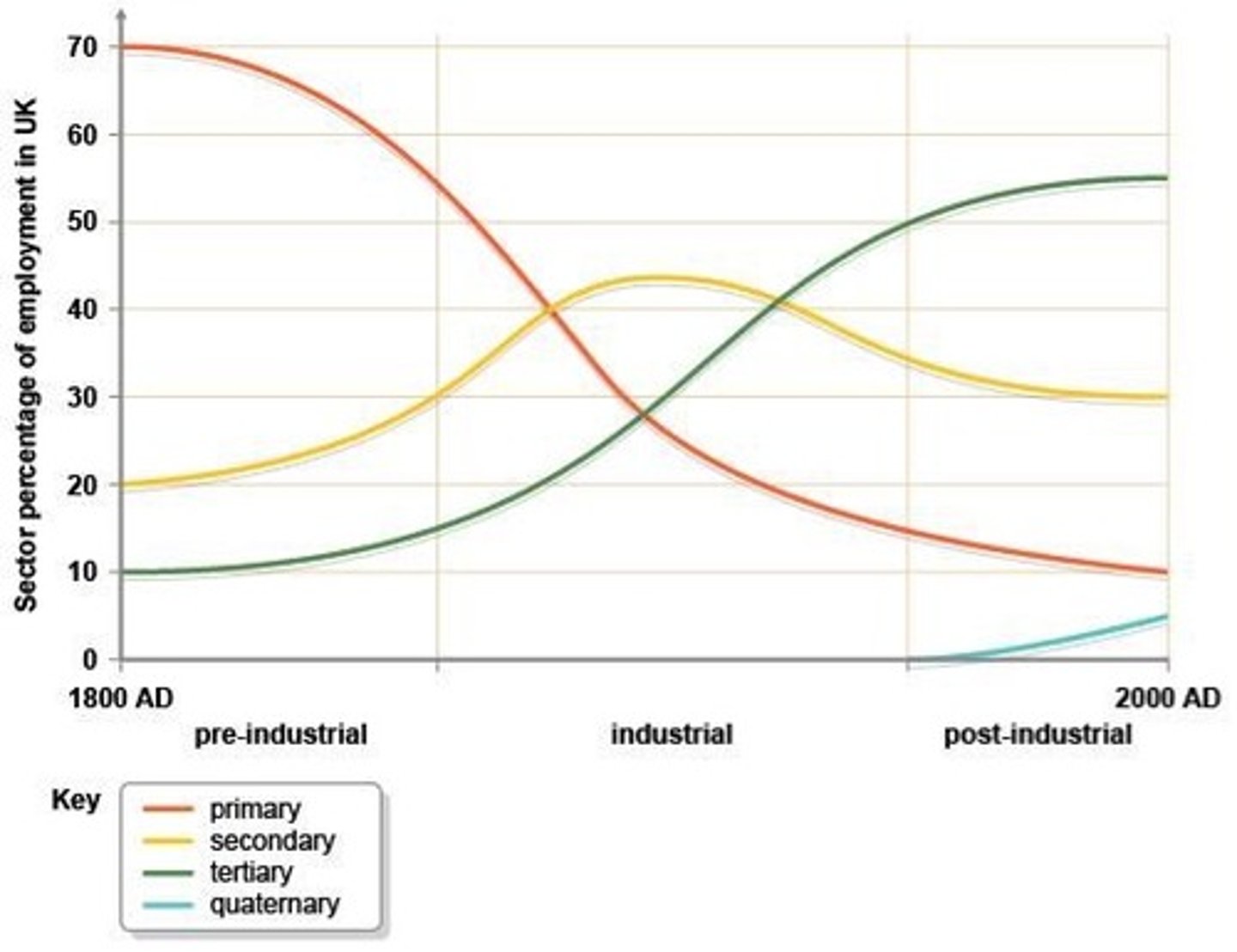
What change marked the difference between the industrial and post-industrial periods?
The difference between the industrial and post-industrial periods was marked by the
emergence of quaternary jobs.
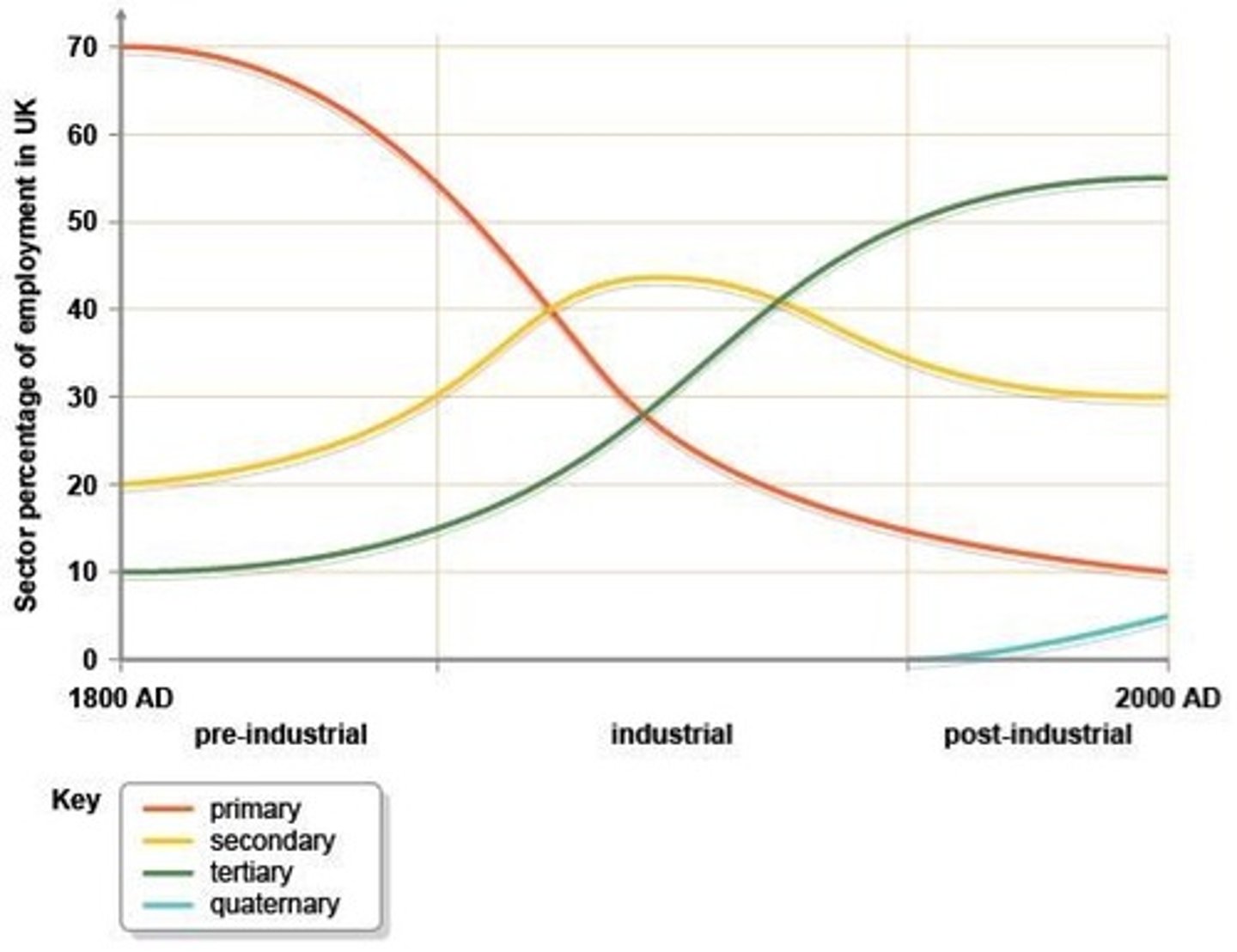
Give one reason for the recent growth of quaternary jobs.
The growth of technology. The development of the internet
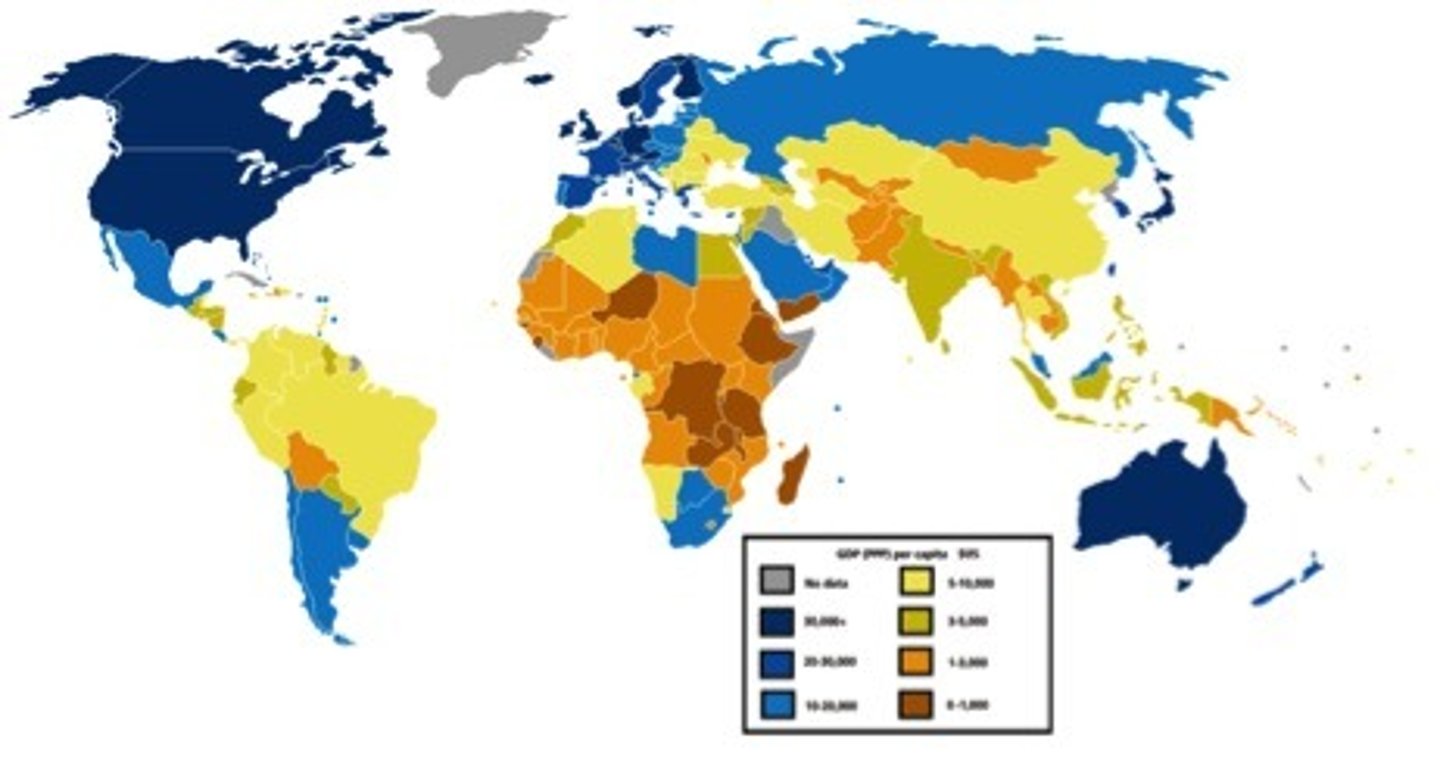
Study the map below of global GDP per person (PPP) in dollars. In as much detail as you can, describe the pattern the map shows.
The areas with the highest GDP per person (over $US 30,000) are North America, Australia and Japan as well as some countries in Europe. The areas with the lowest GDP per person (under $US 3,000) are mainly found in central Africa. Most of Asia and South America have medium GDP per person.
How soil quality has contributed to the development gap between countries:
; Availability of metal ores;
Soil quality contributes to the development gap as it has a big impact on agriculture. Countries with poor soil will find it hard to even grow enough food for their population to eat. Countries with very good soil can feed themselves with extra left over to sell. By exporting food they can then earn money to spend on trade in other products which helps their economy to grow.
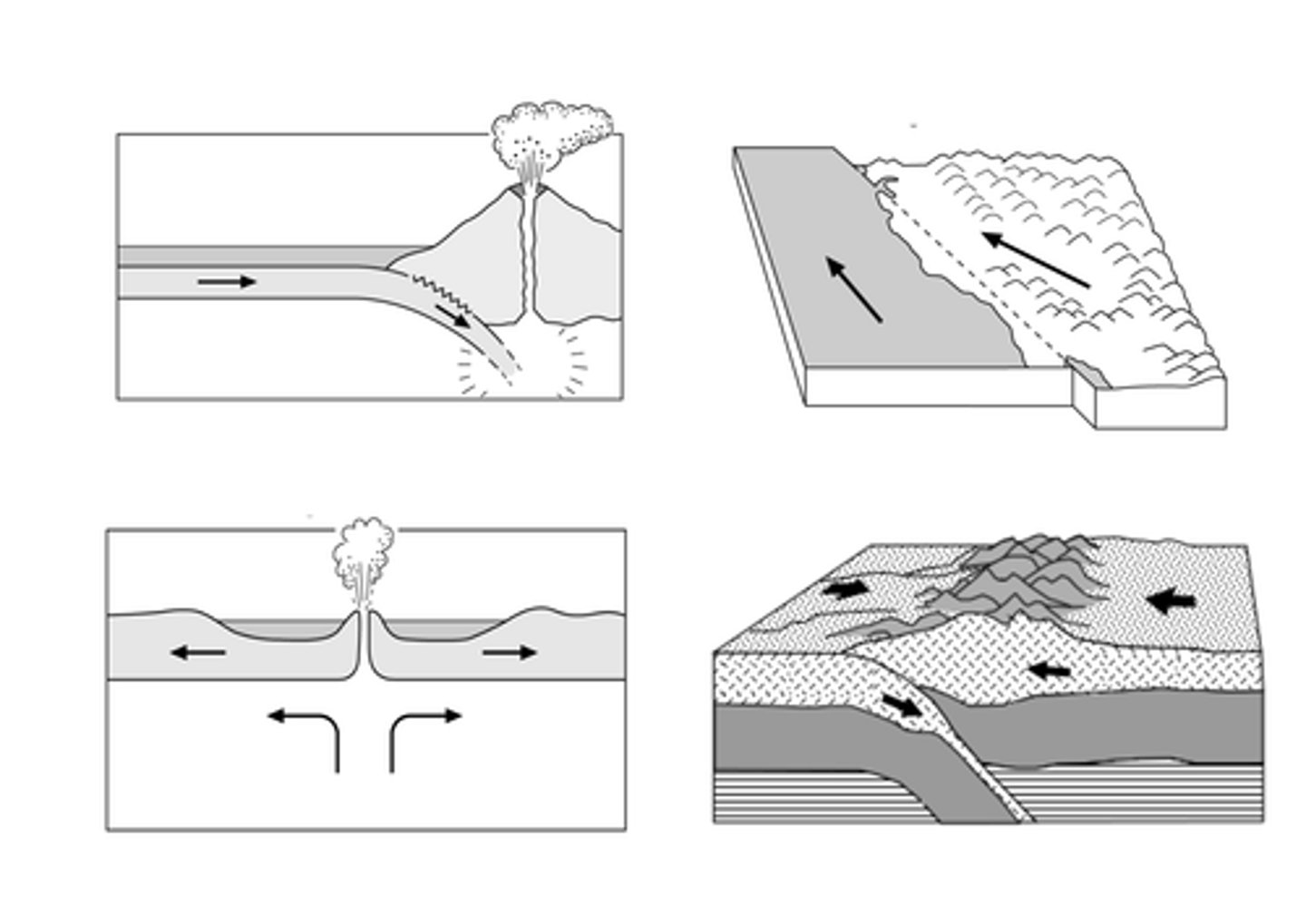
Earthquakes and volcanoes occur in specific places around the earth's crust. Explain why this is, trying to give as much detailed information as you can on the processes that occur. (Hint: You may want to draw a diagram to help you. Make sure you use the vocabulary you have learned)
The earth's surface is made up of lots of tectonic plates that move around. This movement leads to earthquakes and volcanoes.
1. Where two plates are moving towards each other, one is forced down into the mantle where it melts. This excess molten rock can then force it's way to the surface as a volcano. Sometimes if the two plates are the same mass the earth is pushed upwards and mountain ranges are formed like the Himilayas.
2. Where two plates are sliding past each other, they often get stuck due to friction. Pressure builds up until it is finally released as seismic waves during an earthquake.
3. Where two plates pull away from each other it forms a rift zone and lava is released to create a new crust in the gaps.
Explain 3 reasons why people may choose to live in areas at risk of natural hazards.
People may live in dangerous areas for lots of different reasons.
1. Tectonic areas tend to have good soils for farming
2. Geothermal areas and volcanoes might attract tourists, which creates jobs.
3. Places of tectonic activity often are also areas where there are valuable minerals.
4. Some people may have been born there and are used to the risk.
5. Other people may feel that it would take too much time, money and effort to move.
a. Put the events from Russian history below into chronological order:
1. Then Stalin took over and aimed to make USSR a great industrial power.
2. In 1917 there was a revolution and the Tsar was deposed.
3. The Russian Empire began as the state of Muscovy, rules by princes.
4. The Bolsheviks were a group of communists led by Lenin.
5. After WWII, other leaders followed. Then Mikhail Gorbachev took over and wanted people to have more freedom.
6. As Russia became more powerful, the Tsars and nobility grew more wealthy.
3. The Russian Empire began as the state of Muscovy, rules by princes.
6. As Russia became more powerful, the Tsars and nobility grew more wealthy.
2. In 1917 there was a revolution and the Tsar was deposed.
4. The Bolsheviks were a group of communists led by Lenin.
1. Then Stalin took over and aimed to make USSR a great industrial power.
5. After WWII, other leaders followed. Then Mikhail Gorbachev took over and wanted people to have more freedom.
Choose one of Russia's main biomes. Describe what it is like and where it is found.
Tundra is one of Russia's main biomes. The climate is very cold so most of the soil is under permafrost, making it hard for plants and animals to survive. There are no trees but there may be small plants such as flowers and lichen. Animals include arctic foxes and reindeer. The tundra is found in the north of Russia in Siberia
Climate change
a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century onwards and attributed largely to the increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide produced by the use of fossil fuels.
climate change mitigation
The effort to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases or increase the rate at which they are removed from the air, thereby slowing the pace and reducing the severity of climate change. Electric vehicles, green energy like wind, solar, tidal and hydropower
What is the biggest problem facing our world today and what can we do about it?
I believe that the biggest problem facing our world today is global warming. The world is getting hotter because the greenhouse layer is getting thicker due to the gases such as CO2 and methane released through the burning of fossil fuels, industrial farming and deforestation. As global population grows and countries develop the amount of gases we release is unsustainable.
The effects of global warming include ice caps melting, sea-level rise, more extreme storms and droughts, changes in crops and diseases spreading more easily. These effects will be devastating for the natural world and the lives of millions of people, particularly those who live in low-lying and poorer countries. For example; more severe hurricanes in the Caribbean and Central America; flooding in Bangladesh; severe drought in parts of Africa and the middle east; forest fires in Australia, the Amazon and South Western USA.
The best way to reduce global warming is to reduce our ecological footprint (the amount of land needed to support each person), keep the global population steady, and switch to all renewable energy as quickly as possible.
Governments need to make strict international emissions targets and stick to them. The UK Government has committed that the UK will be net-zero by 2050. Governments can also help by subsidising renewable energy and only building renewable power stations. Governments can also encourage investment in green technology like electric vehicles and hydrogen power.
Individuals can also make a difference however with the lifestyle choices they make, including using public transport and bicycles more, buying electric cars, recycling, switching to renewable energy tariffs, becoming vegetarian/vegan and buying more second-hand products.
Impact of European Exploration and colonisation
- Diseases were brought; killed many indigenous people
- Europeans built infrastructure, buildings, roads, railways and canals
- Started slavery in Colonial America
- New crops and animals were brought over from Europe
- Tobacco became a major industry, new crops like corn were discovered in the Americas
- natural resources were exploited like the gold mines in South Africa, copper mines in Zambia and tin in Malaysia
- Many people were converted to Christianity
Unreliable rainfall
Around 60 percent of crops in developing countries would not survive without regular rainfall. In areas where rainfall is unreliable either there is too much rain, and damaging storms ruin the crops, or there is too little rain, leaving the plants starved for water and farmers trying to irrigate the land. Either way, climate change will increase the likelihood of unreliable rainfall. This will negatively affect economies and make it more difficult for farms to produce food.
Impact of malaria on developing countries
Malaria is a leading cause of child deaths in Africa. According to the World Health Organisation, 70% of all malaria deaths are children under five. Before the Covid pandemic, Malaria was the fifth cause of death from infectious diseases worldwide (after respiratory infections, HIV/AIDS, diarrheal diseases, and tuberculosis), but is the second leading cause of death from infectious diseases in Africa and the number one killer of children under the age of five. As malaria's incidence increases, so do death rates. The population at highest risk includes children, pregnant women, and the non-immune. Along with disease and death come economic losses. Social and economic consequences are directly related to the severity of malaria's increased impact. As a result of malaria, children spend days away from school and adults lose workdays. Age distribution of the population is also affected by the disease - older people developed so immunity but children under five and pregnant women are most at risk.
Availability of metal ores
The development of civilisation has relied heavily on the discovery of metals. Prehistoric man used metals to build tools and weapons and as our knowledge has developed, metals have played an essential role in the advancement of agriculture, transport and arts and craft - forging the path to today's modern society. Britain and other European countries exploited the metal resources of countries like South Africa and Malaysia. The exposure of rock minerals and ore deposits to water and oxygen can release toxic chemicals into water systems and food chains, with detrimental effects on ecosystems' health and human health. The environmental costs with extraction and processing were increasingly borne by lesser developed countries.