R functions
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
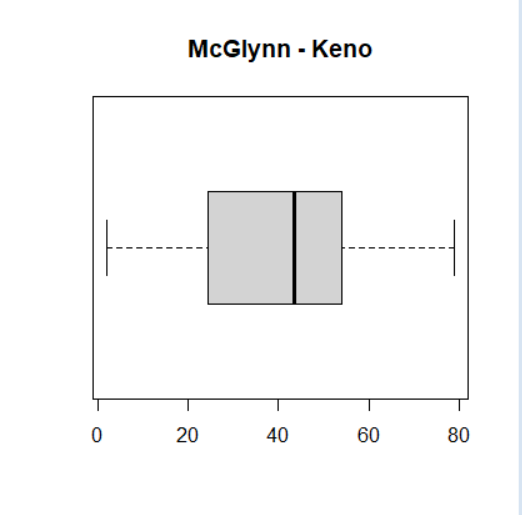
to create a boxplot
boxplot(data)
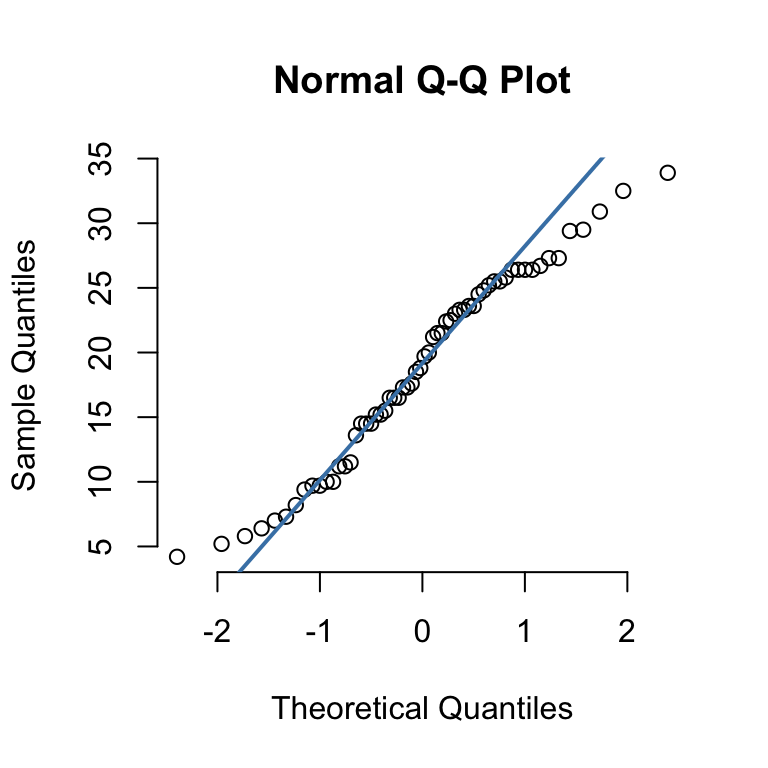
to create a Normal Quantile-Quantile (“QQ”) plot
qqnorm(data)
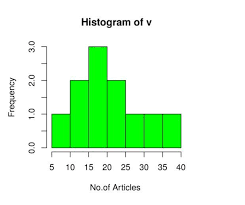
to create a histogram
hist(data)
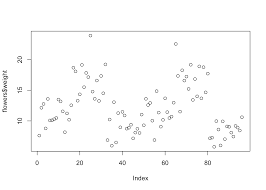
to create a plot graph
plot(data)
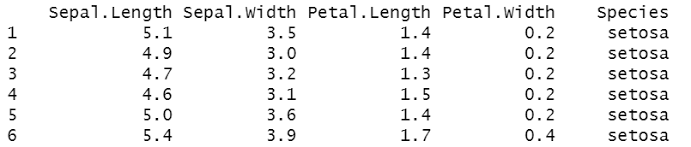
to display the first few rows of R data
head(data)
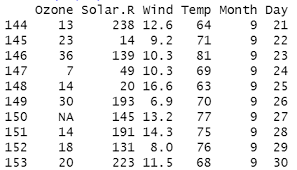
to display the last few rows of R data
tail(data)

to return the dimensions of a data frame
dim(data)
to determine the number of elements in a dataset
length(data)

to generate all possible ways to choose a specific number of items from a larger set, where the order of selection does not matter.
combinations()
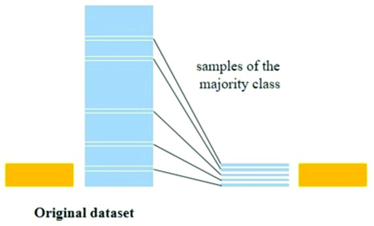
to create a subset of data from a larger dataset
sample()
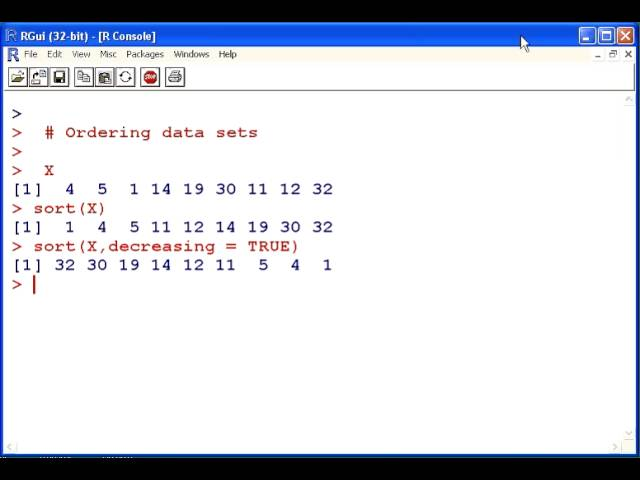
to arrange data into a specific order
sort()
to provide a quick overview of the dataset
summary()
to install packages
install.packages(“gtools”)
to see the package library for R
library(gtools)
to see installed packages in R
installed.packages()
to determine the class or type of an R object
class(df)
to determine the data type or class of a specific column within a data frame
class(df$colname)
similar to a pivot table in excel, used to apply a function (FUN=) to subsets of data within a data frame
aggregate()
part of the “apply()” family of functions and is used to apply a specified function (FUN=) to each element of a list or vector, lists columns vertically
lapply()
part of the “apply()” family of functions and is used to apply a specified function (FUN=) to each element of a list or vector, lists columns horizontally
sapply()
what does “df” stand for
“data frame”
converts various R objects into a data frame structure
as.data.frame()
calculates the sum of values in each row of a data frame.
rowsums(df)
calculates the sum of values in each column of a data frame
colsums(df)
used to calculate the mean of each row in a data frame
rowMean(df)
used to calculate the mean of each column in a data frame
colMean(df)
used to access and modify the column names of data frames
colnames()
sorts data from low to high
order()
3 ways used to create calculated columns
df$new.col.name<-column1+column2
df$new.col.name<-sum(col1+col2)/2
df$new.col.name<-mean(col1+col2)
used to select subsets of data from data frames
subset()
element used to make variables
<-
element used to combine elements
c()
element used to make comments
#