Chapter 5 - Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Main characteristics of carbohydrates
Functional groups: hydroxyl (-OH) and carbonyl (C=O)
Monosaccharides (simple sugars), have a simple form.
1 carbohydrate monomer: usually has several hydroxyls and 1 carbonyl. Number of carbon varies.
Several monomers (monosaccharides) can be joined through glycosidic linkages and form polymers (polysaccharides)
Classification of carbohydrate monomers (monosaccharides)
Based on number of carbons
Trioses (3C)
Pentoses (5C)
Hexoses (6C)
Based on carbonyl group:
at the end: aldose
in the middle: ketose
Glycosidic linkages
Build carbohydrate polymers (polysaccharides); many monomers (monosaccharides) are bonded covalently.
Uses dehydration synthesis.
Starch
A carbohydrate that consists of a polysaccharide of a-glucose monomers. Helix structured, can be digested by humans (energy storage for both humans and plants).
Cellulose
A carbohydrate that consists of a polysaccharide of B-glucose monomers in straight chains (indigestible by humans but used by plants in cell walls.)
LIPIDS
Hydrophobic, non-polar molecules. Store energy, insulate and form membranes.
Types: fats, phospholipids, steroids.
Tryglycerid
Type of fat (lipid). 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acid chains
(3 water molecules are used).
Fatty acids (fats)
Saturated: no double bonds
Cis-unsaturated: double bonds + kink/doblez (liquid)
Trans-unsaturared: double bonds but no kink/no tiene doblez (solid)
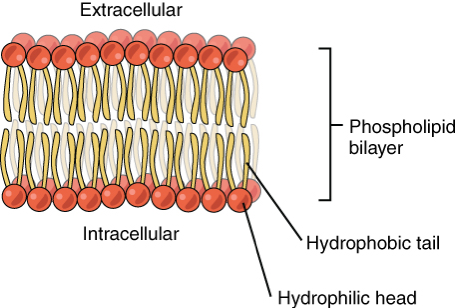
Phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid (lipid): Hydrophilic head (phosphate) and two hydrophobic fatty acid (types of lipid) tails.
Hydrophilic head toward the outside
Hydrophobic tails face toward the inside
only small, non-polar molecules can passively diffuse.
Steroids
Another type of lipid. Four-fused-ring structure.
Ex. Cholesterol (homeostasis)
Ex. Hormones = estrogen or testosterone (growth and development, reproduction).