Milady Esthetics Chapter 4 Disorders & Diseases of the Skin
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
dermatology
branch of medical science that studies and treats the skin and it's disorders
Lesions
structural changes in the tissues caused by damage or injury; any mark, wound or abnormality; 3 types (primary, secondary, tertiary)
primary lesion
lesions in the initial stages of development or change; characterized by flat, non-palpable changes in skin color or by elevations formed by fluid in a cavity, such as vesicles or pustules
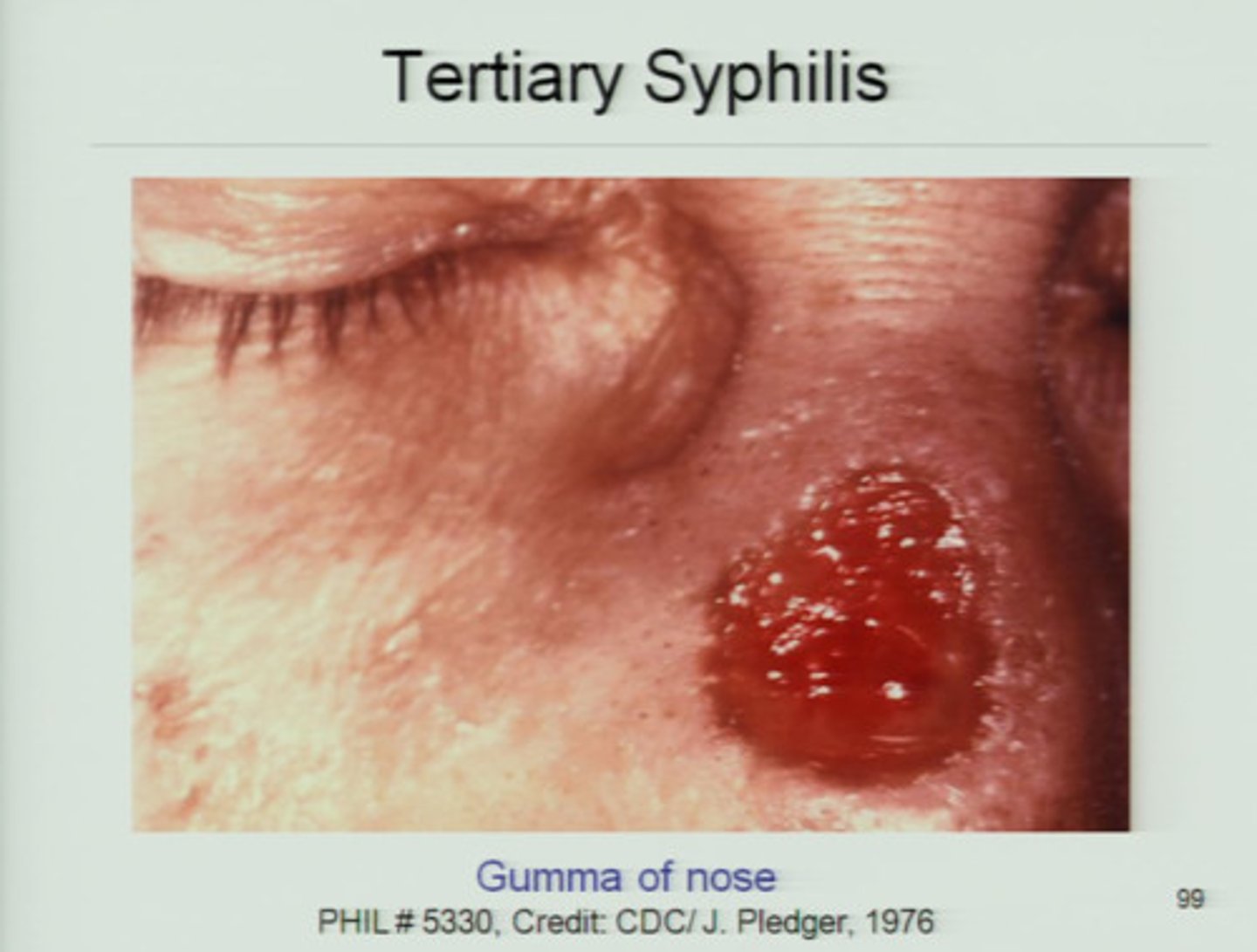
tertiary lesion
also known as vascular lesions; vascular lesions involve the blood or circulatory system
secondary lesion
characterized by piles of material on the skin surface, such as crust or scab. or by depressions in the skin surface, such as an ulcer; these may require a medical referral
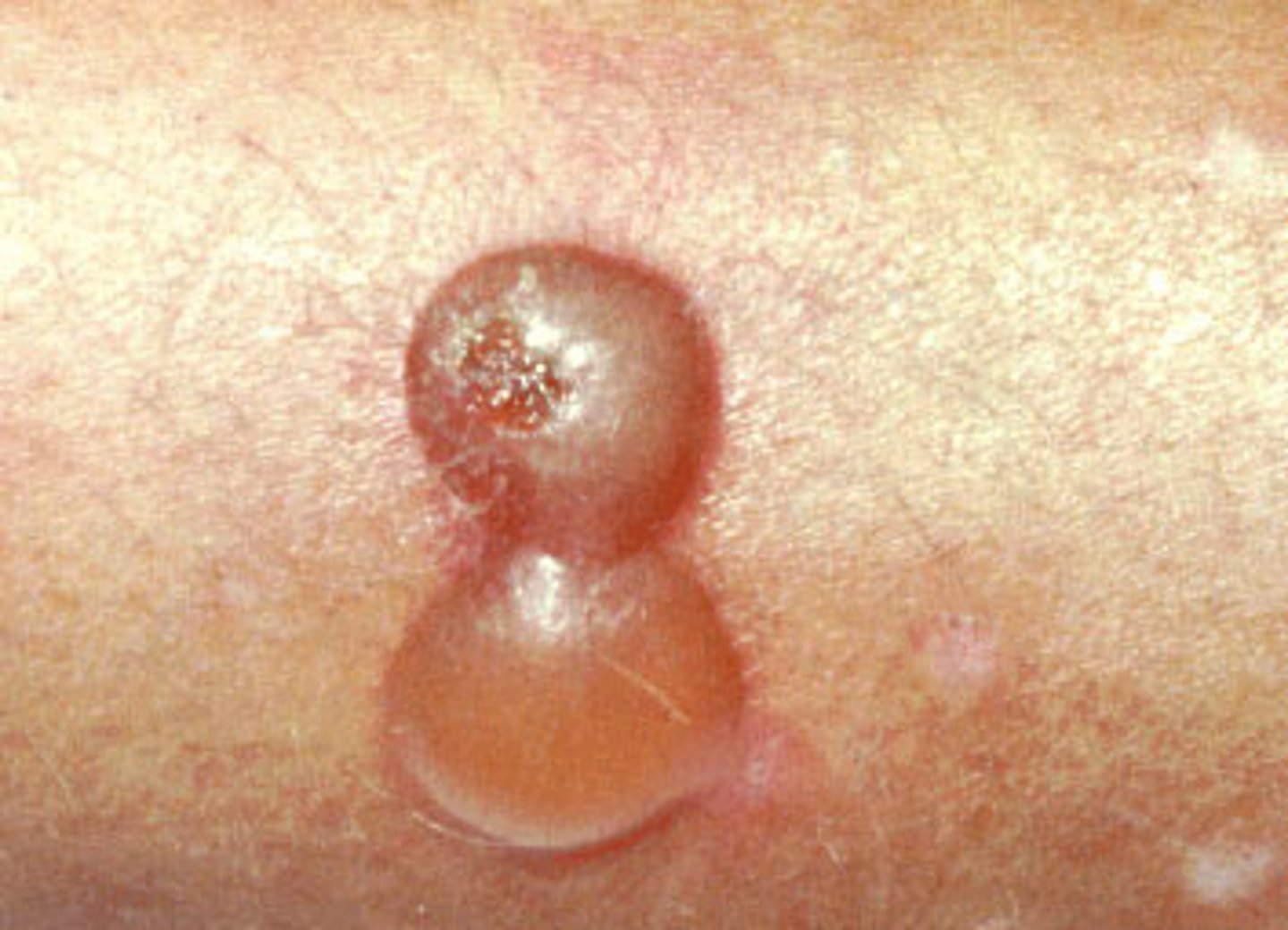
bulla
primary lesion; large blisters containing watery fluid
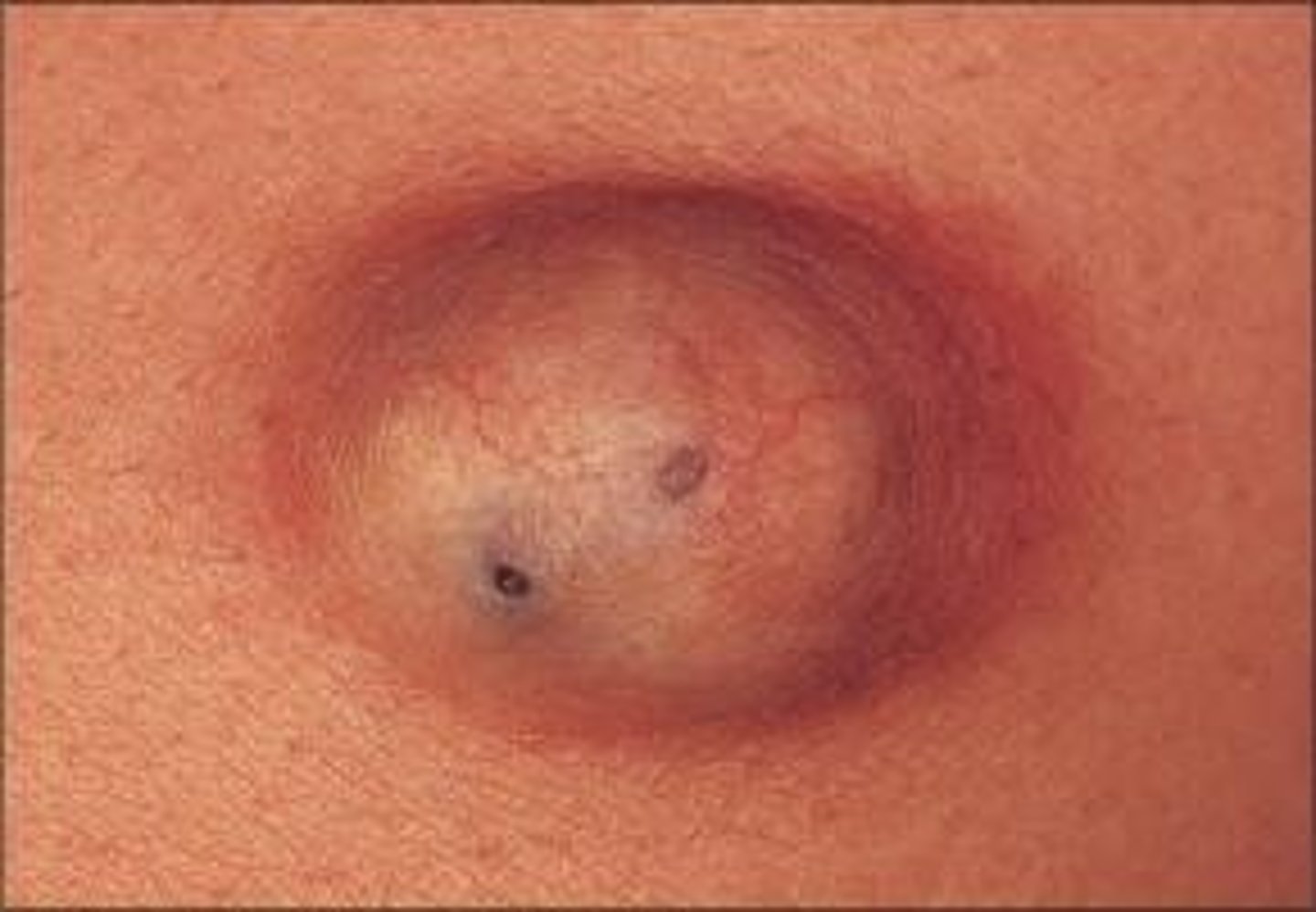
cyst/tubercle
primary lesion; closed, abnormally developed sac that contains pus, semi fluid or morbid matter above or below the skin
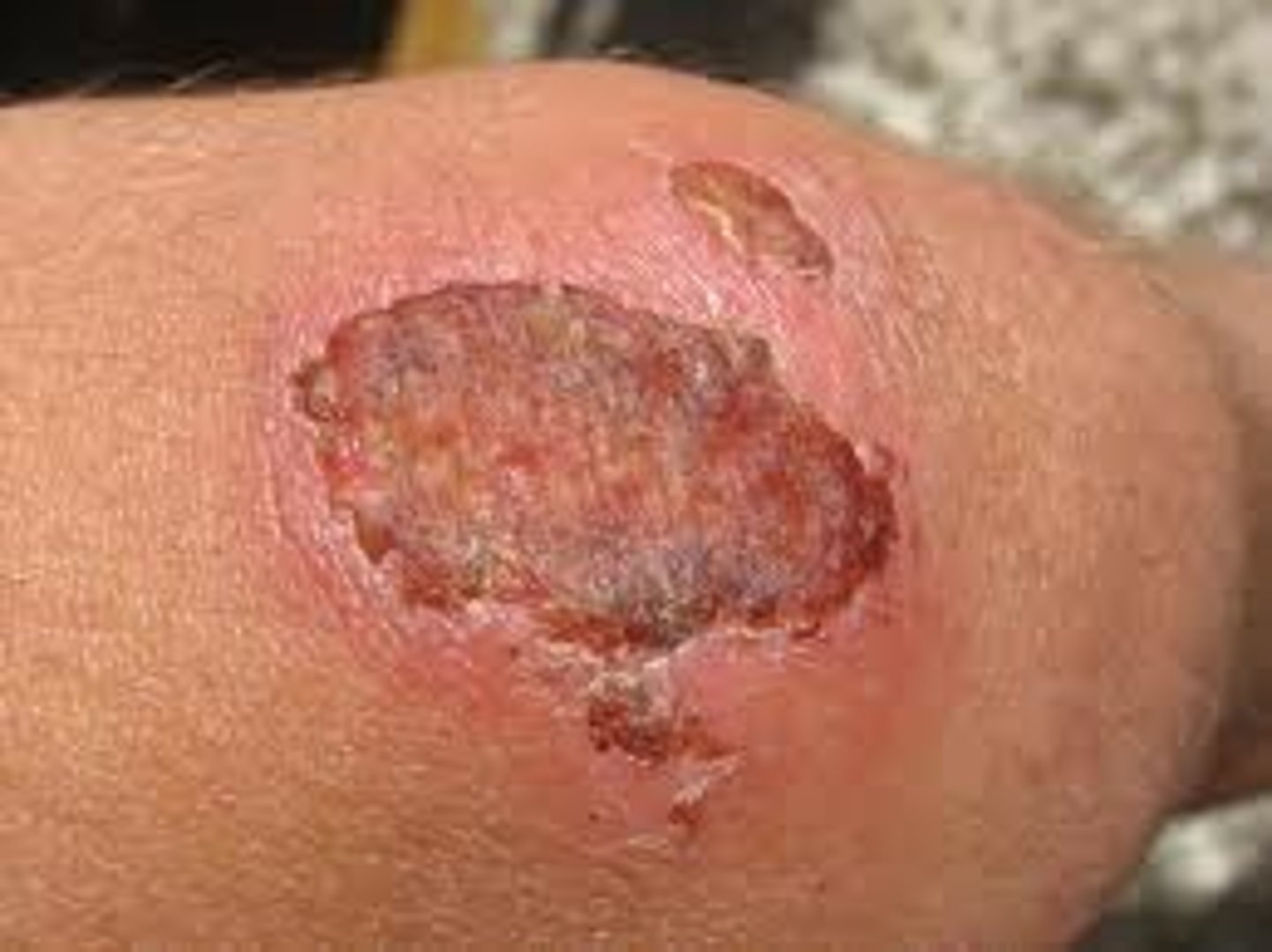
crust
secondary lesion; dead cells that form over a wound or blemish while healing
excoriation
secondary lesion; skin sore or abrasion produced by scratching or scraping
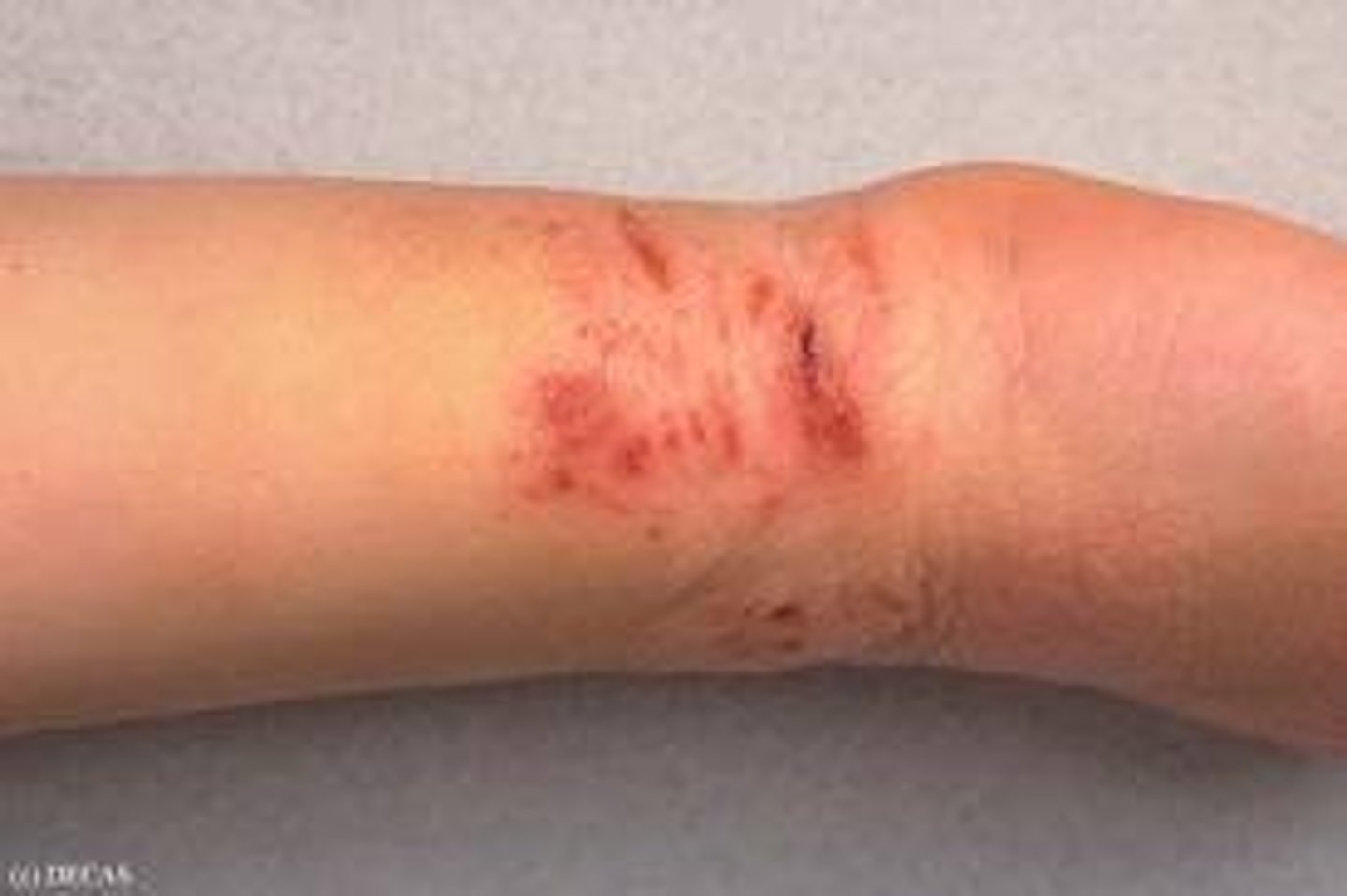
fissure
secondary lesion; crack in the skin that penetrates the dermis
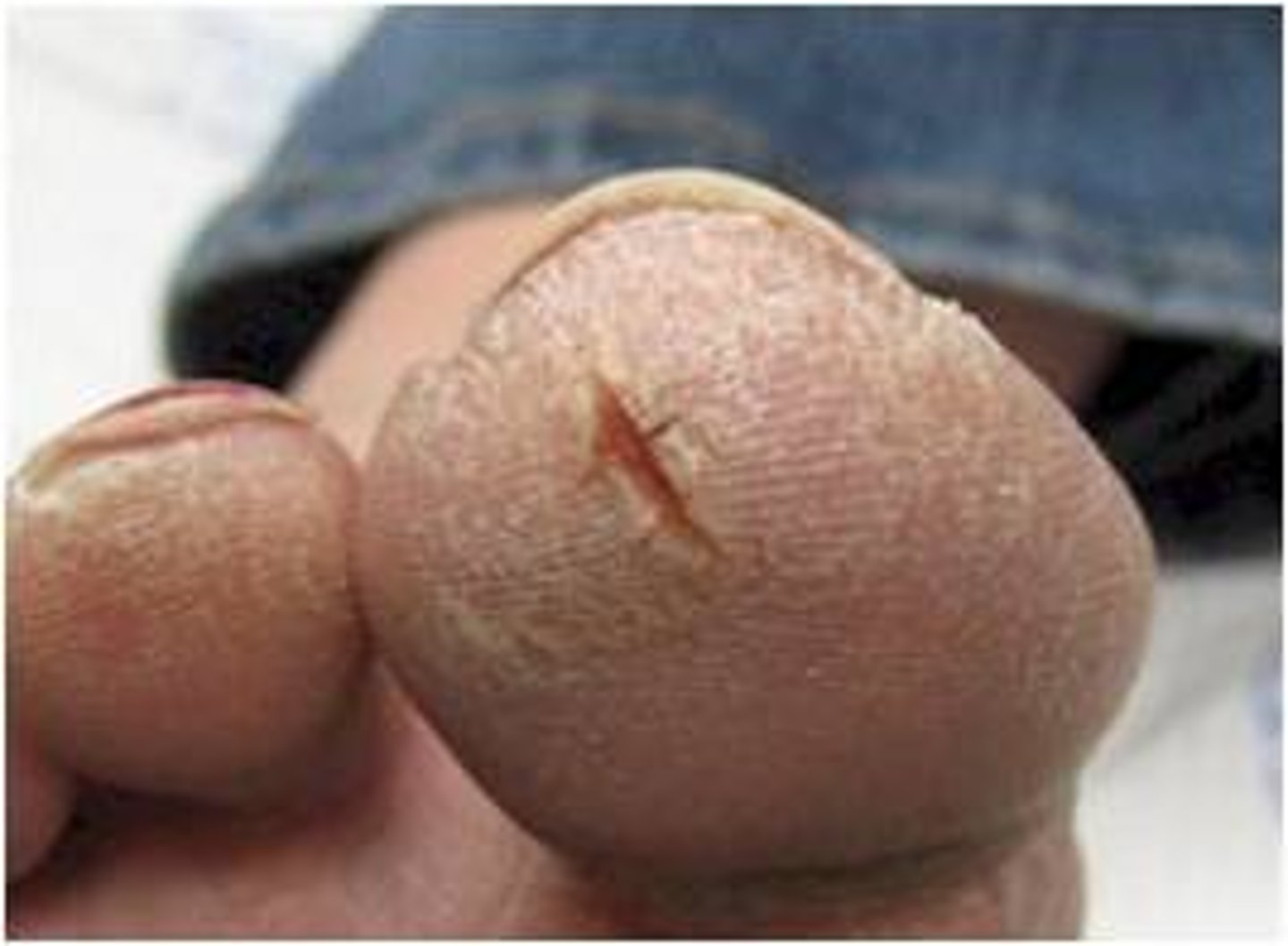
keloid
secondary lesion; thick scar resulting from excessive growth of fibrous tissue
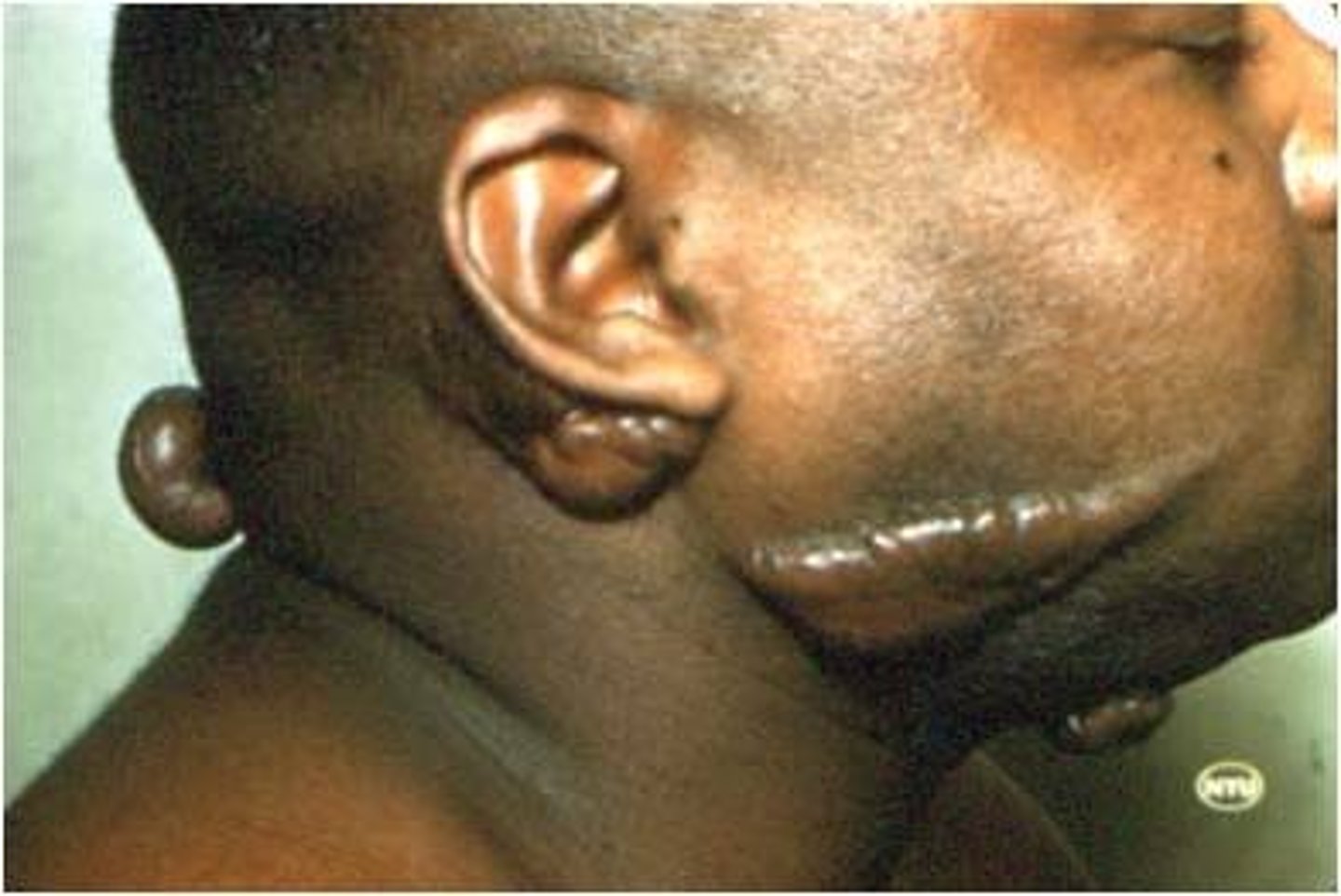
macule
primary lesion; flat spot or discoloration on the skin
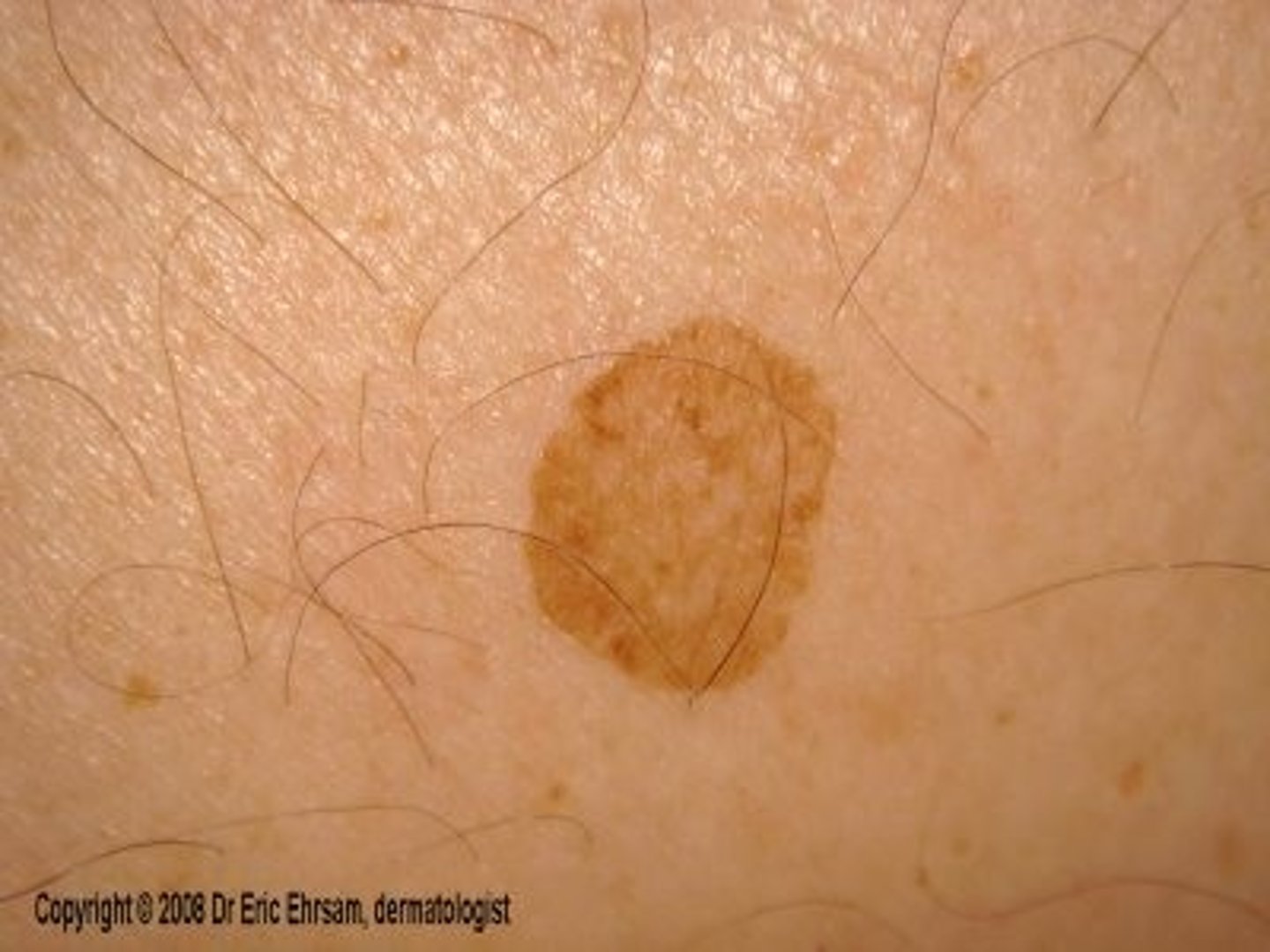
nodule
primary lesion; a solid bump larger than .4 inches that can easily be felt
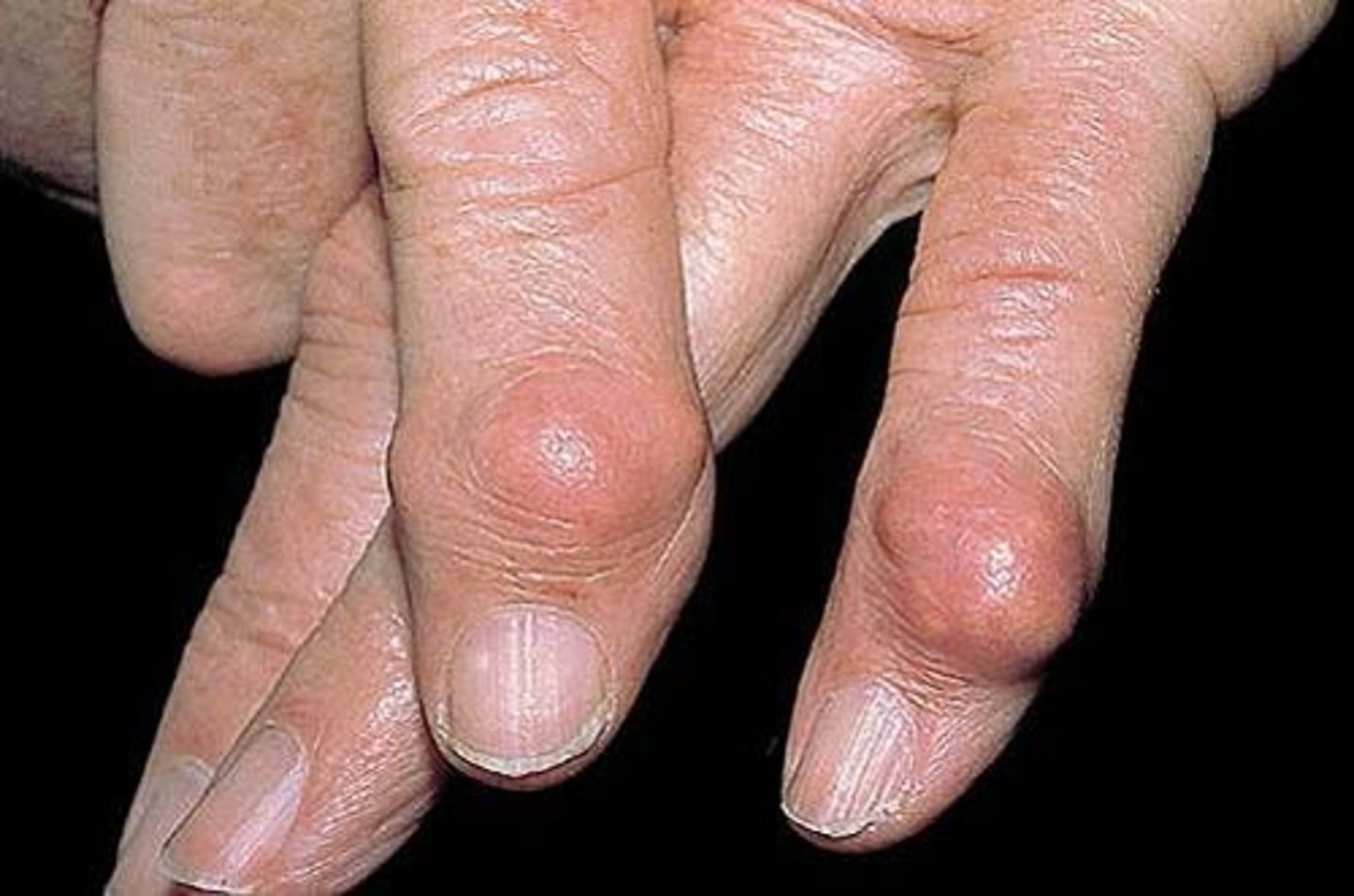
papule
primary lesion; a small elevation on the skin that contains no fluid but may contain pus
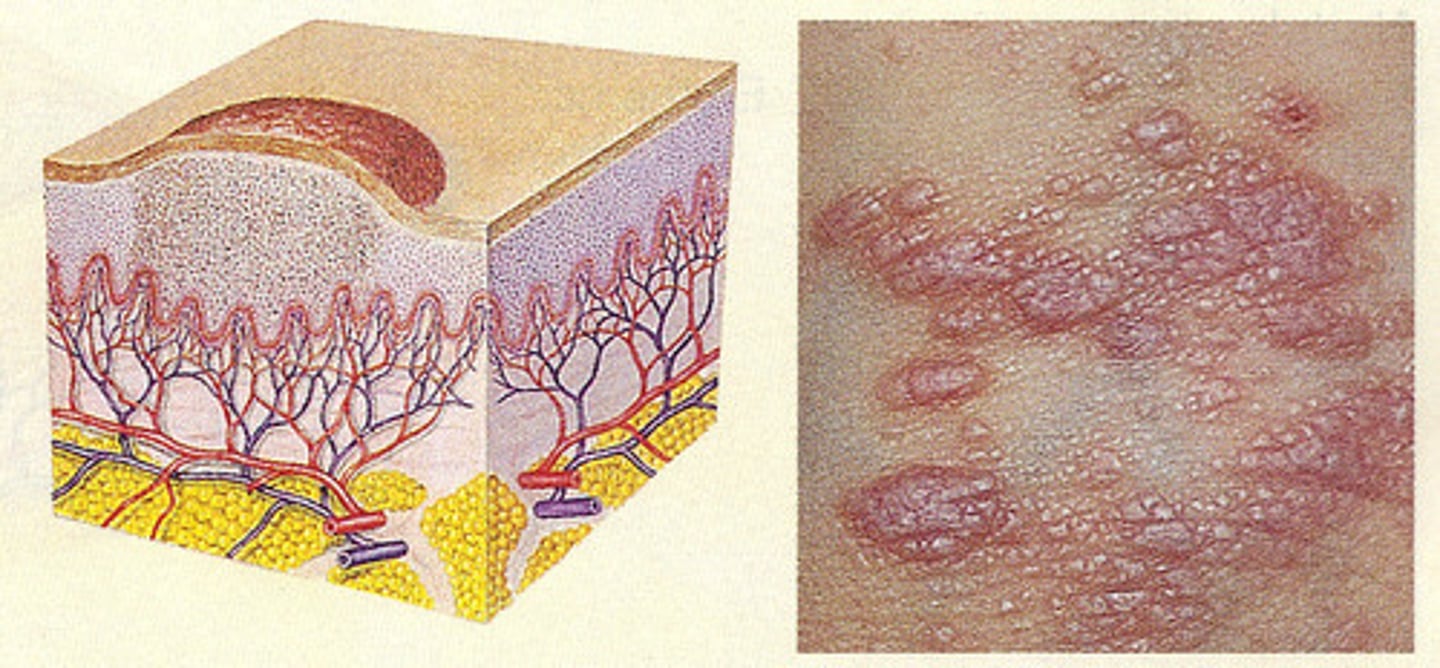
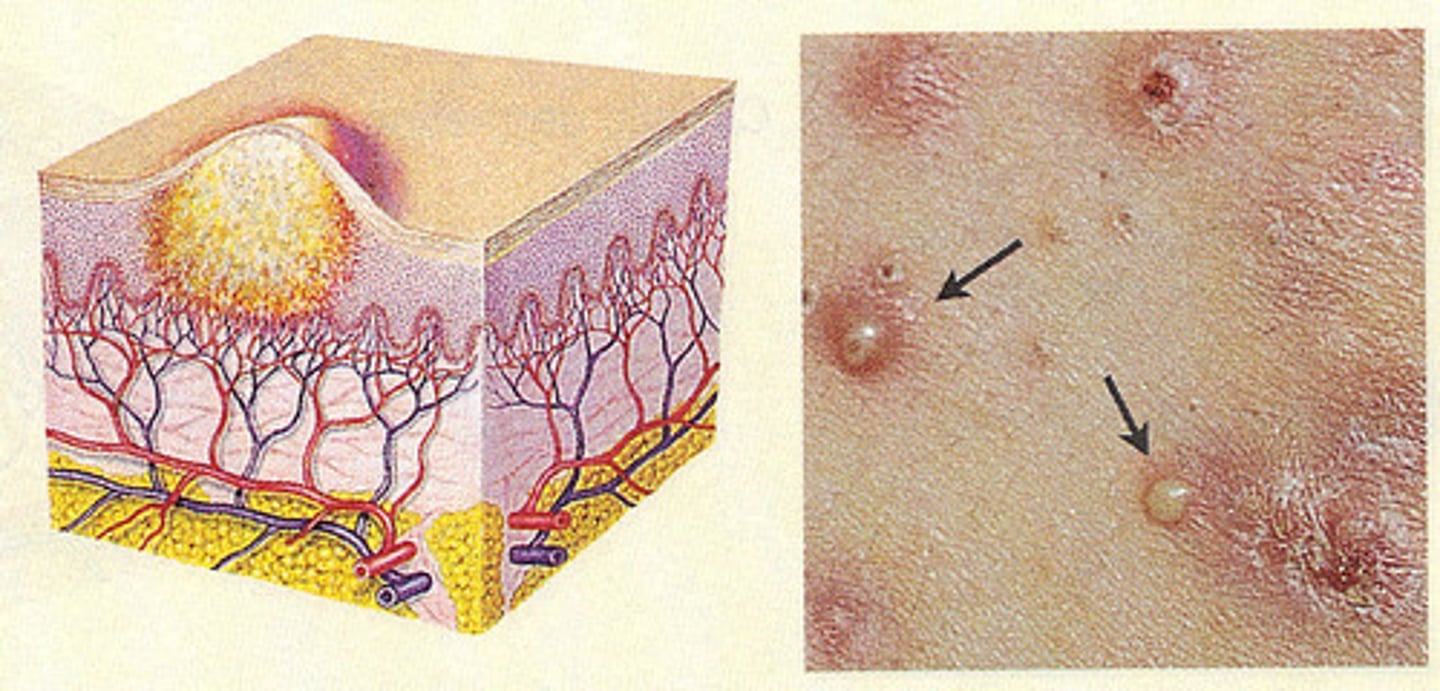
pustule
primary lesion; raised, inflamed papule with a white or yellow center containing pus in the top lesion
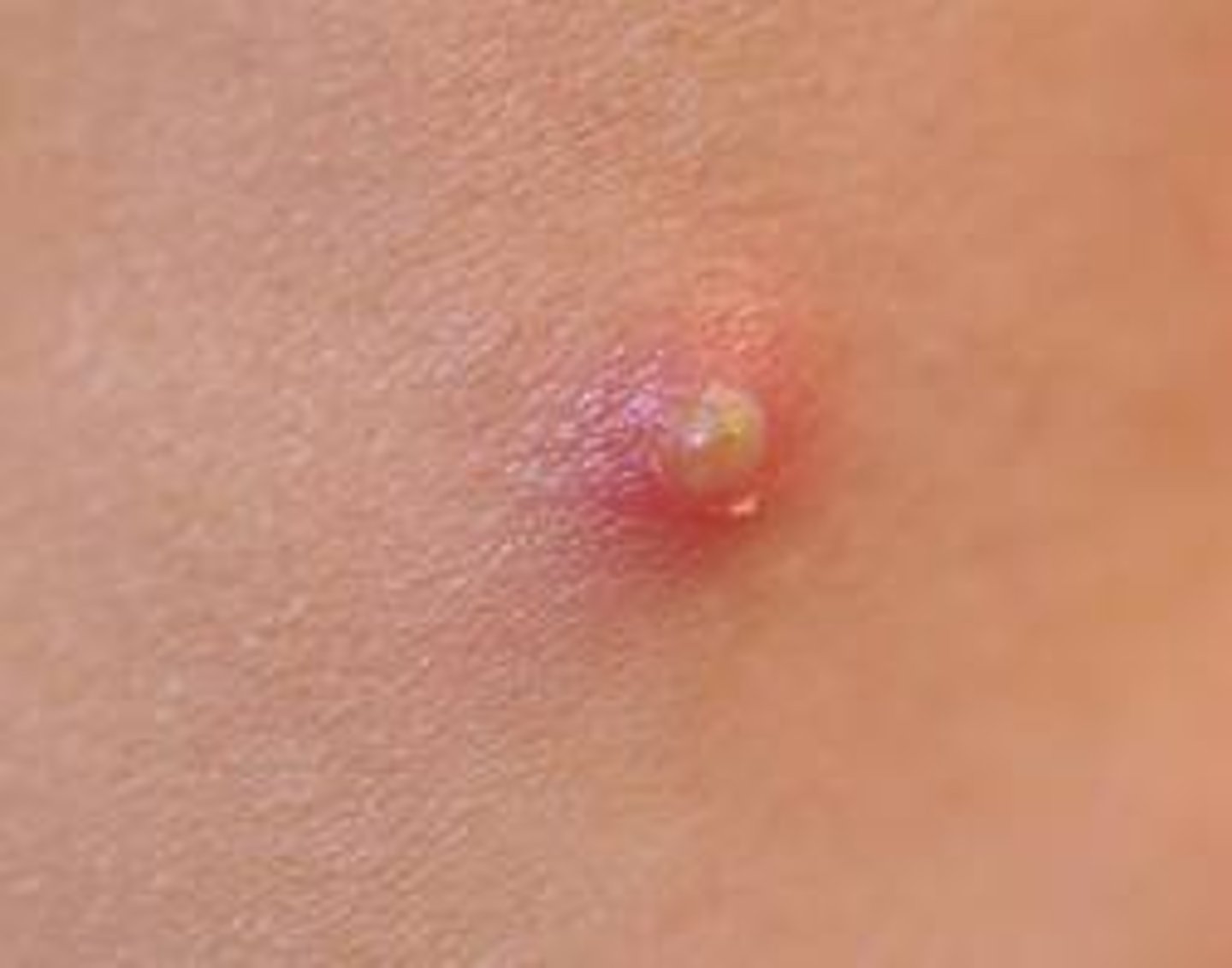
scale
secondary lesion; thin, dry or oily plate of epidermal flakes
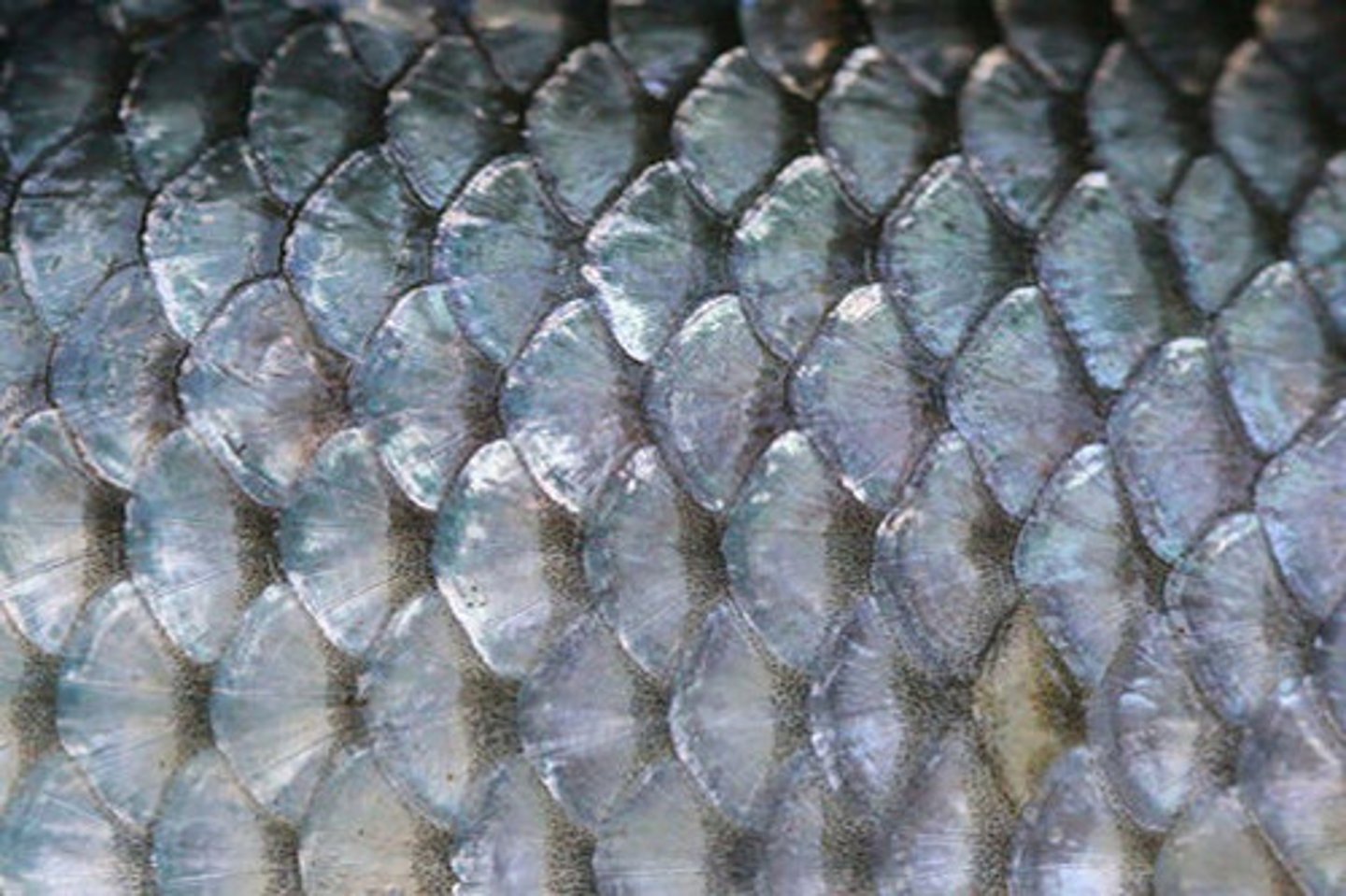

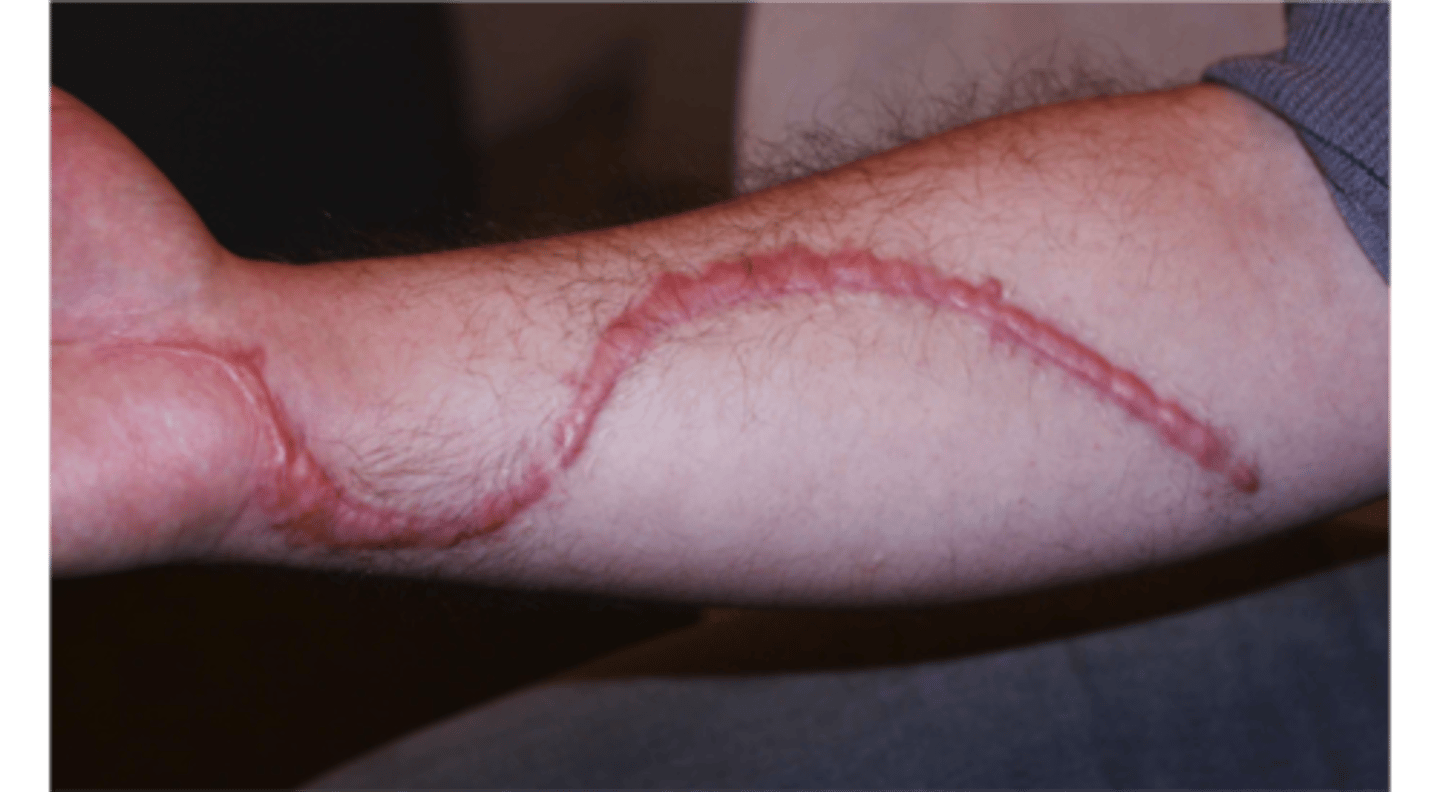
scar/cicatrix
secondary lesion; slightly raised or depressed area of skin that forms as a result of the healing process related to an injury or lesion
tumor
primary lesion; abnormal mass varying in size, shape and color
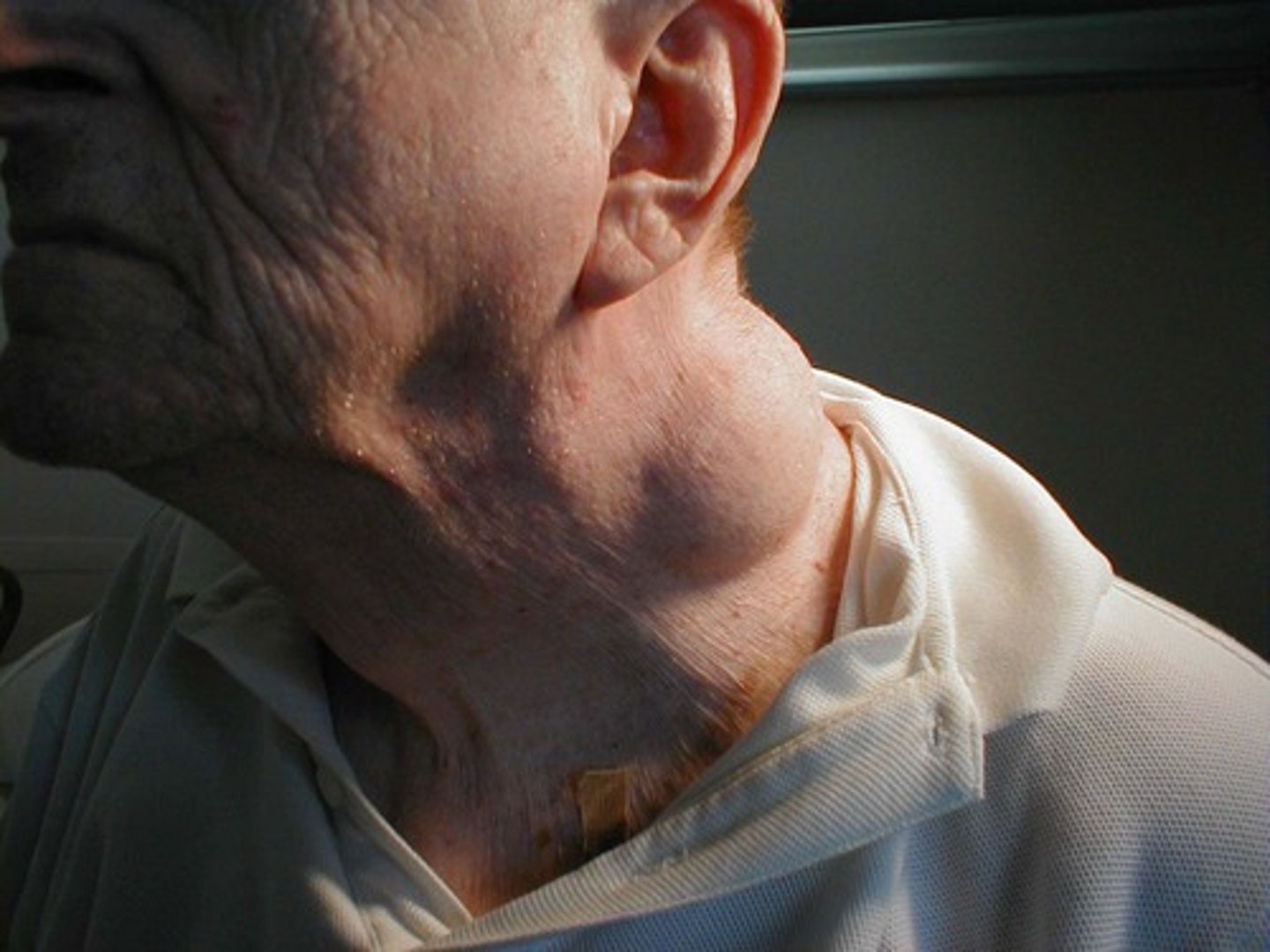
ulcer
secondary lesion; open lesion on skin, accompanied by loss of skin depth and possible weeping of fluids or pus
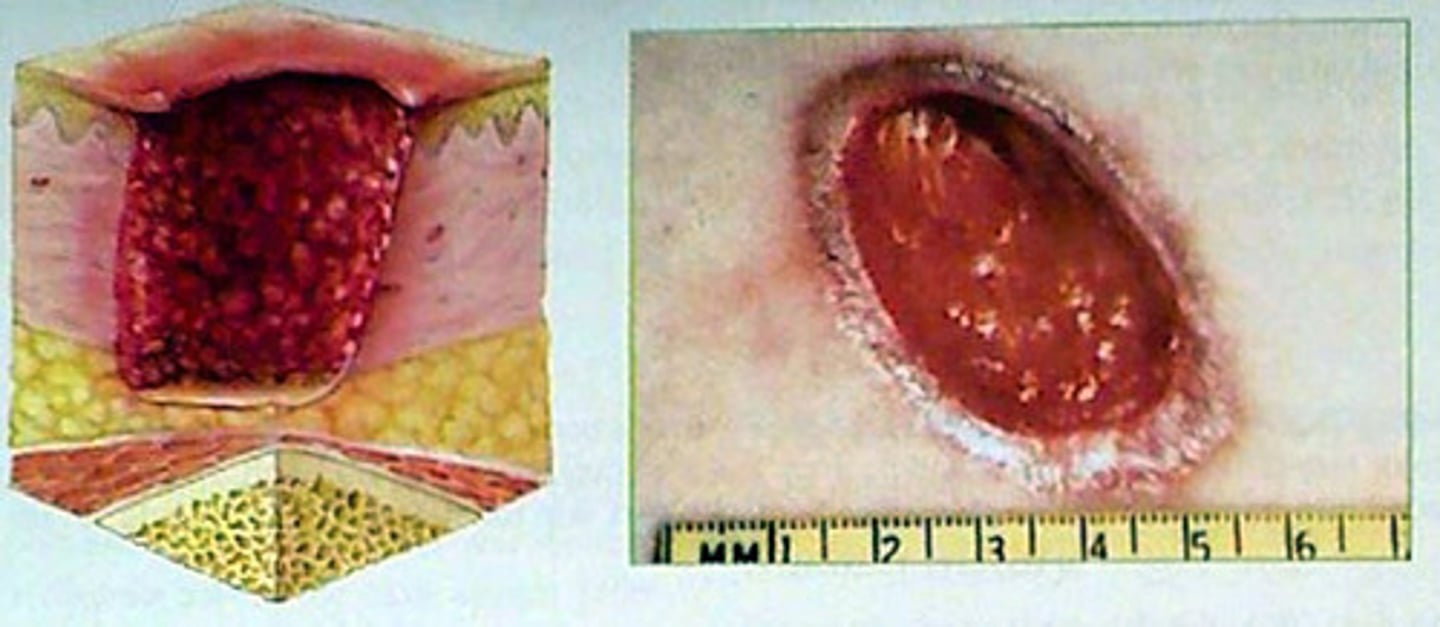
vesicle
primary lesion; small blister or sac containing clear fluid, lying within or just beneath the epidermis
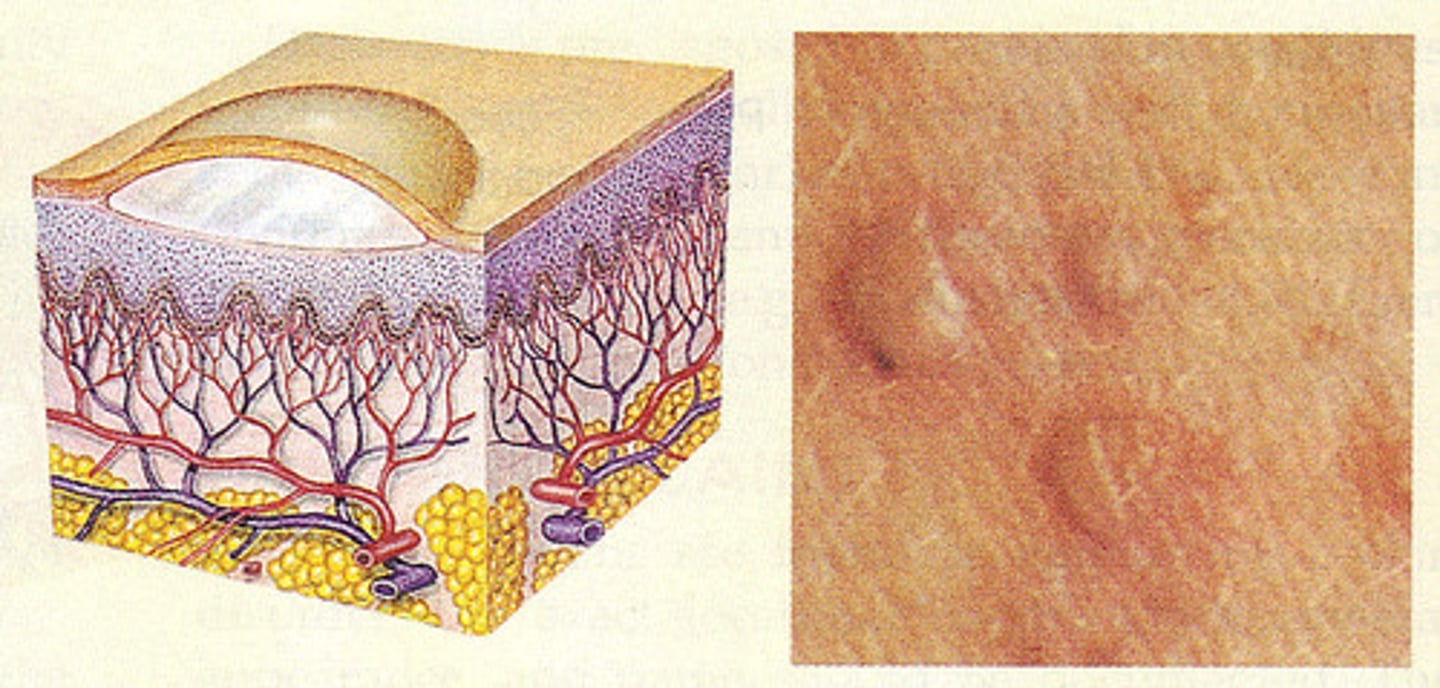
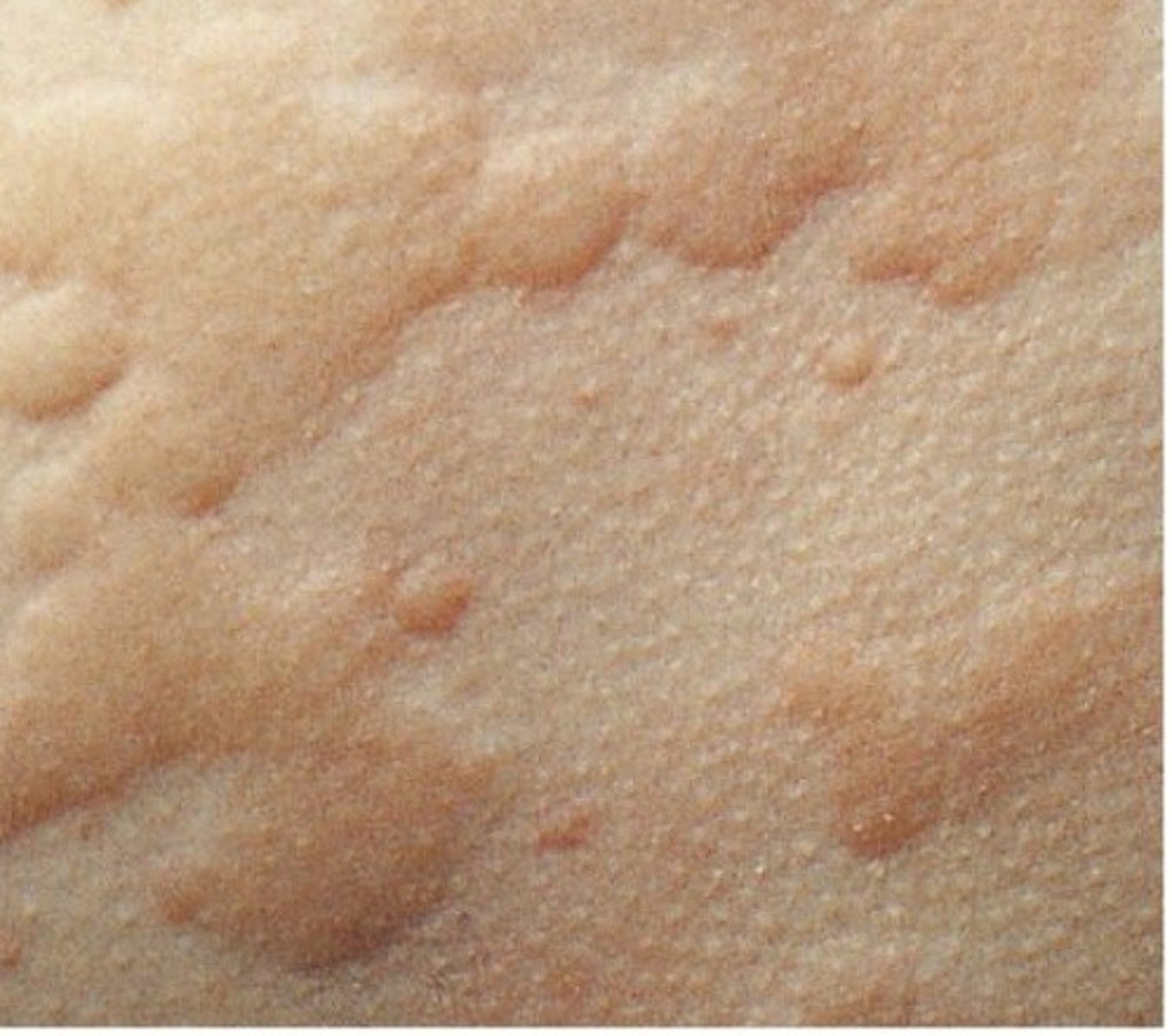
wheal
primary lesion; itchy, swollen lesion that can be caused by a blow, scratch, bite of an insect or urticaria
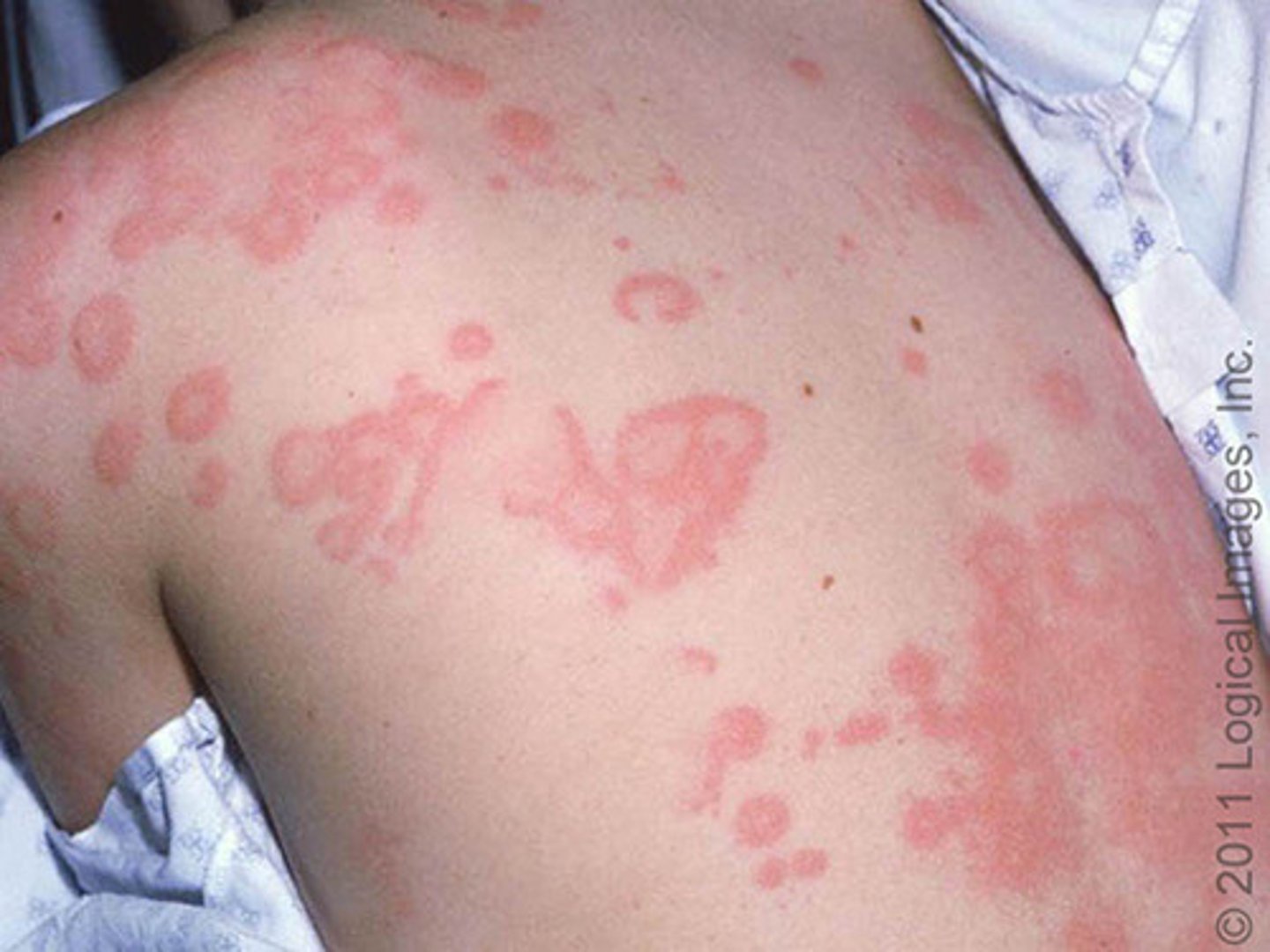
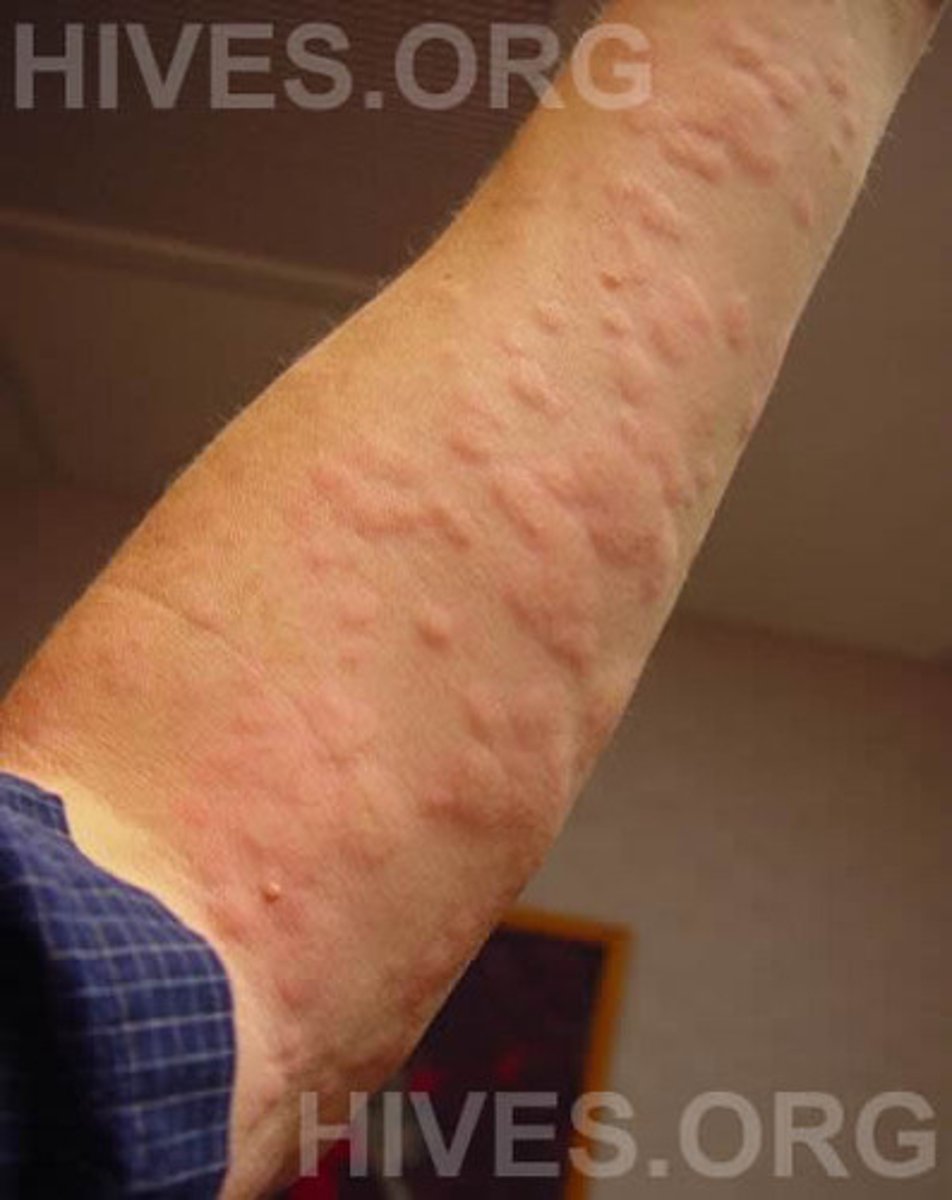
urticaria
hives; caused by an allergic reaction from the body's histamine production
What causes skin cancer
damage to DNA
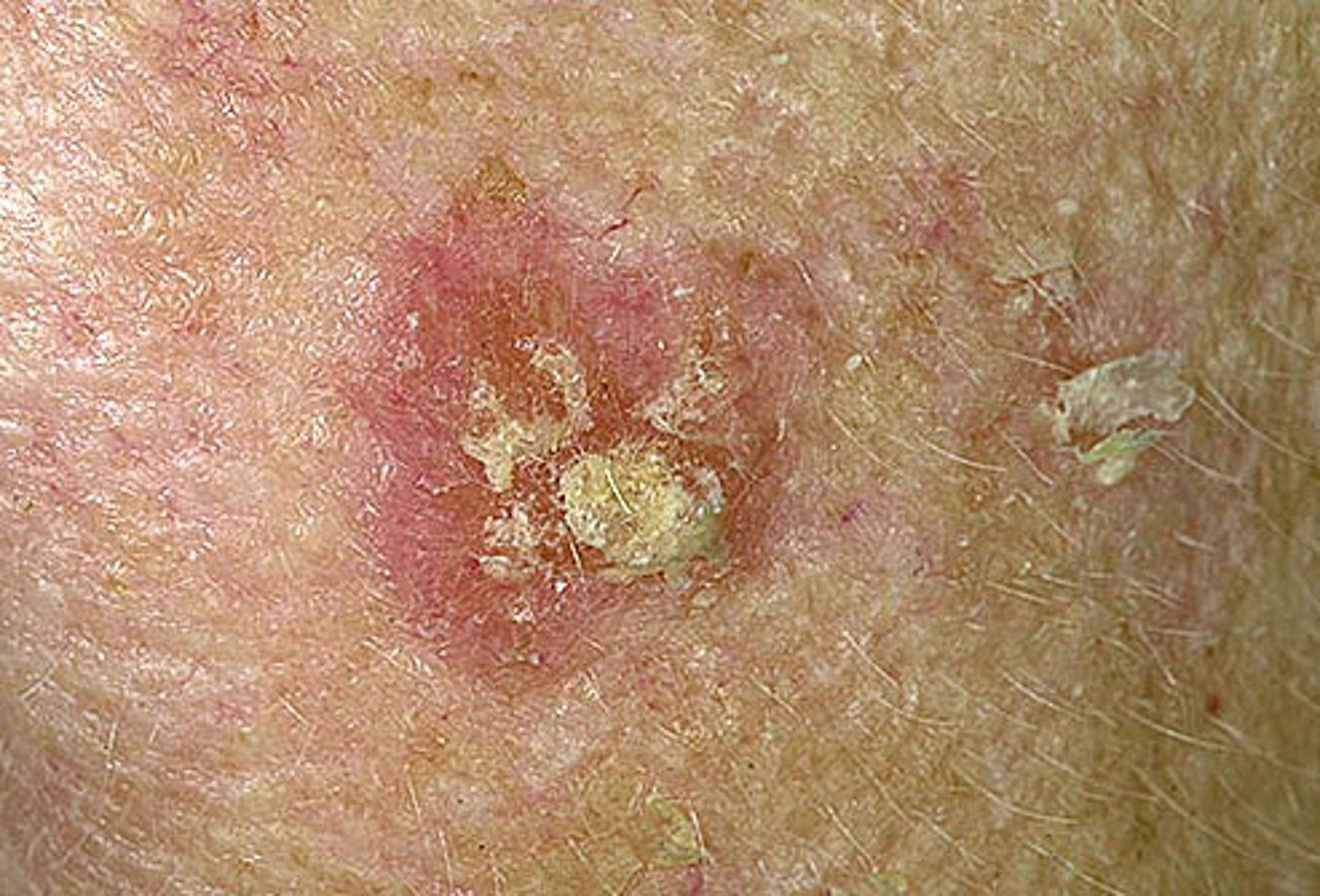
actinic keratosis
pink or flesh colored, feels sharp or rough
basal cell carcinoma
Most common and least severe type of skin cancer
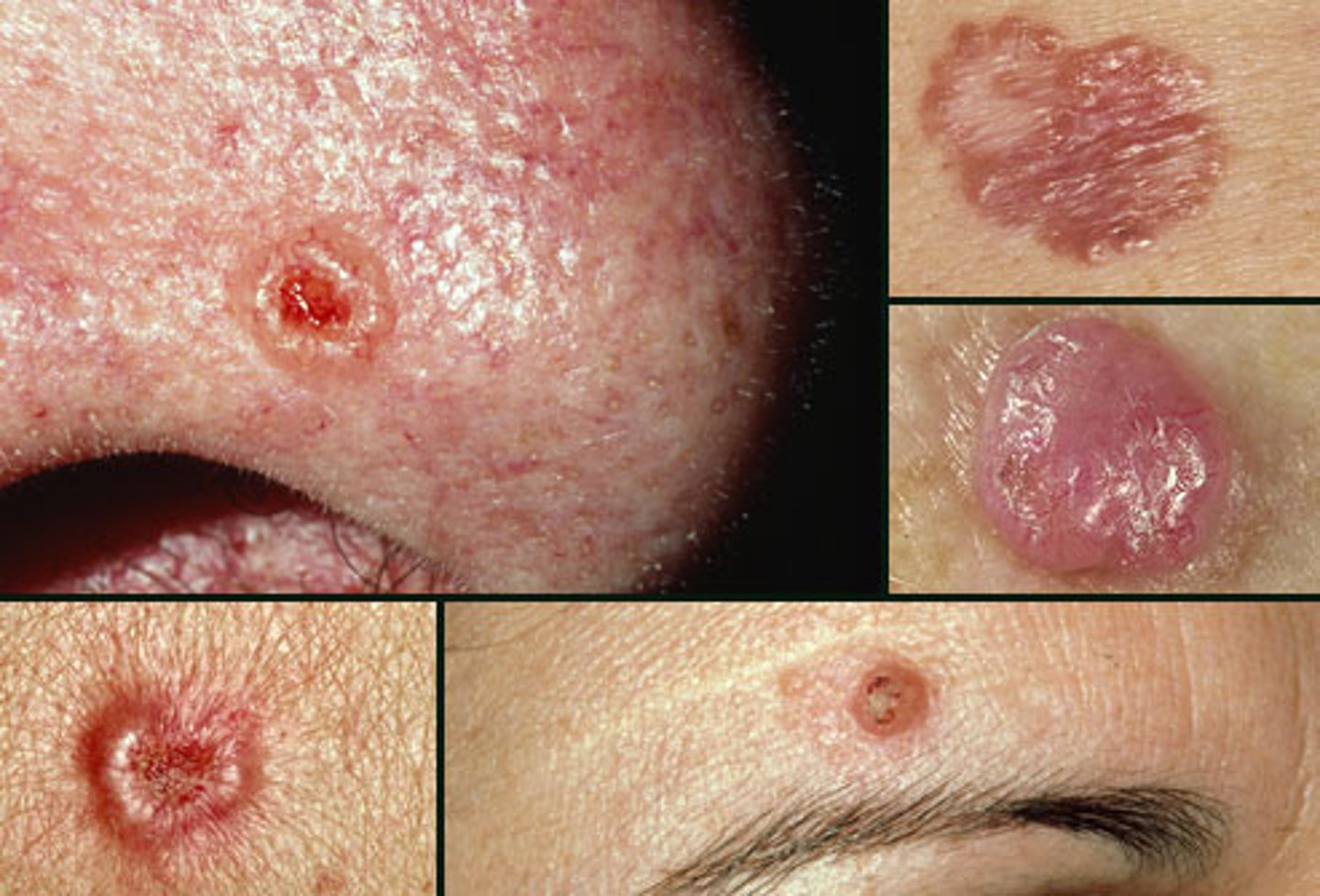
squamous cell carcinoma
characterized by scaly, red or pink pa pules or nodules. can grow and spread to other areas of the body
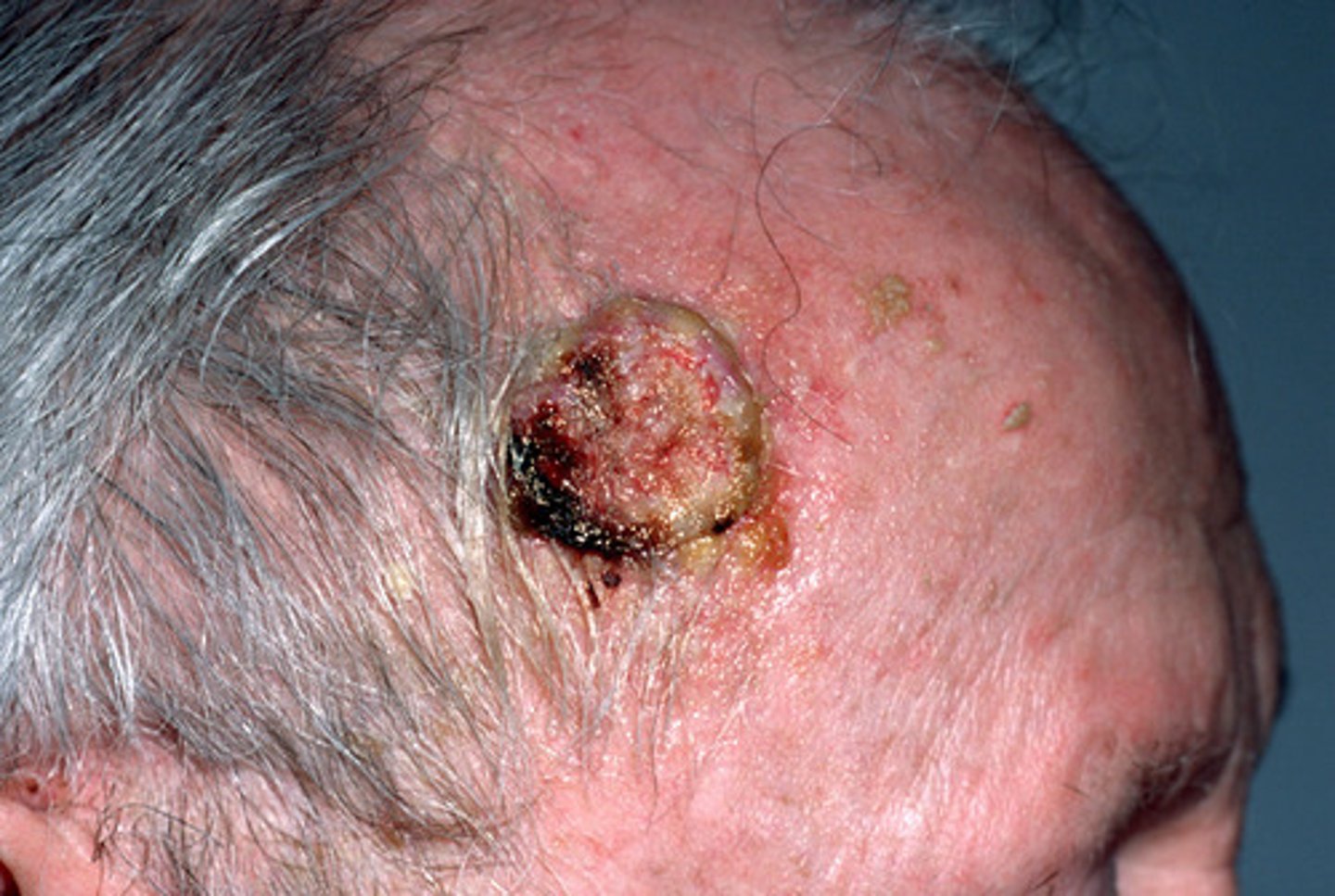
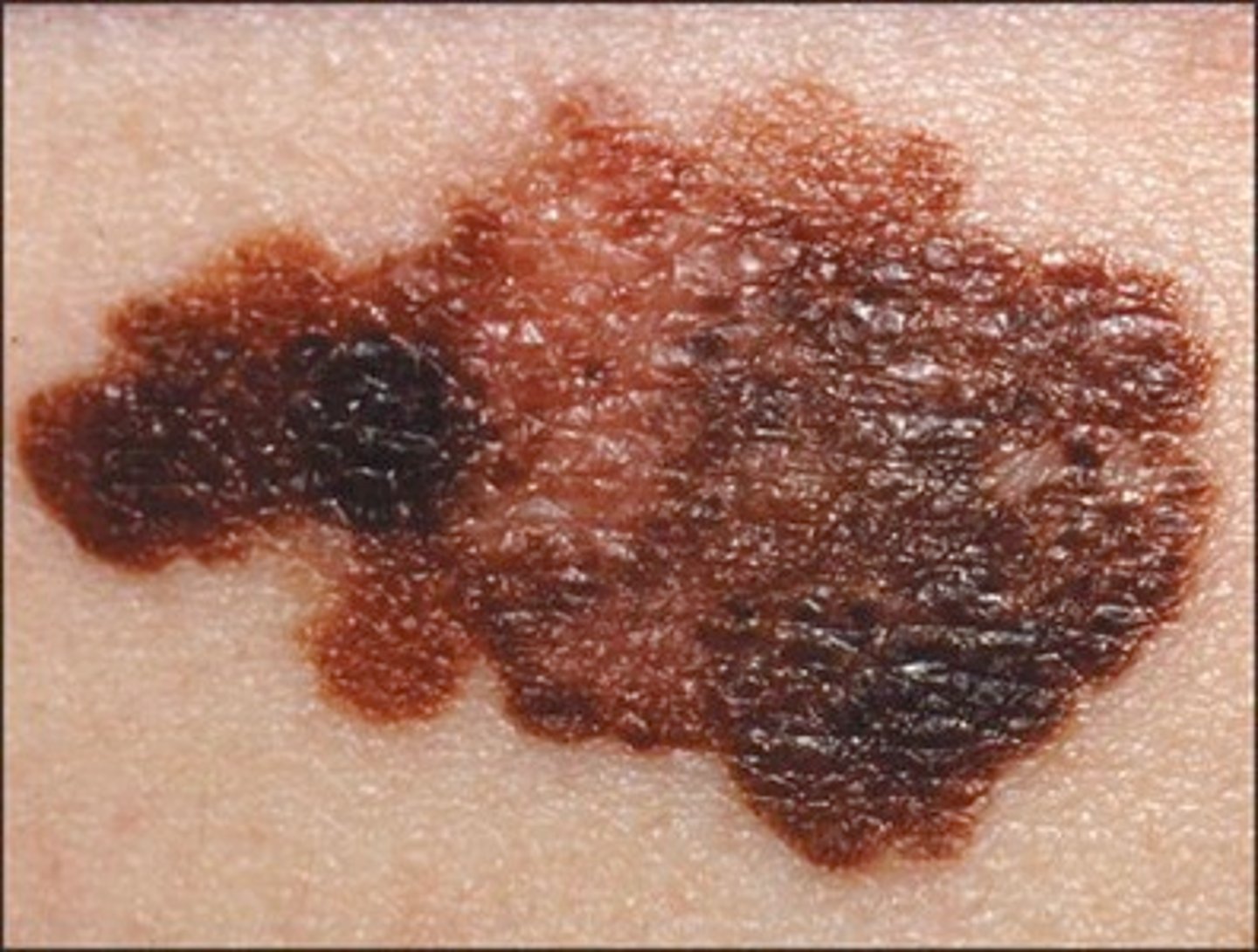
malignant melanoma
deadly, can metastasize throughout the body
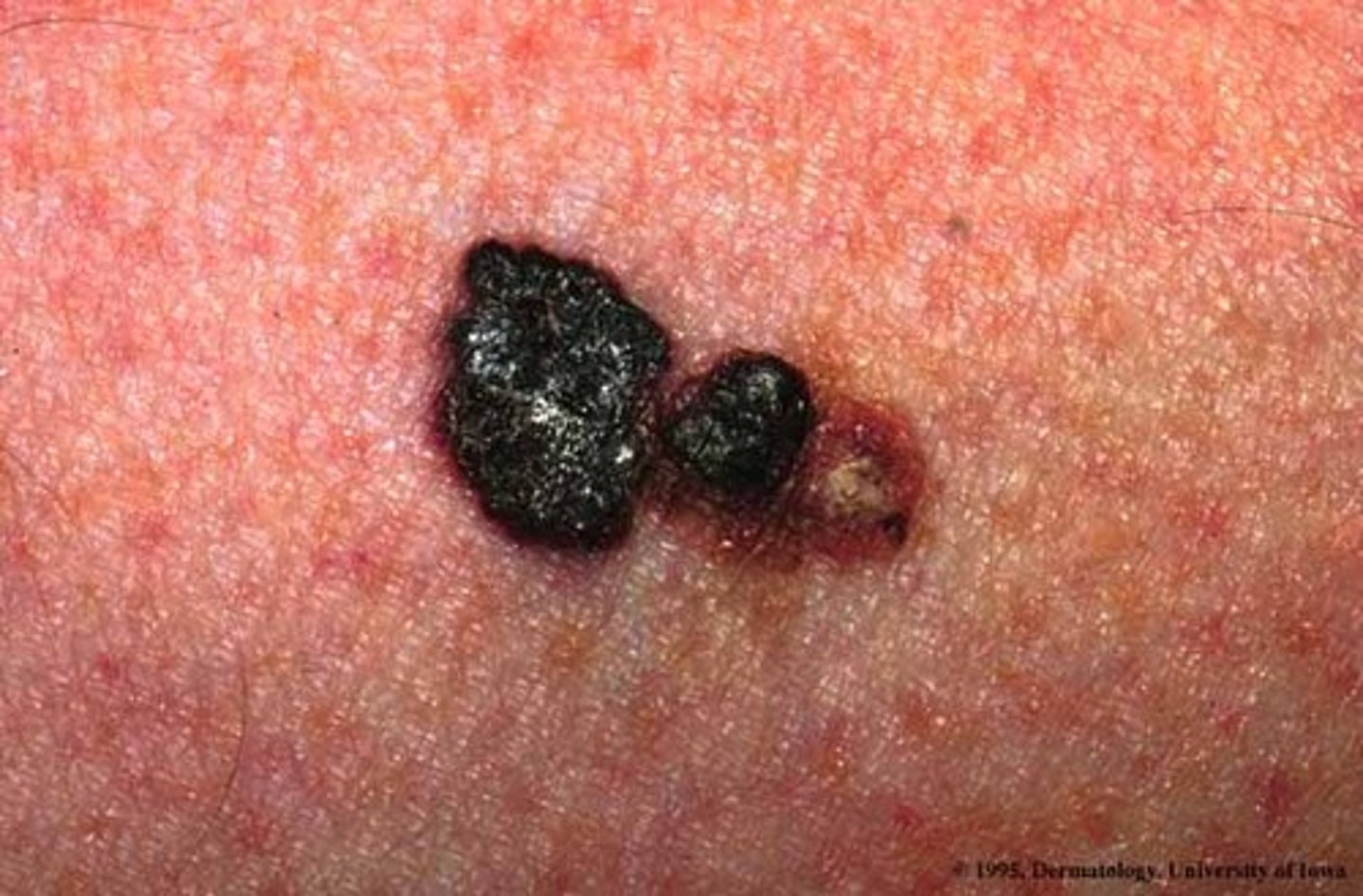
Changes to look for when checking for moles
ABCDE- Asymmetry, irregular Border, Color, Diameter, Evolving appearance

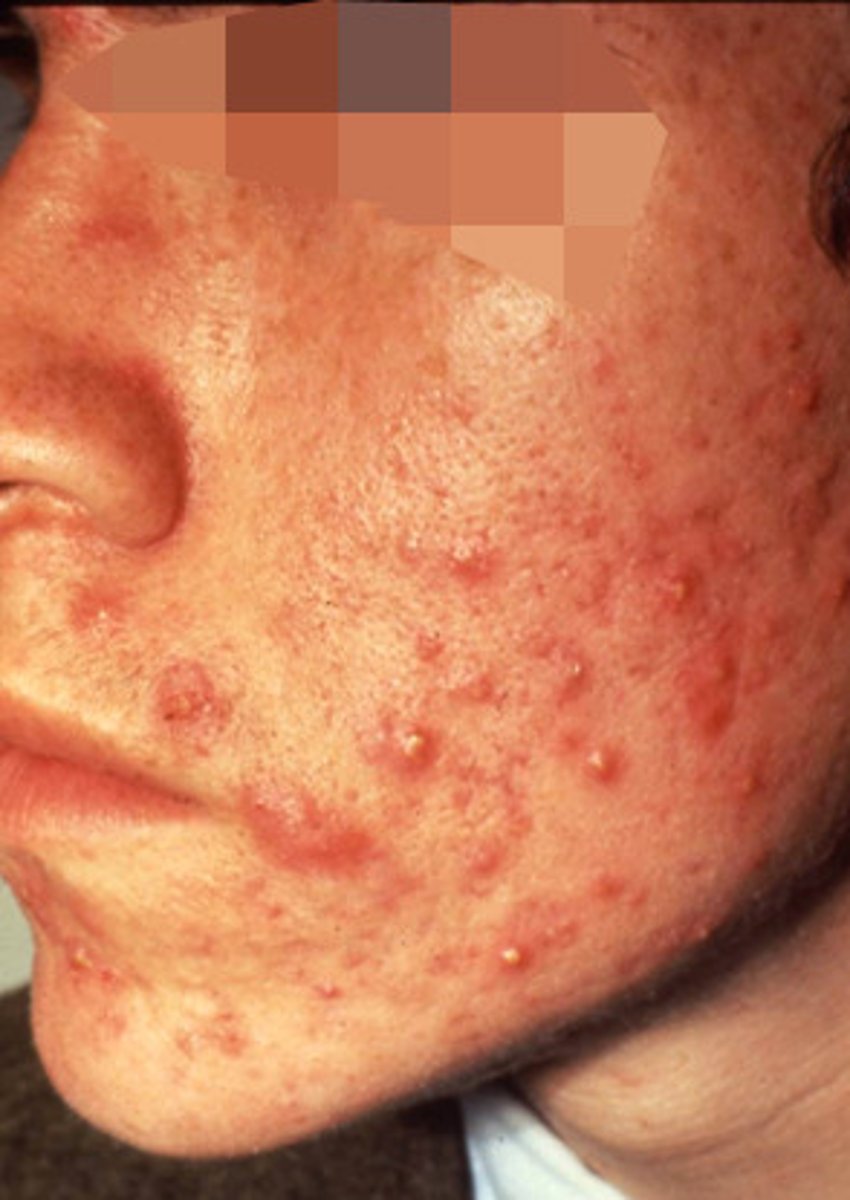
Acne
inflammatory skin disorder of the sebaceous glands, characterized by sebum production; medically known as acne simplex or acne vulgaris
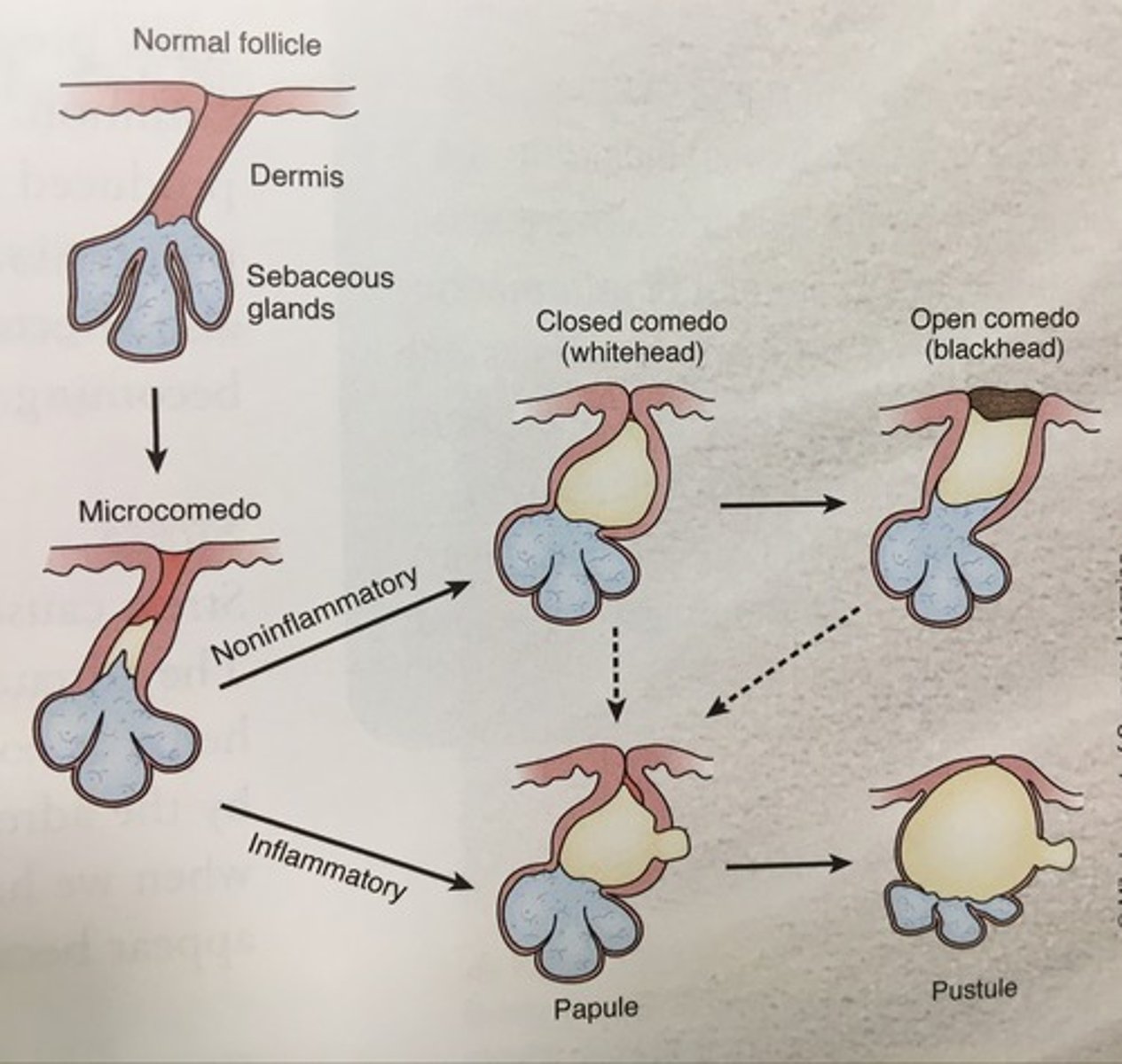
comedo
a non-inflamed build up of cells, sebum and other debris inside follicles
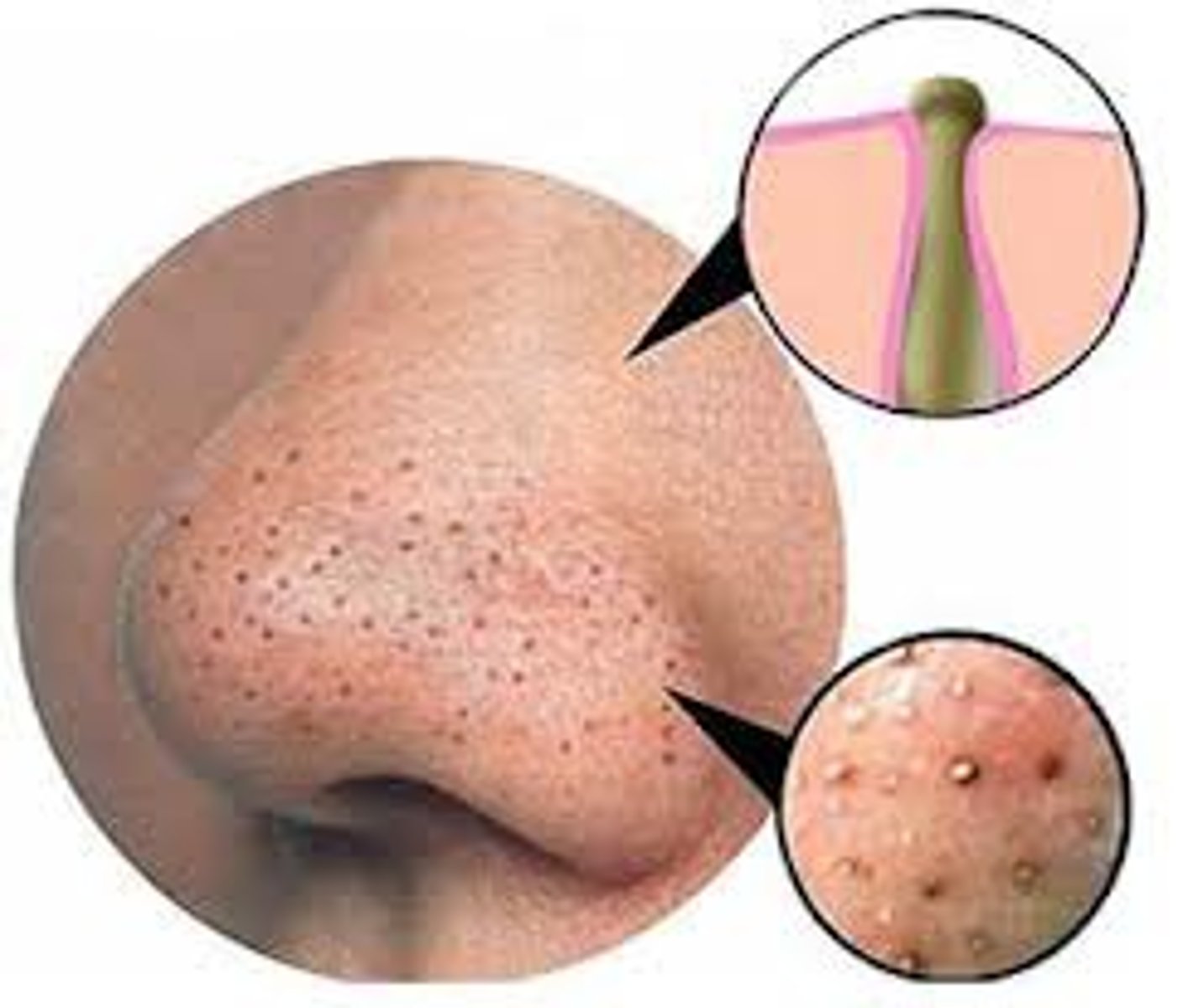
open comedo
Blackhead open at the surface and exposed to air
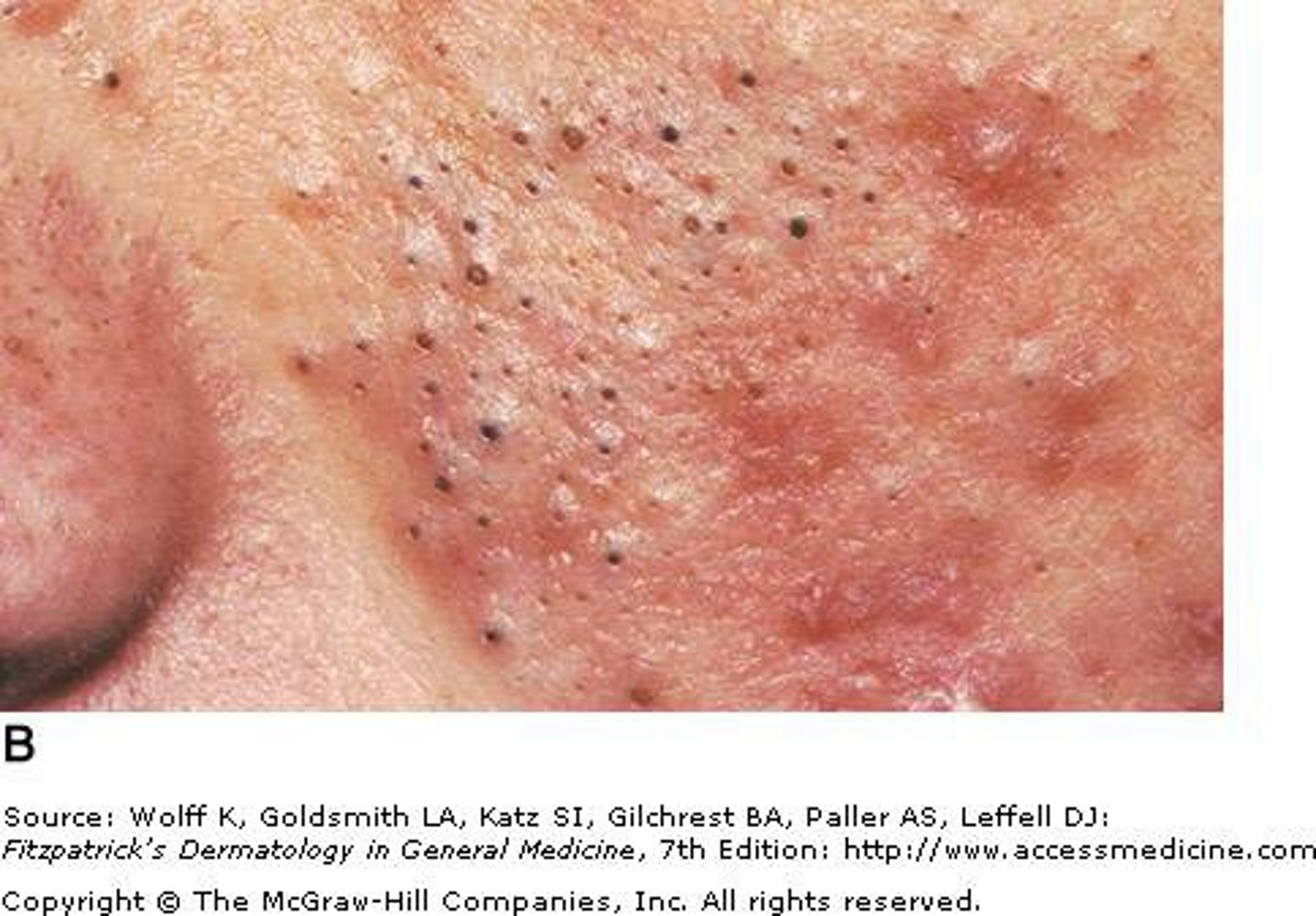
closed comedo
forms when openings of the follicles are blocked with debris
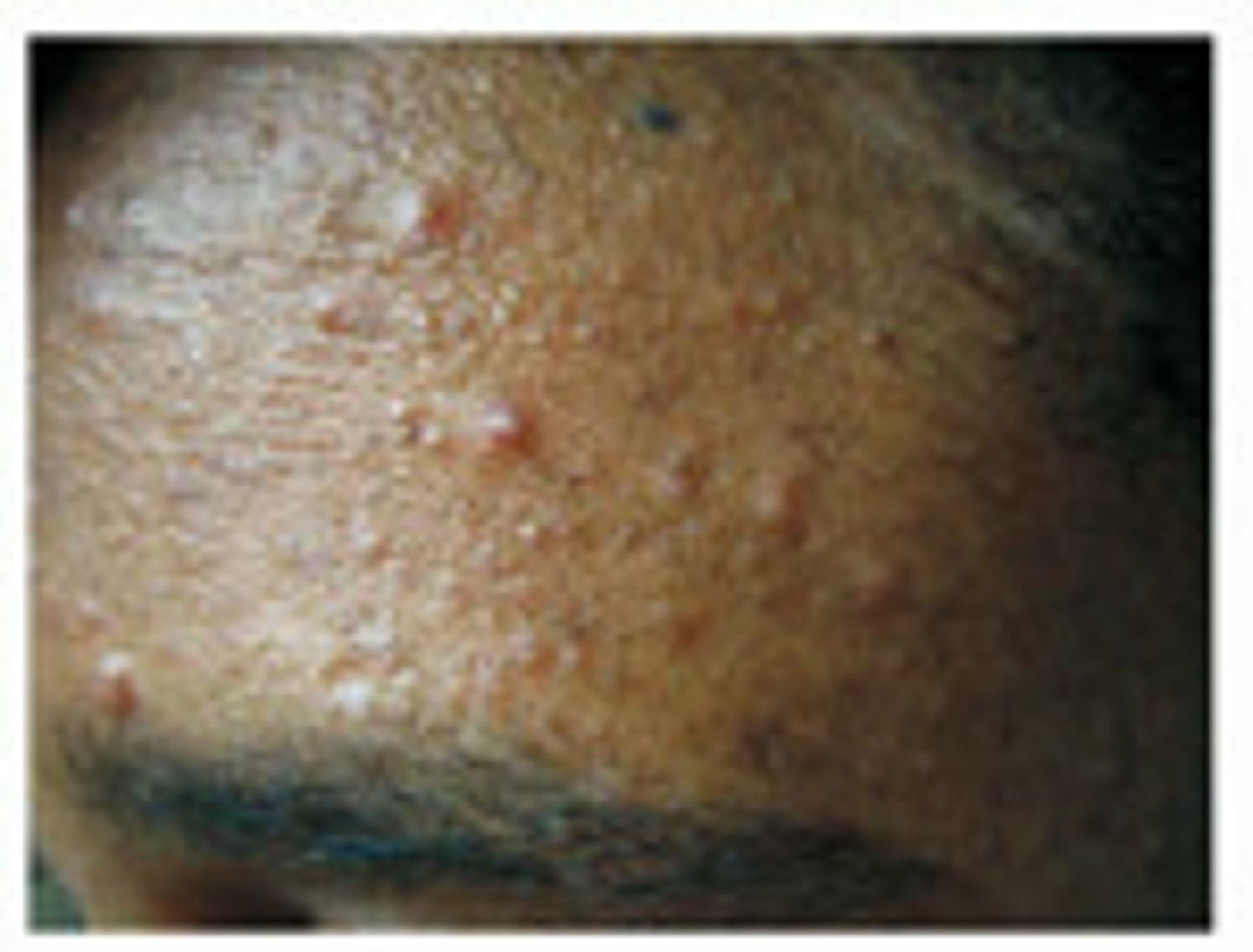
sebaceous filaments
small, solidified impactions of oil without the cell matter; often found on the nose
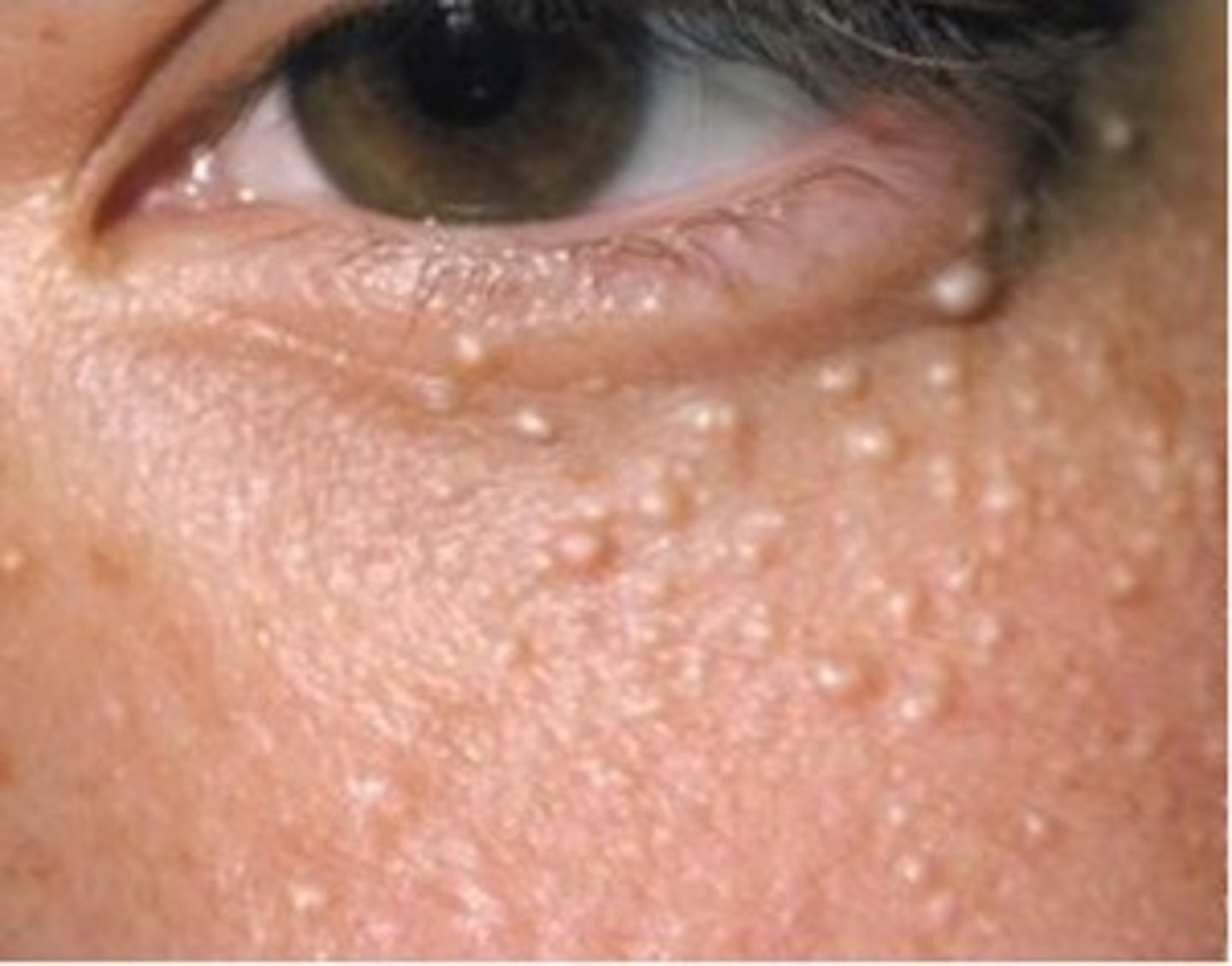
milia
whitish, pearl-like masses of sebum; usually found around the eyes, cheeks and forehead
retention hyperkeratosis
hereditary factor in which dead skin cells build up
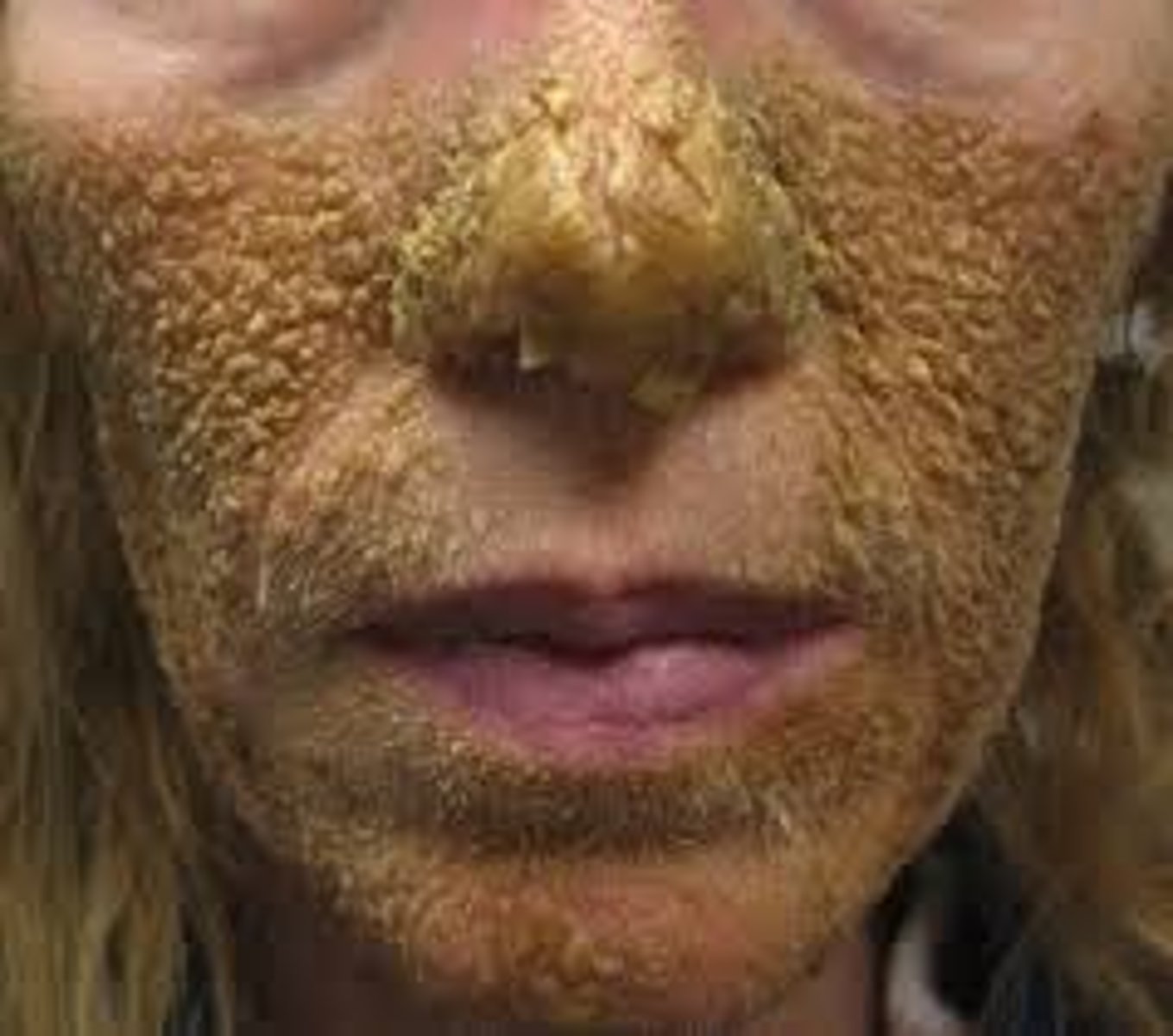
sebaceous hyperplasia
often white, yellow or flesh colored. described as doughnut-shaped with an indentation in the center
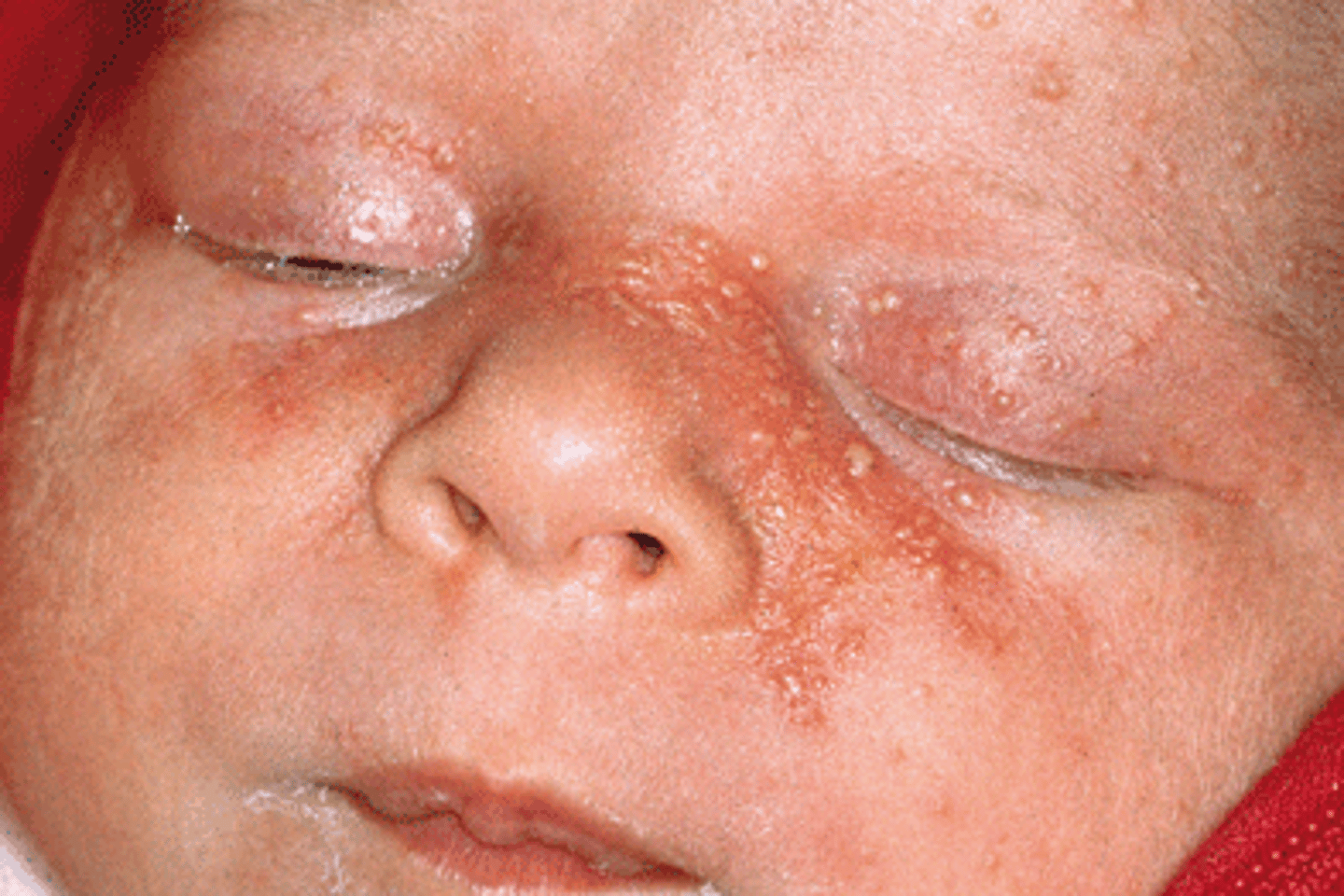
seborrhea
in the scalp, it is called dandruff
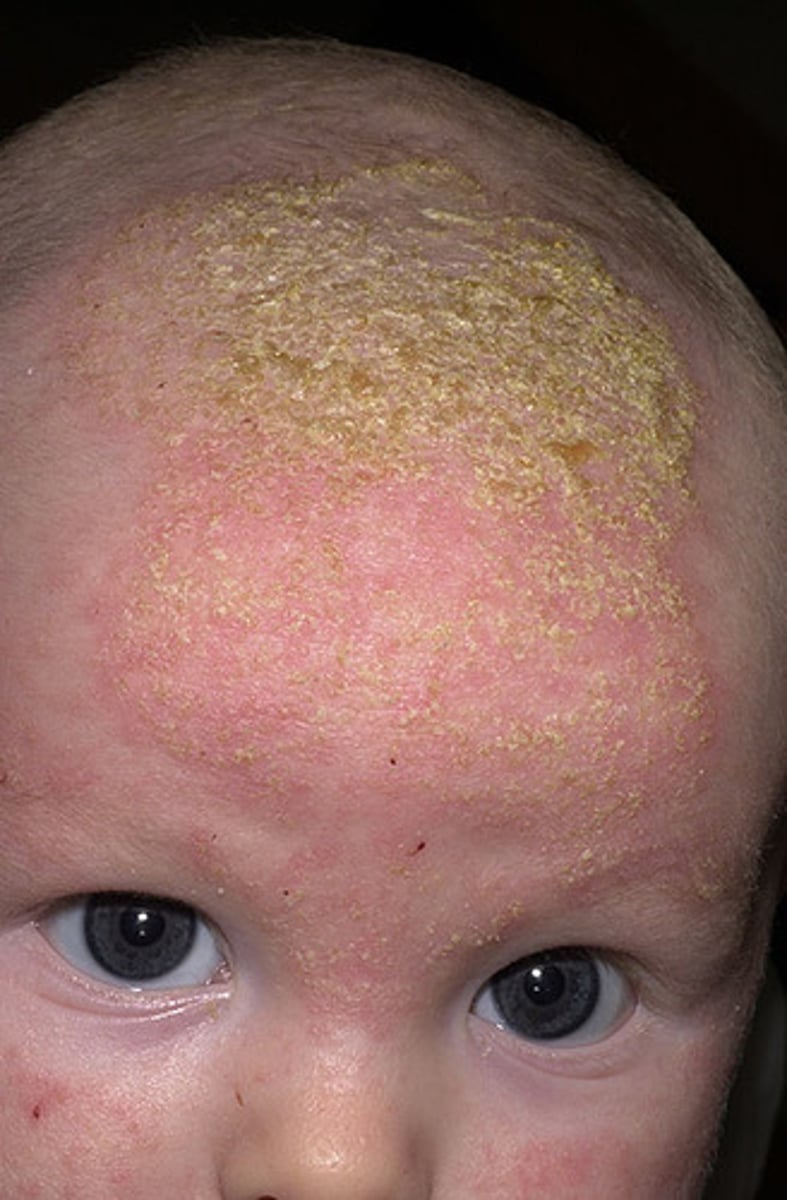
grade 1 acne
minor breakouts, mostly open comedones, some closed comedones and a few papules
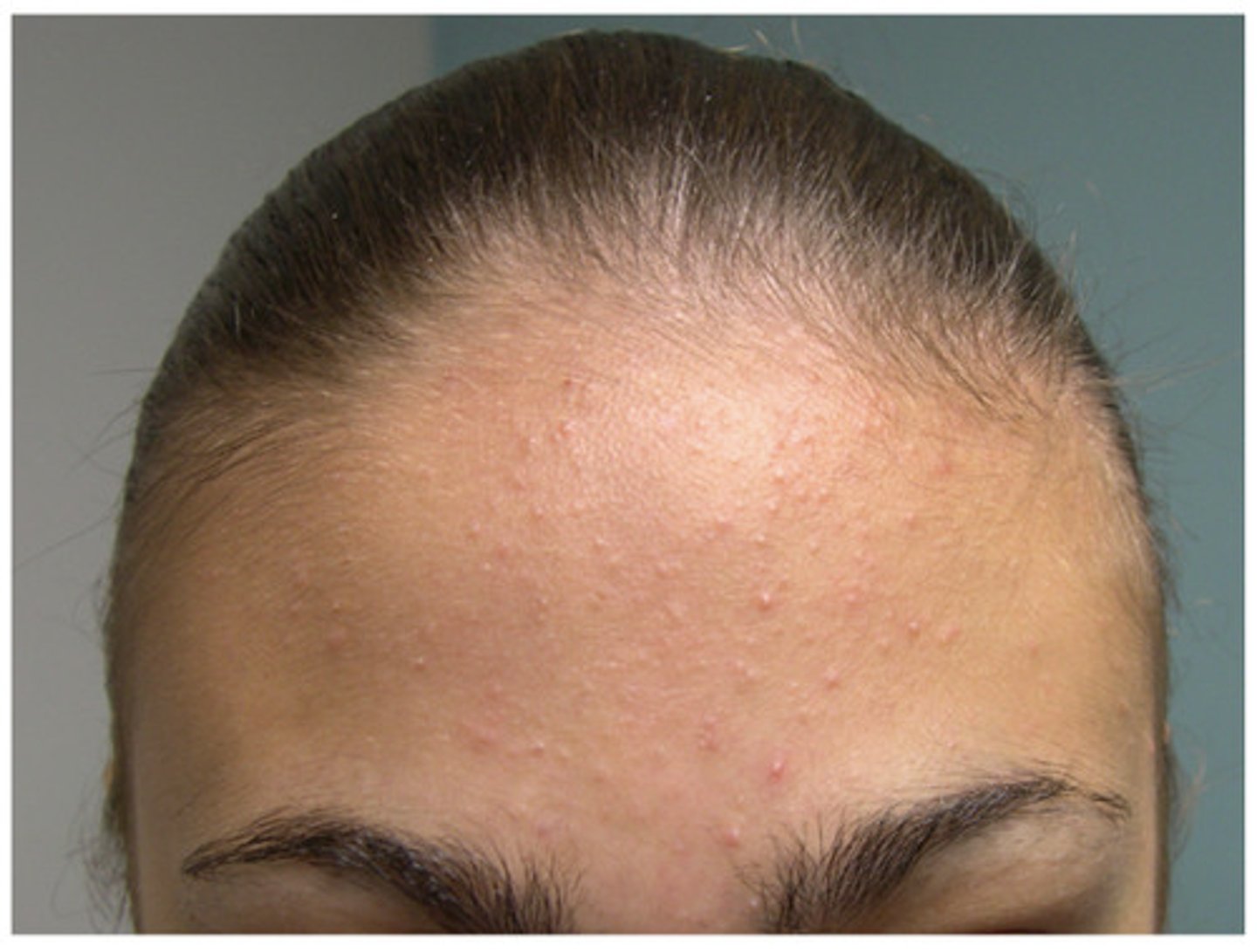
grade 2 acne
many closed comedones, more open comedones and occasional papules and pustules
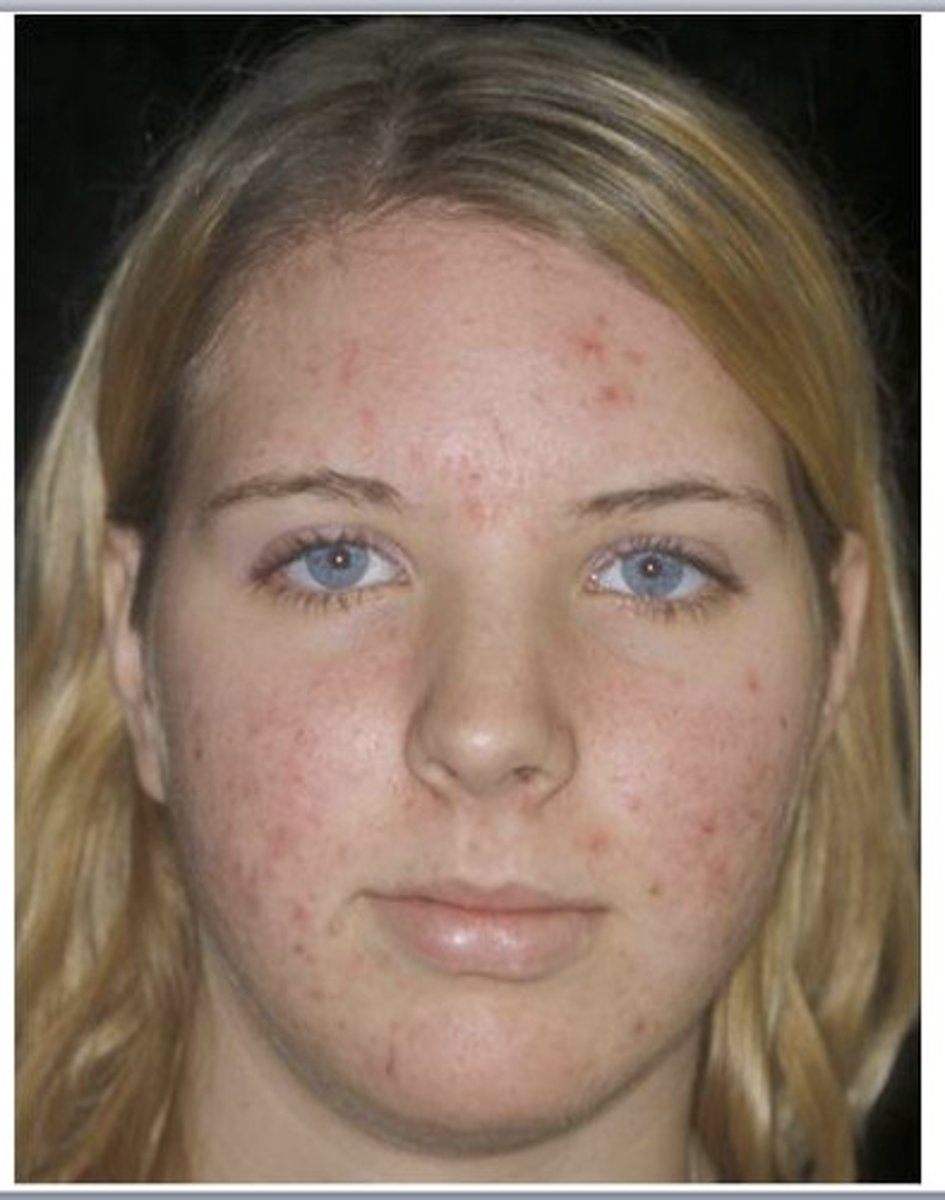
grade 3 acne
red and inflamed, many comedones, papules, and pustules
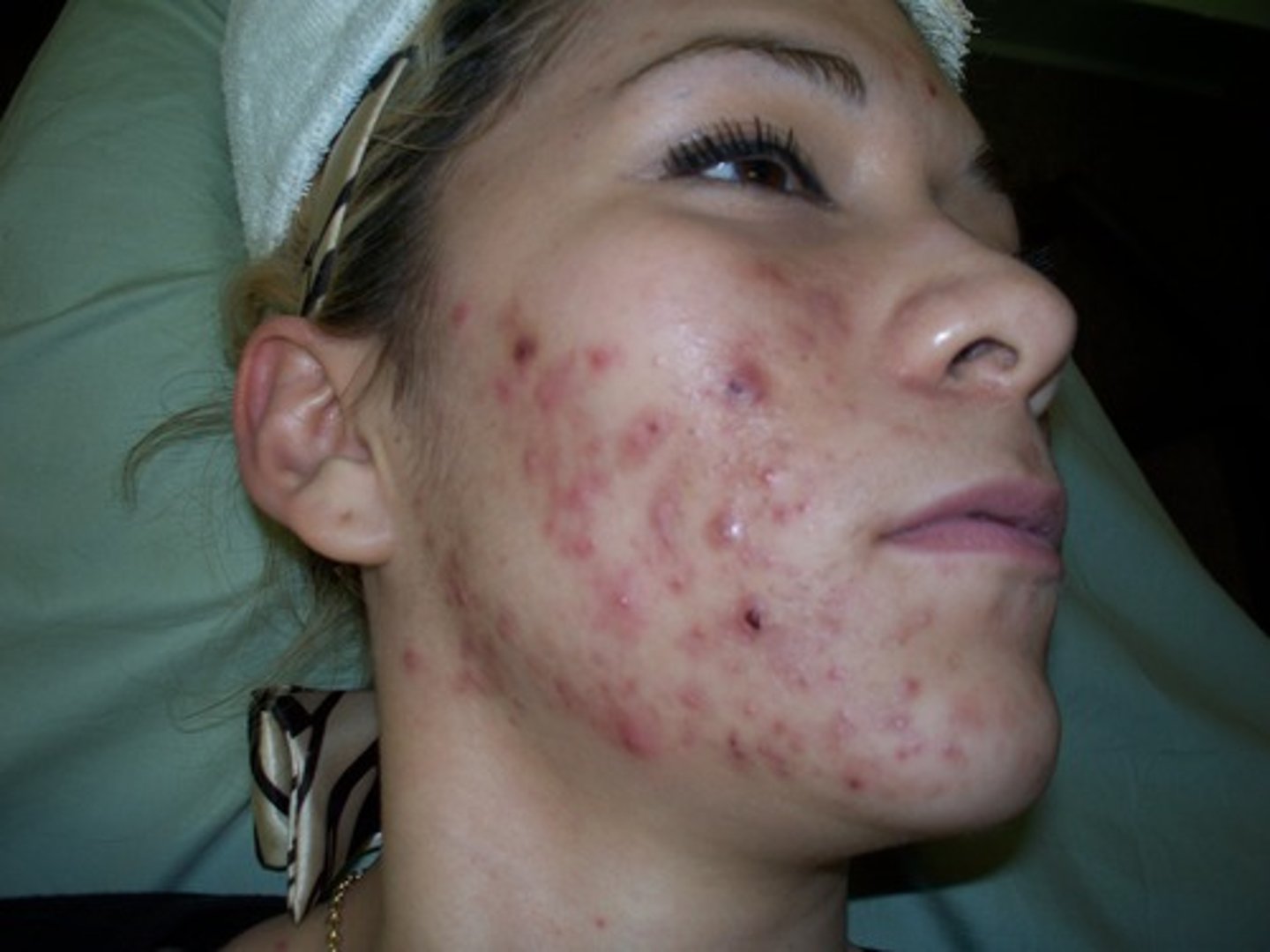
grade 4 acne
cystic acne. cysts with comedones, papules, pustules and inflammation are present. scar formation from tissue damage is common
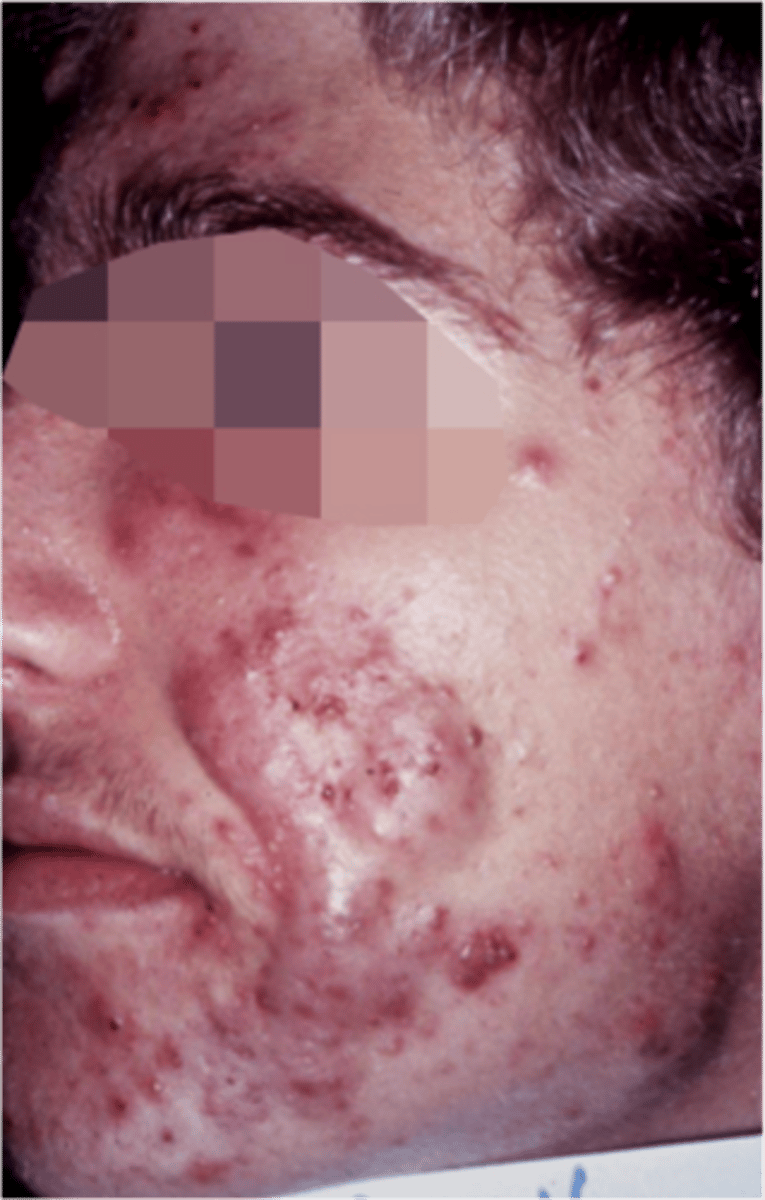
why are medical professionals reducing the use of antibiotic treatments for acne?
the risk of antibiotic resistance
antibiotics for acne can be used
both topically and orally
rosacea
starts with flushing and increasing bouts of redness, can affect the eyes. spicy foods, alcohol, caffeine, temperature extremes, heat & sun aggravate symptoms; soothing facials & light exfoliation treats rosacea
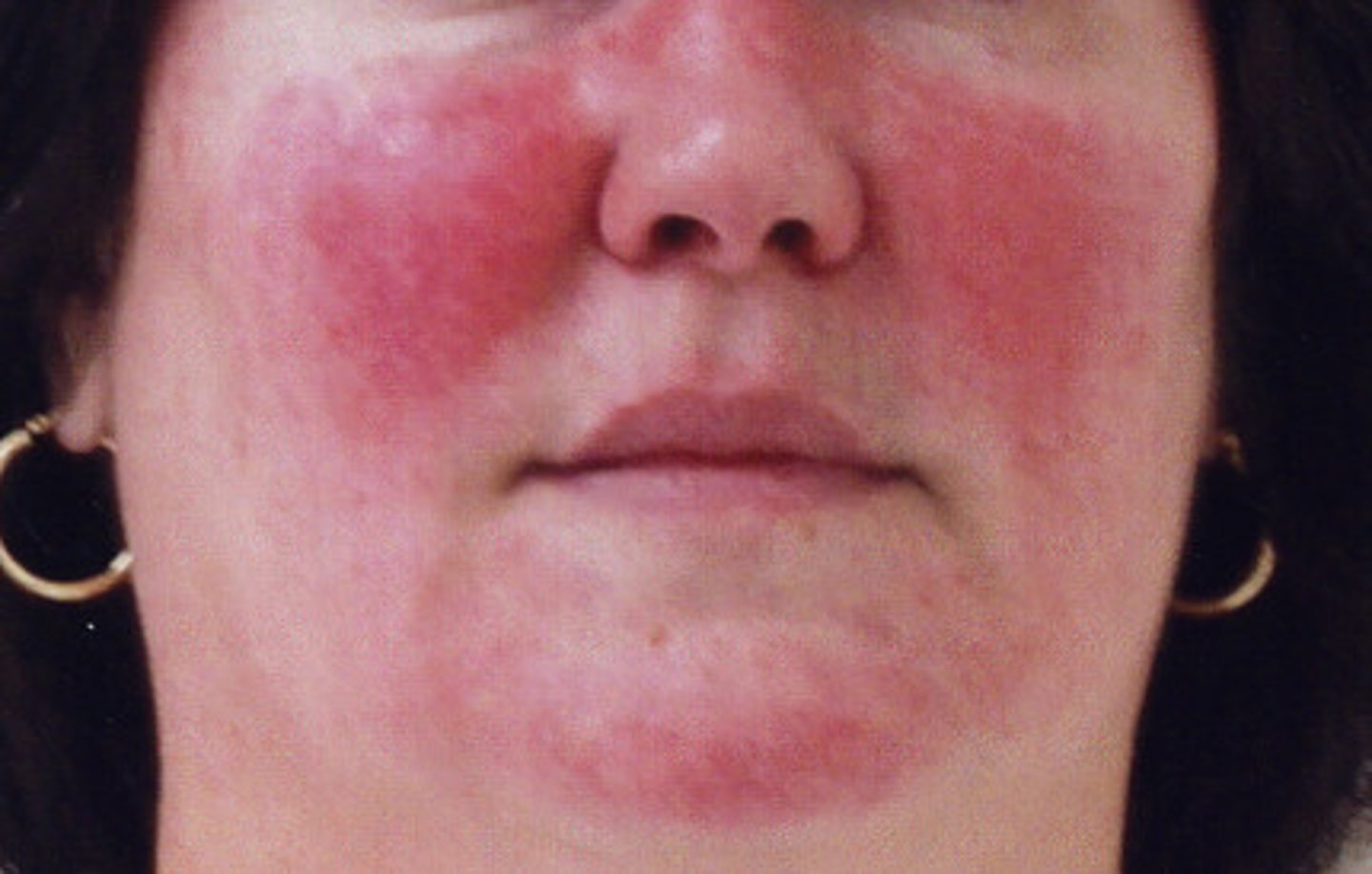
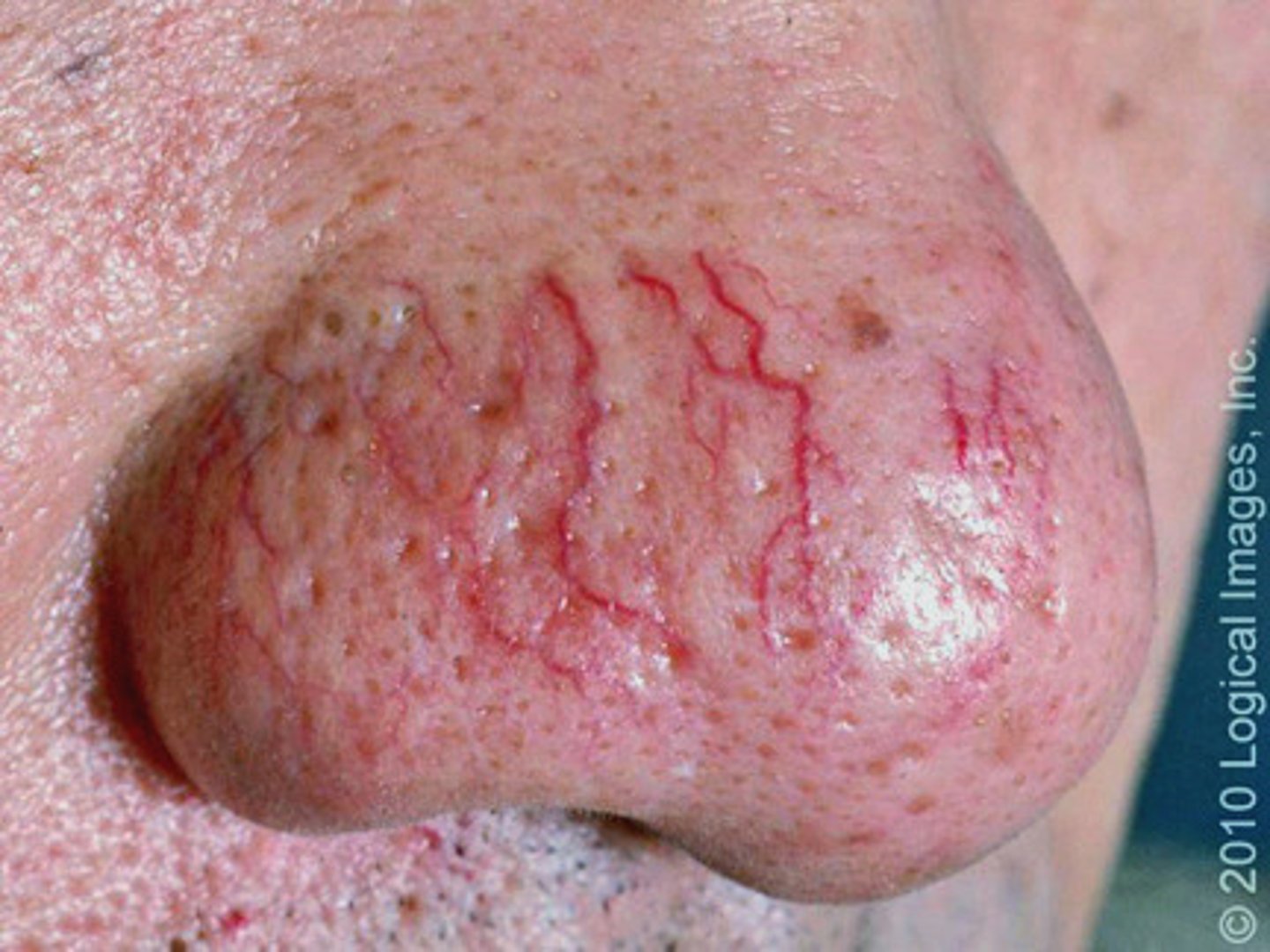
telangiectasia
visible capillaries commonly found on the face, particularly around the nose, cheeks & chin; is a cosmetic irregularity & not a medical condition
sclerotherapy
can cause smaller vessels to disappear; treatment for varicose veins
hyperpigmentation
overproduction of pigment
hypopigmentation
lack of pigment
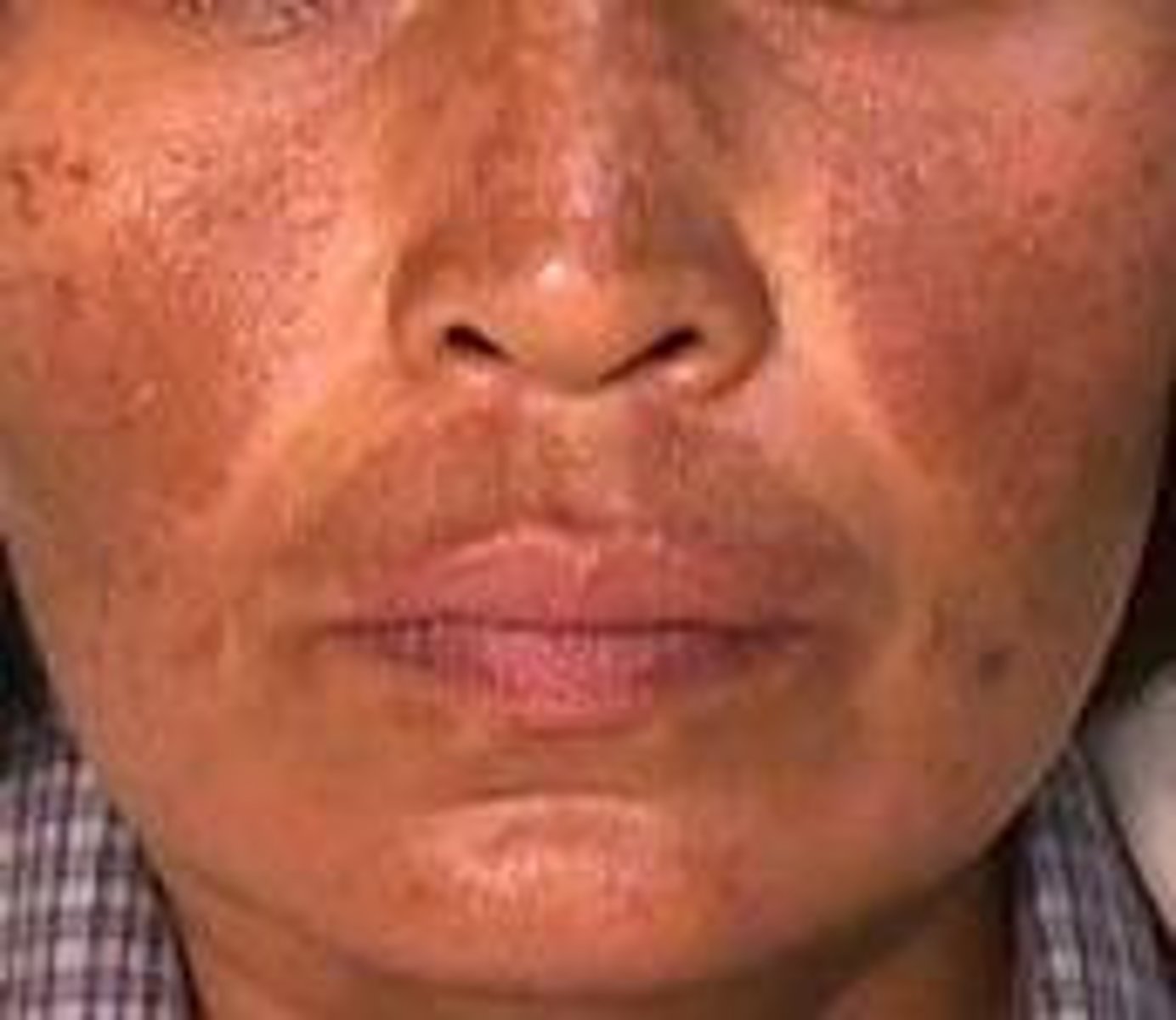
melasma
type of hormonal hyperpigmentation disorder that first appears during pregnancy or with the use of birth control pills; symmetrical. often found on forehead, cheeks, upper lip & chin
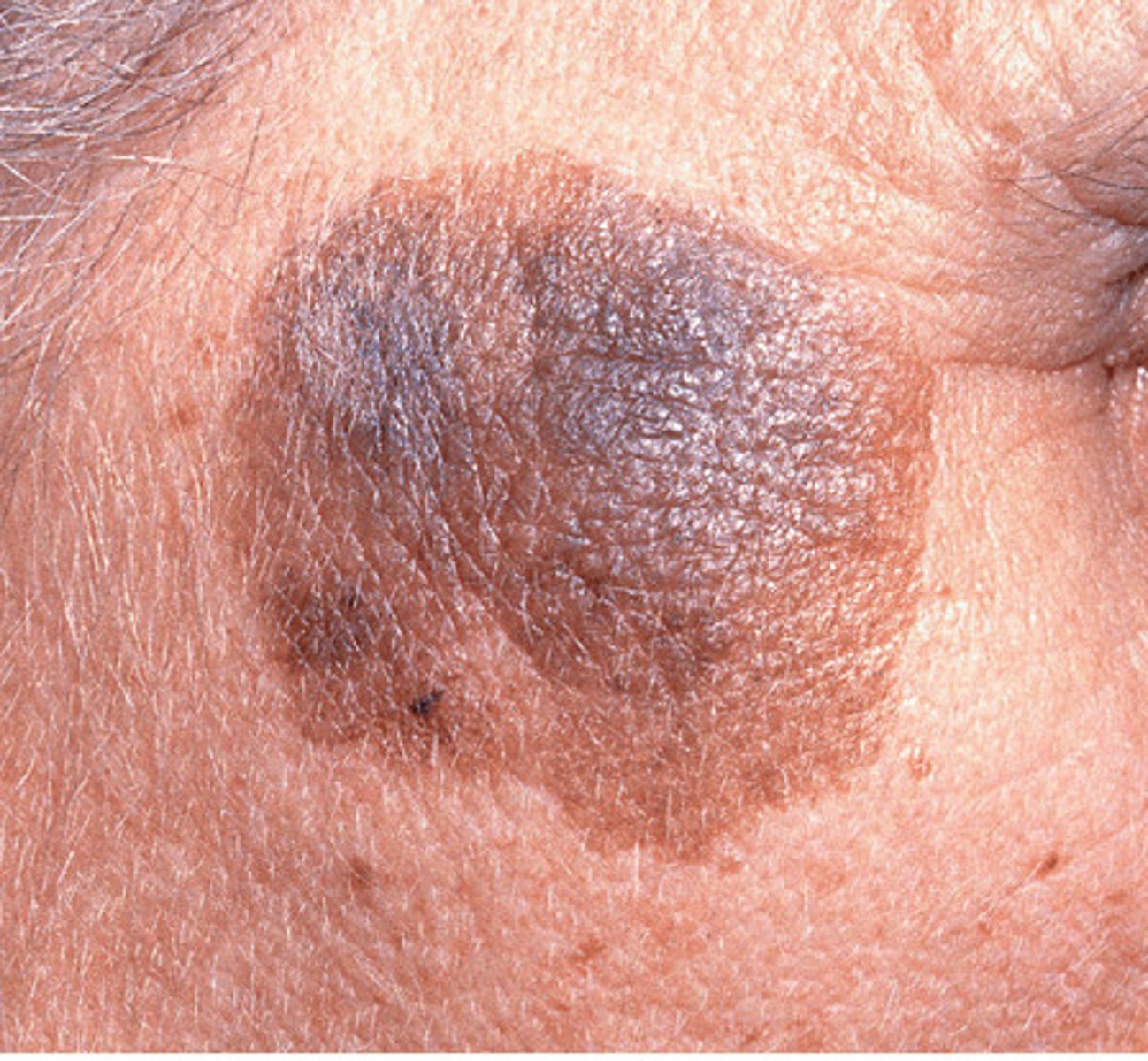
lentigo
Flat, pigmented area similar to a freckle
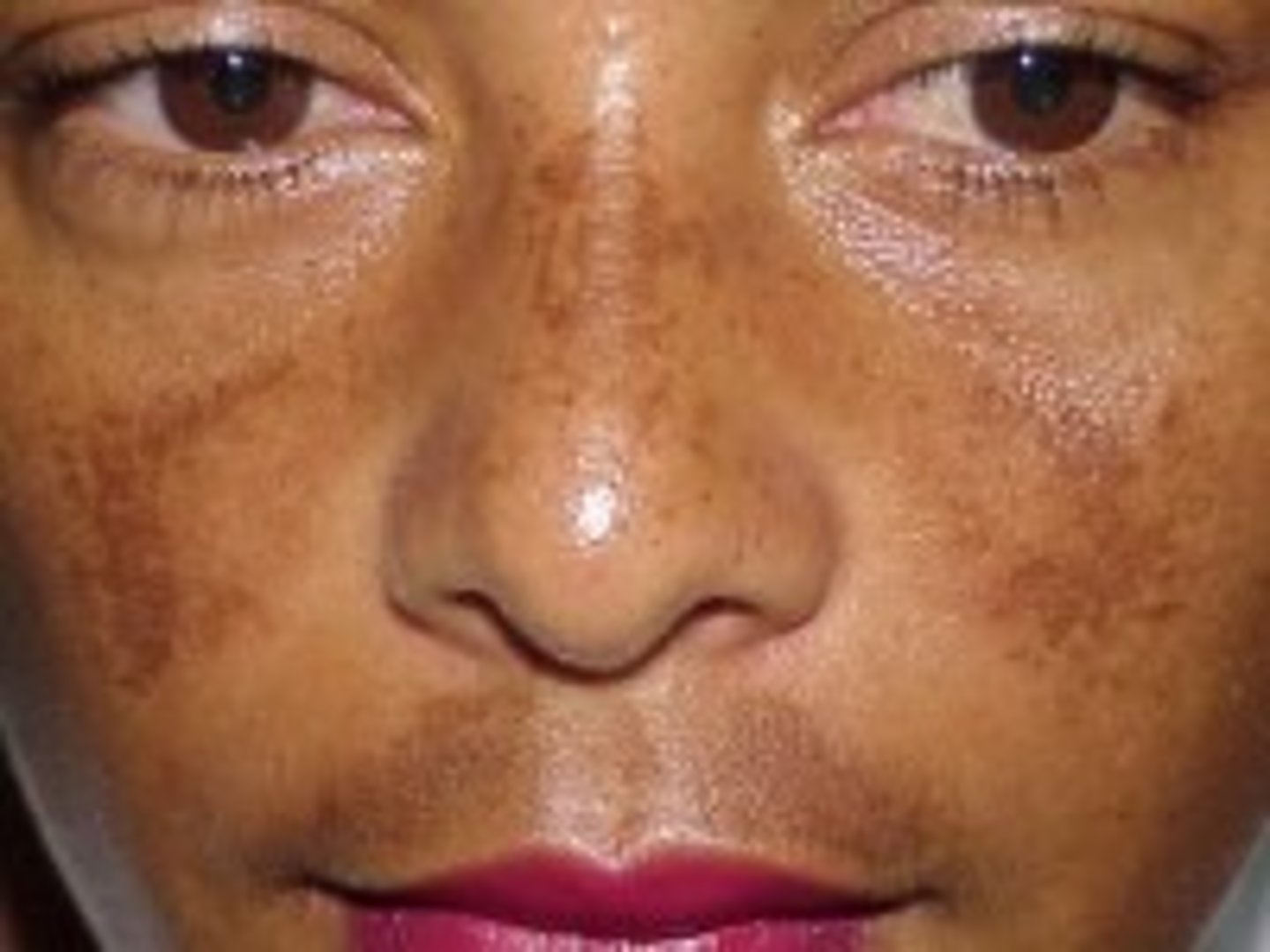
ephelids
known as freckles. tiny, round or oval pigmented areas of skin on areas exposed to the sun
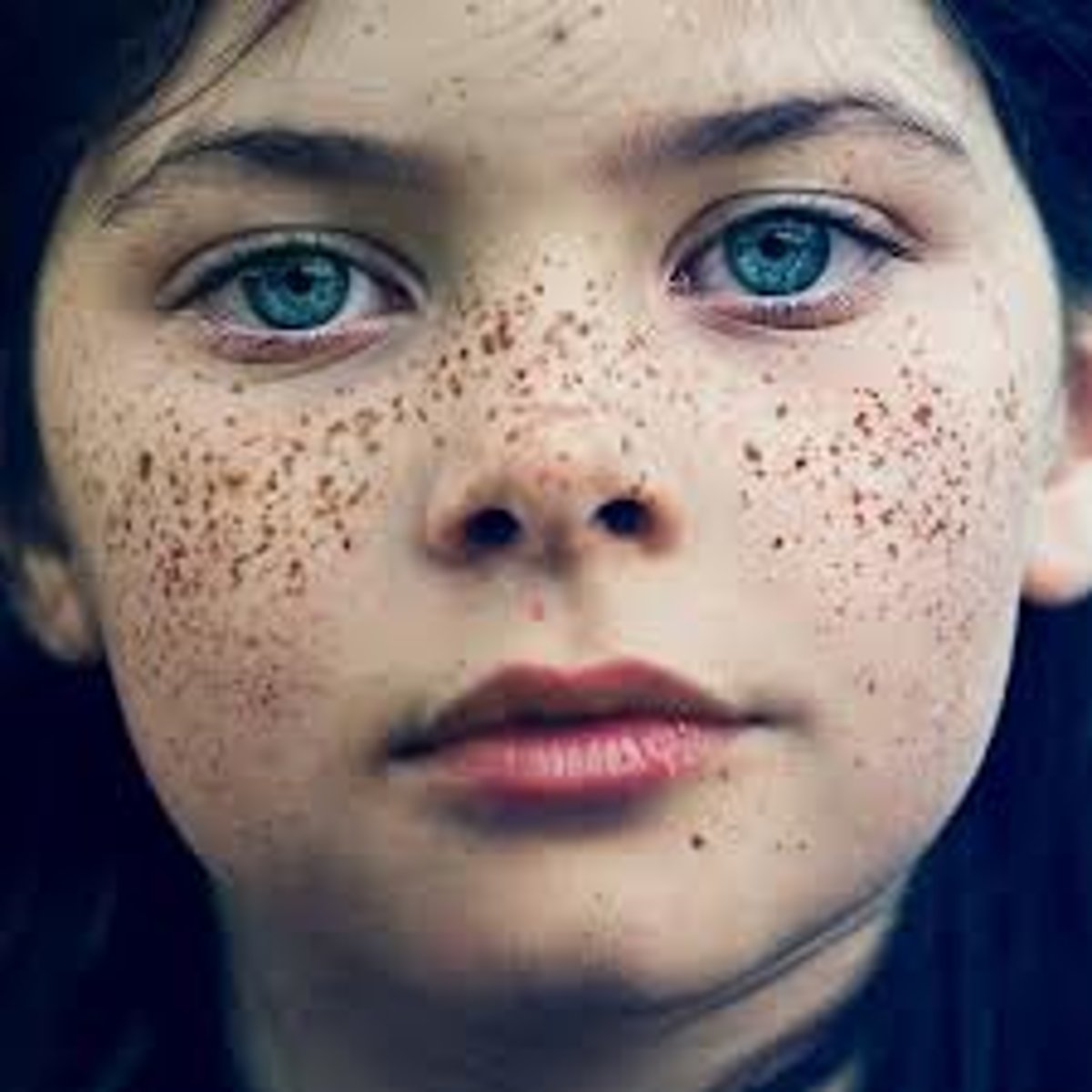

nevus
birthmark
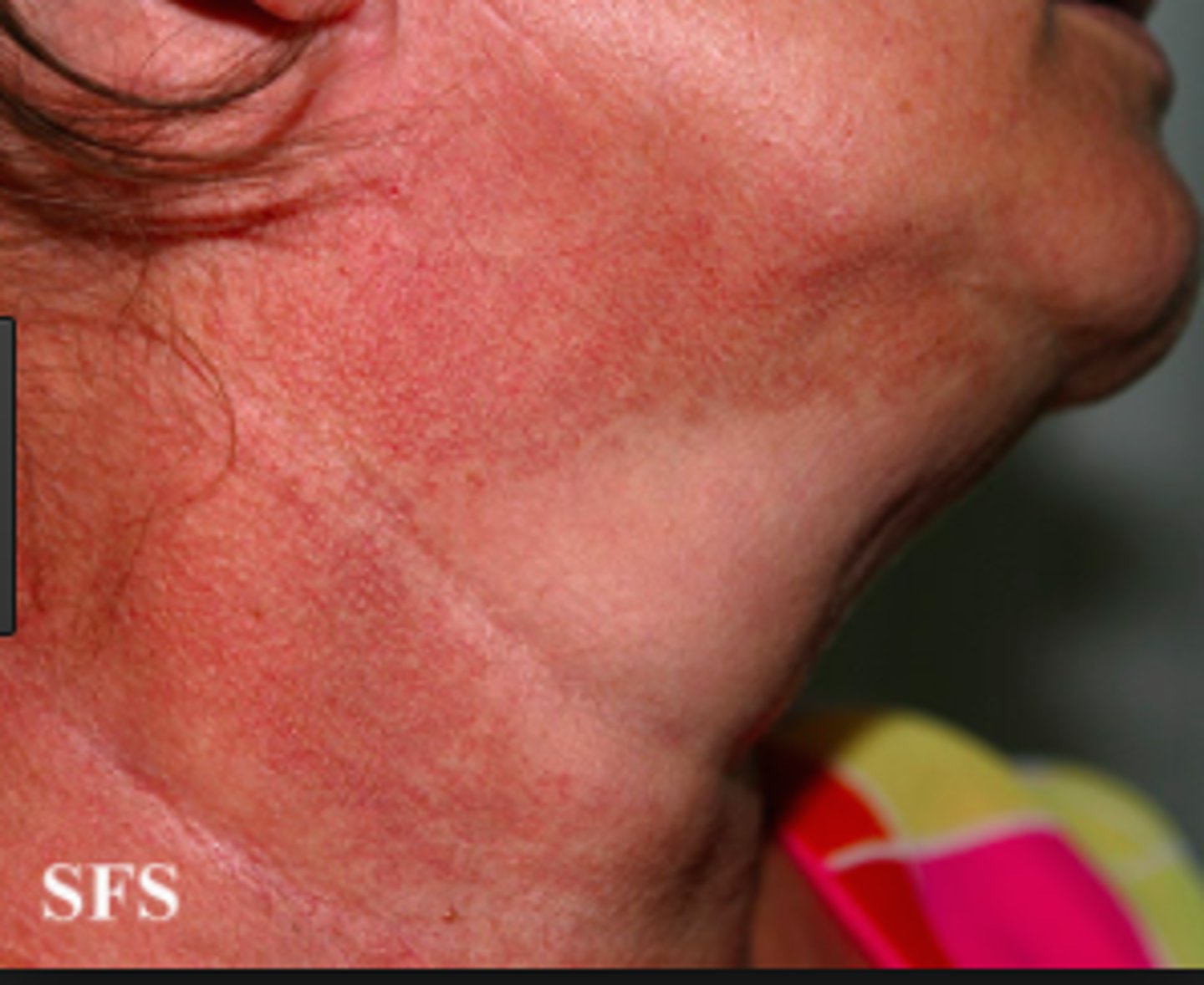
poikiloderma of civatte
skin condition caused by actinic bronzing to the sides of face & neck
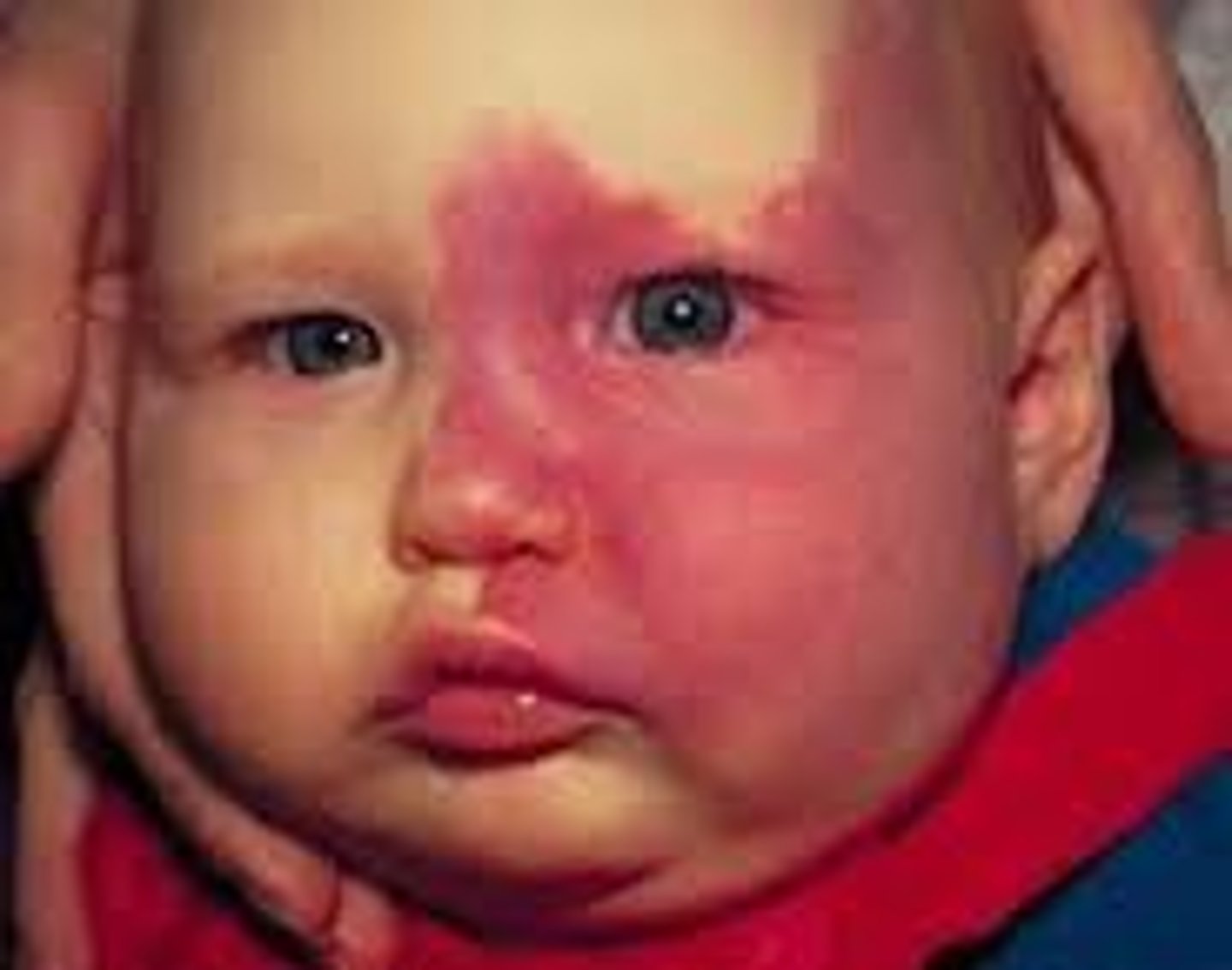
postinflammatory hyperpigmentation
darkened pigmentation due to an injury
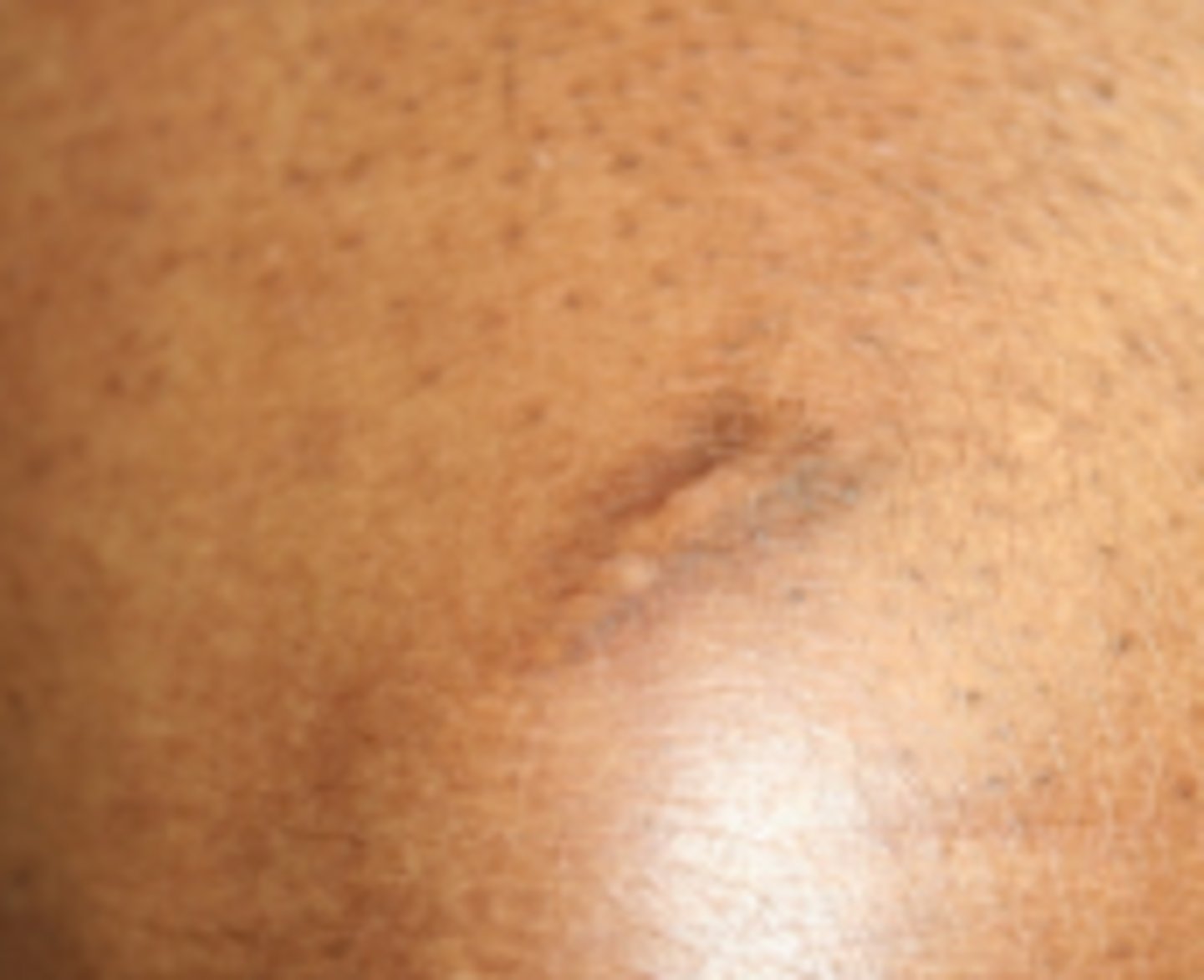
tan
results from exposure to the sun
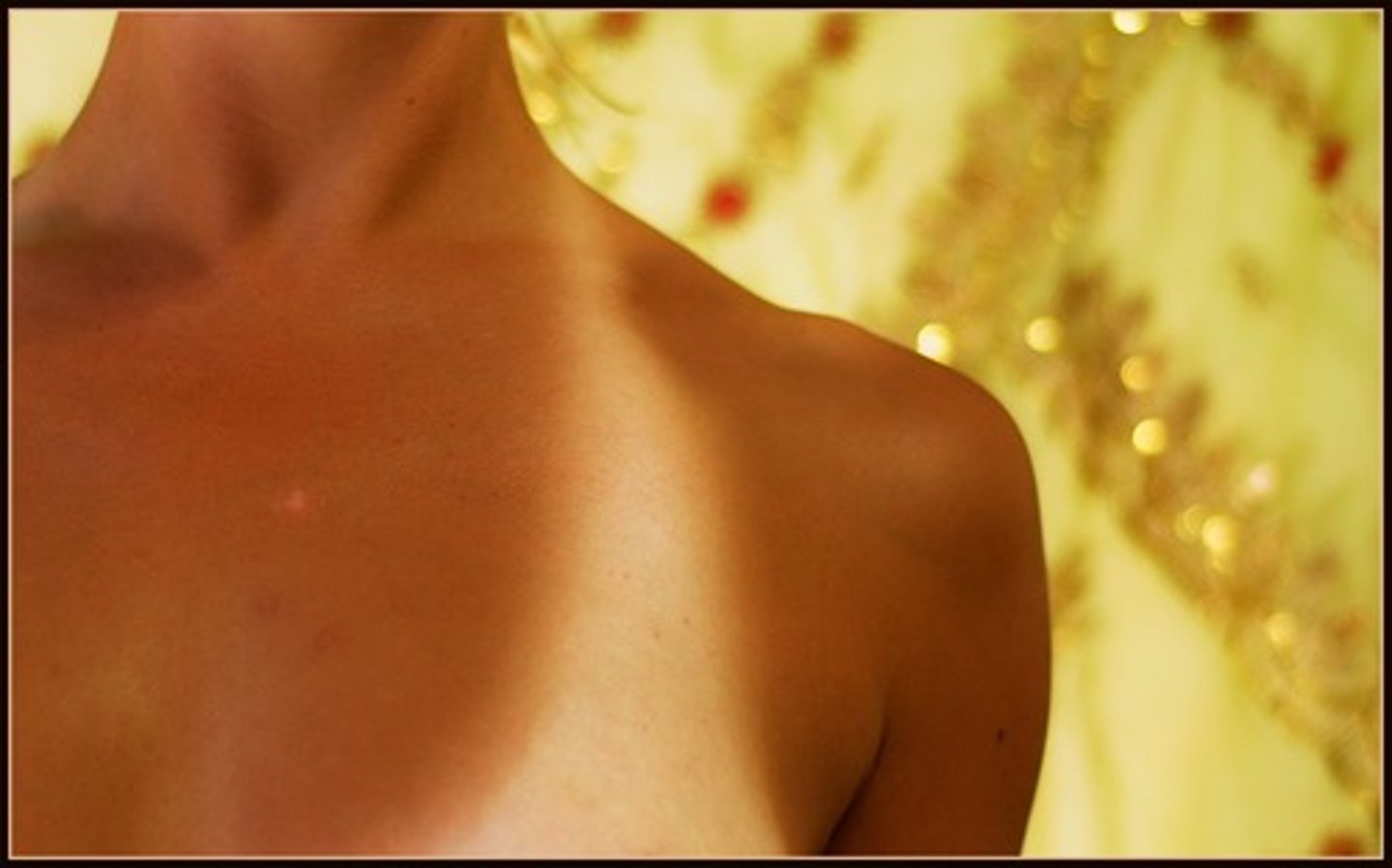

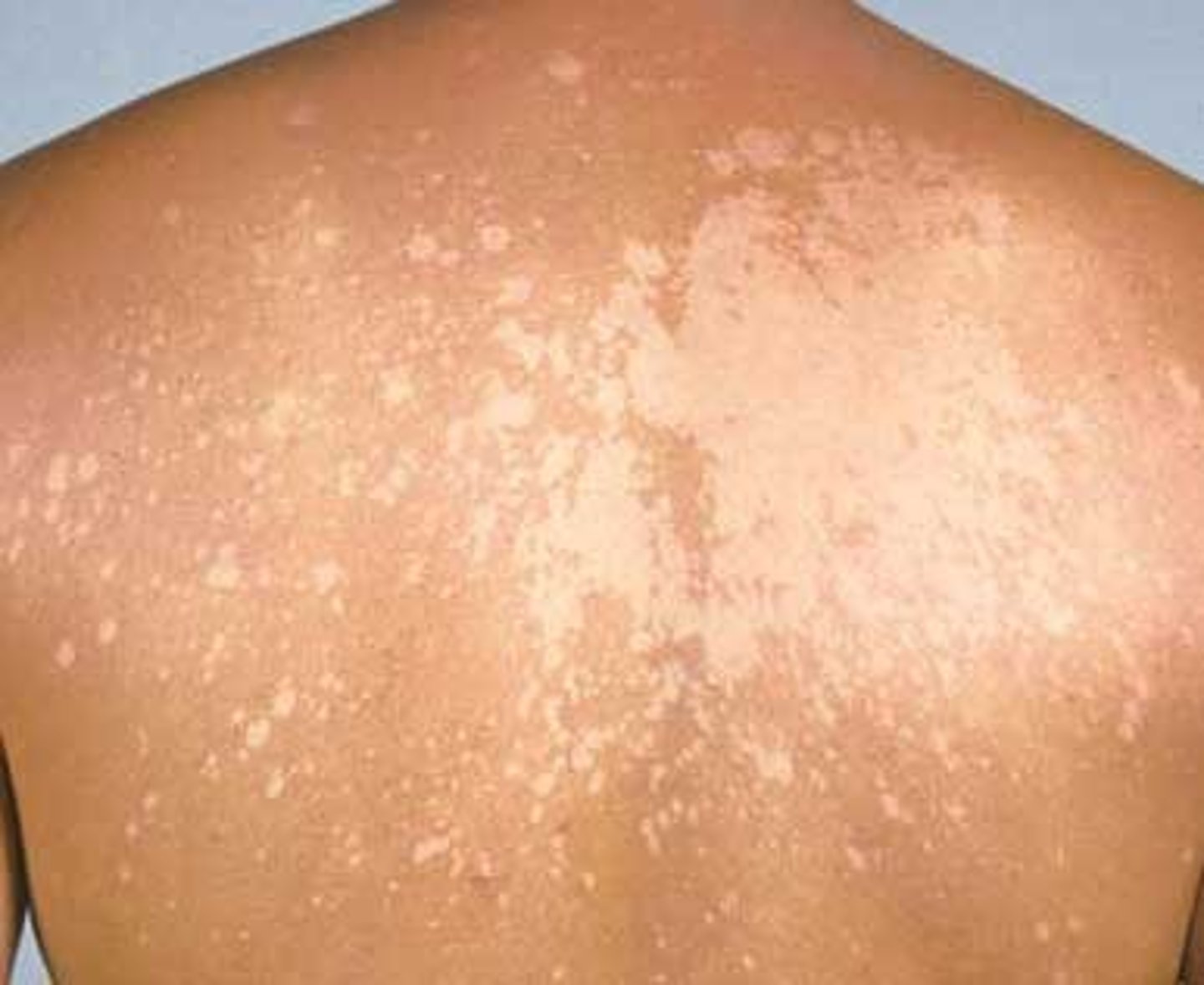
leukoderma
loss of pigmentation leading to light, abnormal patches of depigmented skin; congenital disorder acquired due to immunological & post-inflammatory causes
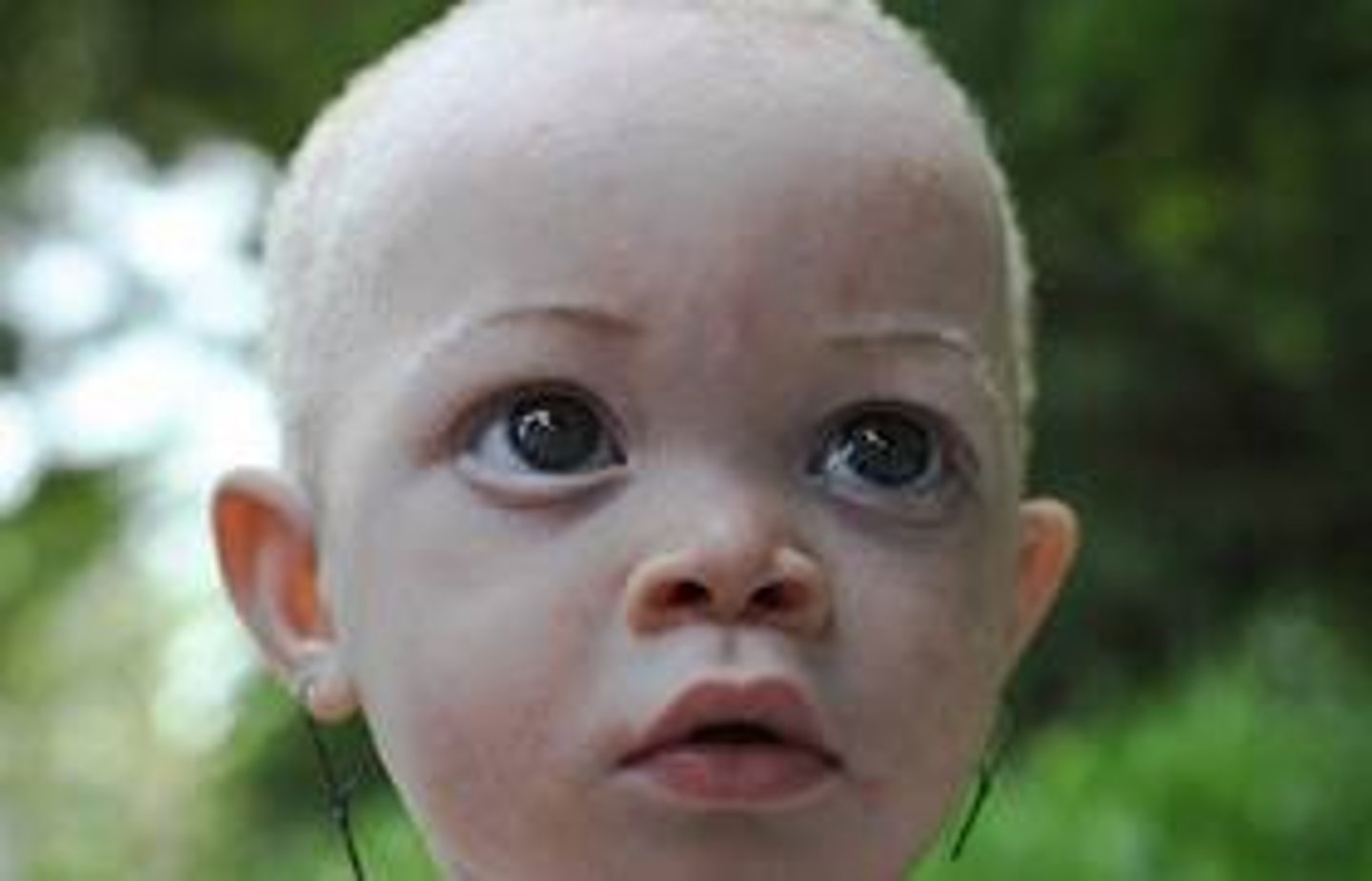
albinism
rare genetic condition; lack of pigment in the body
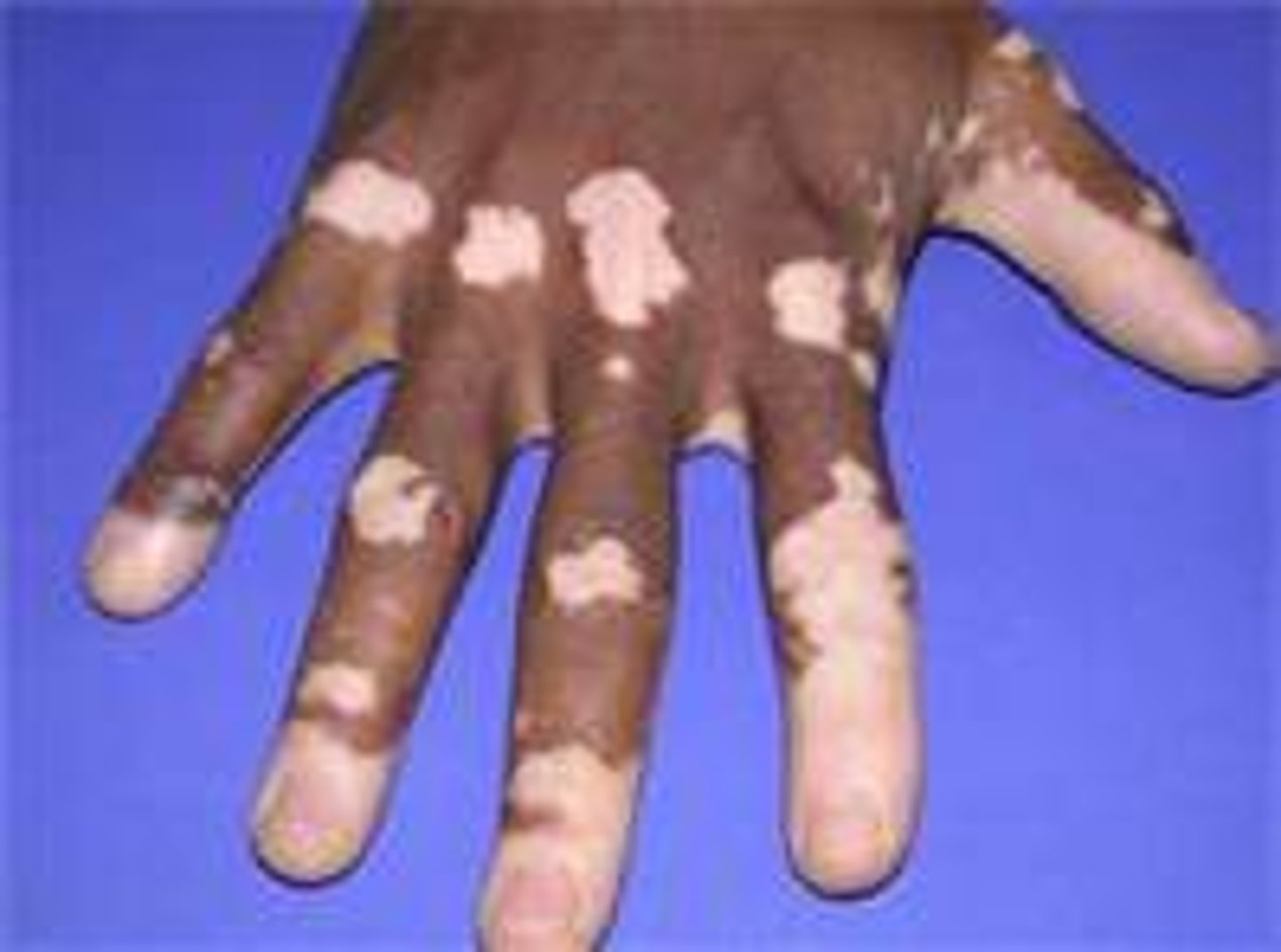
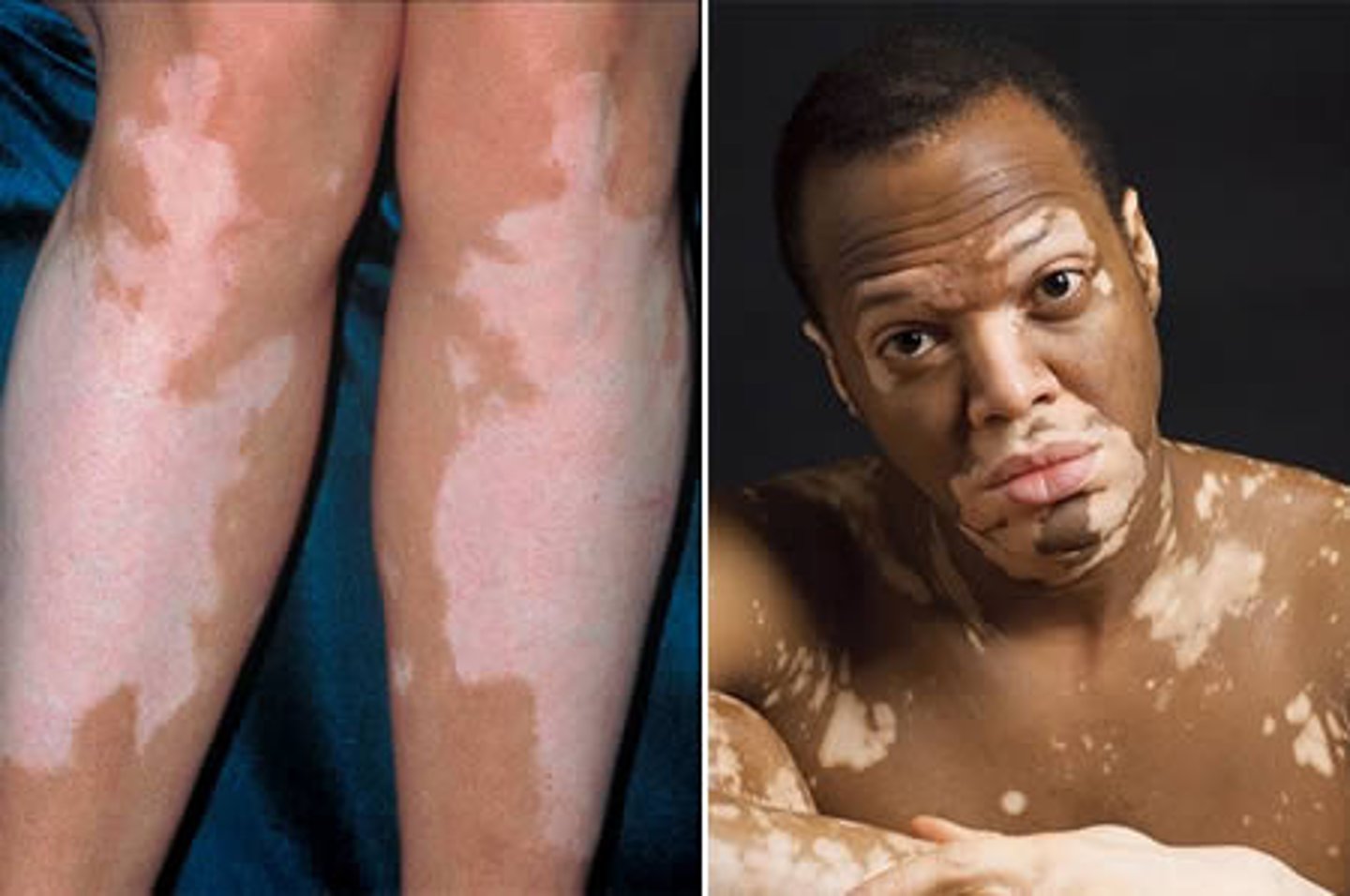
vitiligo
an autoimmune disorder; characterized by irregular white patches of skin that lack pigment
versicolor
fungal condition, caused by yeast. characterized by white, brown or salmon colored flaky patches
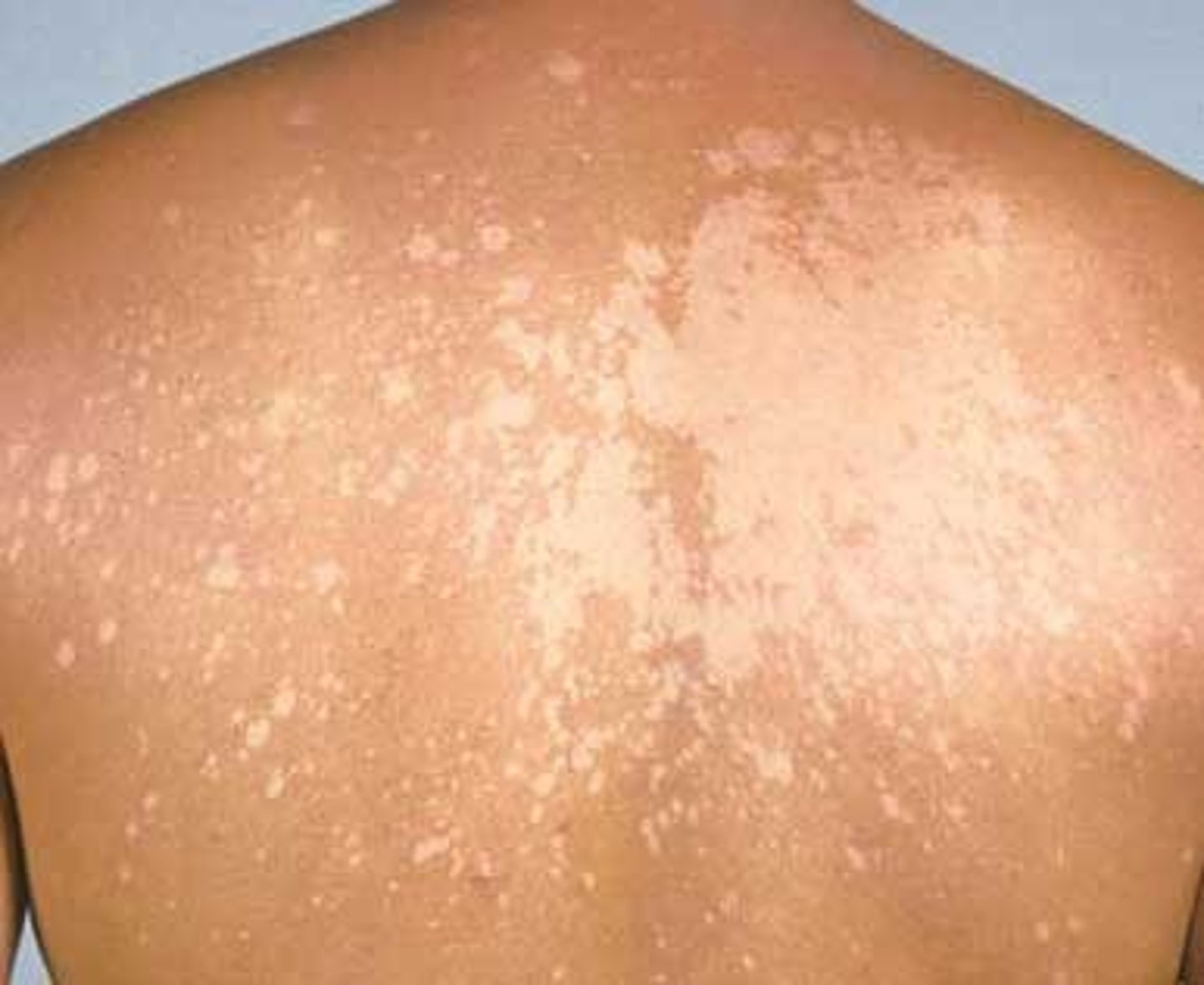
dermatitis
inflammatory condition of the skin
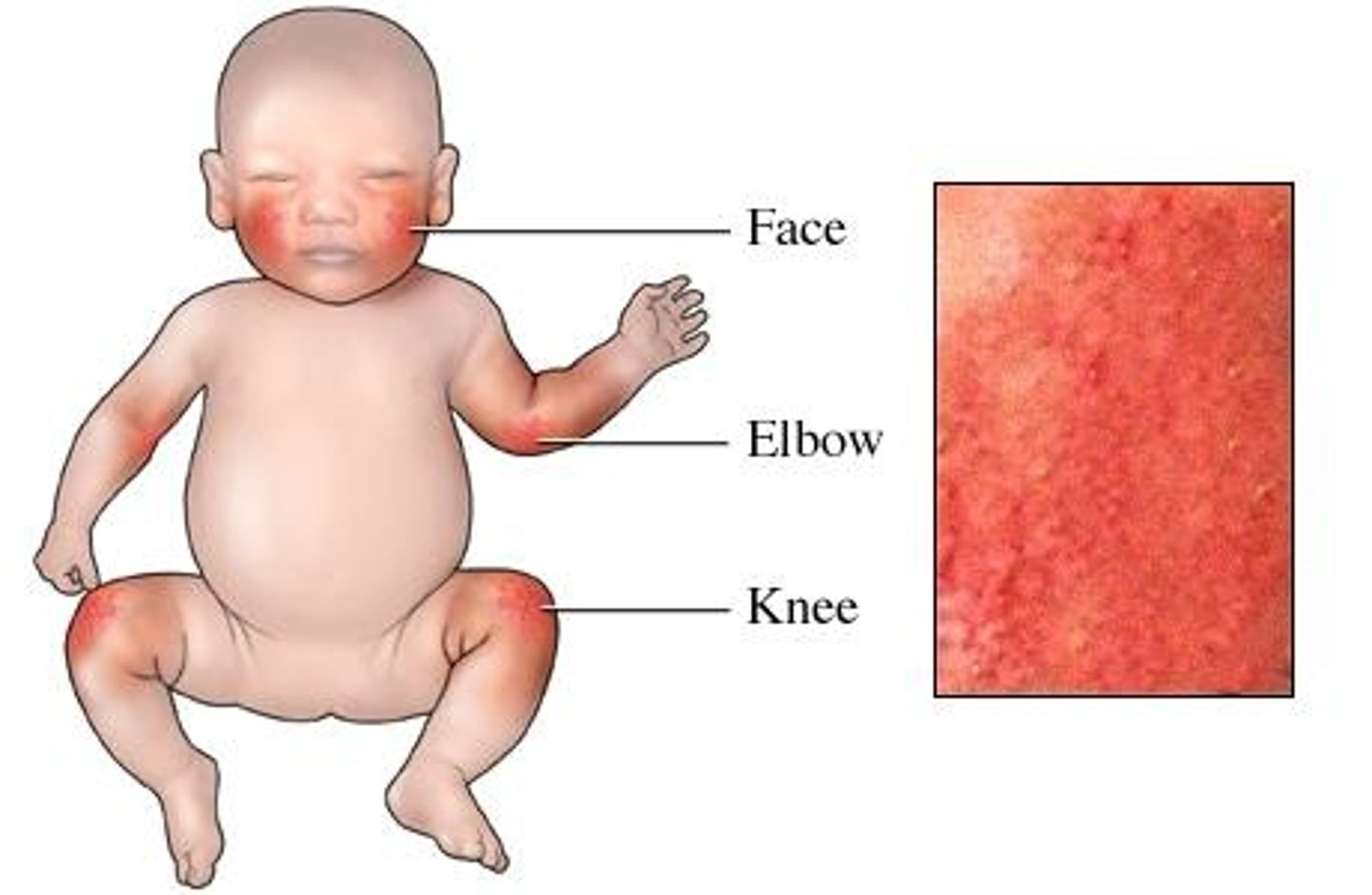
contact dermatitis
caused by occupational disorders from ingredients in cosmetics & chemical solutions
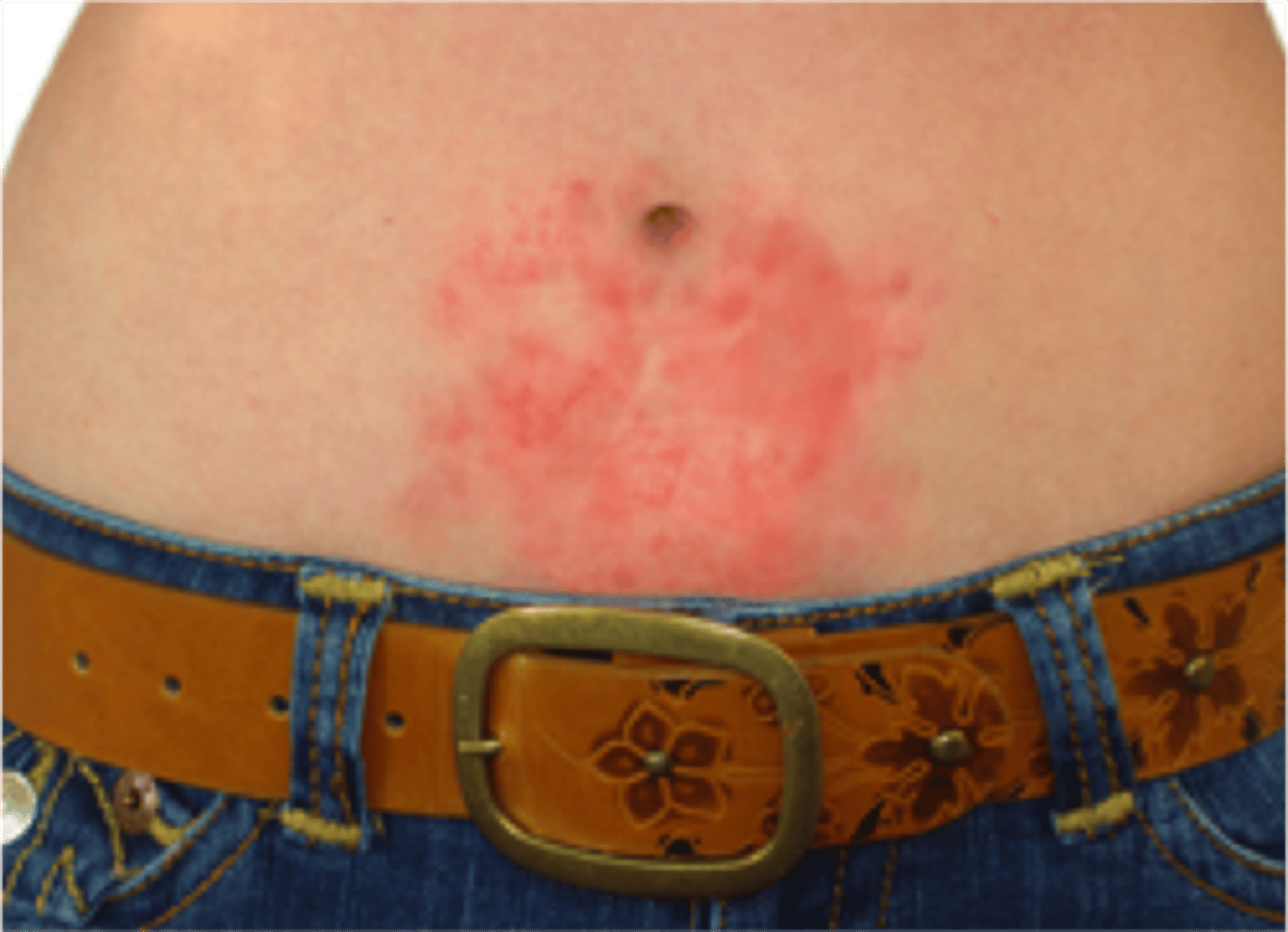
allergic contact dermatitis
caused by exposure to and direct skin contact with an allergen
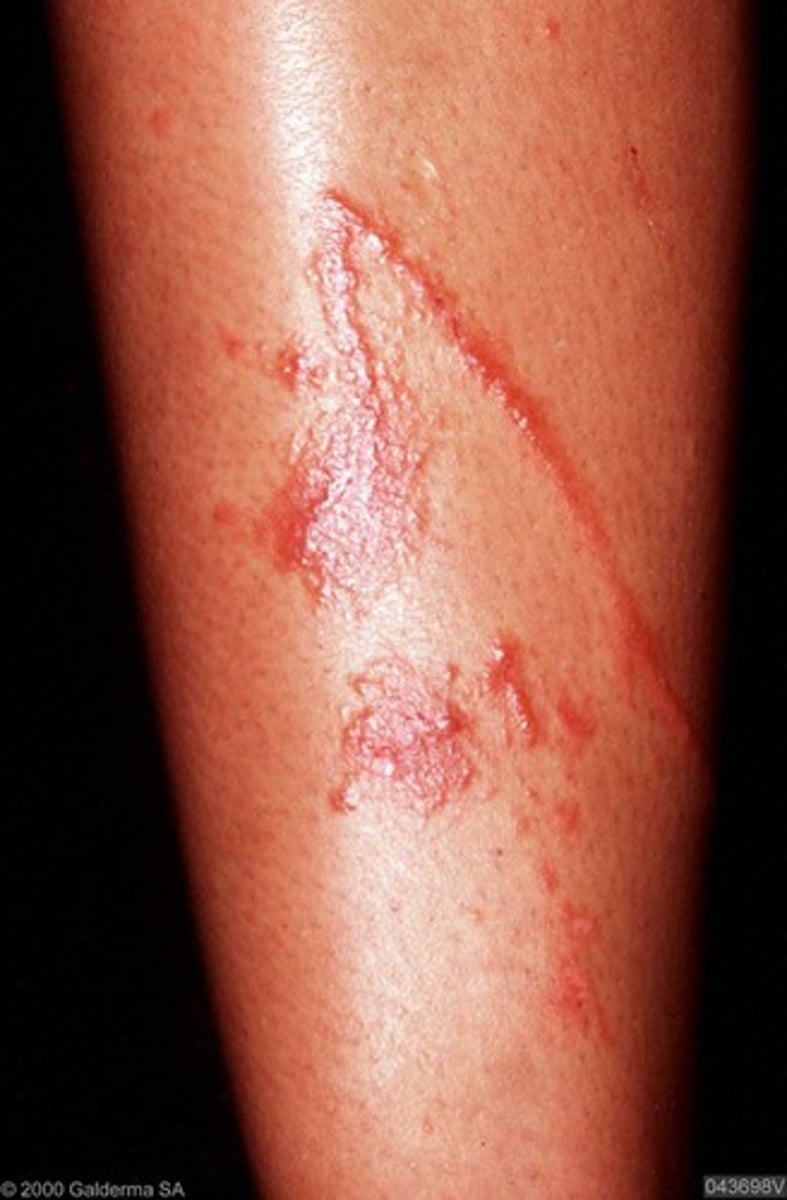
sensitization
increased or exaggerated sensitivity to products

perorial dermatitis
acne-like condition around the moth that may be caused by toothpaste or products used on the face

eczema
an inflammatory, painful itching disease of the skin that can be acute or chronic in nature with dry or moist lesions
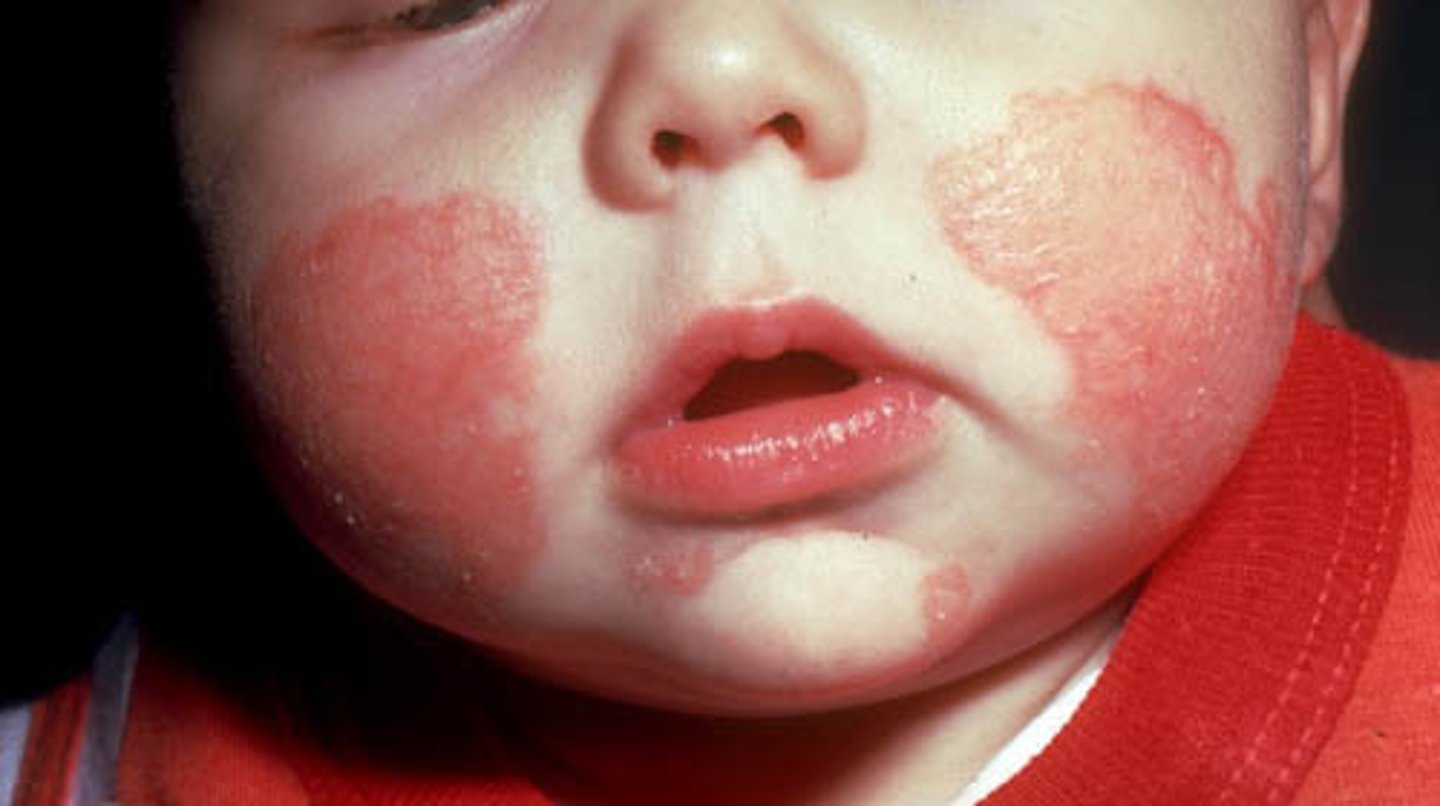
stasis dermatitis
Inflammation of the skin due to decreased circulation
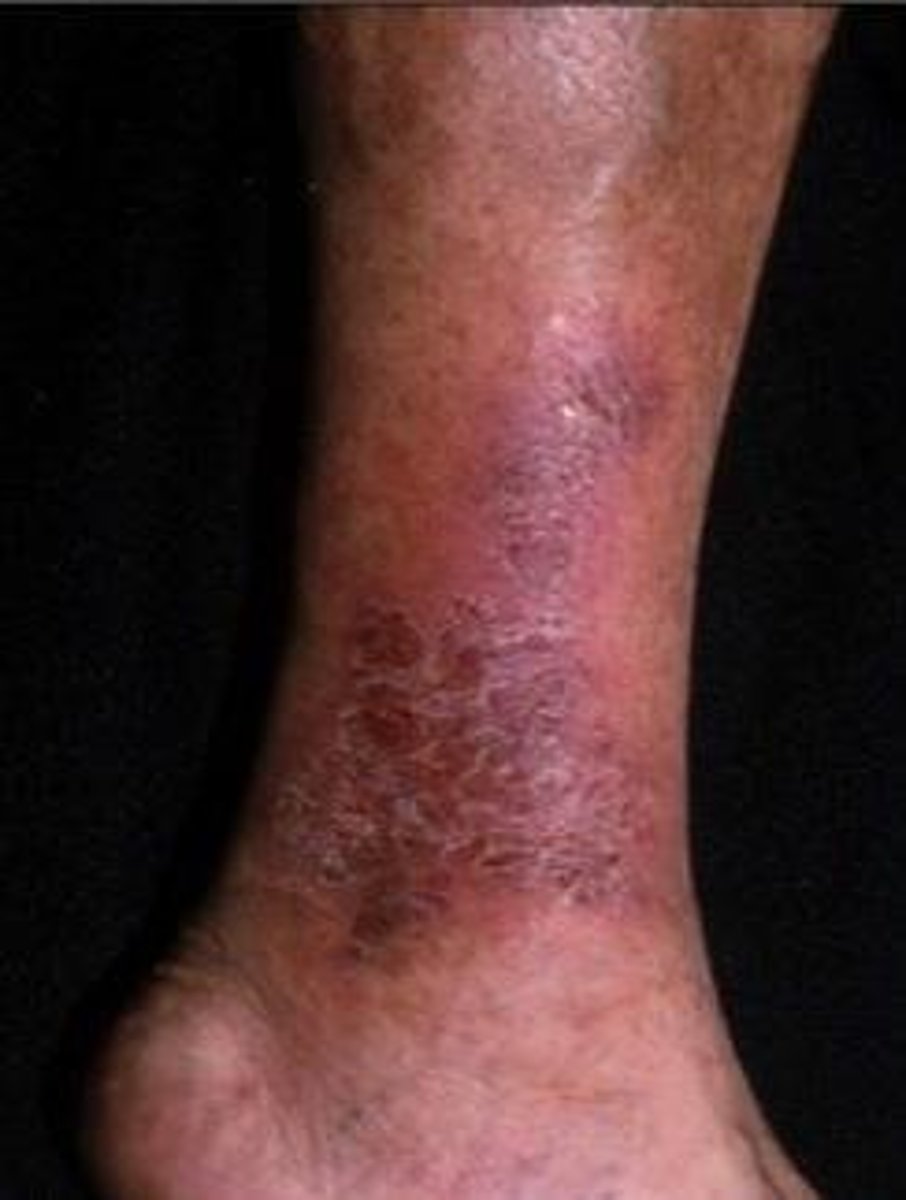
hyperkeratosis
thickening of the skin caused by a mass of keratinocytes
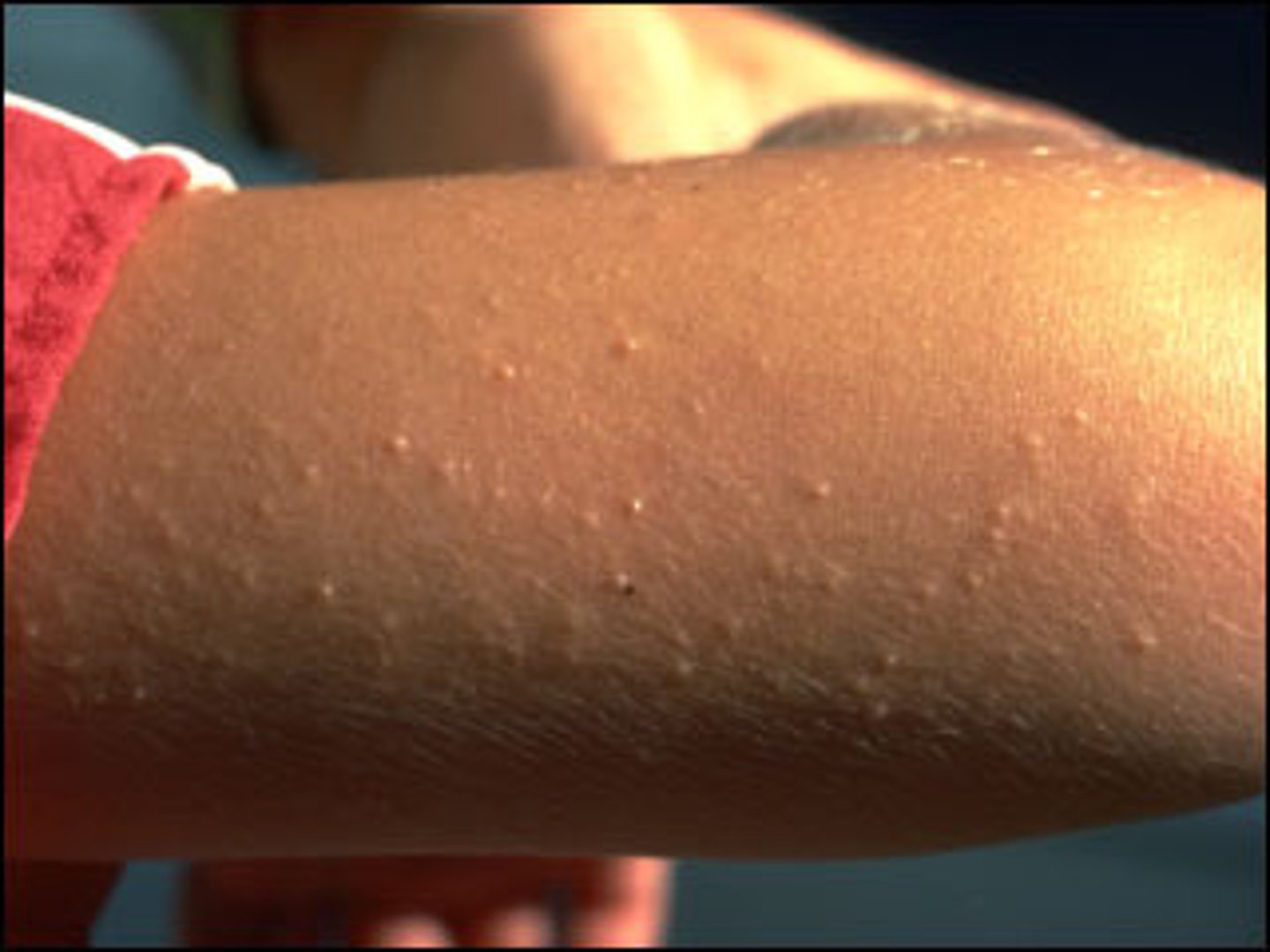
keratoma
an acquired, thickened patch of epidermis. a callus caused by pressure or friction
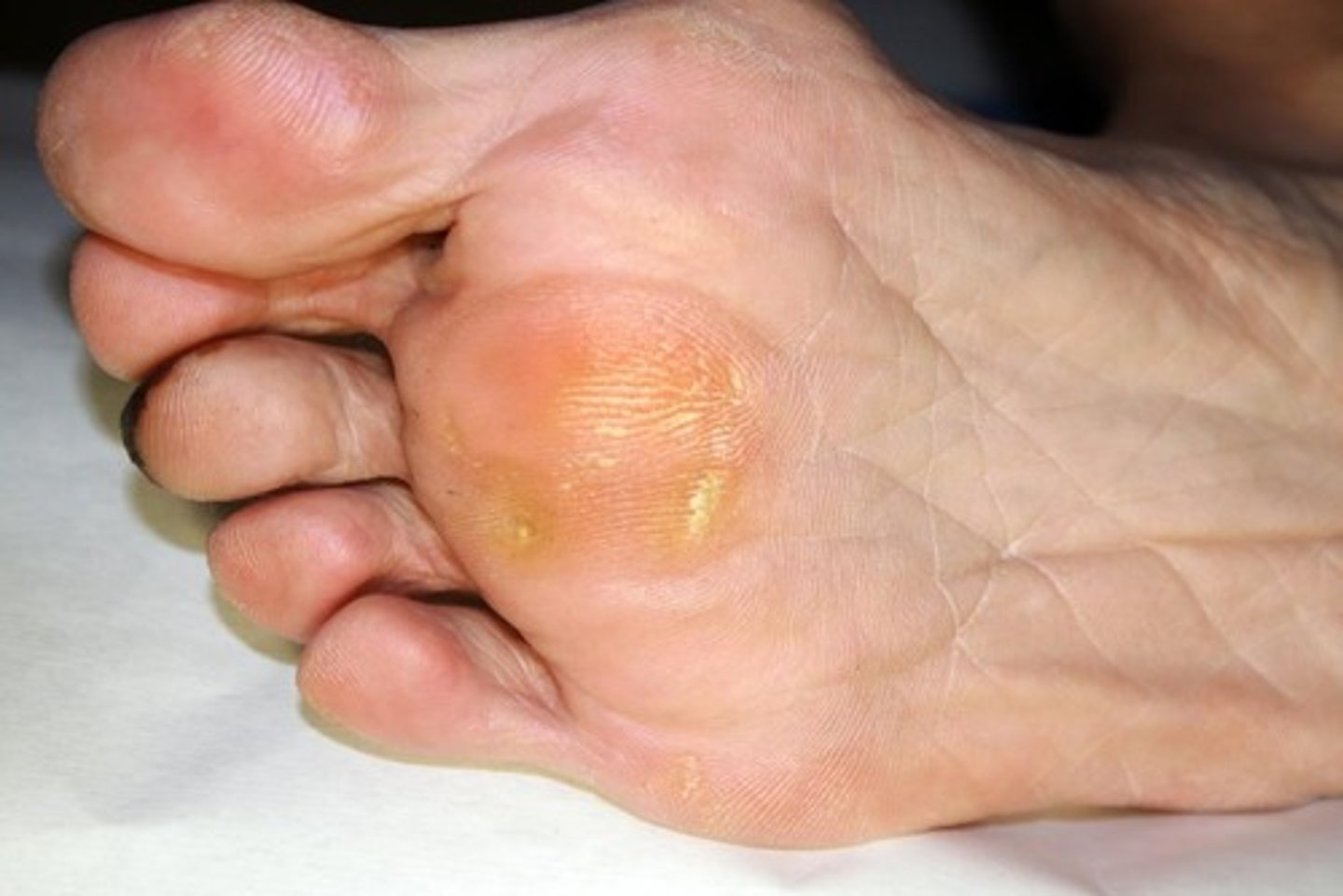
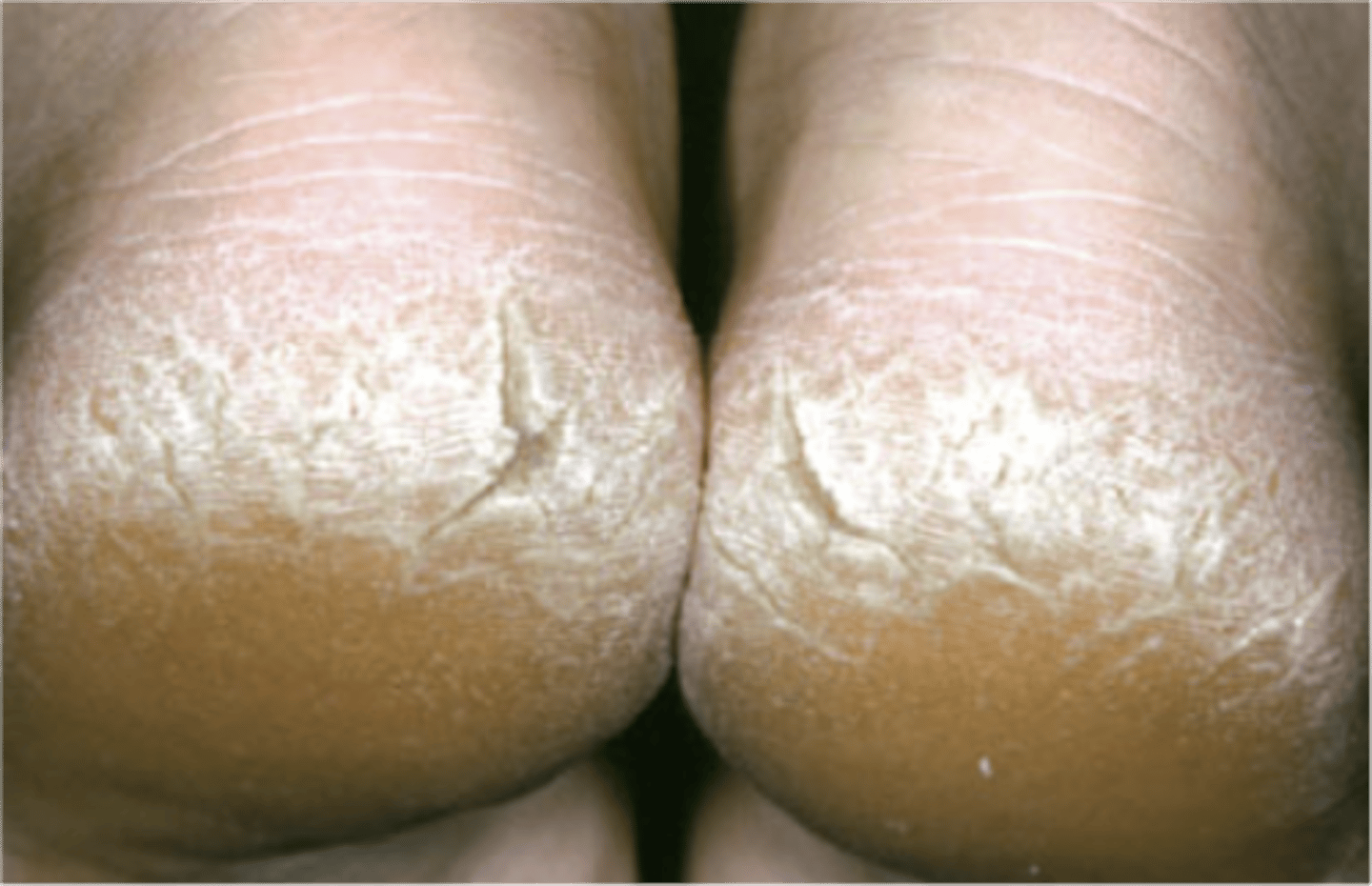
keratosis
abnormally thick buildup of cells
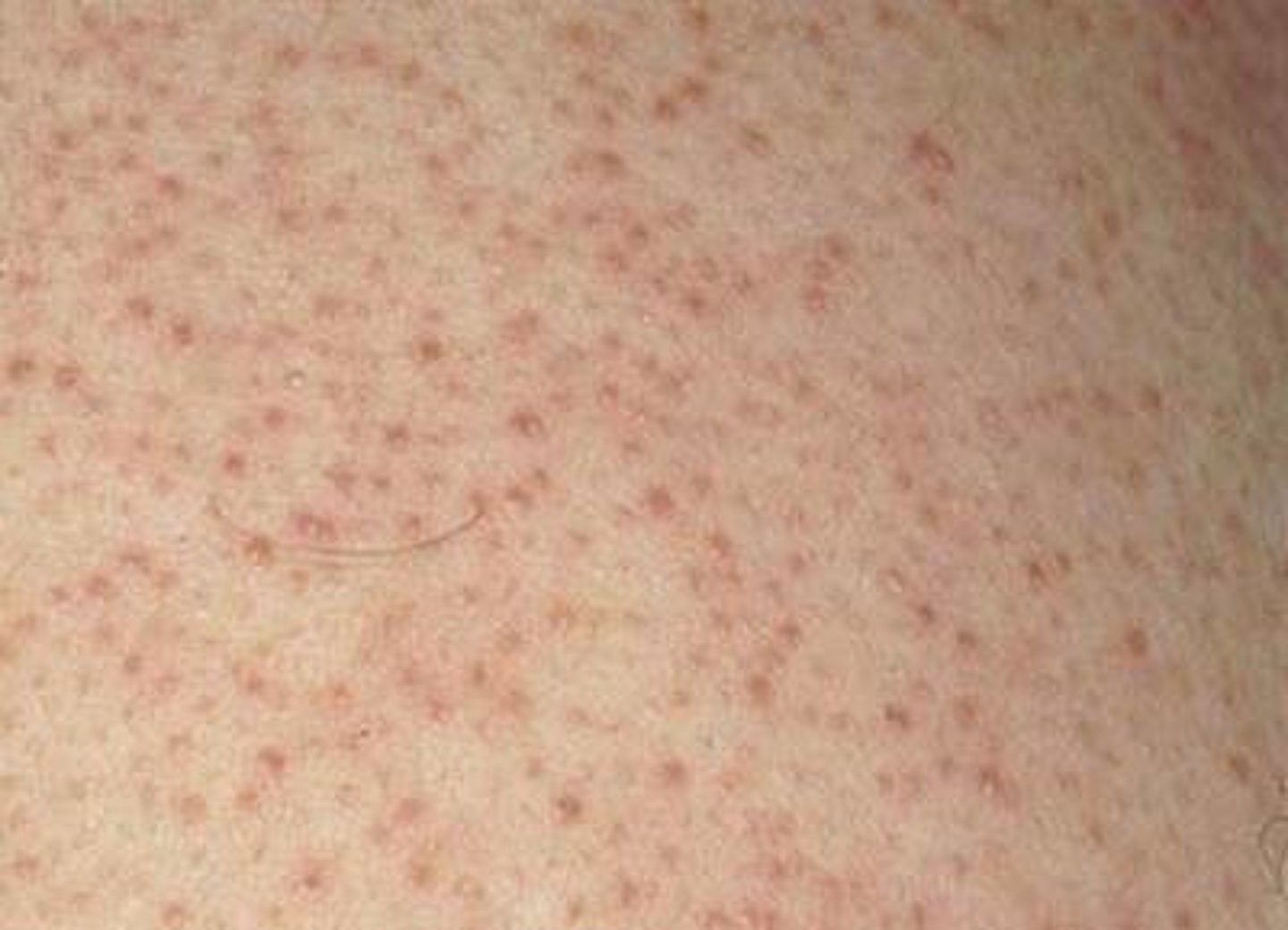
keratosis pilaris
Redness and bumpiness in the cheeks or upper arms; caused by blocked follicles
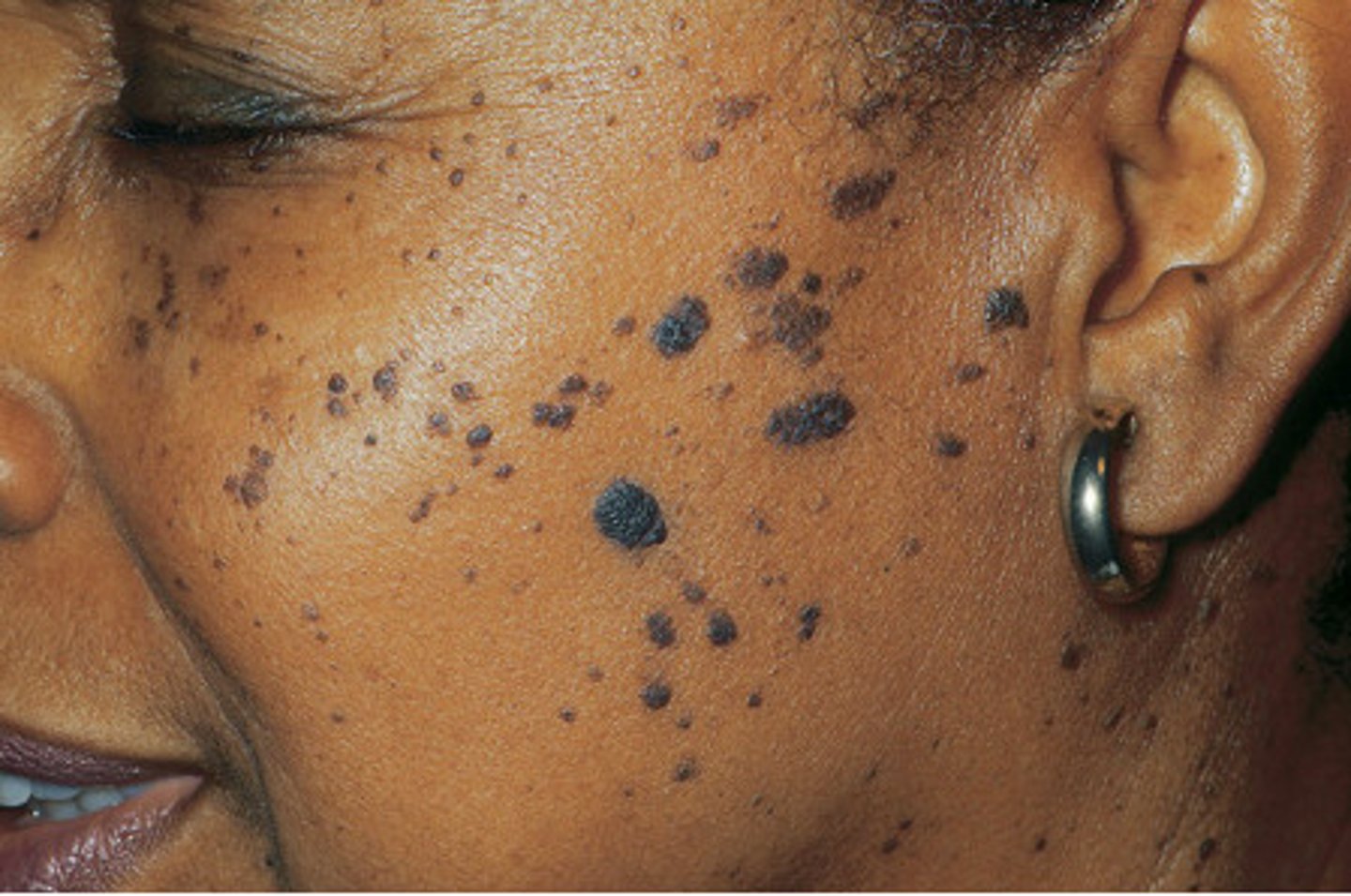
mole
pigmented nevus
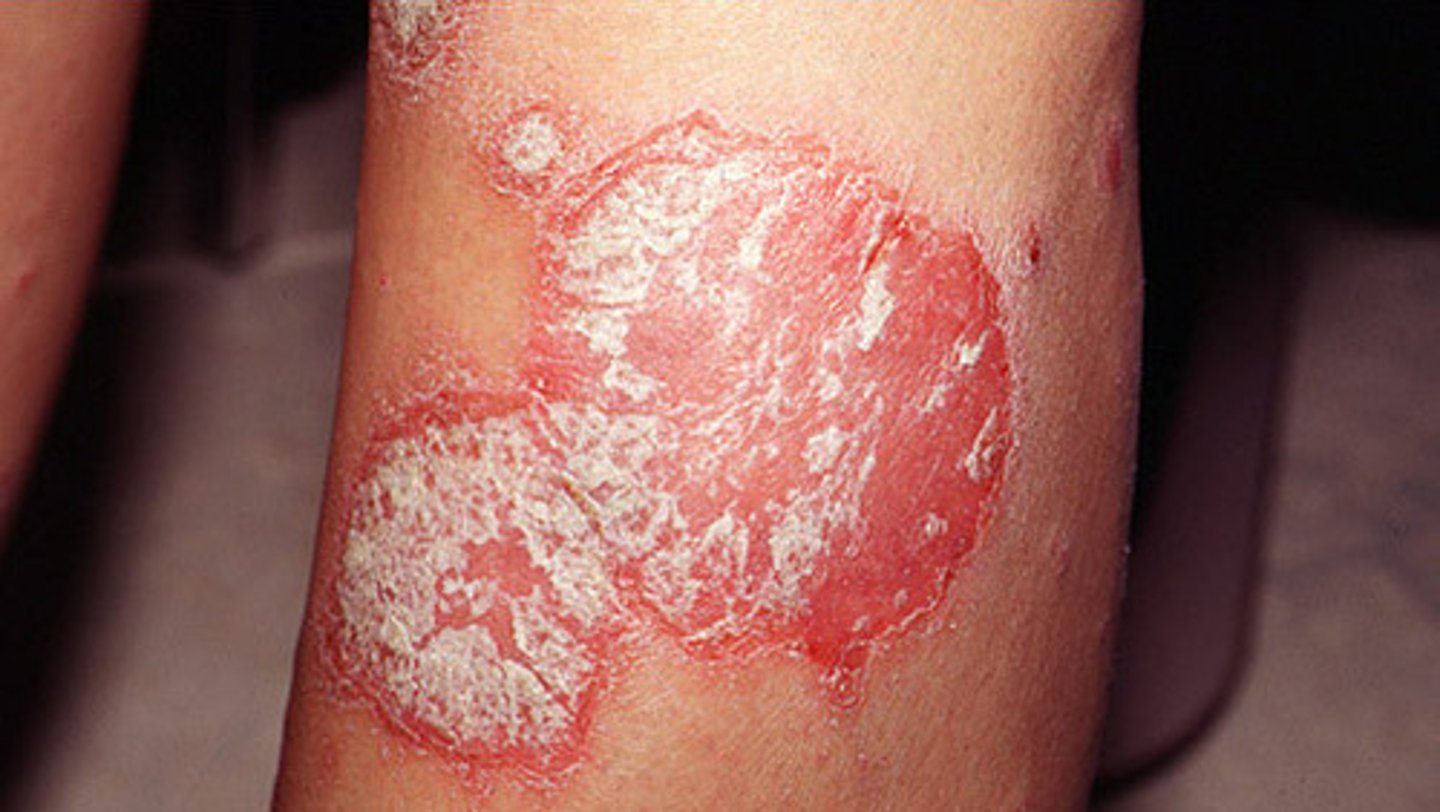
psoriasis
chronic skin condition producing red lesions covered with silvery scales
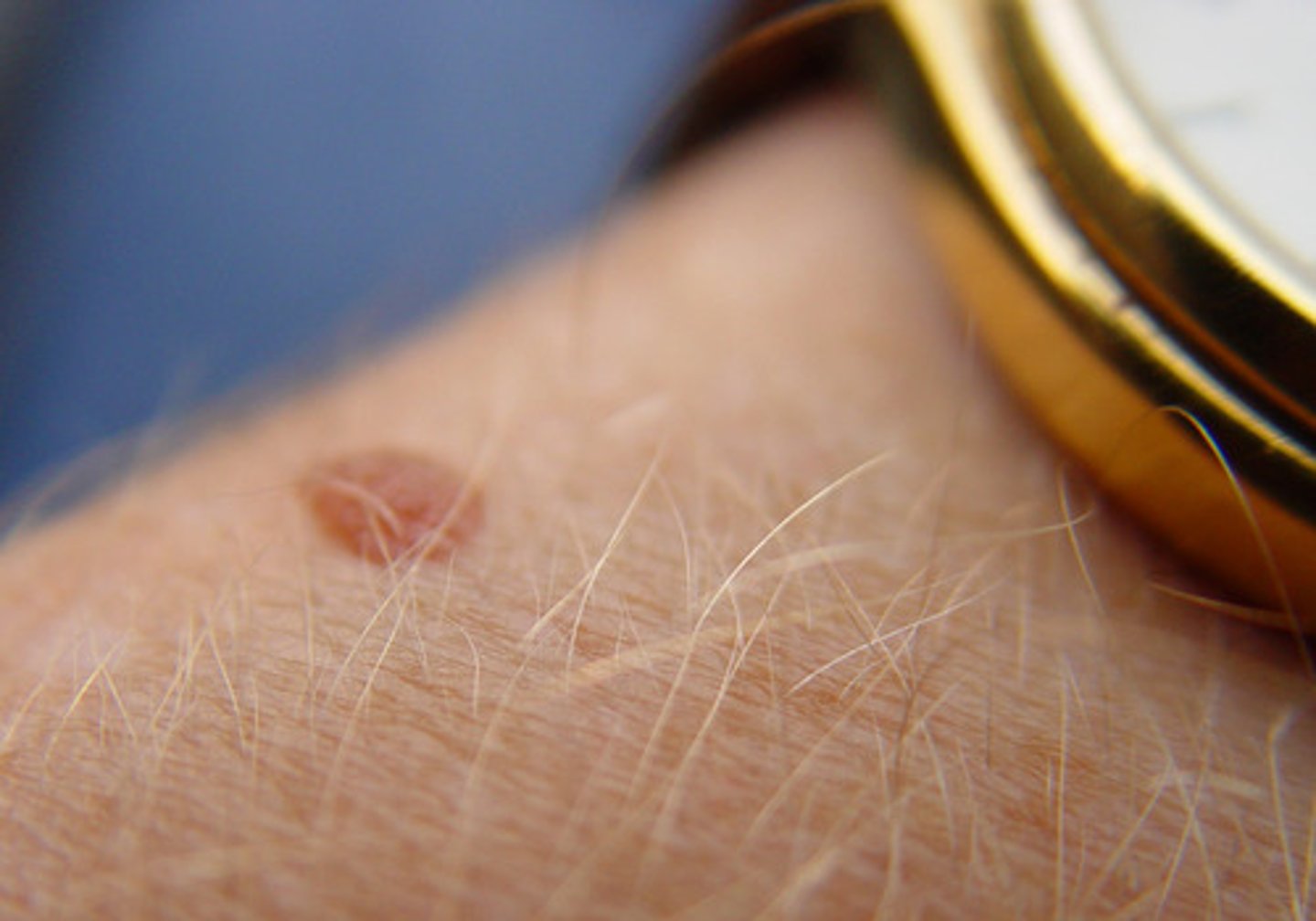
skin tag
small outgrowth or extension of skin that looks like a flap
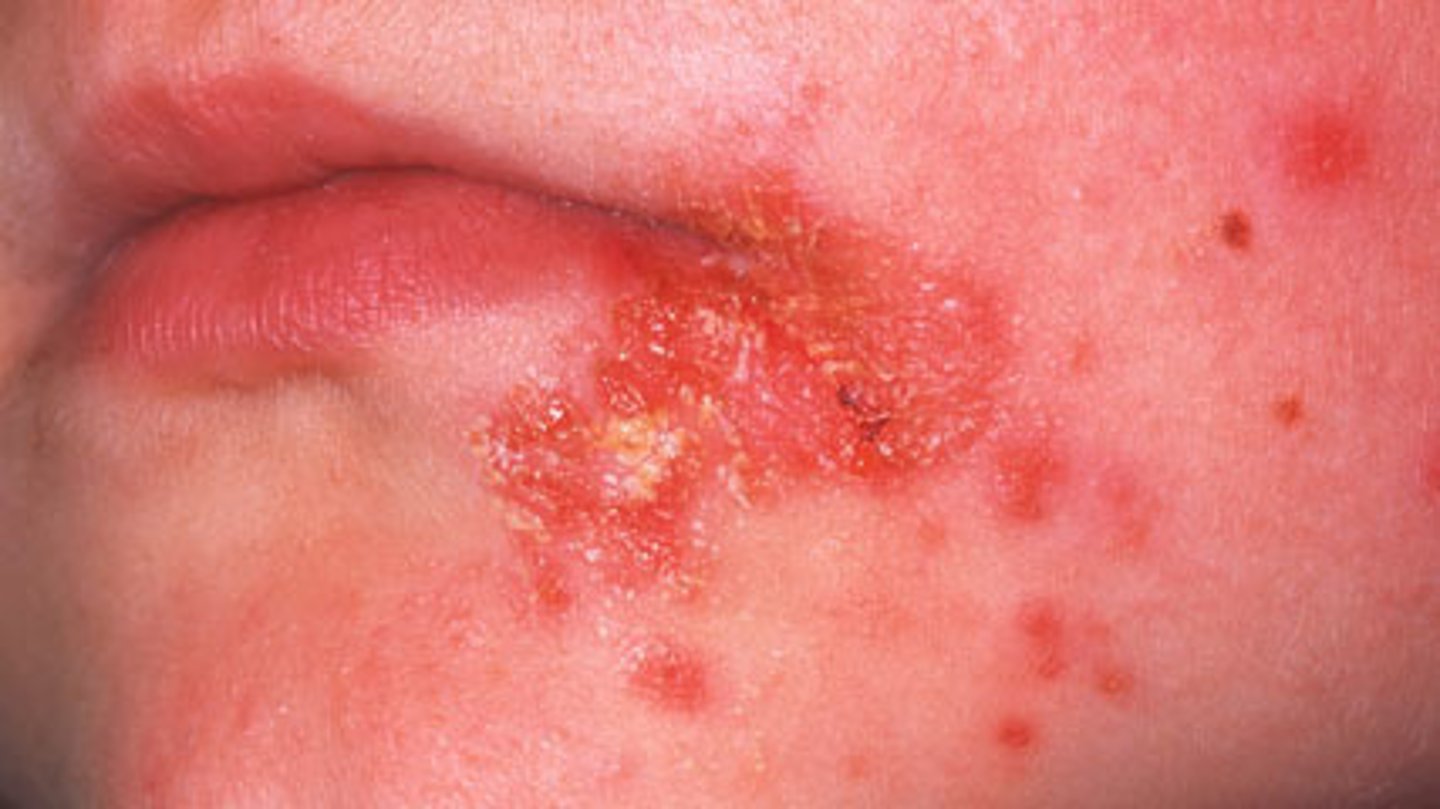
impetigo
clusters of small blisters or crusty lesions
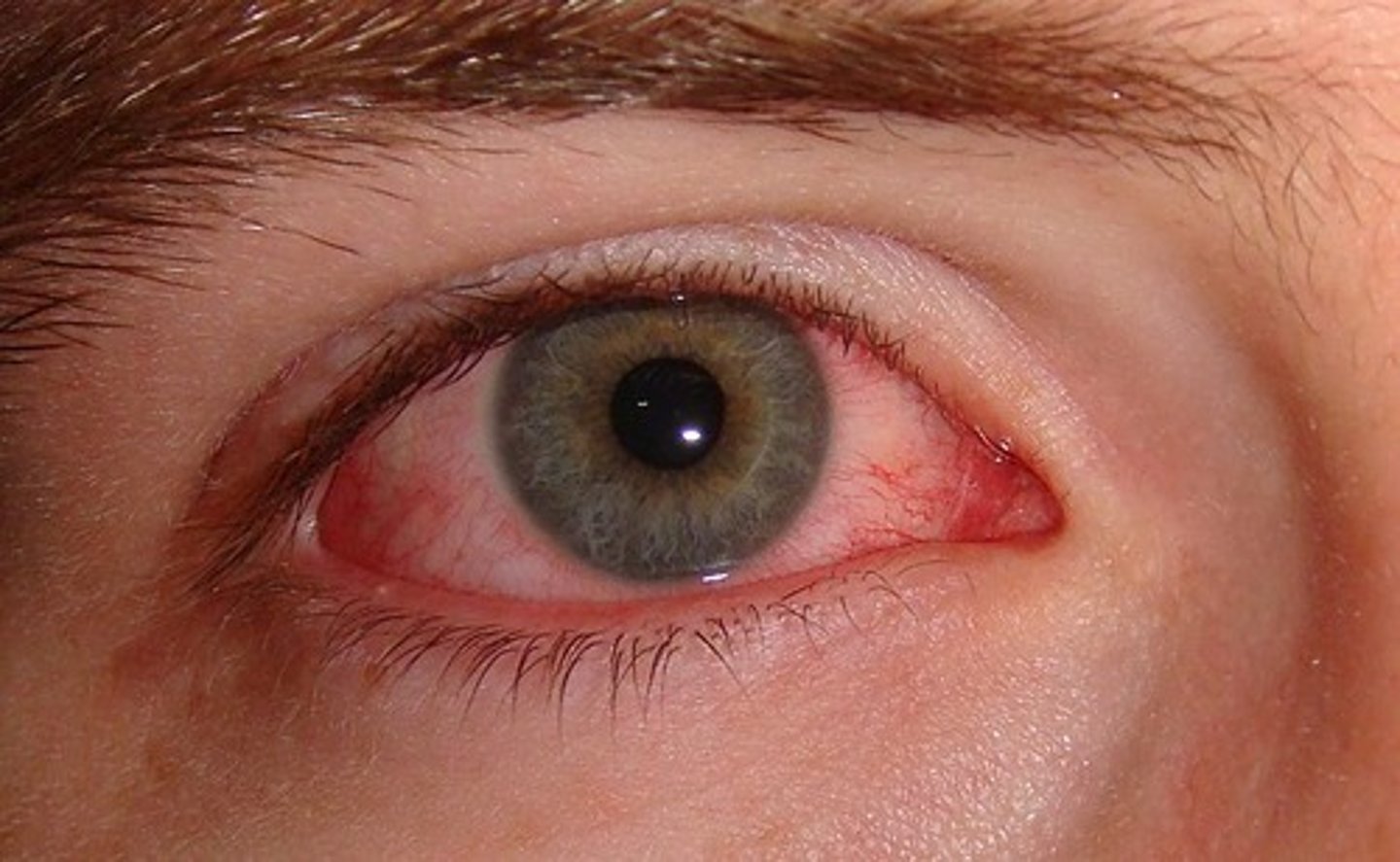
conjunctivitis
pink eye, infection of conjunctiva
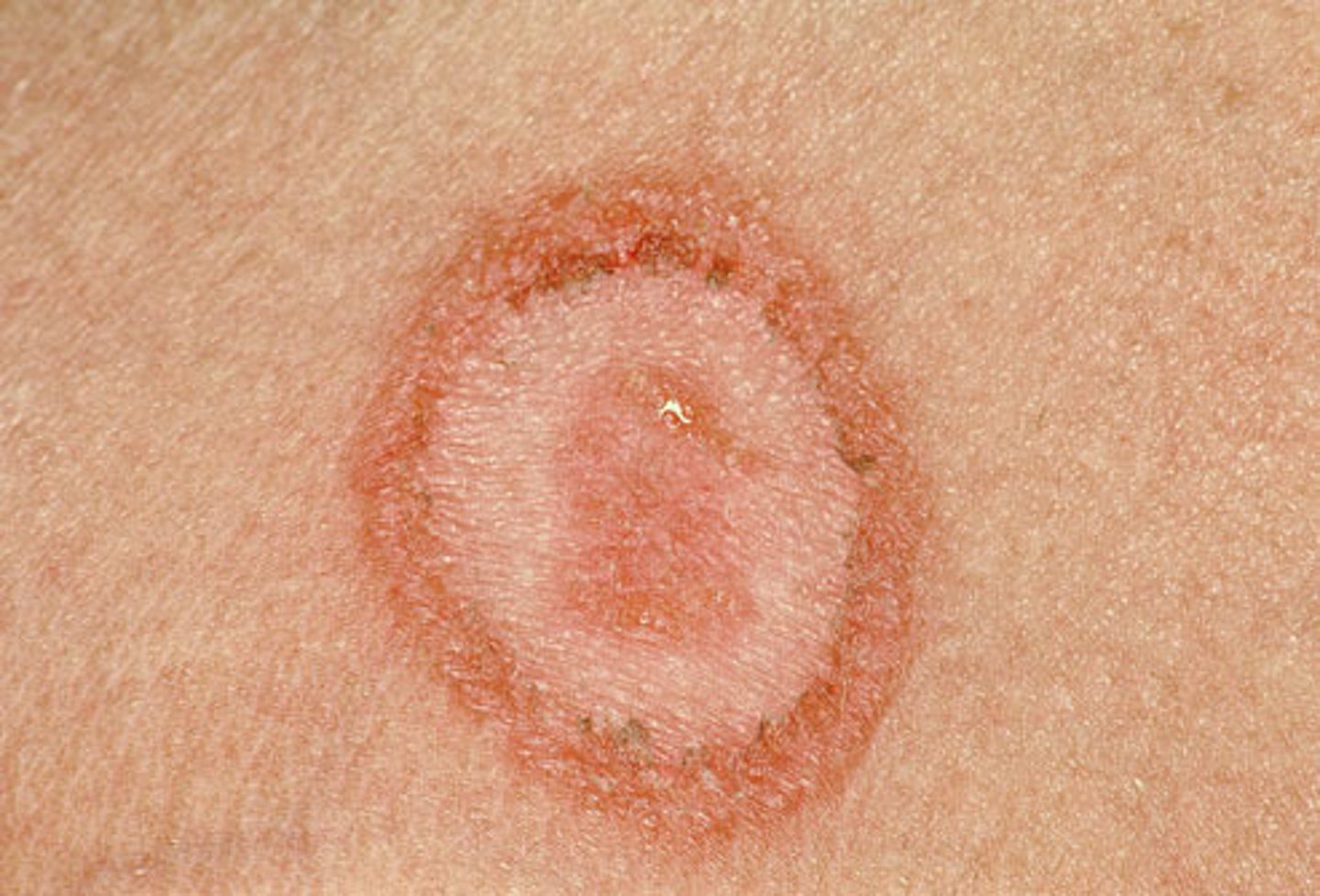
tinea corporis
ringworm
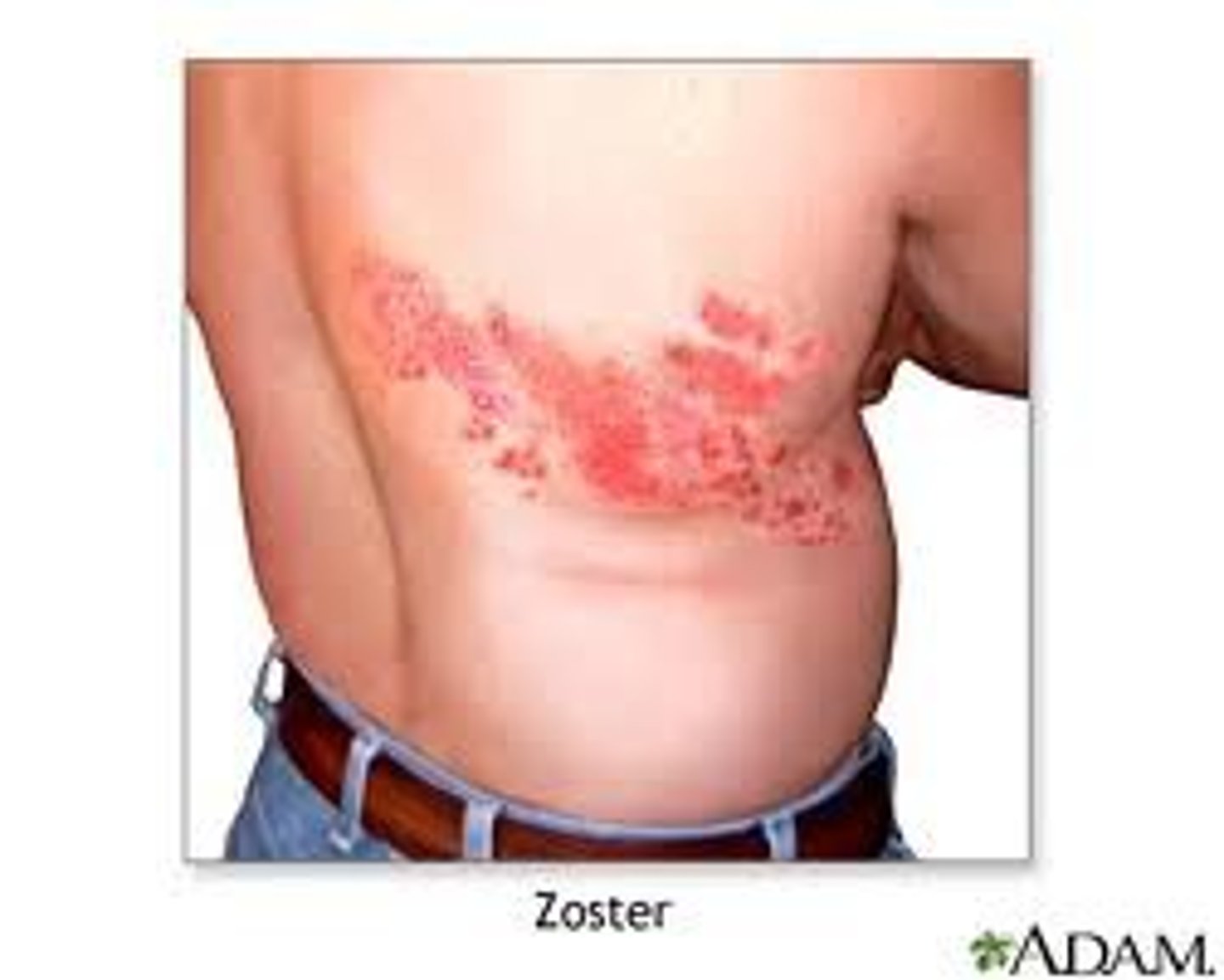
herpes zoster
Shingles; painful red blisters
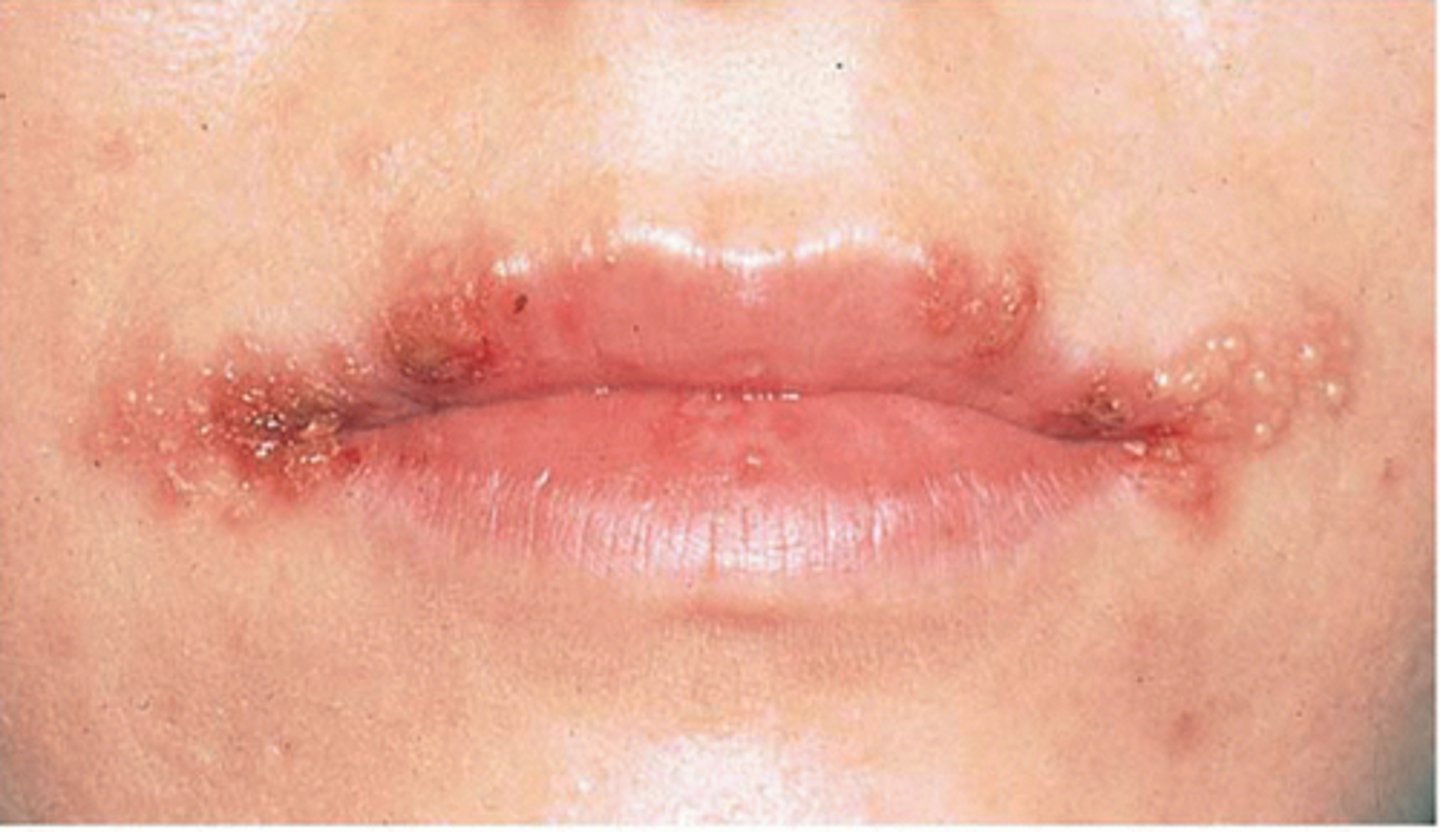
herpes simplex virus 1
Strain of the herpes virus that causes fever blisters or cold sores; it is a recurring, contagious viral infection consisting of a vesicle or group of vesicles on a red, swollen base. The blisters usually appear on the lips or nostrils.
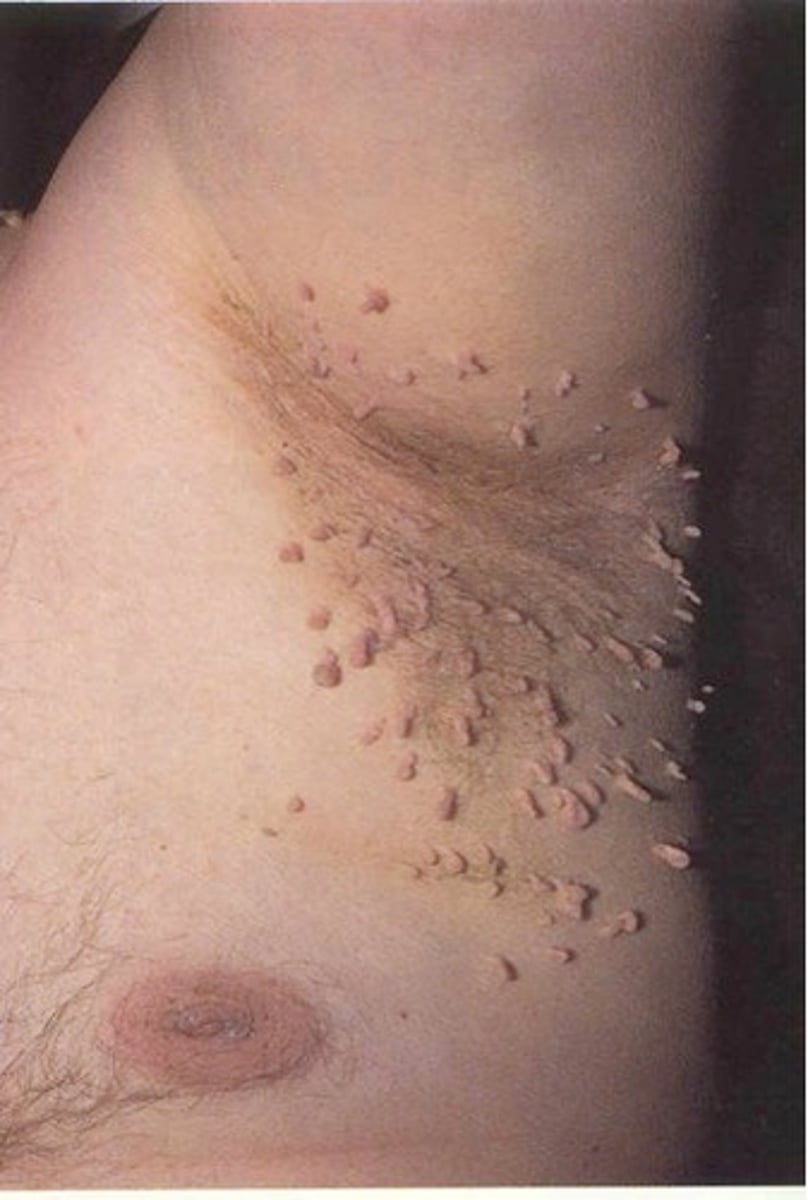
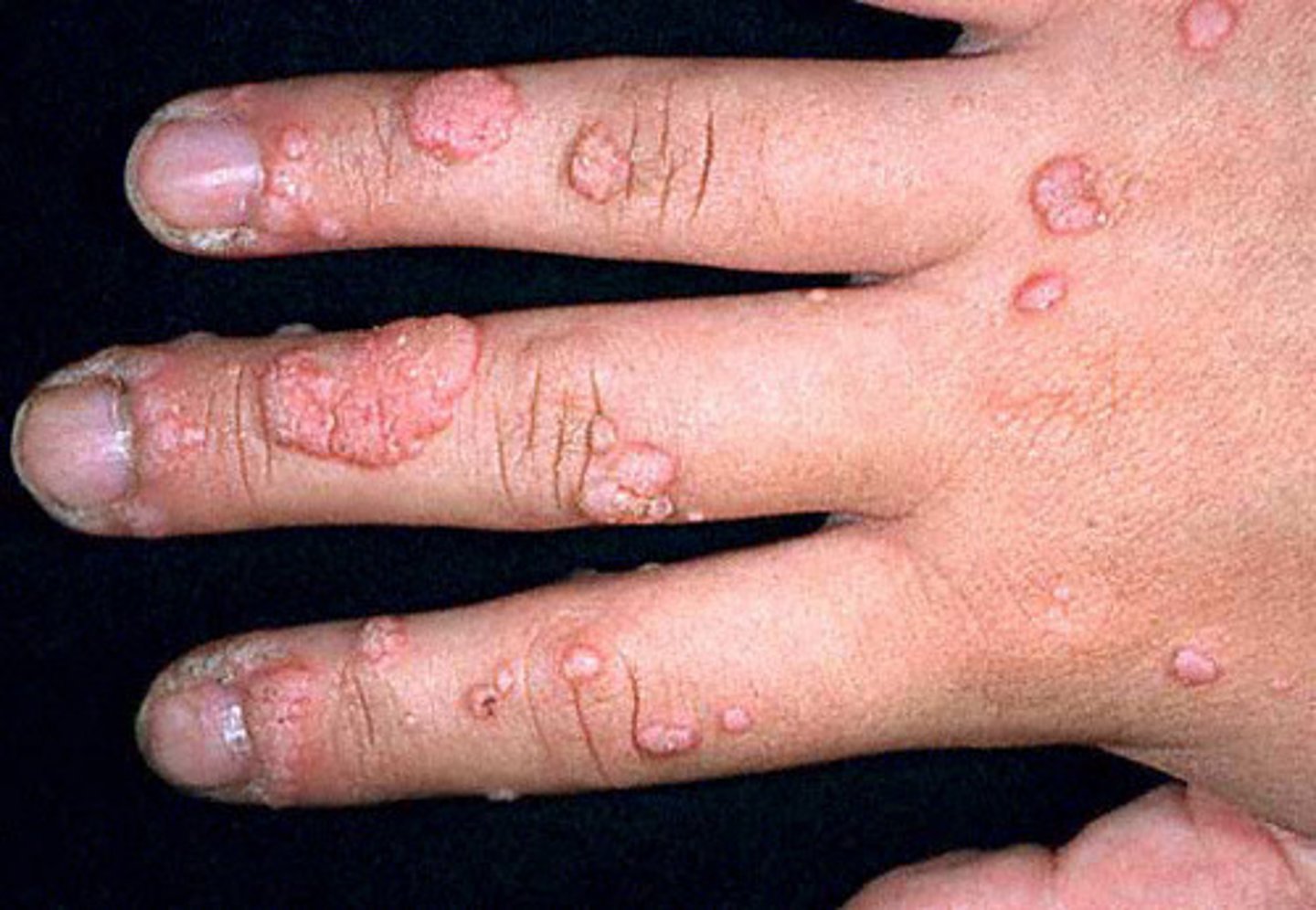
verruca
wart caused by a virus
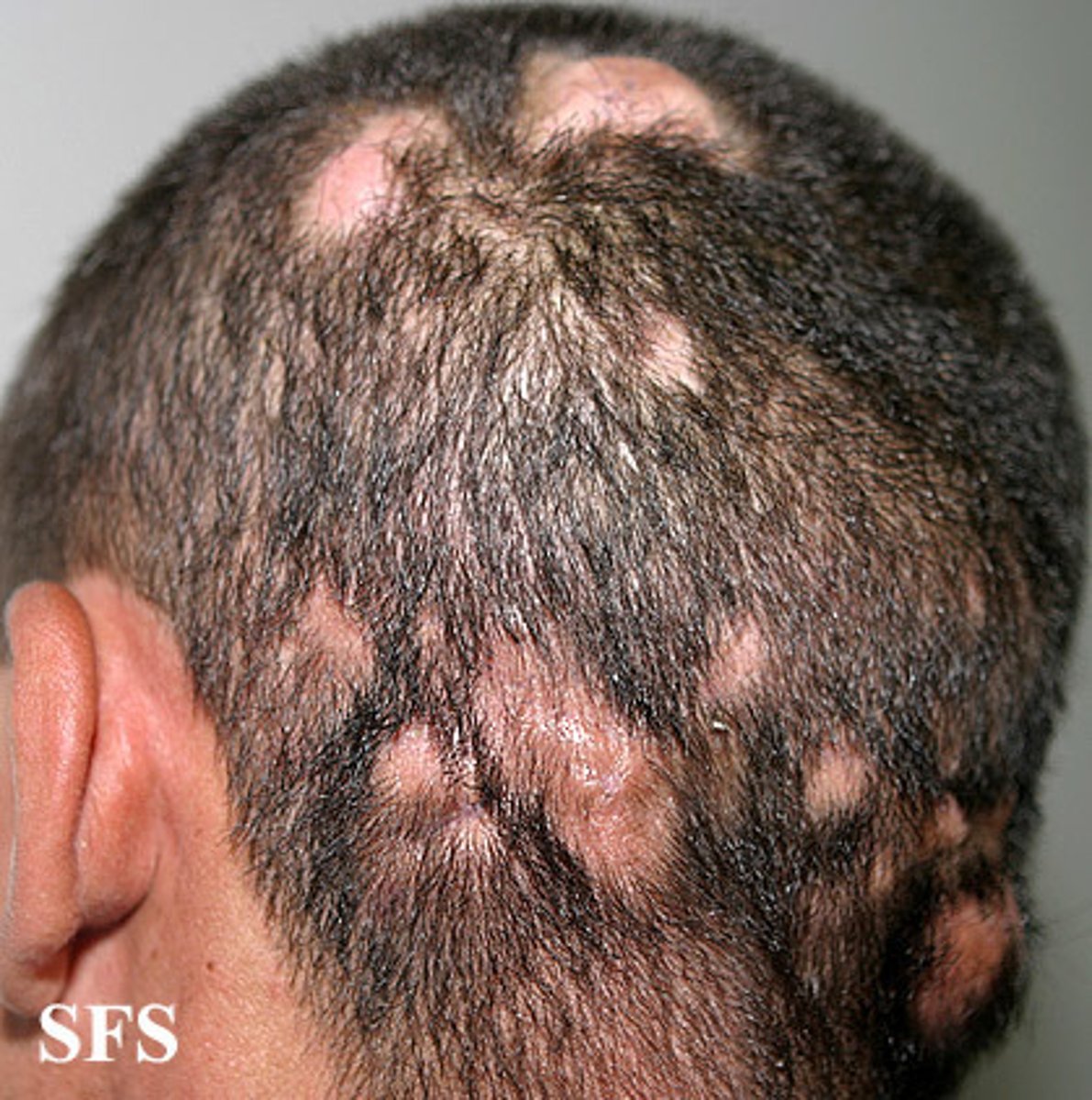
tinea
A fungal infection of the skin, hair, or nails; also known as ringworm.
herpes simplex virus 2
genital herpes; waxing may cause a breakout
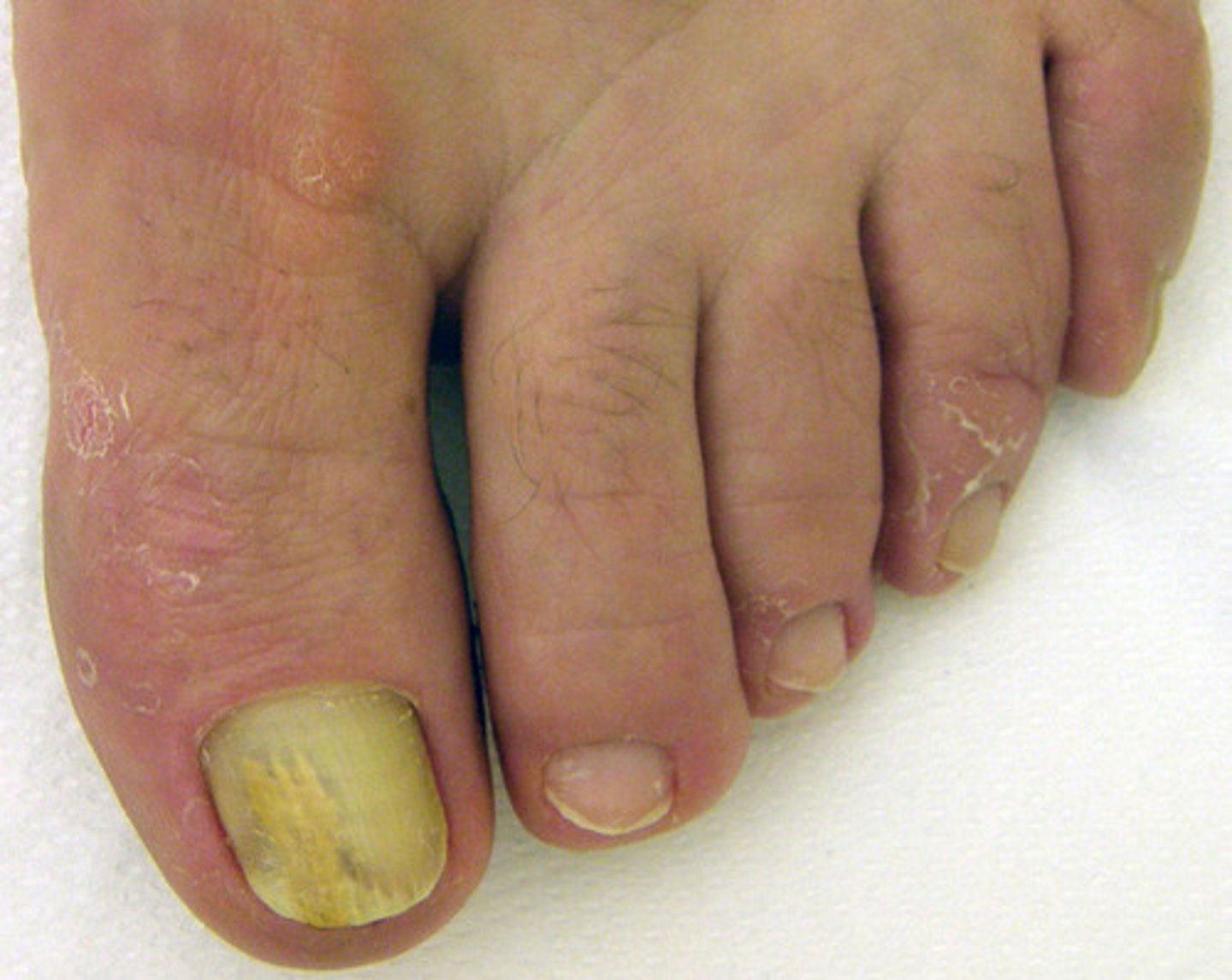
onychomycosis
thick, brittle, discolored nails
dermatillomania
compulsive skin picking, often to the point of physical damage; an impulse control disorder
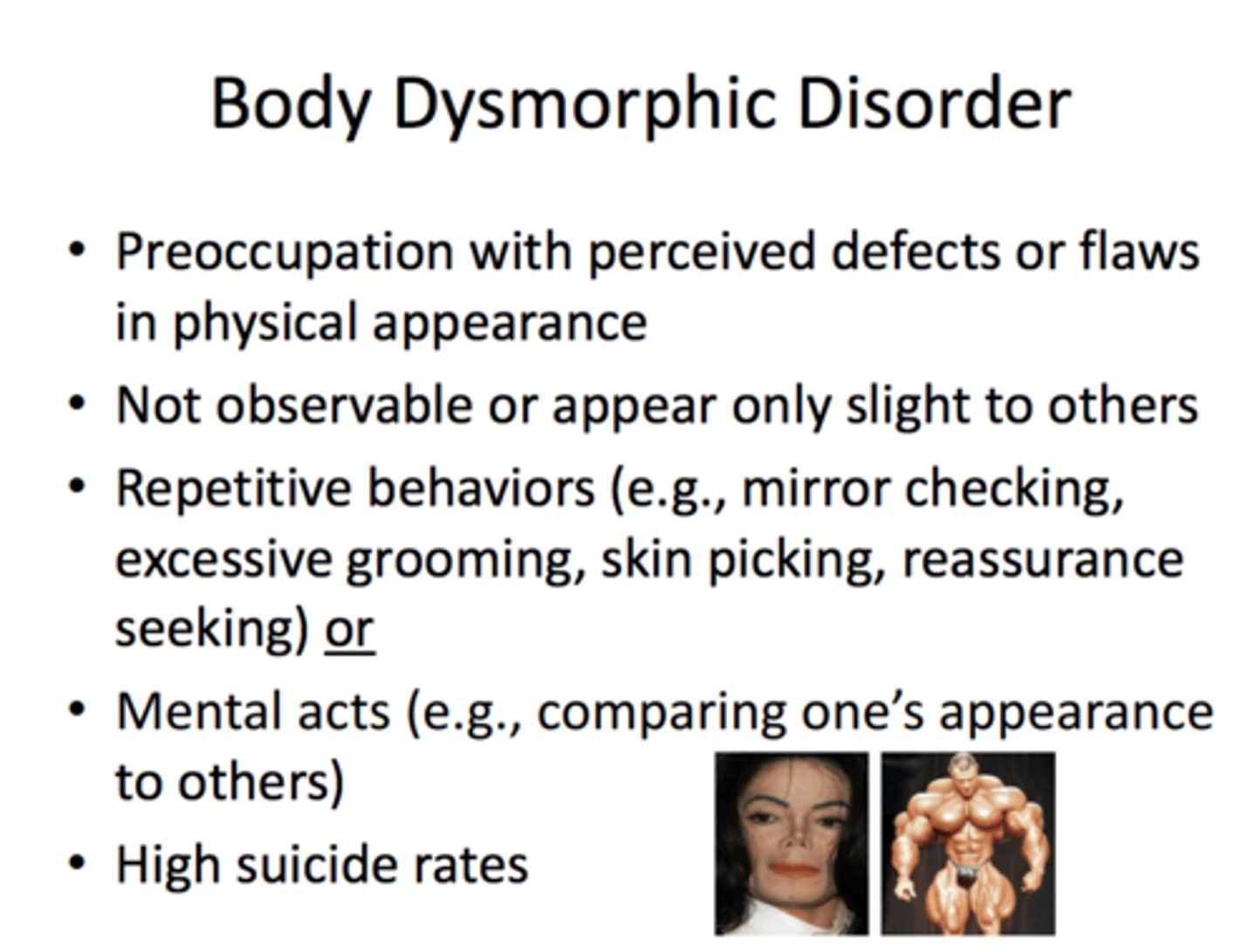
body dysmorphic disorder
a disorder characterized by the unrealistic perception of physical flaws
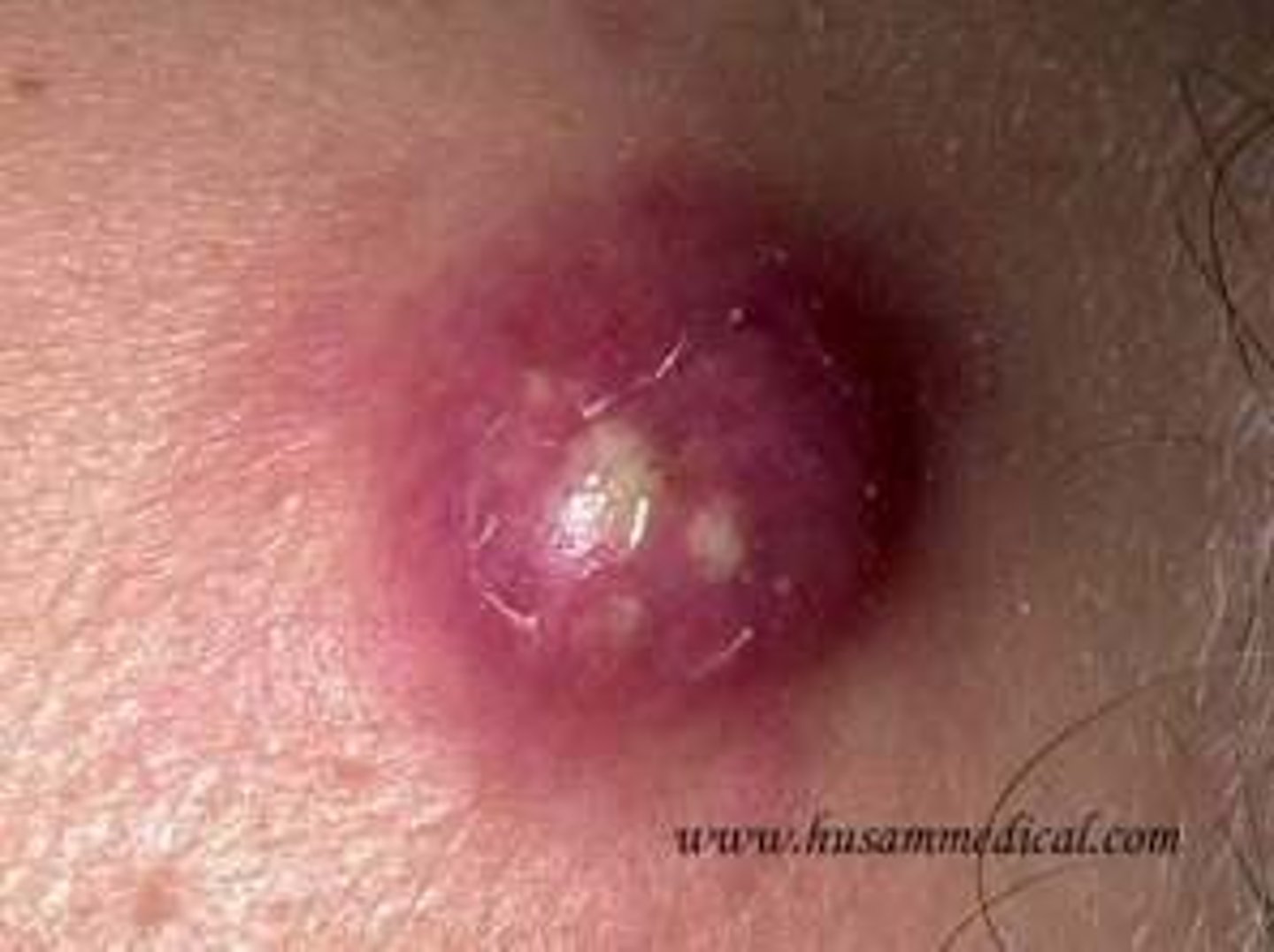
furuncle
boil; suppurative inflammatory skin lesion due to infected hair follicle
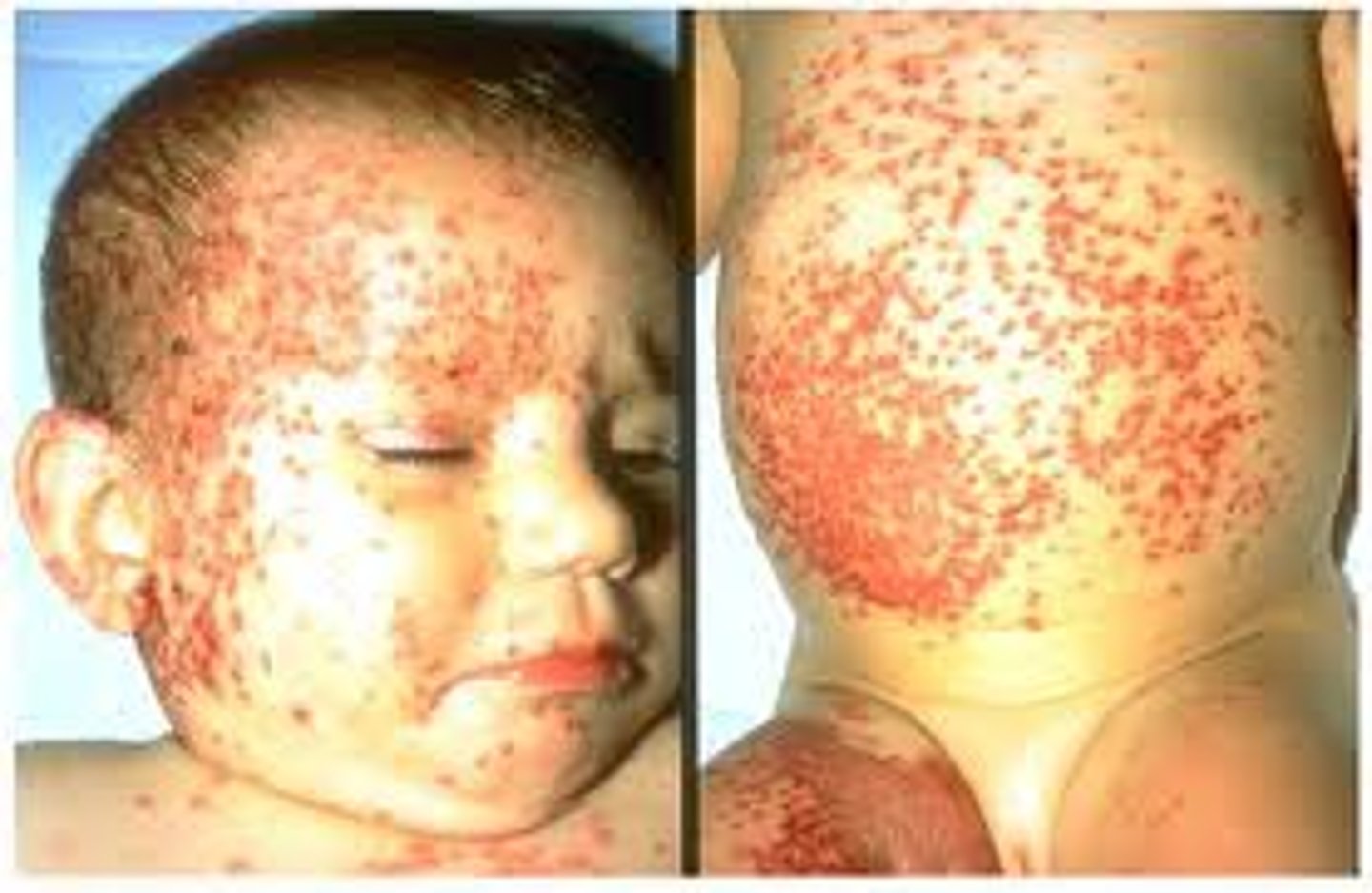
erythema
Redness caused by inflammation; a red lesion is erythemic.
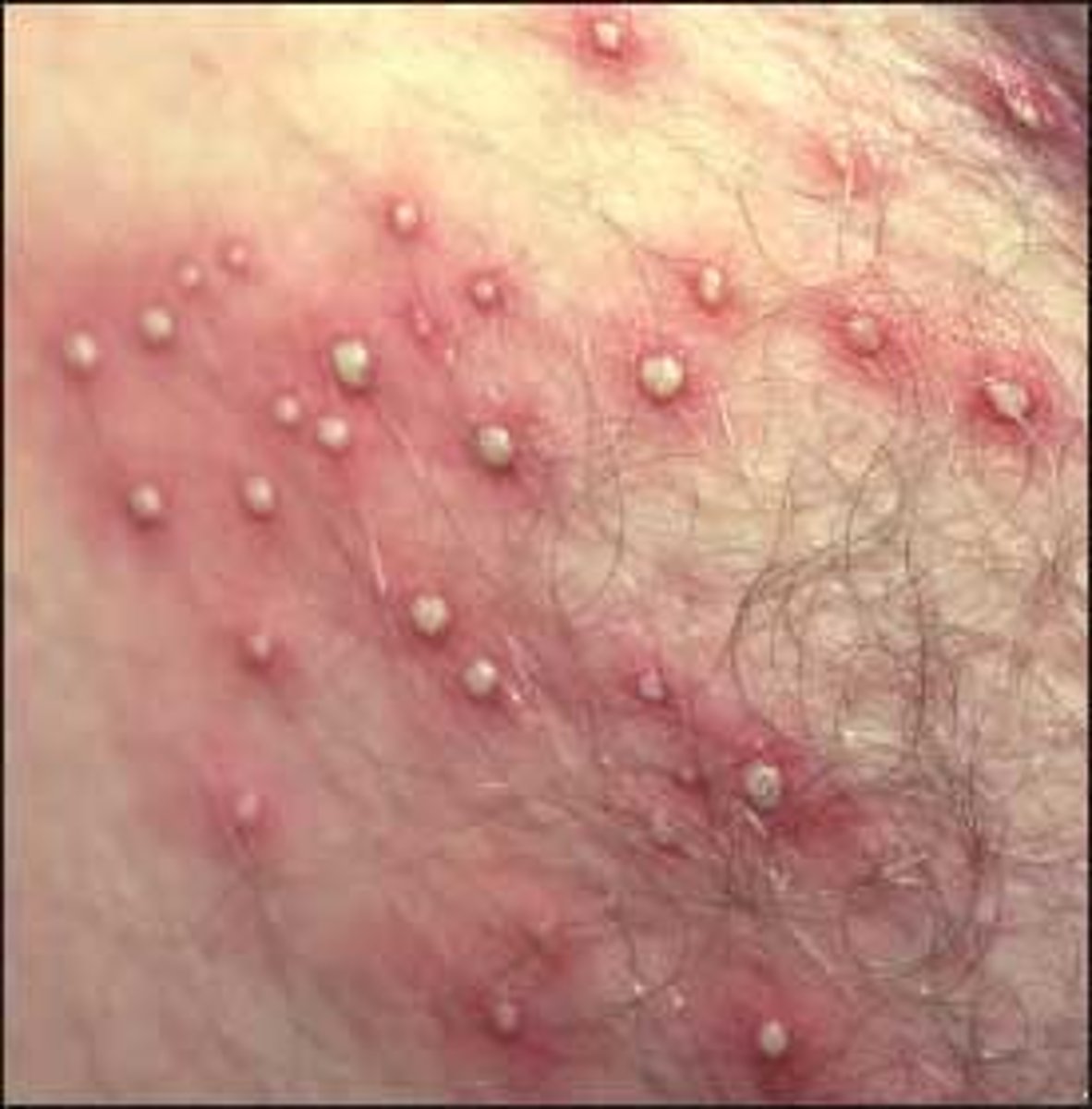
folliculitis
when hair grows under the surface of the skin instead of growing up and out of the follicle, causing a bacterial infection
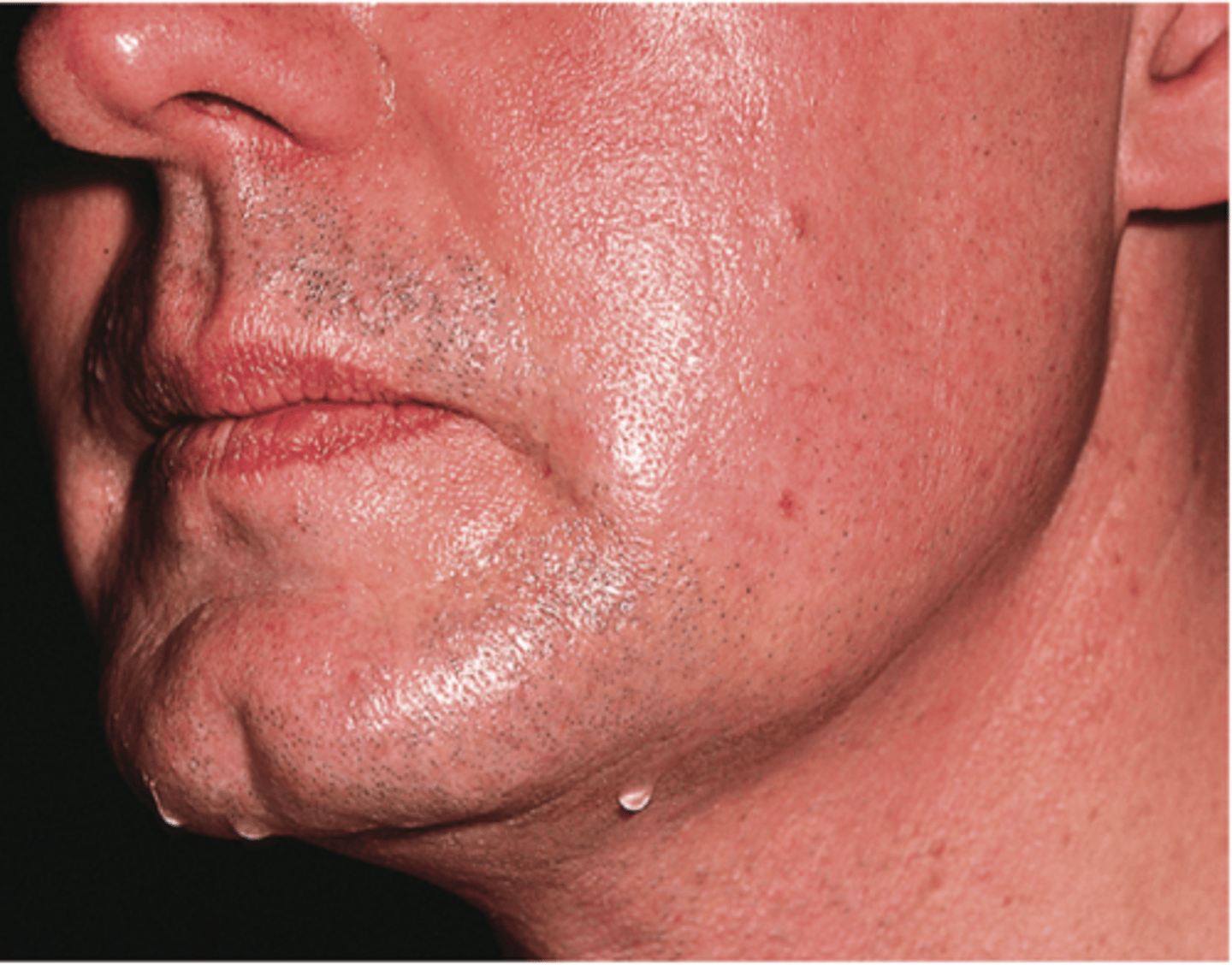
anhidrosis
abnormal condition of no sweat

bromhidrosis
foul smelling perspiration found on armpits or feet

hyperhidrosis
abnormal condition of excessive sweat caused by heat, genetics or medications
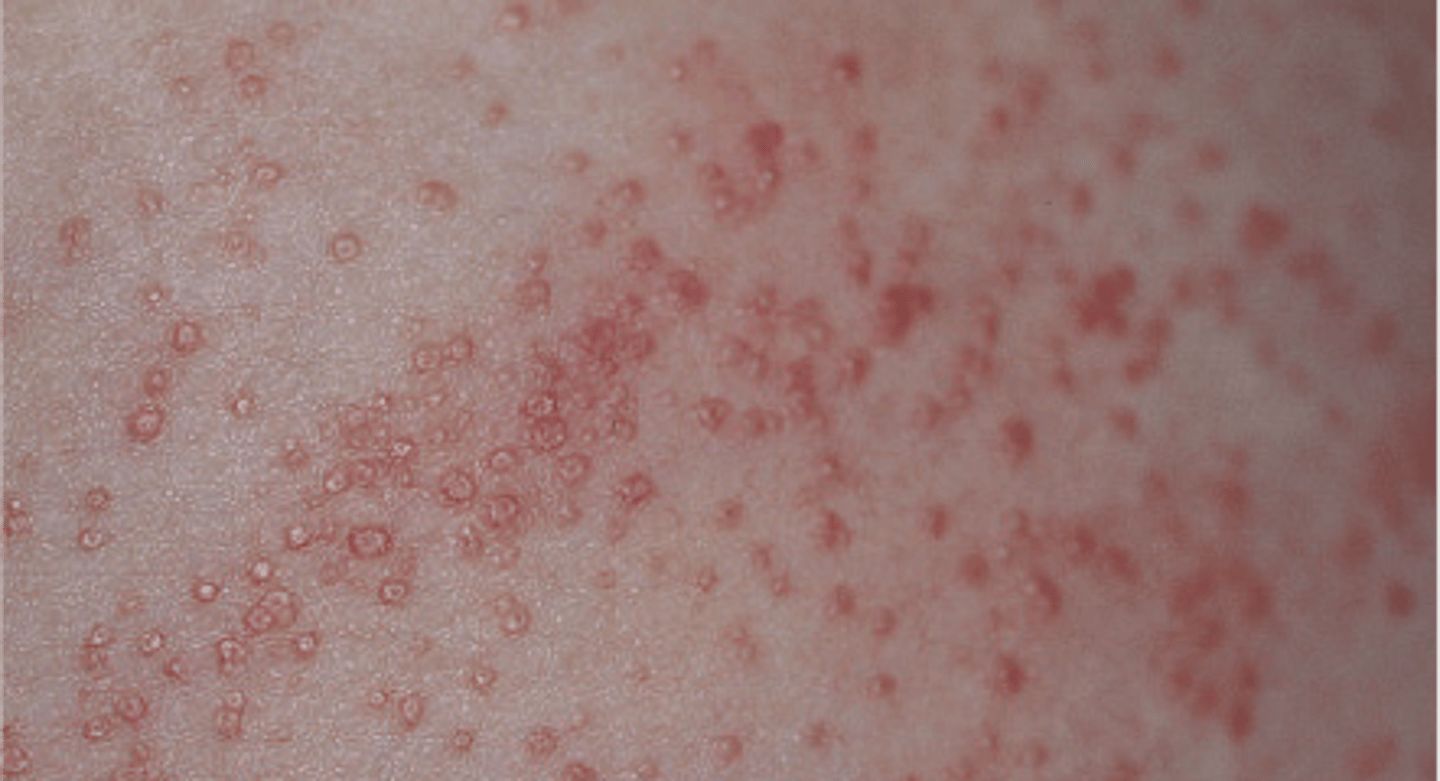
diaphoresis
excessive sweating due to an underlying medical condition

miliaria rubra
Prickly heat; acute inflammatory disorder of the sweat glands
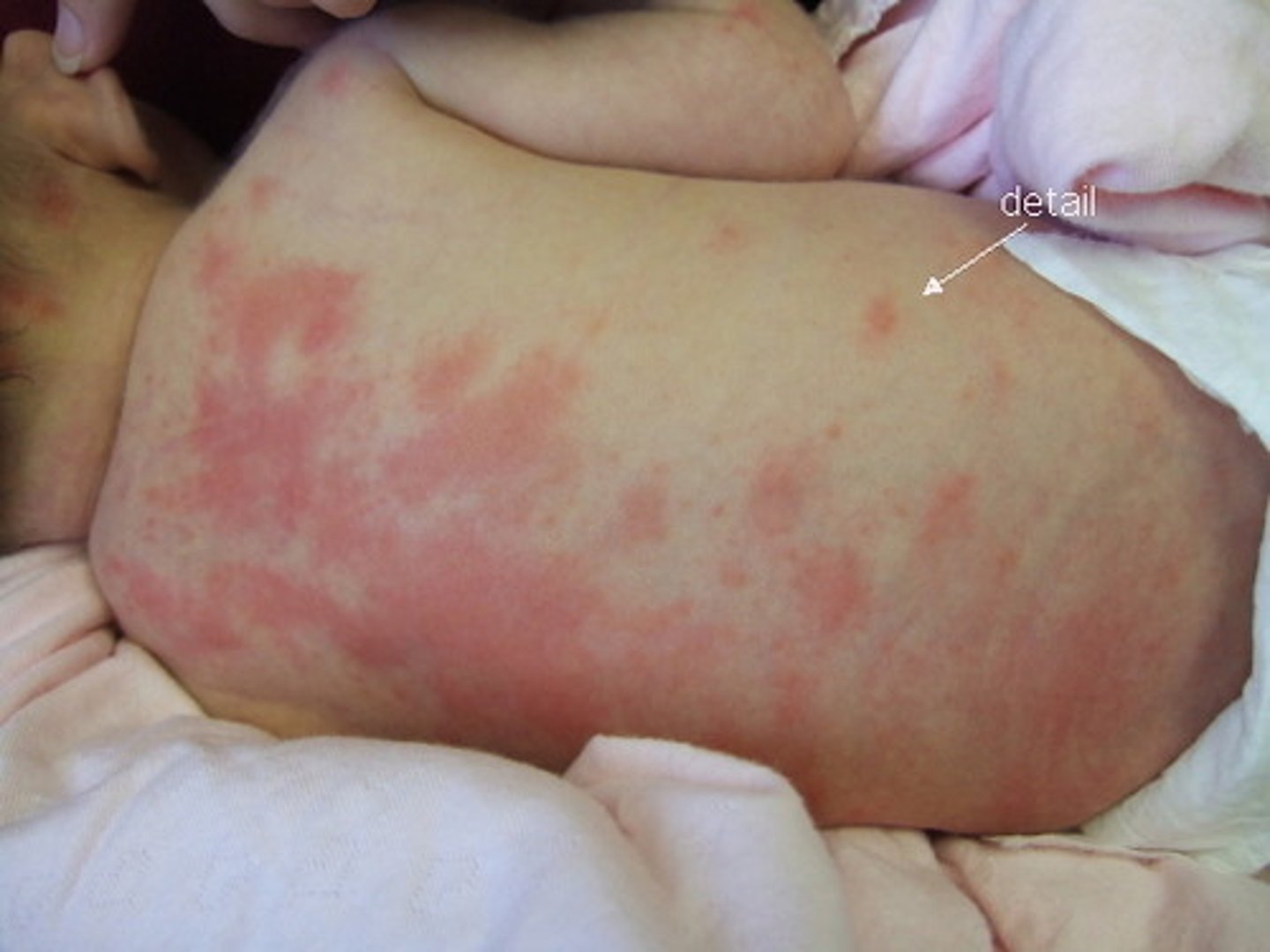
urticaria
medical term for hives