Glencoe Biology Chapter 11 Test
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
True
True or False: Most diseases and disorders are recessive disorders, which are rare, but are mostly common in certain ethnic or small groups..
Homozygous Recessive
Fill In The Blank: In order for a recessive disorder to be expressed, it must be __________________________ ___________________.

Heterozygotes
Heterozygous individuals; only carry the trait - called carriers
Cystic Fibrosis
(Recessive)Most common among Caucasians; most often lethal; mucous build-up in lungs and digestive system; poor digestion & breathing; drugs & therapy to help
Cystic Fibrosis
(Recessive)Mucous build-up in the lungs and digestive system; causes poor digestion and breathing; drugs and therapy can help this
Albanism
(Recessive)Can occur in any race (humans & animals); absence of the skin pigment, called melanin; white hair, very pale skin, and pink pupils; the eyes may be blue or pink; different types; skin causes severe problems

Melanin
Absence of a skin pigment
Albanism
(Recessive)Absence of the skin pigment, called melanin; can cause white hair, very pale skin, and pink pupils (eyes may be blue or pink)
Tay-Sachs Disease
(Recessive)Most common in Penn-Dutch in US & Jewish people with European ancestry; gene is on chromosome 15; a CNS problem; build-up of lipids in the cells due to a lack of enzymes; red spot on back of eye; blindness, loss of movement, and mental deterioration; has no treatment
Tay-Sachs Disease
(Recessive)Build-up of lipids in the cells due to a lack of enzymes, causing a red spot on back of the eye; can lead to blindness, loss of movement, and mental deterioration; has no treatment
PKU
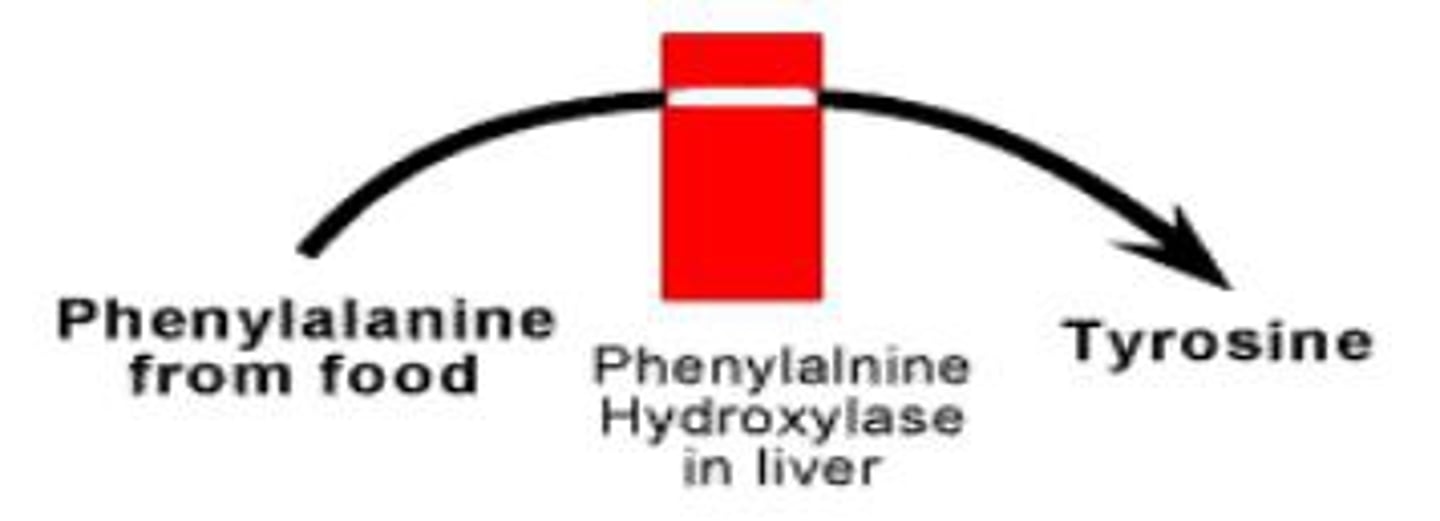
(Recessive)Common among Swedish or Norwegian ancestry; caused by a missing enzyme that is need to change phenylalanine (amino acid) to tyrosine; Phenylalanine builds up in the CNS; leads to mental retardation; noticed when a baby drinks milk
PKU
(Recessive)Caused by a missing enzyme that is needed to change phenylalanine (amino acid) to tyrosine; the phenylalanine builds up in the CNS; leads to mental retardation, noticed when a baby drinks milk.
True
True or False: Mental retardation from PKU can be prevented if the baby is treated with special diet the first 7-10 days of life
Phenylalanine
An kind of amino acid
False (They tend to be recessive)
True or False: Disorders and diseases tend to be dominant.
One
How many dominant alleles are needed in order for a Dominant Genetic Disorder to be expressed?
Huntington's Disease
(Dominant)Rare, hereditary; degeneration of the nervous system; uncontrollable jerky movement of head & limbs; mental deterioration; onset 30-50
Huntington's Disease
(Dominant)Degeneration of the nervous system, causing uncontrollable jerky movement of the head or limbs; mental deterioration
Achondroplasia
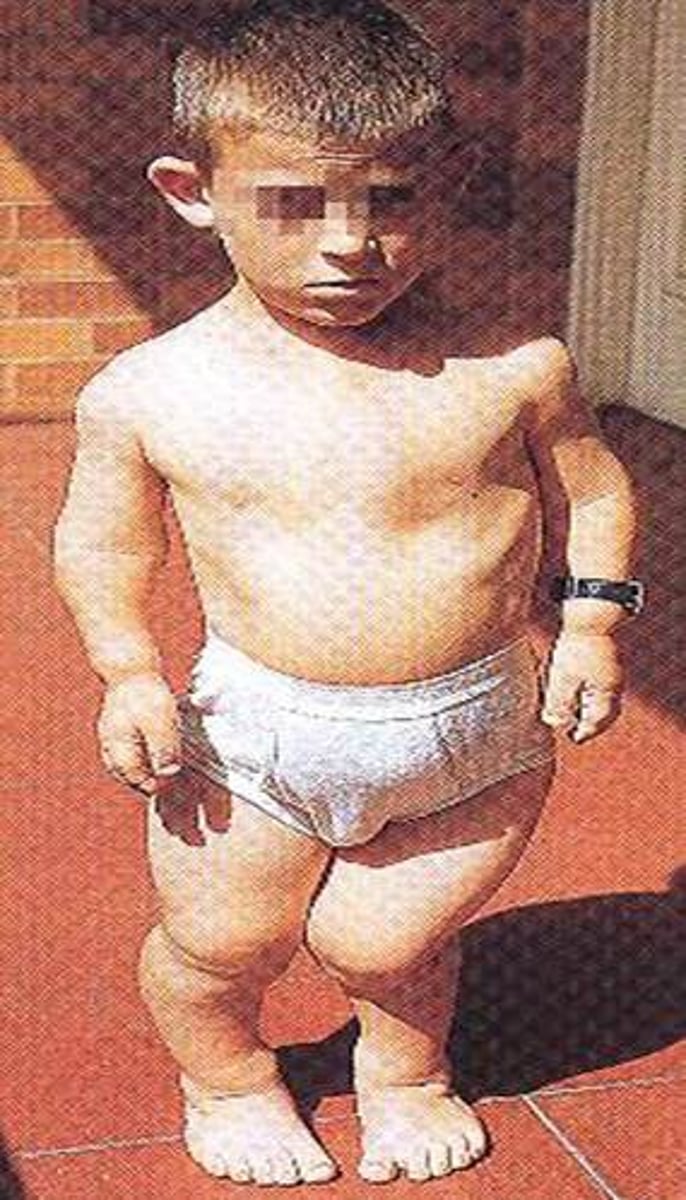
(Dominant)Common form of dwarfism; disorder of bone growth; short limbs; height not exceeding 4 ft; 85% are result of a new mutation
Achondroplasia
Disorder of bone growth, causing short limbs and a height not exceeding 4 feet; 85% are a result of a new mutation
True
True or False: Not all inheritance patterns follow Mendel's Rules.
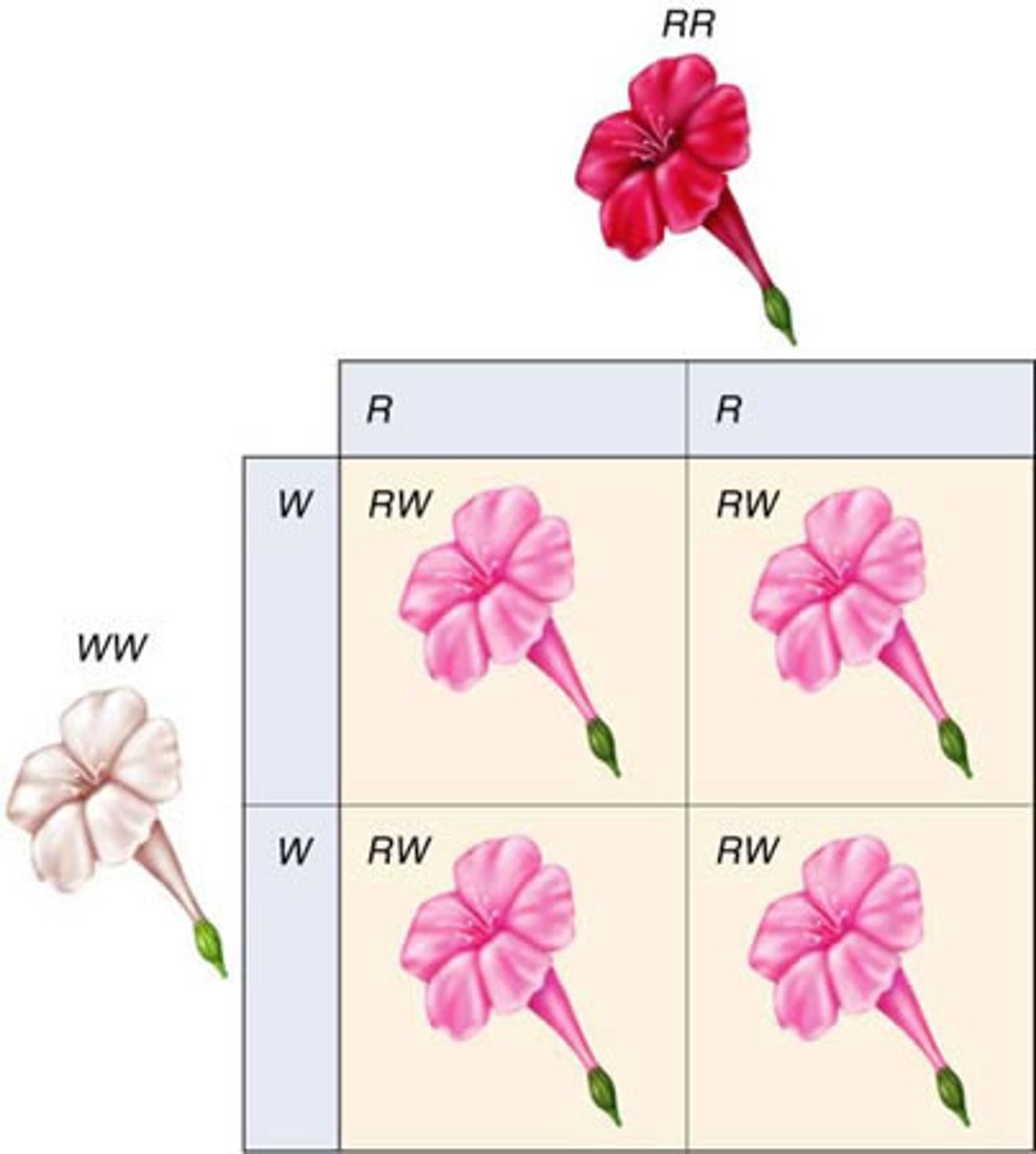
Incomplete Dominance
Some traits have more than one dominant for a trait; traits are inherited incompletely; the phenotype of offspring between 2 homo dominant parents is intermediate (appearance of a third phenotype); neither allele is completely dominant - both produce traits; the alleles combine to give a new trait; ex- R-red + R'R'(white) = RR'(pink)
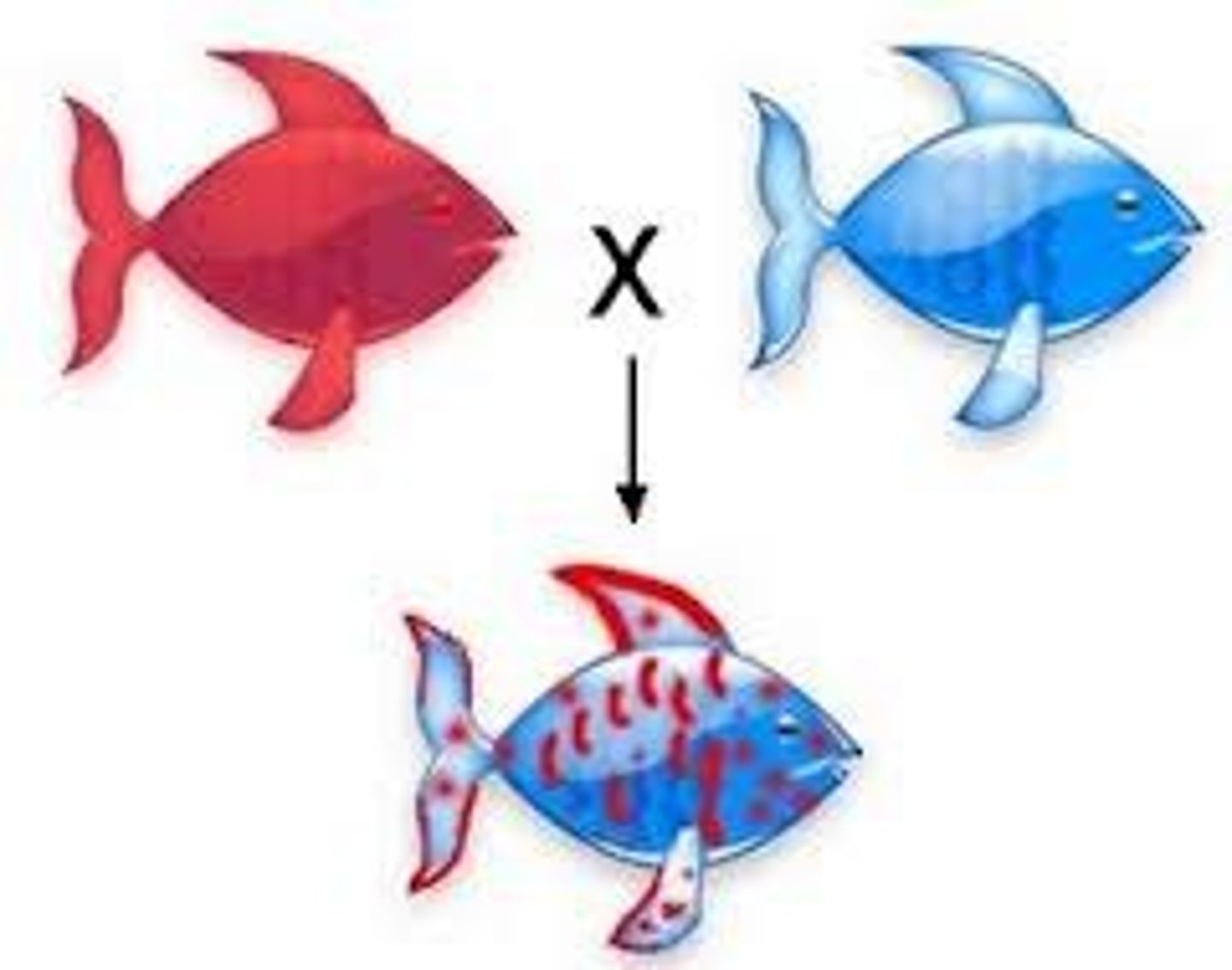
Codominance
Also occurs when there is a trait with more than one dominant form; a combination of two forms of dominance; ex- if both parents are homo dominant, both phenotype will show in offspring; the traits are expressed equally; ex- C-curly hair, S- straight hair, CC + SS=CS offspring with wavy hair (some straight, some curly sections)
True
True or False: To differentiate from Incomplete Dominance, different letters are represented as the dominant traits (no slash).
True
True or False: Sickle Cell Anemia is an example of codominance in humans.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Blood disorder; affects 1 in 12 African Americans; malfunctIion (caused by a missing amino acid in the hemoglobin) of the red blood cells; clogging of the blood vessels; poor circulation; low rbc count (anemia); can cause stroke

True
True or False: Individuals who are heterozygous for Sickle Cell Anemia produce both normal and sickled cells (codominance) and have enough normal hemoglobin to prevent serious effects.
True
True or False: Multiple Phenotypes are determined by greater than 2 alleles, such as blood groups in humans
I^A, I^B, & i
What are the 3 alleles that are involved in blood groups in humans?
I^A & I^B
Which 2 alleles are codominant with each other in blood groups?
Type A
I^A I^A
Type B
I^B I^B
Type AB
I^A I^B
Type O
i i
C'
Fill In The Blank: Coat color: C-black, c-brown, C'-white spotting, c'-white
CC'-black with white spotting
Cc-black and brown for mixture
C'c-brown with white spotting
_____c'-white
40
Fill In The Blank: Different combinations make over _______ different coat colors in rabbits.
Autosomes
The first 22 pairs of chromosomes
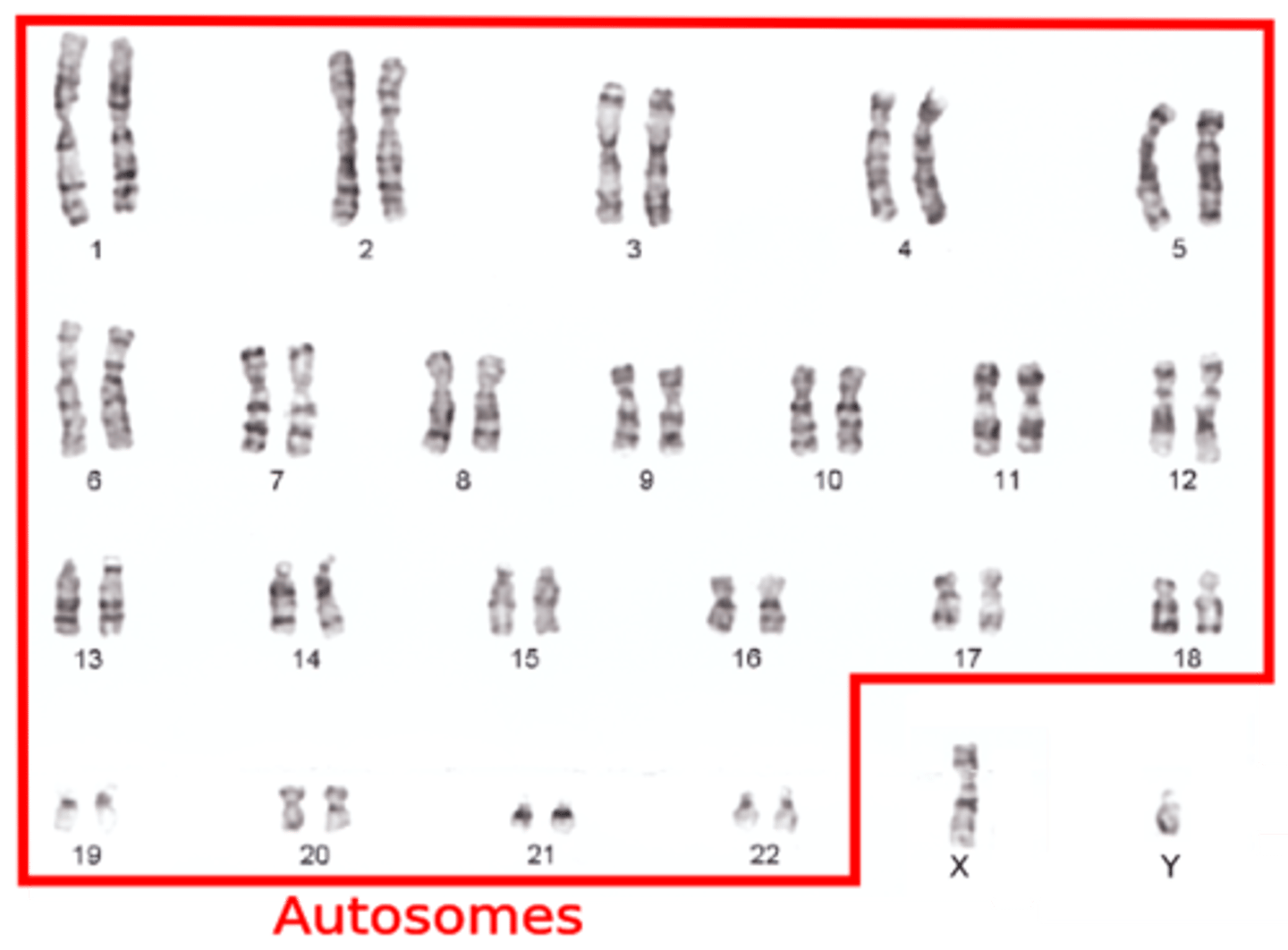
Sex Chromosomes
The 23rd pair of chromosomes; different in males and females; control the inheritance of sex characteristics; thousands of other traits
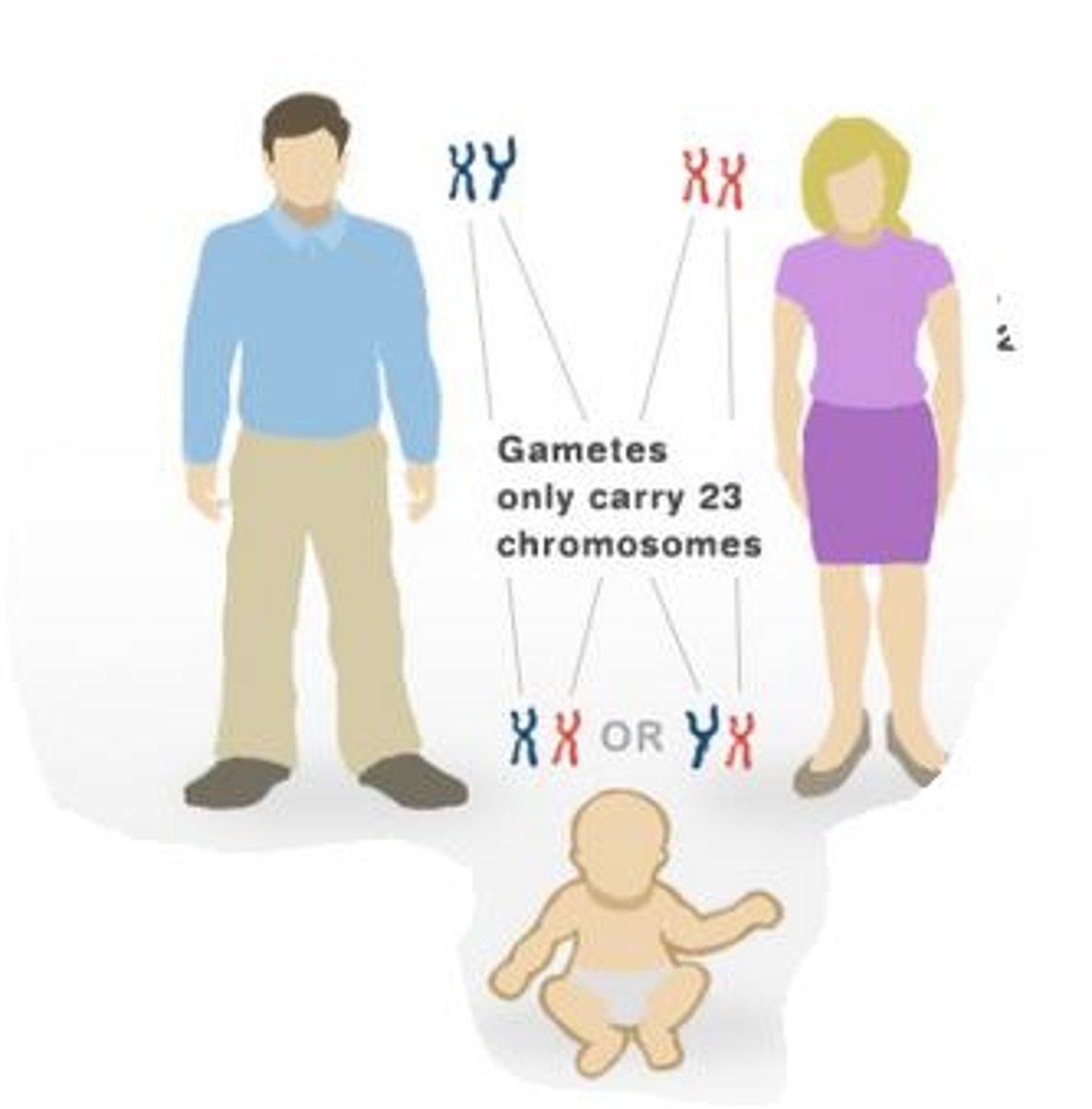
XX
Female

XY
Male

Sex-Linked Trait(s)
Controlled by genes on sex chromosomes; most are on the X allele in humans
Sex-Linked Trait(s)
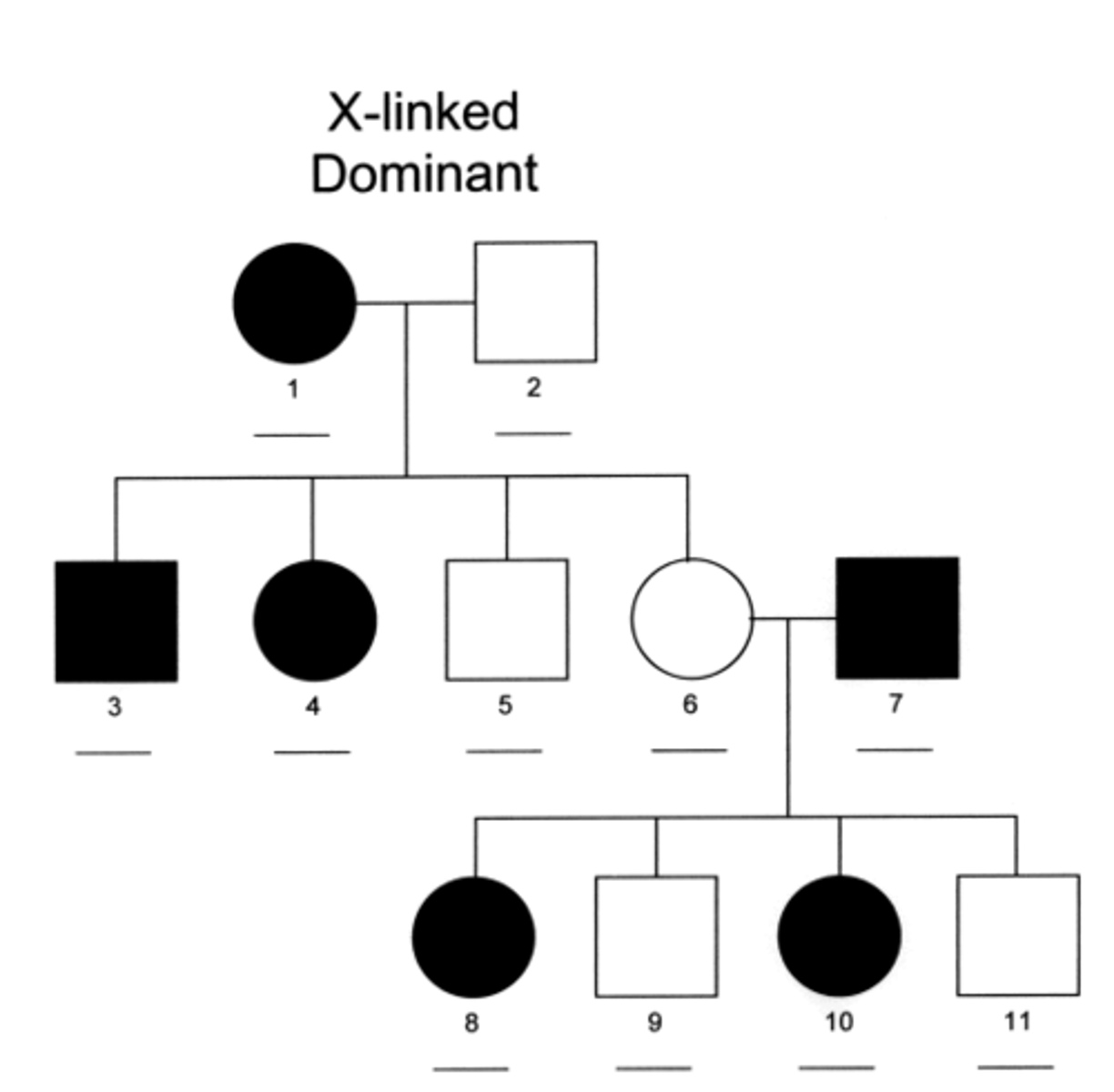
If a trait is X-linked, a male will pass it to a daughter, not a son. The daughter can pass it on (50/50 chance) to her children. If a son inherits it, he will show the recessive phenotype because he will not receive an X-dominant allele from his father to mask it.
Red-Green Color Blindness
Red & green cannot be distinguished; men inherit the recessive allele on their X chromosome; rare in female; hemophilia (disease characterized by the inability to clot blood)
Hemophilia
Disease characterized by the inability to clot blood due to a lack of the clotting enzyme Factor VIII; passed on from mother to son
Polygenic Trait(s)
Traits controlled by more than one pair of genes; 3-5 pairs; include human eye, hair color, skin color, height, body shape, fingerprint patterns; skin color is controlled by three genes: A, B, C
True
True or False: Human eye color, hair color, skin color, height, body shape, & fingerprint patterns are polygenic traits.
False(Capitals are not dominant over lowercase)
True or False: For polygenic traits, capitals are dominant over lowercase.
AABBCC
Darkest shade for skin tone
aabbcc
Lightest shade for skin tone
AaBbCc
Intermediate shade for skin tone
Genetic Makeup
What factor determines potential to develop and function?
Internal Environment
Age, gender, hormones, the existence of an infection, etc.
External Environment
Temperature, nutrition, light, chemicals, infectious agents, etc.
Pedigree(s)
Shows family history of a particular inherited trait; diagram uses symbols for the data
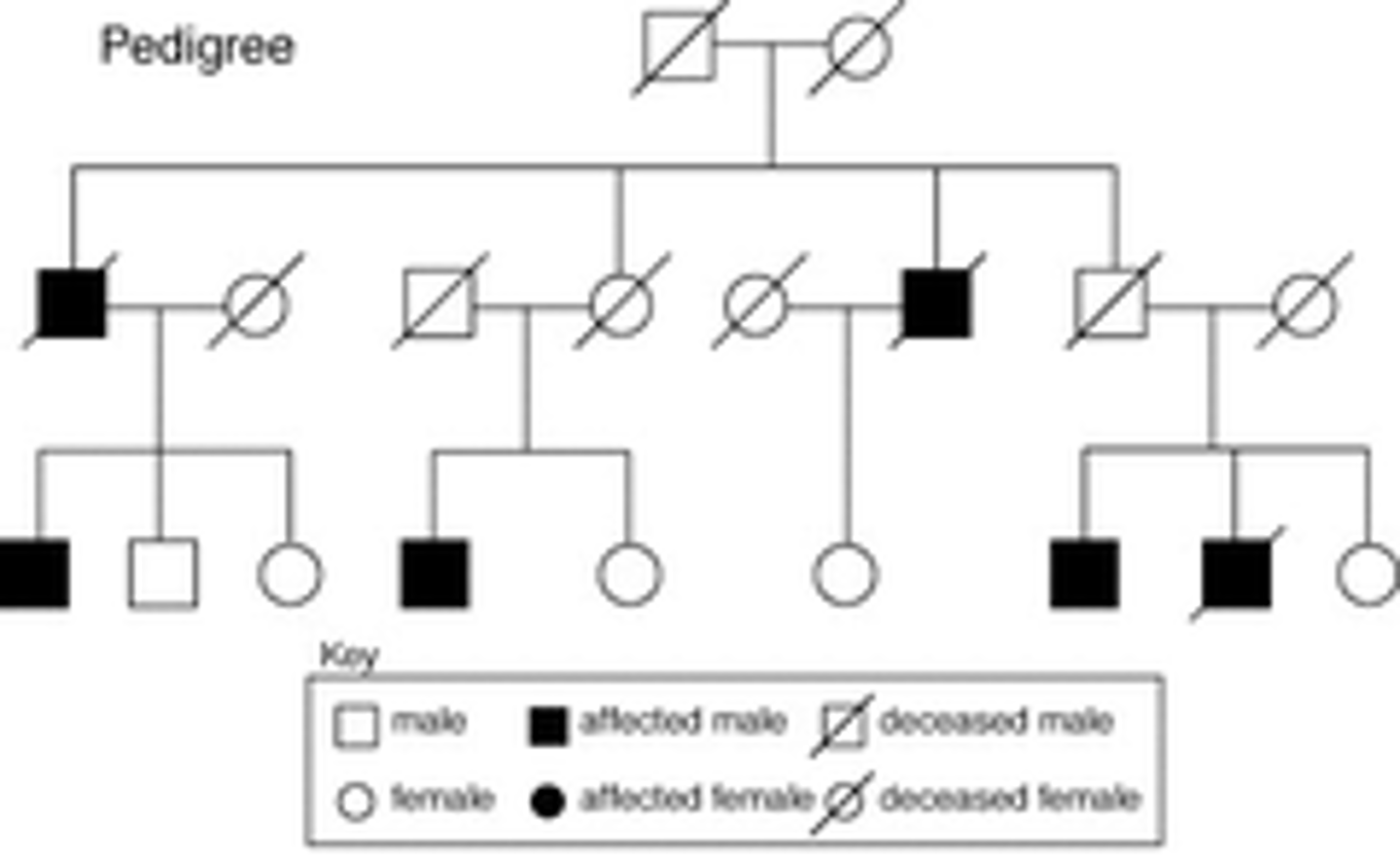
Pedigree Symbols
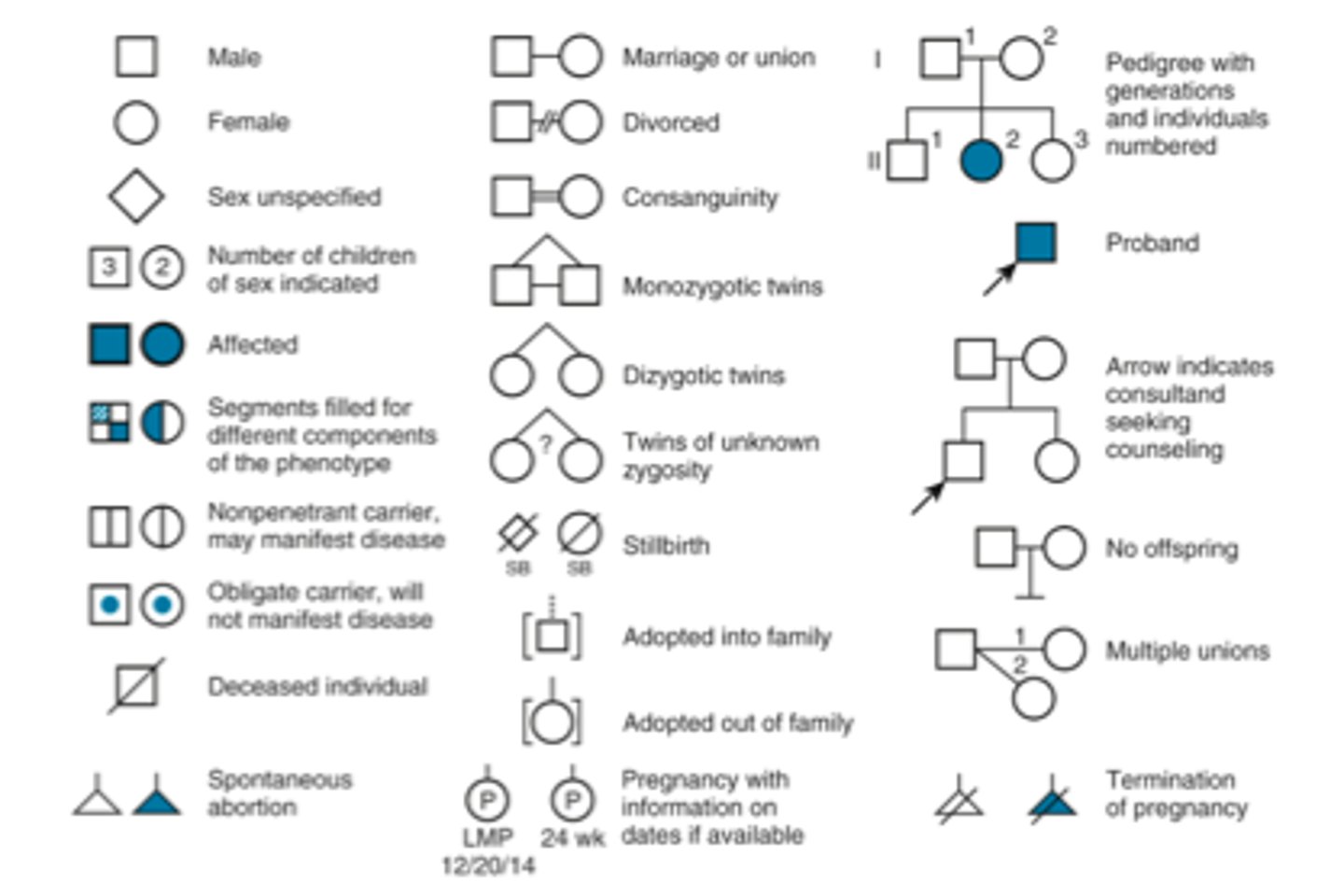
Pedigree (Abortion or Stillbirth)
Pedigree Graph Rules
1. Always label the homo recessive FIRST
2. Give every other individual one capital letter
3. Work backwards from a homo recessive
Heterozygous
Is #4 a Homozygous or a Heterozygous
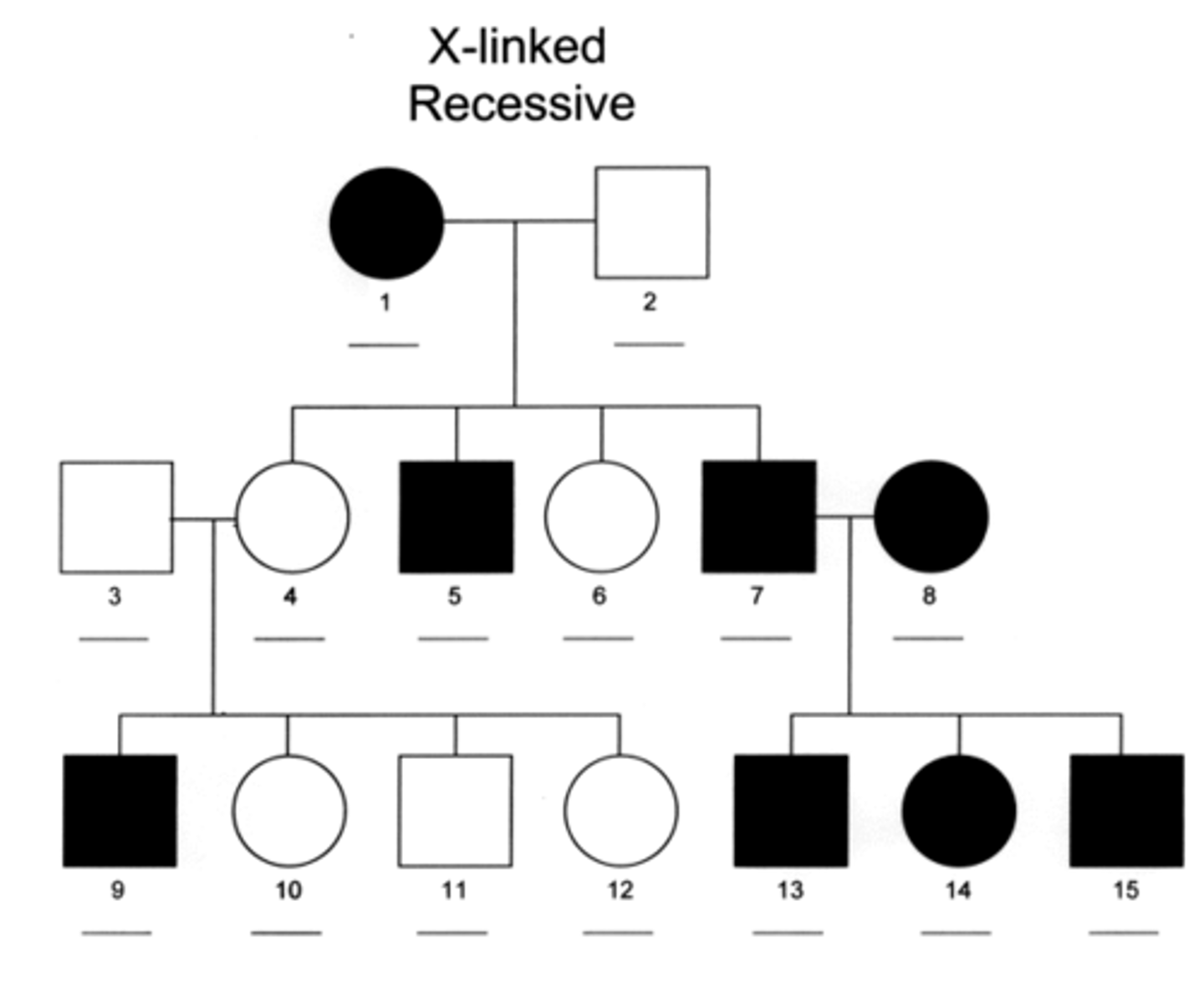
Heterozygous
Is #7 a Homozygous or a Heterozygous