Large Animal Medicine Exam 1
1/565
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
566 Terms
mastitis
inflammation of mammary gland
mastitis is often associated with…
bacterial infection
what is the purpose of the keratin in the teat canal?
it is sticky so it prevents bacteria from traveling up the canal
the blood milk barrier makes it difficult for…
immune cells and antibodies to function
mastitis leads to increased/decreased vascular permeability
increased
what proteins/ions are increased in mastitis milk?
albumin
lactoferrin
sodium
chloride
lactoferrin
acute phase antibacterial for iron sequestration
what cells are more common in mastitis milk?
neutrophils
teat stays open for _____ minutes after milking
20-30
2 categories of mastitis:
clinical and subclinical
clinical mastitis
visibly abnormal milk (mild, moderate, or severe)
subclinical mastitis
visibly normal milk but measurable infection or inflammation
contagious mastitis reservoir is the _______
cow
environmental mastitis reservoir is the _______
environment
what are the major contagious mastitis pathogens?
Staph aureus
Strep agalactiae
mycoplasma spp (mainly M. bovis)
what are the major environmental mastitis pathogens?
coliforms
escherichia coli
klebsiella
strep uberis
what are the minor mastitis pathogens?
coagulase negative staph
mild clinical mastitis appearance:
abnormal milk
moderate clinical mastitis appearance:
abnormal milk
abnormal quarter
severe clinical mastitis appearance:
abnormal milk
abnormal quarter
abnormal cow
clinical mastitis severity is correlated with…
appearance
biggest cost of clinical mastitis is…
milk discard
milk loss vs milk discard
milk loss is milk not produced by cow due to infection
milk discard is milk that has been produced but is dumped out due to infection
farm goals for clinical mastitis case rate is…
<2%
in ontario clinical mastitis is most common during…
fall
incidence of clinical mastitis is highest during ______ days in milk
first 20
subclinical mastitis is detected by…
somatic cell count (SCC)
linear score
a numerical value that describes the linear relationship of SCC with milk loss
typical SCC cut point for mastitis infection:
200,000
regulatory SCC limit mastitis infection:
400,000
california mastitis test
detergent in solution reacts with DNA in neutrophils to form gel
thicker the gel, the more nucleated cells in milk
the california mastitis test is not sensitive/specific
sensitive (only tests positive when SCC is at least 400,000)
milk conductivity increases/decreases with mastitis
increases (more electrolytes in milk)
clinical cure for mastitis is based on…
appearance of milk
bacteriologic cure for mastitis is based on…
culture before and >1 week after treatment
cow factors that affect whether or not mastitis is cured:
parity
SCC
duration of infection
colony count
number or previous cases of clinical mastitis
number of quarters affected
what is the treatment success factor for mastitis?
duration of treatment
most antibiotics used in vet med are time/concentration dependent
time
which pathogens that cause mastitis are easiest to kill?
strep agalactiae
strep spp
staph spp (exception staph aureus)
what is the ideal way to treat mastitis?
targeted therapy based on bacterial cause
intramammary mastitis treatment in a lactating cow:
cetiofur
cephapirin
intramammary mastitis treatment in a dry cow:
cetiofur
cephapirin
cloxacillin
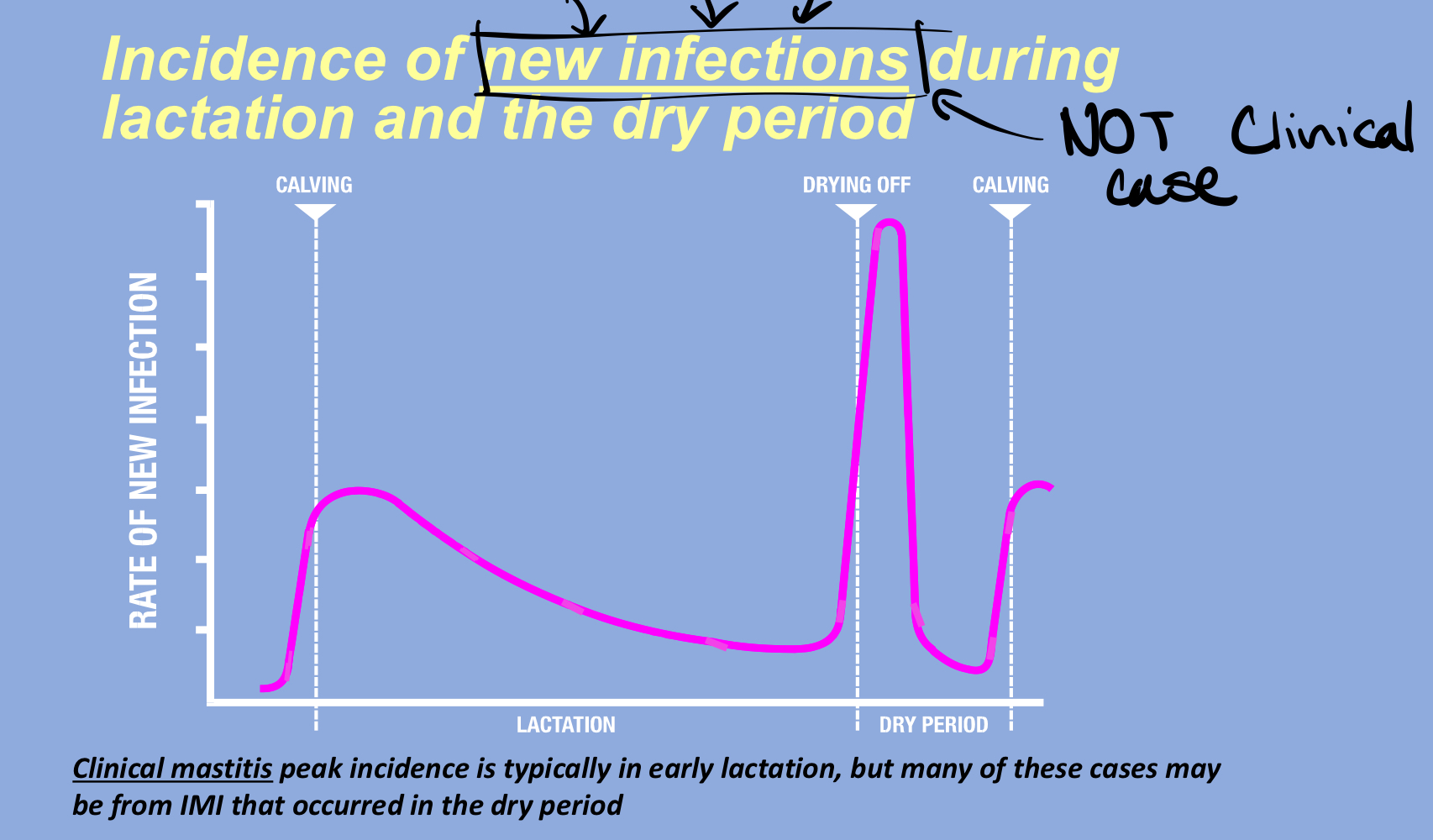
dry period is during…
the last 2 weeks of pregnancy
new infections occur in teats that fail to _______ during the dry period
close
strep agalactiae is very/not susceptible to IMM antibiotic
very
staph aureus tends to establish acute/chronic infections
chronic
what is the dry cow cure rate for staph aureus mastitis?
40-60%
what is the lactating IMM cure rate for staph aureus mastitis?
10-40%
staph aureus mastitis diagnosis:
culture is most sensitive
mycoplasma mastitis clinical signs:
clinical mastitis that is unresponsive to treatment
shifting quarters
mastitis followed by respiratory disease and/or otitis or septic arthritis in cows or calves
there is/isn’t a cure for mycoplasma mastitis
isn’t
environmental mastitis caused by coliforms is usually self-…
resolving
environmental streptococci has a ______ cure rate from IMM antibiotics
40-65%
coliform mastitis peak bacterial growth precedes…
clinical signs
what is the temperature of a cow udder?
35 degrees C
e coli mastitis is typically ______ duration while klebsiella mastitis is ______ duration
short; long
________ from gram negative coliforms can lead to severe mastitis in 12-24hrs
endotoxin
vaccine for endotoxin leads to a ______ drop in clinical coliform mastitis cases
75%
when should cows be vaccinated for coliform mastitis?
just before dry period
treatment for severe coliform mastitis:
anti-inflammatories
fluids
systemic antibiotics if targeting bacteremia
____ of severe mastitis cases are bacteremic
1/3
udder edema is associated with increased risk for…
clinical mastitis
udder cleft dermatitis
exudative, ulcerative dermatitis between right and left halves of udder, or between udder and inner thigh possibly caused by spirochetes
why is there a focus on swine farm biosecurity?
disease
international trade
risk of foreign animal diseases and emerging diseases
what are some emerging diseases in swine farms?
african swine fever
PRRS
circovirus
PED
Swine dysentary
what are some production limiting diseases in swine farms?
PRRS
Circovirus
disease entry on a swine farm:
pig-to-pig
other animals
airborne spread, manure, deadstock management
people
fomites
how to prevent pig-to-pig transmission:
one source of breeding stock
test breeding stock herd
purchased semen
off site early weaning
isolation and/or acclimation barn
CAZ (controlled access zone) includes:
pig farm yard
buildings and driveways
CAZ has what kind of access?
limited
RAZ (restricted access zone) includes:
where pigs are housed
RAZ has what kind of access?
defined entry protocol
multi-site production in swine
pigs from multiple sow barns move off-site into one nursery barn
how long is swine gestation?
115 days
when are pregnancy checks done on sows?
25-35 days
42-56 days
what are piglet weights when born?
1-1.5 kg
what are piglet weights when weaned?
5 kg
what is the goal weight of nursery pigs?
5 kg → 25-30 kg
when naturally breeding swine, how many sows per 1 boar?
20
majority of sows are bred through…
AI
what is the goal weight of grow-finisher pigs?
25-30 kg → 110-115 kg by 6 months old
what is the goal weight of gilt selection at 20-30 weeks?
74-140 kg
what is the goal weight for sows?
135-300 kg
what is the goal weight for boars?
360+ kg
what are common sow breeds?
yorkshire
landrace
what are common boar breeds?
duroc
hampshire
synthetics
when are nursing piglets weaned?
16-28 days
what is goal preweaning mortality?
<8-10%
List the major pathogens that cause diarrhea in neonatal pigs and the timeline in which they occur:
e. coli (colibacillosis): <12 hrs
clostridium perfringens: <12 hrs
swine enteric coronavirus diseases (PED and TGE viruses): 2 days
cystoisospora suis (coccidiosis): 5 days
rotavirus: 5 days
e coli are/aren’t part of normal flora of pigs
are
pathogenic e. coli strains of swine:
ETEC (eneterotoxigenic)
VTEC (verotoxigenic)
SEPEC (septicemic)
ETEC signs:
single, multiple, or all pigs of litter affected
alkaline diarrhea (watery in newborns, creamy in older nursing pigs)
dehydration, lethargy, weakness, death
peracute form: death before signs appear
ETEC pathogenesis:
adhere to small intestine mucosa by fimbrial adhesins
colonization of jejunal/ileal mucosa
production of enterotoxins
secretory diarrhea
kinds of ETEC fimbrial adhesins:
F4 (K88)
F5 (K99)
F6 (987P)
F41
kinds of ETEC enterotoxins:
Sta (STI), STb (STII)
LT
ETEC pathology:
dehydration
dilated, fluid filled small intestine
congestion of small intestine vasculature
dilated stomach
diagnosing ETEC:
history and age of onset
alkaline fecal pH
culture from gut loop or rectal swabs
histopathology with minimal villus atrophy
PCR for fimbria and enterotoxin genes
what should be submitted for necropsy in neonatal swine diarrhea?
2-3 live piglets in acute stage (ill <24 hrs)
not treated
clinical signs present
ETEC control:
prevent chilling
hygiene
stop cross fostering between affected and unaffected litters
commercial killed bacterins that offer protection against adhesisn and enterotoxins
autogenous bacterins
ETEC treatment:
electrolyte and dextrose solutions
antimicrobials
parenteral (ceftiofur, trimethoprim sulfa)
oral (neomycin)